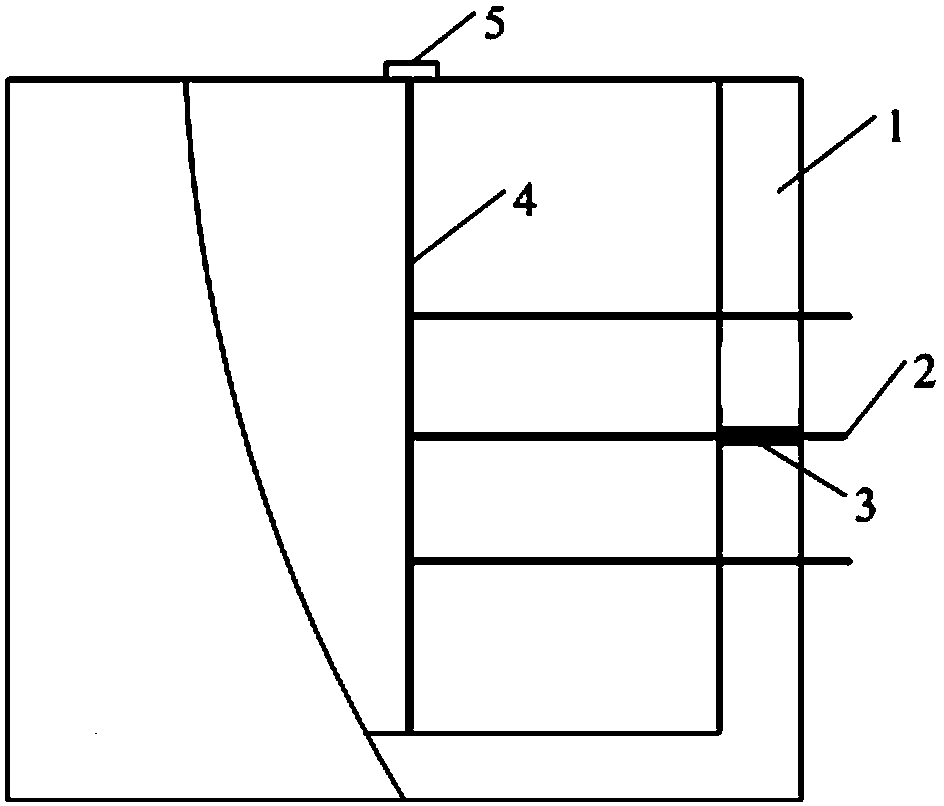
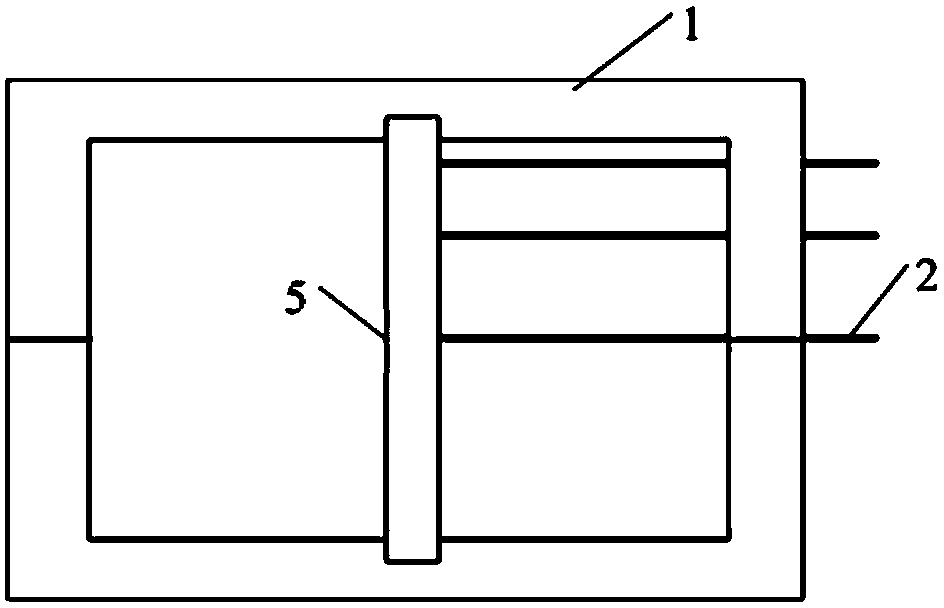
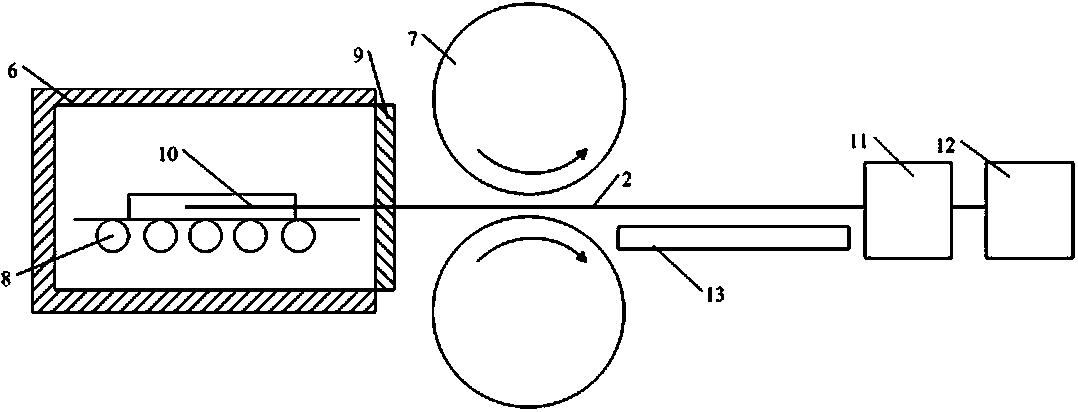
Method for measuring temperature change in magnesium alloy rolling process
A rolling process, temperature change technology, applied in metal rolling, metal rolling, temperature control and other directions, can solve the problems of difficult to obtain detection technology, limited direct detection of temperature rise, etc., to improve uniformity and accuracy, Guaranteed stability and accuracy, small heat loss before rolling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Heating and melting the AZ31 magnesium alloy, pouring it into the casting device at 660°C to make a billet inlaid with a thermocouple, the homogenization treatment system is 430°C for 10 hours, and the surface is milled to obtain a slab to be rolled; The rolled slab is heated to 350°C in a heating furnace with a roller table and kept warm for 60 minutes, and then rolled in a rolling mill with a roll diameter of Ф380mm and the roll is not heated. The rolling speed is 100m / min; the pass reduction rate is 5%, and the slab to be rolled falls on the heat shield after being rolled; the obtained slab thickness direction center (H / 2), H / 4 and the temperature change curves near the surface layer with time are as follows Figure 4 △ in the figure is the temperature-time curve at H / 2, ○ is the temperature-time curve at 2mm from the surface, and the other is the temperature-time curve at H / 4.
Embodiment 2
[0047] Heating and melting the AZ31 magnesium alloy, pouring it into the casting device at 680°C to make a billet inlaid with a thermocouple, the homogenization treatment system is 350°C for 24 hours, and the surface is milled to obtain a slab to be rolled; The rolled slab is heated to 200°C in a heating furnace with a roller table and kept warm for 60 minutes, and then rolled in a rolling mill with a roll diameter of Ф380mm and the roll is not heated. The rolling speed is 5m / min; the pass reduction rate is 35%, and the slab to be rolled falls on the heat shield after being rolled; the temperature curves of the center (H / 2), H / 4 and the surface near the obtained slab thickness direction with time are as follows: Figure 5 △ in the figure is the temperature-time curve at H / 2, ○ is the temperature-time curve at 2mm from the surface, and the other is the temperature-time curve at H / 4.
Embodiment 3
[0049] Heating and melting the AZ31 magnesium alloy, pouring it into the casting device at 710°C to make a billet inlaid with a thermocouple, the homogenization treatment system is 400°C for 12 hours, and the surface is milled to obtain a slab to be rolled; The rolled slab is heated to 400°C in a heating furnace with a roller table and kept warm for 60 minutes, and then rolled in a rolling mill with a roll diameter of Ф380mm and the roll is not heated. The rolling speed is 300m / min; the pass reduction rate is 17%, and the slab to be rolled falls on the heat shield after being rolled; the temperature curves of the center (H / 2), H / 4 and the surface layer near the obtained slab thickness direction with time are as follows: Figure 6 △ in the figure is the temperature-time curve at H / 2, ○ is the temperature-time curve at 2mm from the surface, and the other is the temperature-time curve at H / 4.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com