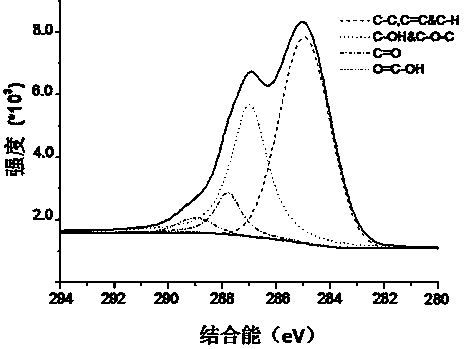
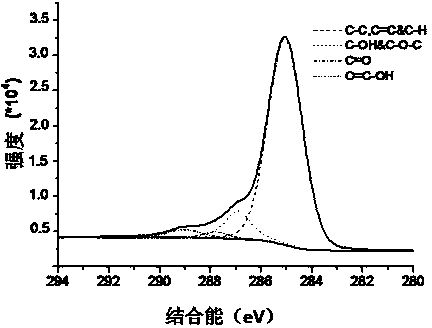
Preparation method of graphene
A technology of graphene and graphite, which is applied in the field of material preparation, can solve the problems of high oxygen content of graphene, easy explosion, limited application, etc., and achieve the effect of simple operation and high degree of reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Technical route: (1) graphite → (2) preparation of graphite oxide → (3) crushing of graphite oxide → (4) reduction of graphite oxide to graphene.
[0020] (1) Graphite: 99.9% purity
[0021] (2) Graphite oxide: Weigh 12 g of graphite with a purity of 99.9% in (1), add 10 g of potassium peroxodisulfate (analytical pure), 10 g of phosphorus pentoxide (analytical pure), 48 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid (mass Fraction 98%) in a round-bottomed flask, stirred and reacted in a water bath at 80 °C for 4.5 h, after the reaction was completed, 500 mL of deionized water was added, filtered and washed until neutral, and dried at 60 °C to obtain pre-oxidized graphite. Weigh 2 g of the above-mentioned pre-oxidized graphite, add 1 g of sodium nitrate (analytical pure), 46 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid, stir in ice bath for 30 min, slowly add 6 g of potassium permanganate (analytical pure), and react for 45 min in ice bath. min. Then the mixture was heated to 35 °C, stirred for...
Embodiment 2
[0026] The same method as in Example 1 was used to prepare small pieces of graphite oxide, and the small pieces of graphite oxide were placed in a nitrogen-hydrogen mixed flow, the hydrogen volume concentration was 5%, the flow rate was 40 mL / min, and the mixture was raised to 300 ℃, kept for 15 min, and finally cooled down to room temperature in nitrogen-hydrogen mixed gas (flow rate 40 mL / min) to obtain graphene with a specific surface area of 285 m 2 / g.
Embodiment 3
[0028] The same method as in Example 1 was used to prepare small pieces of graphite oxide, and the small pieces of graphite oxide were placed in the nitrogen-hydrogen mixed flow, the hydrogen volume concentration was 5%, the flow rate was 60 mL / min, and the mixture was raised to Keep at 400 ℃ for 2 h, and finally cool down to room temperature in nitrogen-hydrogen mixed gas (flow rate 60 mL / min) to obtain graphene with a specific surface area of 326 m 2 / g.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com