Ceramic agent for hot galvanized plate and preparation method of ceramic agent
A vitrification agent and zirconium technology, applied in the coating process of metal materials, etc., can solve the problems of unobvious color of vitrification film, instability of neutral salt spray, production and environmental impact, etc., and achieve good corrosion resistance, Variety of metal ions, good corrosion resistance and stability
- Summary
- Abstract
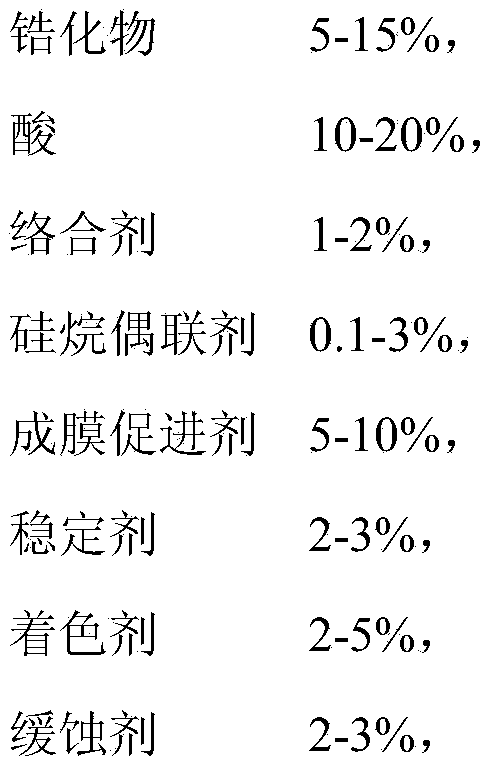
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0037] 1) Weigh 10 parts of sodium fluozirconate, 10 parts of fluotitanic acid, 2 parts of sodium citrate, 2 parts of silane coupling agent KH-5602, 5 parts of sodium nitrobenzenesulfonate, 3 parts of sodium perborate, and 5 parts of cerium nitrate Parts, 3 parts of p-tolylthiourea;
[0038] 2) Add sodium fluozirconate to deionized water accounting for 2 / 3 of the total weight of all raw materials and stir evenly;
[0039] 3) Add sodium citrate to the solution prepared in step 2) and stir until dissolved;
[0040] 4) Add fluozirconic acid to the solution prepared in step 3) and stir until uniform;
[0041] 5) Add silane coupling agent KH-560 into the solution prepared in step 4) and stir until dissolved;
[0042] 6) Add sodium nitrobenzenesulfonate to the solution prepared in step 5) and stir until dissolved;
[0043] 7) Add sodium perborate in the solution prepared in step 6) and stir evenly;
[0044] 8) Add cerium nitrate in the solution prepared in step 7) and stir evenl...
example 2
[0048] 1) Weigh 15 parts of sodium fluozirconate, 10 parts of fluosilicate, 5 parts of nitric acid, 2 parts of sodium citrate, 3 parts of silane coupling agent KH-5603, 5 parts of sodium nitrobenzenesulfonate, and 3 parts of sodium perborate , 5 parts of ammonium vanadate, 3 parts of p-tolylthiourea;
[0049] 2) Add sodium fluozirconate to deionized water accounting for 2 / 3 of the total weight of all raw materials and stir evenly;
[0050] 3) Add sodium citrate to the solution prepared in step 2) and stir until dissolved;
[0051] 4) Add fluosilicic acid and nitric acid to the solution prepared in step 3) and stir until uniform;
[0052] 5) Add silane coupling agent KH-560 into the solution prepared in step 4) and stir until dissolved;
[0053] 6) Add sodium nitrobenzenesulfonate to the solution prepared in step 5) and stir until dissolved;
[0054] 7) Add sodium perborate in the solution prepared in step 6) and stir evenly;
example 3
[0059] 1) Weigh 15 parts of zirconium oxychloride, 10 parts of fluosilicic acid, 5 parts of sulfuric acid, 2 parts of sodium tartrate, 3 parts of silane coupling agent KH-1713, 5 parts of sodium nitrobenzenesulfonate, 3 parts of sodium fluoroborate, 2 parts of ammonium vanadate, 3 parts of ammonium molybdate, 3 parts of propyl sulfide;
[0060] 2) adding sodium zirconium oxychloride to deionized water accounting for 2 / 3 of the total weight of all raw materials and stirring evenly;
[0061] 3) Add sodium tartrate to the solution prepared in step 2) and stir until dissolved;
[0062] 4) Add fluosilicic acid and sulfuric acid to the solution prepared in step 3) and stir until uniform;
[0063] 5) Add silane coupling agent KH-171 into the solution prepared in step 4) and stir until dissolved;
[0064] 6) Add sodium nitrobenzenesulfonate to the solution prepared in step 5) and stir until dissolved;
[0065] 7) Add sodium fluoroborate to the solution prepared in step 6) and stir ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com