Preparation method of in-situ-polymerization graphene microemulsion
An in-situ polymerization and graphene technology, applied in the field of nanomaterials, can solve the problems of no nanomaterials, demulsification, etc., and achieve the effects of strong operability, small dispersed particle size, and avoiding demulsification.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] In situ polymerization-grade graphene microemulsions were prepared by the following steps:
[0029] Step 1: Add 400mL deionized water to the flask;
[0030] Step 2: Add 3g of intercalation agent sodium lauryl sulfate, fully dissolve;
[0031] Step 3: Add 5g of graphene, stir and disperse for 15 minutes;
[0032] Step 4: Put it into the ultrasonic processor for 15 minutes, and the ultrasonic power is 500 watts;
[0033] Step 5: heat up to 70°C, add 2.4g of n-hexadecanol as an emulsified micellar protective agent;
[0034] Step 6: Add 200 mL of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose ether aqueous solution with a concentration of 2%, and stir thoroughly;
[0035] Step 7: Put it into an ultrasonic processor for processing, the ultrasonic power is 500 watts, and the processing time is 60 minutes.
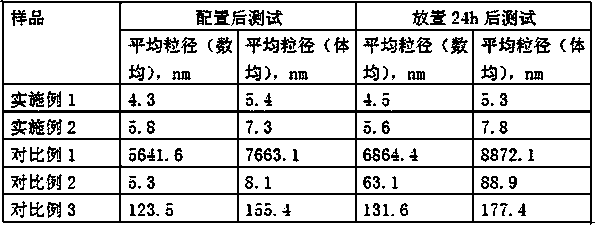
[0036] Obtain in-situ polymerization grade graphene microemulsion. The particle size was tested with a laser particle size distribution analyzer, see Table 1.
[0037]
Embodiment 2
[0039] In situ polymerization-grade graphene microemulsions were prepared by the following steps:
[0040] Step 1: Add 400mL deionized water to the flask;
[0041] Step 2: Add 10 g of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate as an intercalation agent and fully dissolve;
[0042] Step 3: Add 10g of graphene, stir and disperse for 15 minutes;
[0043] Step 4: Put it into an ultrasonic processor for 30 minutes, and the ultrasonic power is 1000 watts;
[0044] Step 5: heat up to 70°C, add 10 g of n-stearyl alcohol, an emulsified micelle protective agent;
[0045] Step 6: Add 200 mL of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose ether aqueous solution with a concentration of 2%, and stir thoroughly;
[0046] Step 7: Put it into an ultrasonic processor for processing, the ultrasonic power is 1000 watts, and the processing time is 120 minutes.
[0047] Obtain in-situ polymerization grade graphene microemulsion. The particle size was tested with a laser particle size distribution analyzer, see Tabl...
Embodiment 3
[0049] In situ polymerization-grade graphene microemulsions were prepared by the following steps:
[0050] Step 1: Add 400mL deionized water to the flask;
[0051] Step 2: Add 5 g of sodium dodecyl sulfate and 5 g of sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate as intercalation agents, and fully dissolve;
[0052] Step 3: Add 50g of graphene, stir and disperse for 15 minutes;
[0053] Step 4: Put it into the ultrasonic processor for 15 minutes, and the ultrasonic power is 500 watts;
[0054] Step 5: heat up to 70°C, add 30g of n-heptadecanol, an emulsified micellar protective agent;
[0055]Step 6: Add 200 mL of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose ether aqueous solution with a concentration of 2%, and stir thoroughly;
[0056] Step 7: Put it into an ultrasonic processor for processing, the ultrasonic power is 500 watts, and the processing time is 60 minutes.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com