Method for recovering copper, indium, gallium and selenium
The technology of a copper indium gallium selenide and a recovery method is applied in the field of non-ferrous metal metallurgy, which can solve the problems of complex process and high cost, and achieve the effect of efficient recovery, simplicity and recovery
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
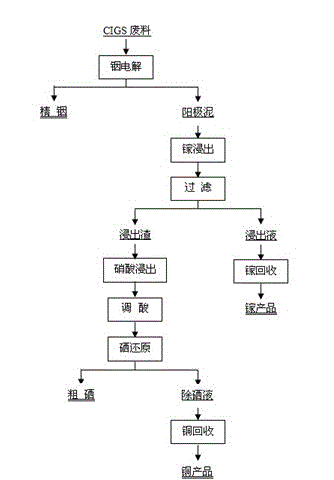
[0056] Using 3 kg of CIGS waste as raw material, the composition of the raw material is: 19.8% by weight of copper, 25.4% by weight of indium, 5.7% by weight of gallium, and the balance being selenium.
[0057] 1. CIGS electrolysis steps
[0058] This raw material is put into an indium electrolytic cell, and electrolytic refining is carried out in a hydrochloric acid solution.
[0059] The electrolysis conditions are: the electrolyte is hydrochloric acid solution, the pH is 2.5, and the electrolysis temperature is 35°C.
[0060] As a result, indium is electrodeposited on the cathode side, whereby refined indium can be obtained from CIGS waste. The indium obtained by this method is about 0.76 kg, and the recovery rate of indium reaches 99.94%.
[0061] 2. Gallium separation and recovery steps
[0062] The hydroxide precipitate formed by gallium and the copper-selenium anode slime are leached with hydrochloric acid to obtain hydrochloric acid leaching solution and hydrochlori...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Using 3 kg of CIGS waste as raw material, the composition of the raw material is: 19.8% by weight of copper, 25.4% by weight of indium, 5.7% by weight of gallium, and the balance being selenium.
[0068] 1. CIGS electrolysis steps
[0069] This raw material is put into an indium electrolytic cell, and electrolytic refining is carried out in a sulfuric acid solution.
[0070] The electrolysis conditions are: the electrolyte is a sulfuric acid solution, the pH is 3.0, and the electrolysis temperature is 18°C.
[0071] As a result, indium is electrodeposited on the cathode side, whereby refined indium can be obtained from CIGS waste. The indium obtained by this method is about 0.756 kg, and the recovery rate of indium reaches 99.21%.
[0072] 2. Gallium separation and recovery steps
[0073] The hydroxide precipitate formed by gallium and the copper-selenium anode slime are leached with sulfuric acid to obtain a sulfuric acid leaching solution and a sulfuric acid leachi...
Embodiment 3
[0078] Using 3 kg of CIGS waste as raw material, the composition of the raw material is: 19.8% by weight of copper, 25.4% by weight of indium, 5.7% by weight of gallium, and the balance being selenium.
[0079] 1. CIGS electrolysis steps
[0080] This raw material is put into an indium electrolytic cell, and electrolytic refining is carried out in a hydrochloric acid solution.
[0081] The electrolysis conditions are: the electrolyte is hydrochloric acid solution, the pH is 2.8, and the electrolysis temperature is 25°C.
[0082] As a result, indium is electrodeposited on the cathode side, whereby refined indium can be obtained from CIGS waste. The indium obtained by this method is about 0.758 kg, and the recovery rate of indium reaches 99.48%.
[0083] 2. Gallium separation and recovery steps
[0084] The hydroxide precipitate formed by gallium and the copper-selenium anode slime are leached with sodium hydroxide solution to obtain sodium hydroxide leaching solution and sod...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com