Phosphorus-free textile scouring agent
A scouring agent and textile technology, which is applied in the field of saponin-free textile scouring agent, can solve the problems of poor wool effect and whiteness, low permeability and wettability, etc., and achieve good hair effect, whiteness, and penetration The effect of improving performance and wetting and dispersing properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
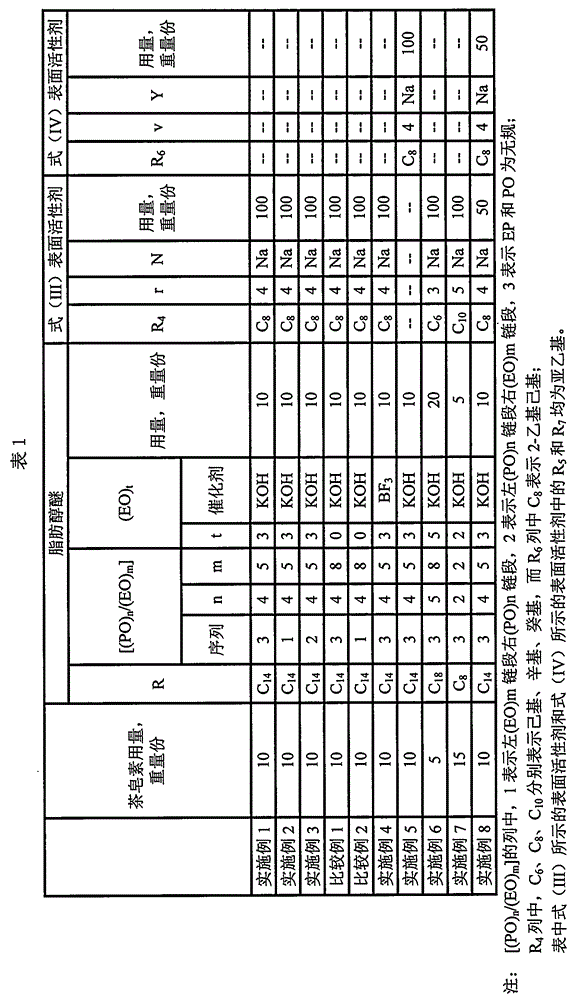
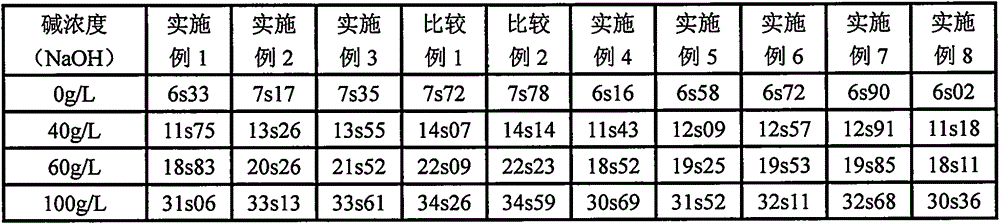
Embodiment 1
[0063] 1. Synthesis of Fatty Alcohol Ether
[0064] Into a dry 2 L reaction kettle with stirring, electric heating mantle and internal water cooling coil was charged 2 moles of tetradecyl alcohol and potassium hydroxide. Seal the reaction kettle, replace the air in the reaction kettle with nitrogen for three times, start stirring, heat up to 80°C and carry out vacuum treatment under the gauge pressure of -0.07MPa for 60 minutes, then raise the temperature to 120°C and maintain this temperature, and pass through ethylene oxide 18 moles of alkylene oxide mixture (10 moles of ethylene oxide, 8 moles of propylene oxide), keep the gauge pressure of the reactor at 0.15MPa by controlling the feed rate of the ethylene oxide mixture, and add the epoxy After the mixture of ethylene oxide and propylene oxide, mature at 120°C for 1 hour, then add 6 moles of ethylene oxide, keep the gauge pressure of the reactor at 0.15Mpa by controlling the speed of adding ethylene oxide, mature at 120°C ...
Embodiment 2
[0071] 1. Synthesis of Fatty Alcohol Ether
[0072] Into a dry 2 L reaction kettle with stirring, electric heating mantle and internal water cooling coil was charged 2 moles of tetradecyl alcohol and potassium hydroxide. Seal the reaction kettle, replace the air in the reaction kettle with nitrogen for three times, start stirring, heat up to 80°C and carry out vacuum treatment under the gauge pressure of -0.07MPa for 60 minutes, then raise the temperature to 120°C and maintain this temperature, and pass through ethylene oxide 10 moles of alkanes, the gauge pressure of the reactor is kept at 0.15 MPa by controlling the feeding speed of ethylene oxide, after the addition of ethylene oxide, it is matured at 120°C for 1 hour, and then 8 moles of propylene oxide are fed in, and the pressure is controlled by controlling the loop The feeding speed of propylene oxide keeps the gauge pressure of the reactor at 0.15MPa. After adding propylene oxide, it is aged at 120°C for 1 hour, and t...
Embodiment 3
[0079] 1. Synthesis of Fatty Alcohol Ether
[0080] Into a dry 2 L reaction kettle with stirring, electric heating mantle and internal water cooling coil was charged 2 moles of tetradecyl alcohol and potassium hydroxide. Seal the reaction kettle, replace the air in the reaction kettle with nitrogen for three times, start stirring, heat up to 80°C and carry out vacuum treatment at a gauge pressure of -0.07MPa for 60 minutes, then raise the temperature to 120°C and maintain this temperature, and pass in propylene oxide 8 moles, keep the gauge pressure of the reactor at 0.15MPa by controlling the feed rate of propylene oxide, after adding propylene oxide, mature at 120°C for 1 hour, then feed 16 moles of ethylene oxide, The feed rate of alkane keeps the gauge pressure of the reactor at 0.15MPa. After adding ethylene oxide, mature at 120°C for 1 hour, cool down to 70°C, neutralize with acetic acid, and then carry out vacuum dehydration at a gauge pressure of -0.07MPa The fatty al...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com