Biomedical degradable magnesium-based bulk amorphous alloy and preparation method thereof
An amorphous alloy and biomedical technology, which is applied in the field of biomedical degradable Mg-Zn-Ca-Sr bulk amorphous alloy and its preparation, can solve the problems of limiting the application of magnesium-based amorphous alloy, etc., and achieves mobility Good, good mechanical properties, morphologically healthy effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
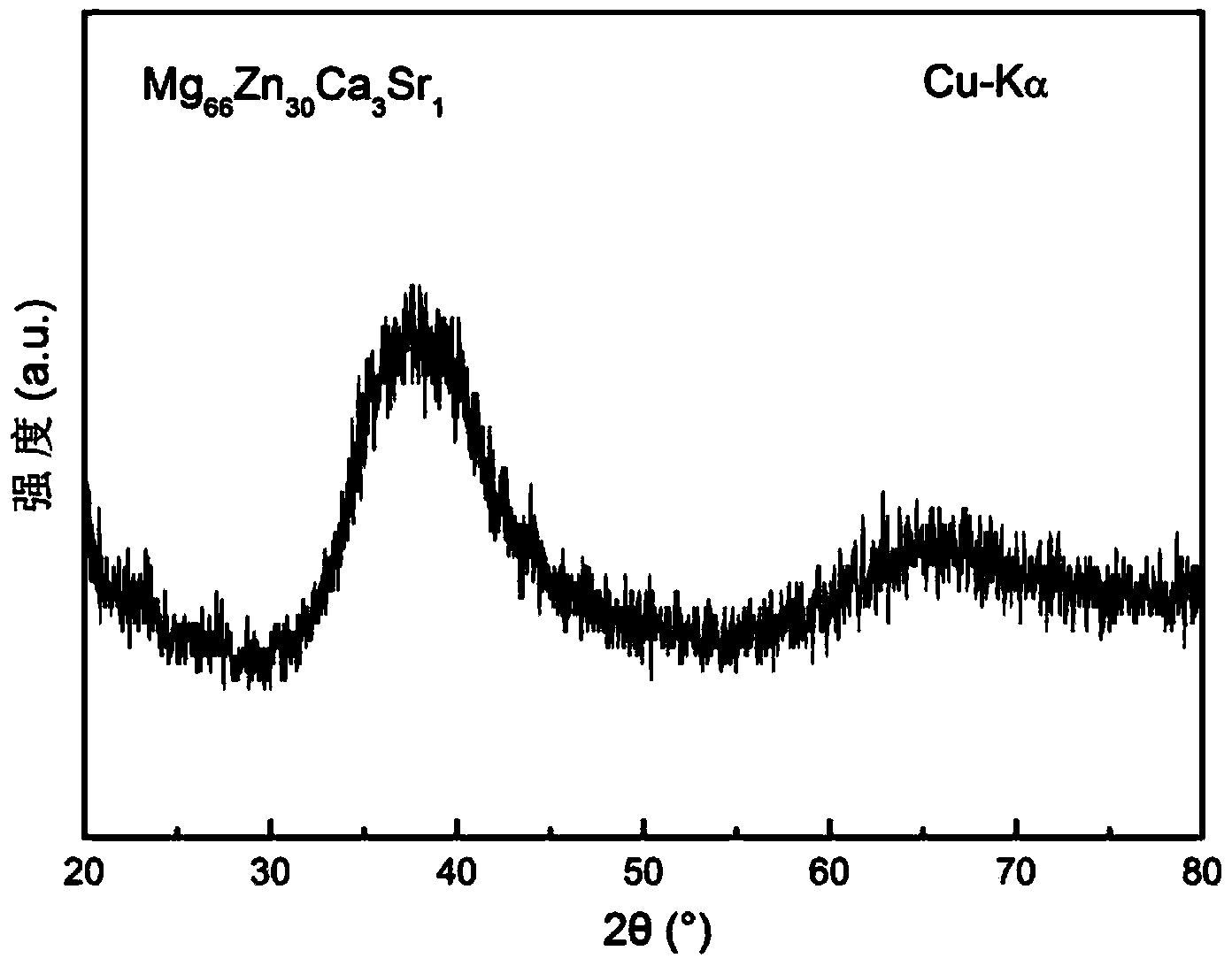
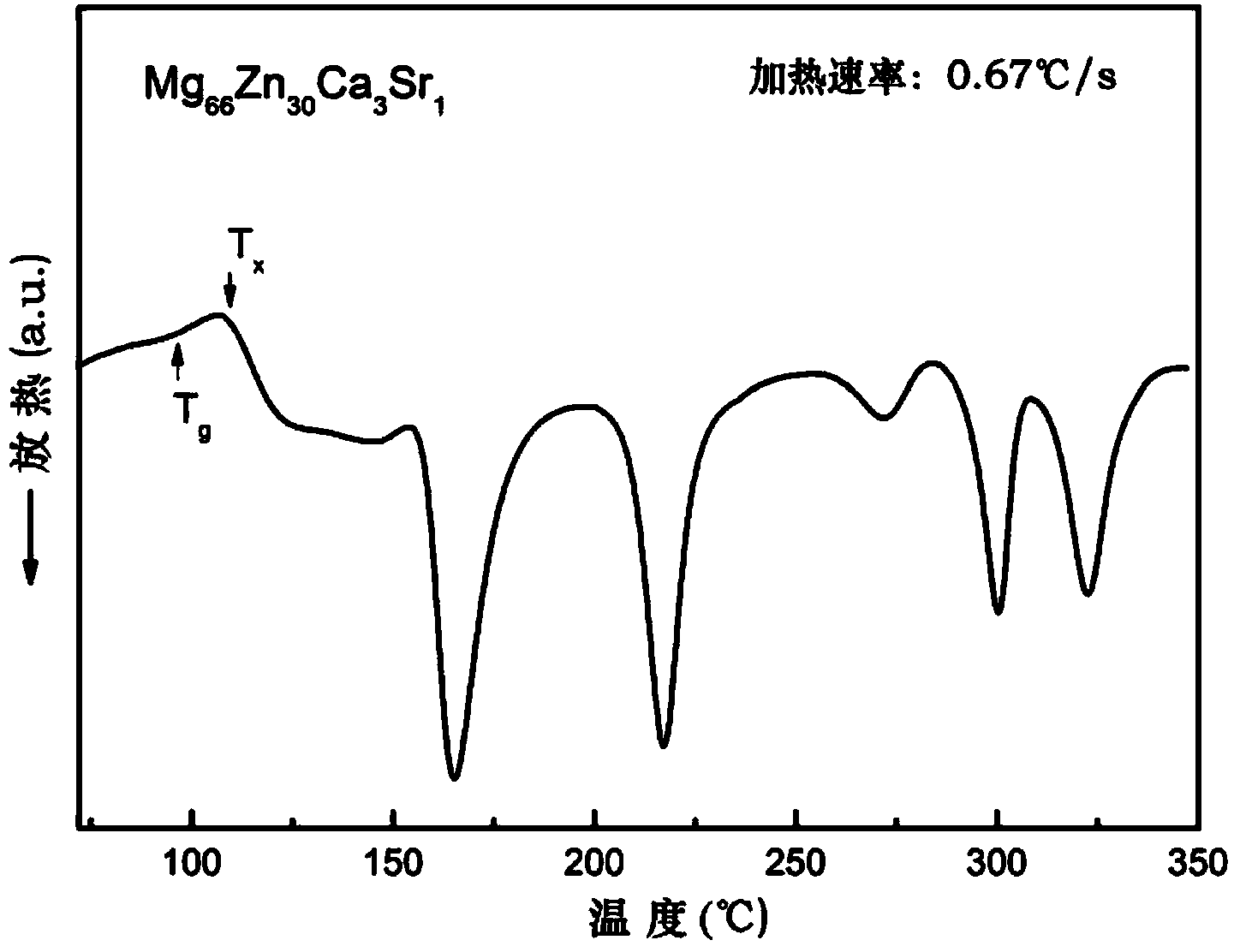
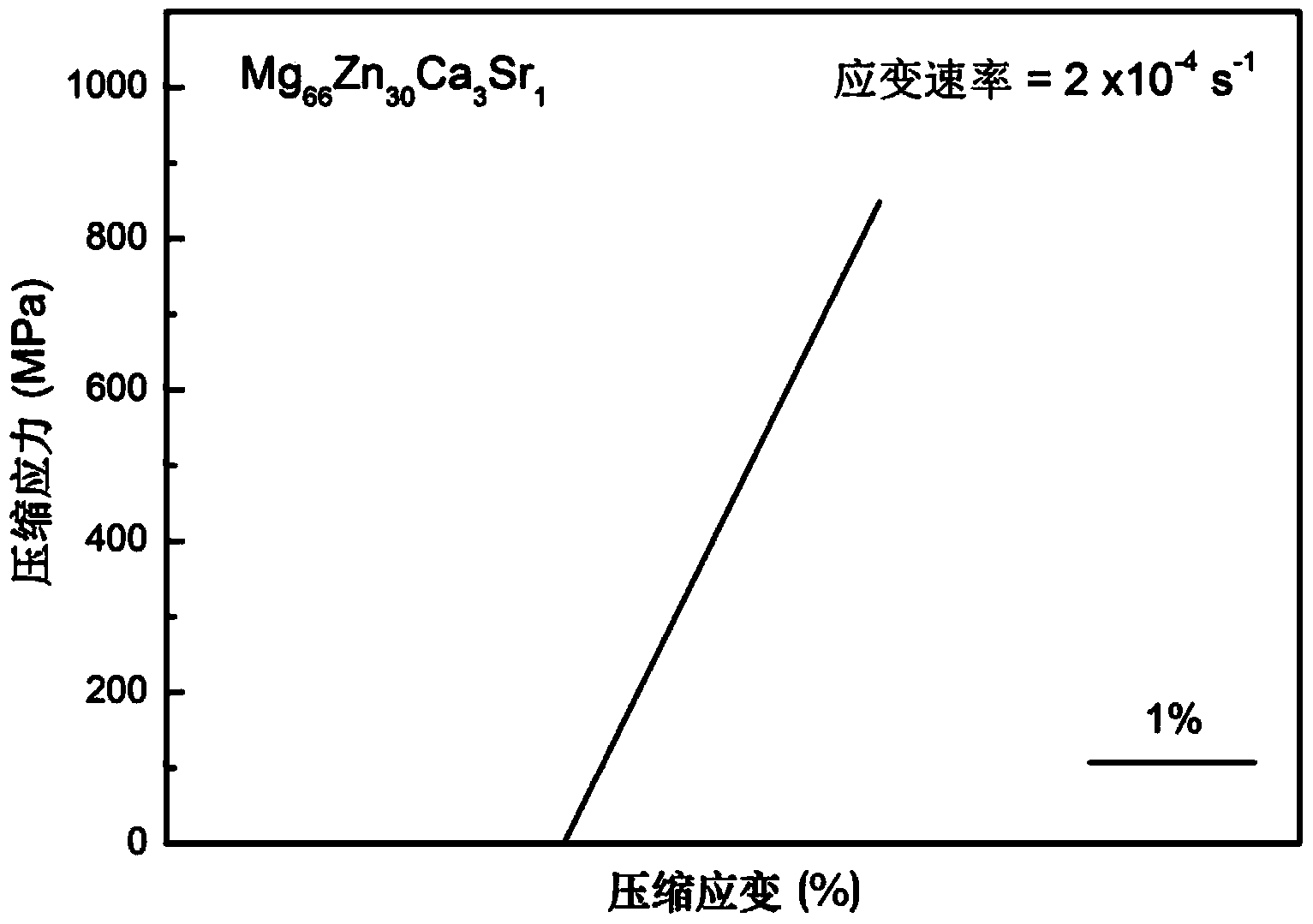
[0036] Mg with a diameter of 2 mm was prepared by copper mold casting 66 Zn 30 Ca 3 Sr 1 bulk amorphous alloy
[0037] Step 1: Ingredients
[0038] by Mg 66 Zn 30 Ca 3 Sr 1 The nominal composition of each element is weighed, wherein, the mass percentage purity of magnesium (Mg) is 99.9%; the mass percentage purity of zinc (Zn) is 99.9%; the mass percentage purity of calcium (Ca) is 99.9%; strontium (Sr) The mass percent purity is 99%;
[0039] Step 2: Smelting Mg 66 Zn 30 Ca 3 Sr 1 Master Alloy
[0040] Put the required raw materials weighed in step 1 into the vacuum induction melting furnace, and adjust the vacuum degree of the vacuum chamber of the melting furnace to 2×10 -2 Pa, and then filled with high-purity argon to make the vacuum of the vacuum chamber to 0.8×10 5 Pa, the melting temperature is 800°C, and after smelting for 15 minutes, it is cooled with the furnace and taken out to obtain the first alloy ingot;
[0041] Turn over the first alloy ingot, p...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Mg with a diameter of 2 mm was prepared by copper mold casting 66 Zn 30 Ca 2.5 Sr 1.5 bulk amorphous alloy
[0055] Step 1: Ingredients
[0056] by Mg 66 Zn 30 Ca 2.5 Sr 1.5 The nominal composition of each element is weighed, wherein, the mass percentage purity of magnesium (Mg) is 99.9%; the mass percentage purity of zinc (Zn) is 99.9%; the mass percentage purity of calcium (Ca) is 99.9%; strontium (Sr) The mass percent purity is 99%;
[0057] Step 2: Smelting Mg 66 Zn 30 Ca 2.5 Sr 1.5 Master Alloy
[0058] Put the required raw materials weighed in step 1 into the vacuum induction melting furnace, and adjust the vacuum degree of the vacuum chamber of the melting furnace to 2×10 -2 Pa, and then filled with high-purity argon to make the vacuum of the vacuum chamber to 0.8×105 Pa, the melting temperature is 800°C, and after smelting for 15 minutes, it is cooled with the furnace and taken out to obtain the first alloy ingot;
[0059] Turn over the first allo...
Embodiment 3
[0070] Mg with a diameter of 2 mm was prepared by copper mold casting 73 Zn 23 Ca 3.5 Sr 0.5 bulk amorphous alloy
[0071] Step 1: Ingredients
[0072] by Mg 73 Zn 23 Ca 3.5 Sr 0.5 The nominal composition of each element is weighed, wherein, the mass percentage purity of magnesium (Mg) is 99.9%; the mass percentage purity of zinc (Zn) is 99.9%; the mass percentage purity of calcium (Ca) is 99.9%; strontium (Sr) The mass percent purity is 99%;
[0073] Step 2: Smelting Mg 73 Zn 23 Ca 3.5 Sr 0.5 Master Alloy
[0074] Put the required raw materials weighed in step 1 into the vacuum induction melting furnace, and adjust the vacuum degree of the vacuum chamber of the melting furnace to 2×10 -2 Pa, and then filled with high-purity argon to make the vacuum of the vacuum chamber to 0.8×10 5 Pa, the melting temperature is 850°C, and after smelting for 15 minutes, it is cooled with the furnace and taken out to obtain the first alloy ingot;
[0075] Turn over the first al...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| critical dimension | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com