Patents
Literature
68 results about "Graphene monolayer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
About Monolayer Graphene Oxide. Graphene Oxide (GO) is a recently developed nanomaterial in the form of graphene, a single atom-thick layer of carbon atoms, with various oxygen-containing functionalities.
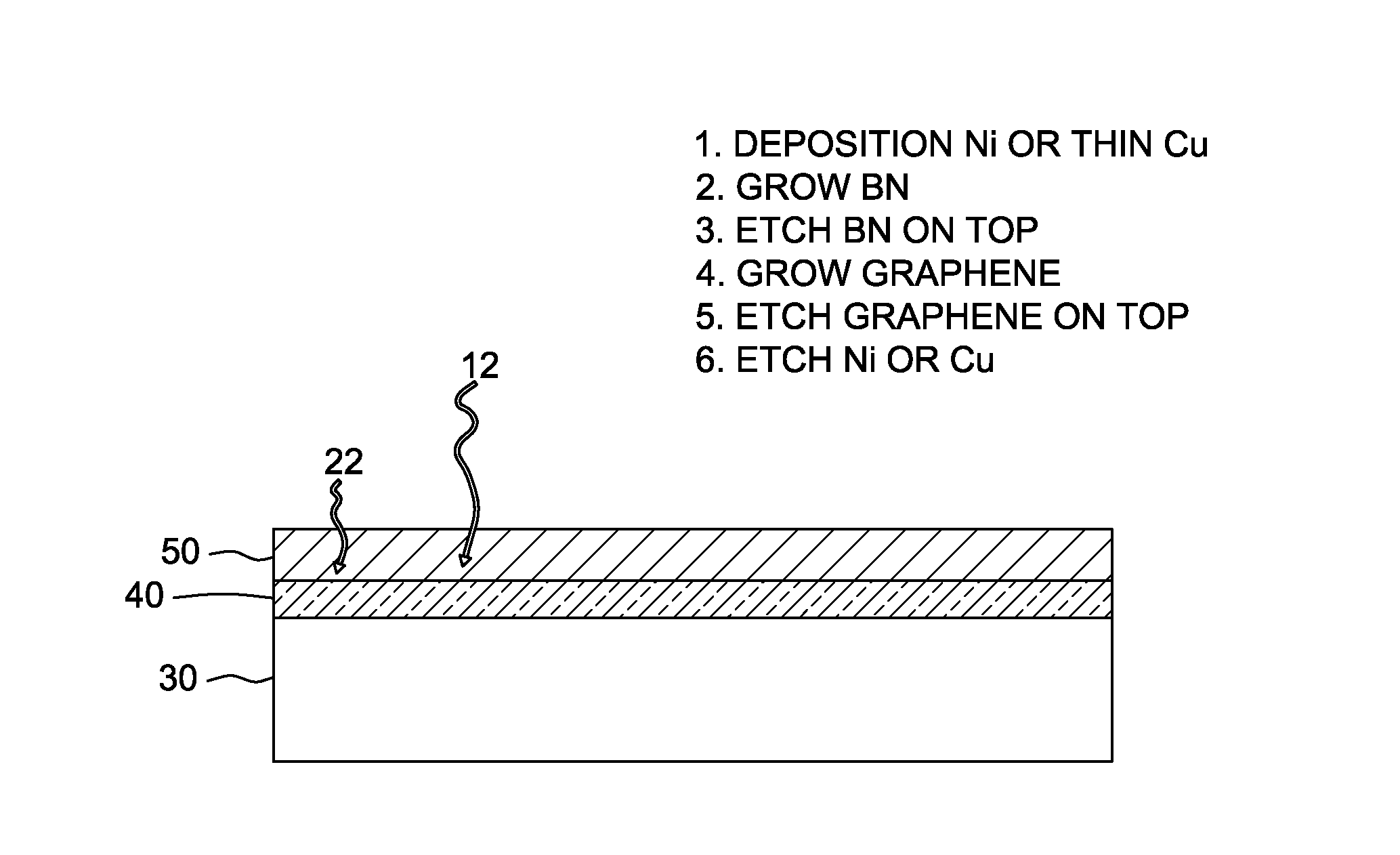
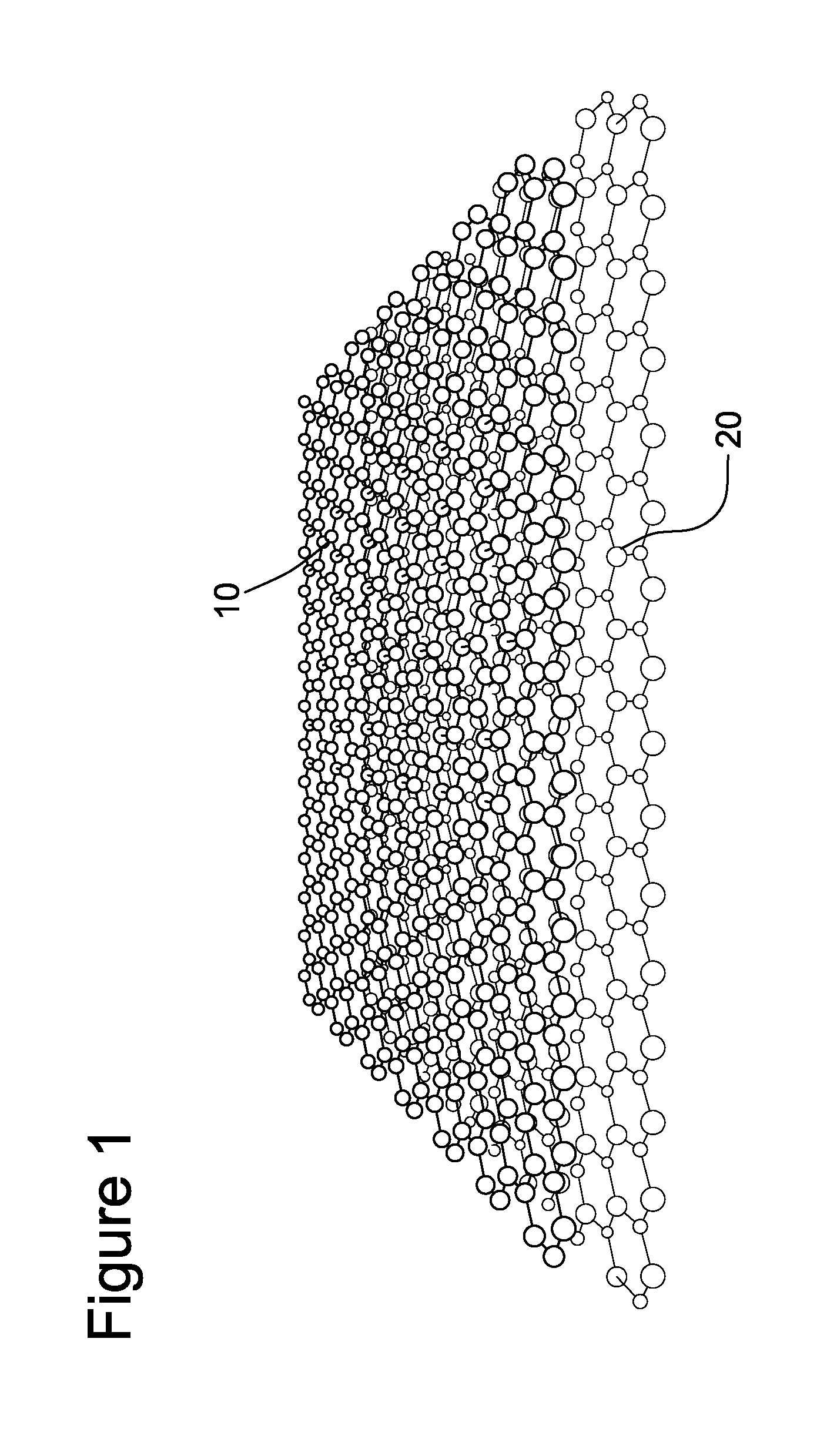
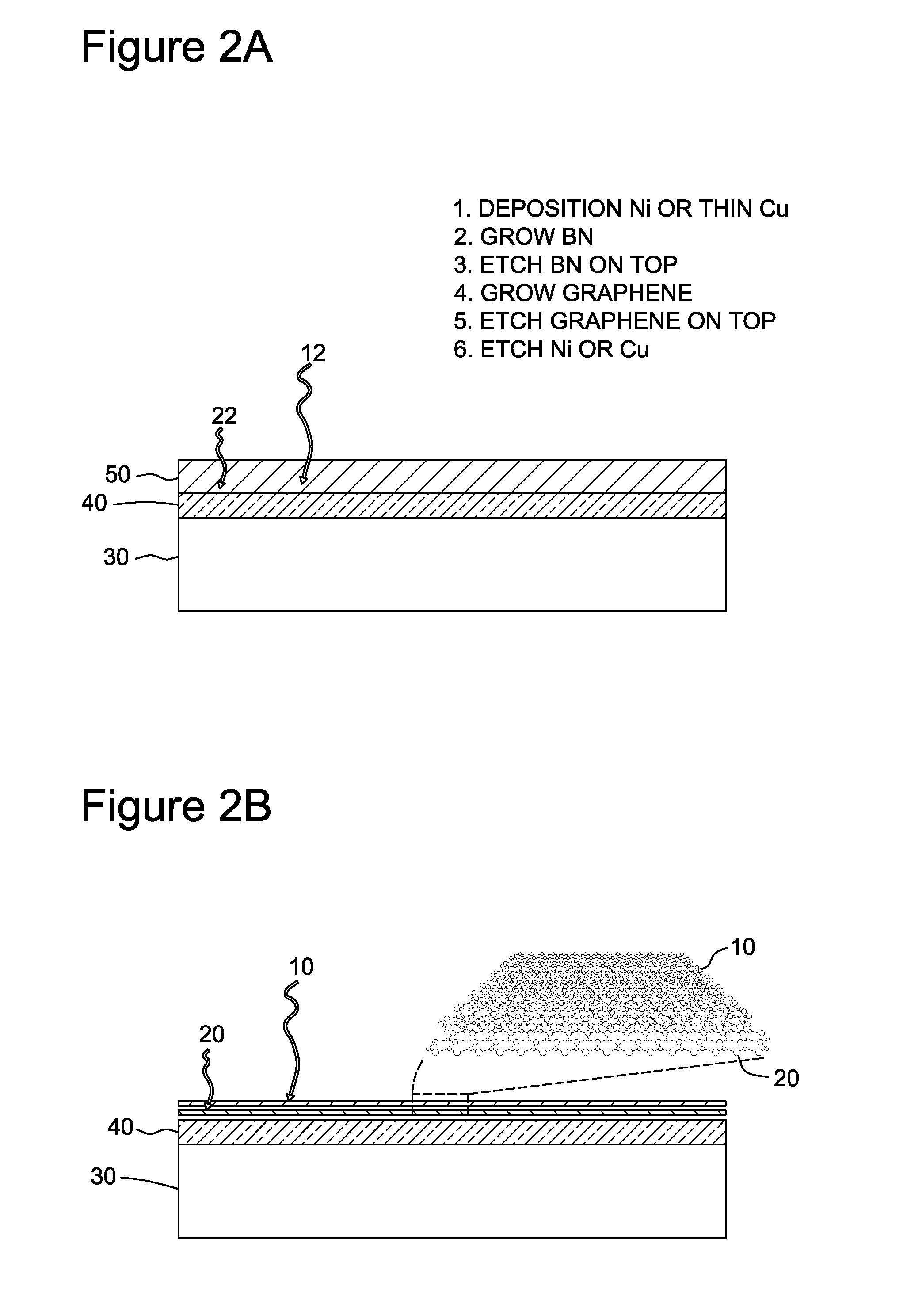
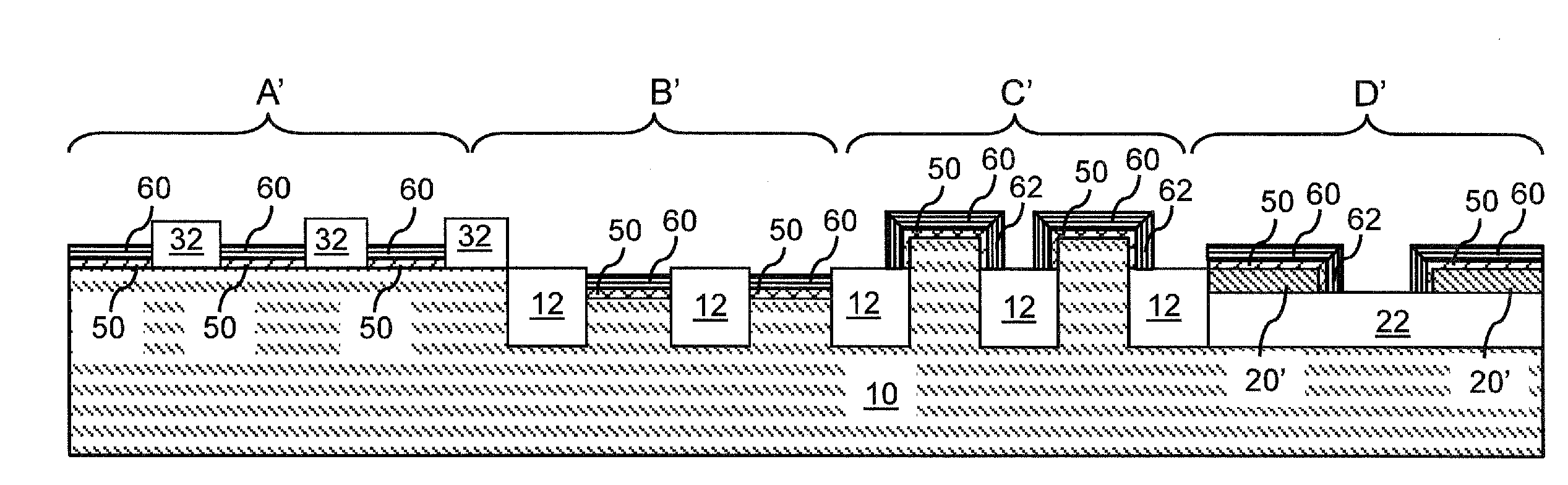
Direct and sequential formation of monolayers of boron nitride and graphene on substrates
ActiveUS20130240830A1Material nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBoron nitrideCvd graphene
The invention generally related to a method for preparing a layer of graphene directly on the surface of a substrate, such as a semiconductor substrate. The layer of graphene may be formed in direct contact with the surface of the substrate, or an intervening layer of a material may be formed between the substrate surface and the graphene layer.
Owner:KANSAS STATE UNIV RES FOUND +1
Graphene growth on a carbon-containing semiconductor layer
A semiconductor-carbon alloy layer is formed on the surface of a semiconductor substrate, which may be a commercially available semiconductor substrate such as a silicon substrate. The semiconductor-carbon alloy layer is converted into at least one graphene layer during a high temperature anneal, during which the semiconductor material on the surface of the semiconductor-carbon alloy layer is evaporated selective to the carbon atoms. As the semiconductor atoms are selectively removed and the carbon concentration on the surface of the semiconductor-carbon alloy layer increases, the remaining carbon atoms in the top layers of the semiconductor-carbon alloy layer coalesce to form a graphene layer having at least one graphene monolayer. Thus, a graphene layer may be provided on a commercially available semiconductor substrate having a diameter of 200 mm or 300 mm.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Methods of fabricating graphene using alloy catalyst
Methods of fabricating graphene using an alloy catalyst may include forming an alloy catalyst layer including nickel on a substrate and forming a graphene layer by supplying hydrocarbon gas onto the alloy catalyst layer. The alloy catalyst layer may include nickel and at least one selected from the group consisting of copper, platinum, iron and gold. When the graphene is fabricated, a catalyst metal that reduces solubility of carbon in Ni may be used together with Ni in the alloy catalyst layer. An amount of carbon that is dissolved may be adjusted and a uniform graphene monolayer may be fabricated.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Graphene membrane with regular angstrom-scale pores
InactiveUS8979978B2Uniform pore sizeMaterial nanotechnologySemi-permeable membranesVacancy defectPore diameter
Technologies are generally described for perforated graphene monolayers and membranes containing perforated graphene monolayers. An example membrane may include a graphene monolayer having a plurality of discrete pores that may be chemically perforated into the graphene monolayer. The discrete pores may be of substantially uniform pore size. The pore size may be characterized by one or more carbon vacancy defects in the graphene monolayer. The graphene monolayer may have substantially uniform pore sizes throughout. In some examples, the membrane may include a permeable substrate that contacts the graphene monolayer and which may support the graphene monolayer. Such perforated graphene monolayers, and membranes comprising such perforated graphene monolayers may exhibit improved properties compared to conventional polymeric membranes for gas separations, e.g., greater selectivity, greater gas permeation rates, or the like.
Owner:EMPIRE TECH DEV LLC
Method for rapidly and nondestructively transferring graphene
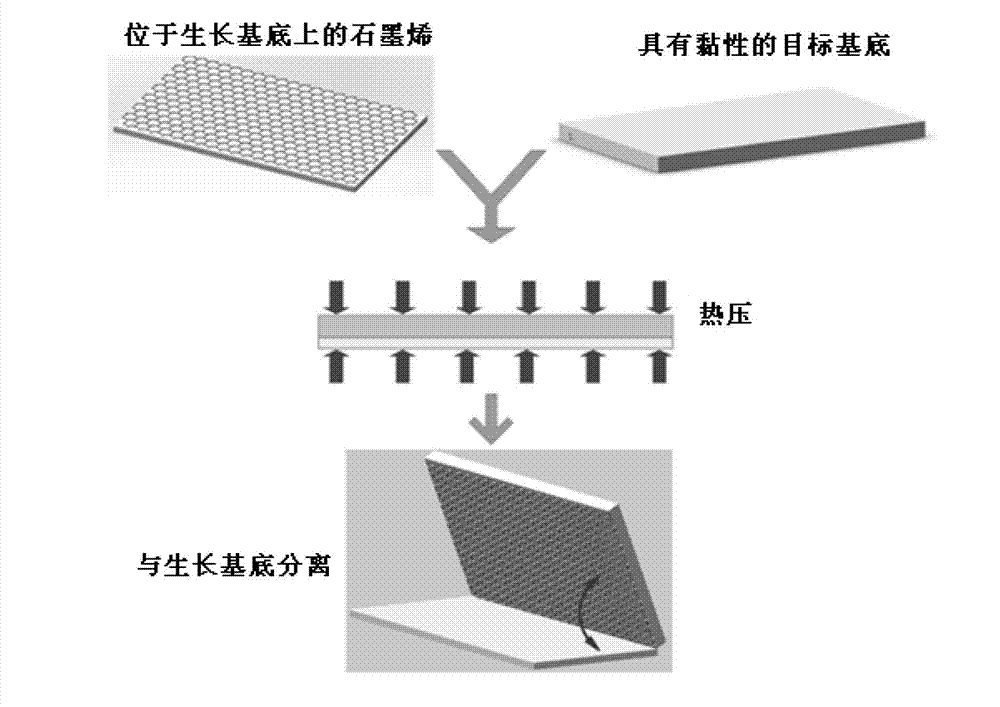
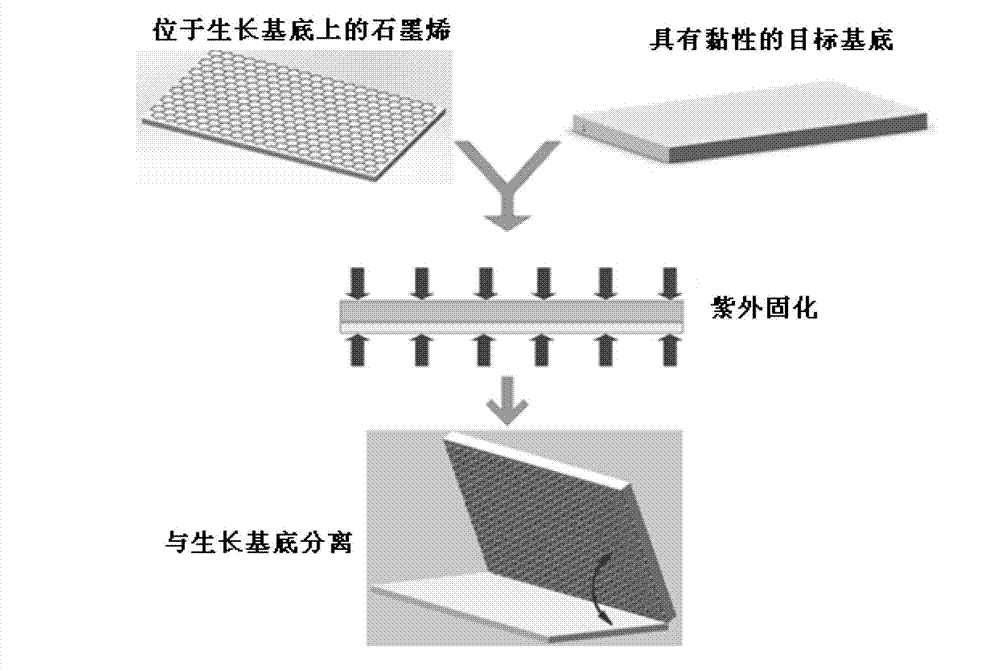
The invention discloses a method for rapidly and nondestructively transferring graphene. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) coating a thermosetting adhesive or an optical curing adhesive on the surface of a target substrate; (2) attaching the surface of the target substrate, which is obtained in the step (1) and is coated with the thermosetting adhesive or the optical curing adhesive, to the graphene, thus forming a target substrate / graphene / growth substrate composite structure; (3) performing hot-press treatment or UV-irradiation curing treatment on the target substrate / graphene / growth substrate composite structure obtained in the step (2); (4) performing growth substrate stripping on the target substrate / graphene / growth substrate composite structure treated in the step (3). The large-area high-quality graphene can be transferred to the target substrate under the condition that the growth substrate is not corroded, the obtained graphene has a high single-layer property and relatively high uniformity, the pollution of organic adhesive residues and metal substrate dissolution on the graphene in the transfer process is avoided, and the growth substrate can be repeatedly used and is economic and environment-friendly.
Owner:CHONGQING GRAPHENE TECH +1
Methods of fabricating graphene using alloy catalyst
Methods of fabricating graphene using an alloy catalyst may include forming an alloy catalyst layer including nickel on a substrate and forming a graphene layer by supplying hydrocarbon gas onto the alloy catalyst layer. The alloy catalyst layer may include nickel and at least one selected from the group consisting of copper, platinum, iron and gold. When the graphene is fabricated, a catalyst metal that reduces solubility of carbon in Ni may be used together with Ni in the alloy catalyst layer. An amount of carbon that is dissolved may be adjusted and a uniform graphene monolayer may be fabricated.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
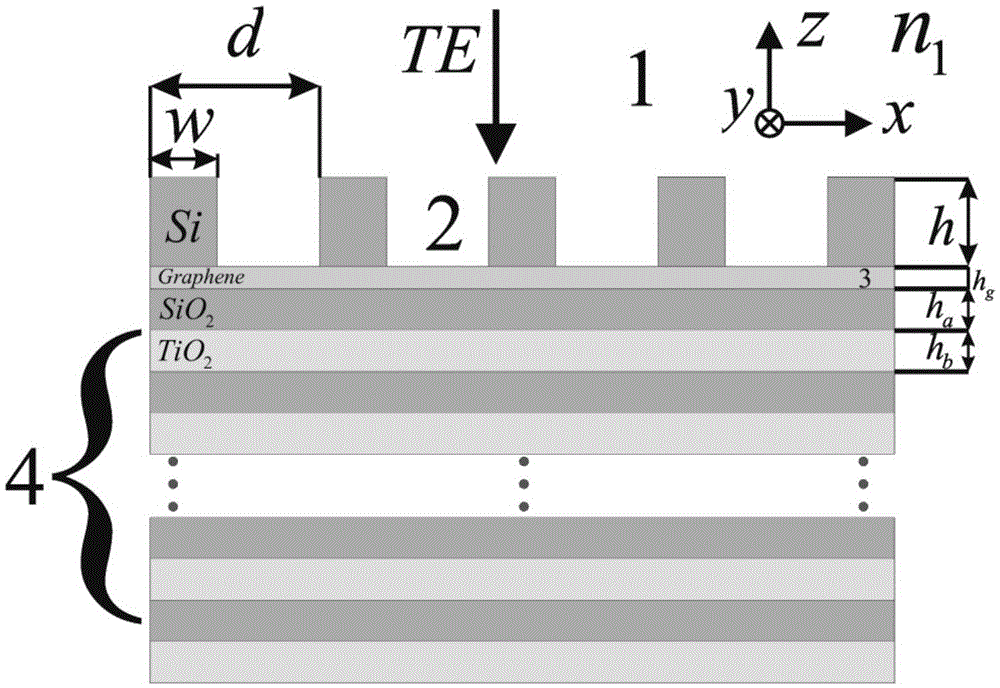
Spectrum selective absorber based on single-layer graphene and Bragg grating
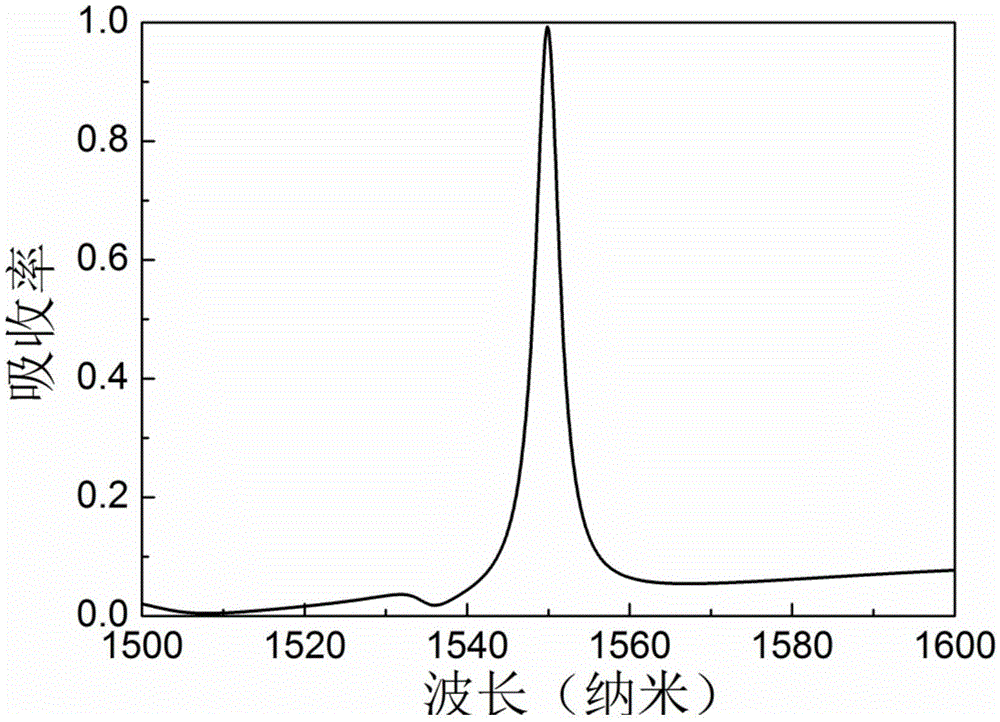
The invention provides an ultra-narrow-band TE polarization spectrum selective absorber based on a single-layer graphene and a Bragg grating. The absorber comprises a dielectric grating layer, the single-layer graphene and a Bragg grating layer; wherein the dielectric grating layer, the single-layer graphene and the Bragg grating layer are successively arranged from top to bottom. The period, the ridge width and the thickness of the dielectric grating layer are respectively 574-576 nanometers, 548-550 nanometers and 219-221 nanometers. The Bragg grating layer is composed of at least 20 pairs of low-refractivity dielectric panels and high-refractivity dielectric panels. The thickness of each low-refractivity dielectric panel is 340-350 nanometers, and the thickness of each high-refractivity dielectric panel is 165-175 nanometers. The spectrum selective absorber can be manufactured according to optical holographic recording technology or electron-beam direct-writing device and micro-electron deep-etching process. The ultra-narrow-band TE polarization spectrum selective absorber has advantages of convenient material acquisition, low manufacture cost, large-batch production and important use prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of graphene
The invention provides a preparation method of graphene. The method comprises steps as follows: a graphene oxide aqueous solution is subjected to ultrasonic treatment, then the pH value of the solution is adjusted to be alkaline, a reducing agent and an alcohol polymer are added, and graphene is obtained after the mixture is heated to be subjected to a reaction. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that the graphene oxide aqueous solution is subjected to ultrasonic treatment, graphene oxide is layered and dispersed further, and the alcohol polymer is added to the solution to be used as a polymerization inhibitor, so that obtained graphene is high in single-layer ratio and uniform in flake diameter; besides, the preparation method is simple, and the cost is relatively low.
Owner:SHANDONG OBO NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Graphene membrane with regular angstrom-scale pores
Technologies are generally described for perforated graphene monolayers and membranes containing perforated graphene monolayers. An example membrane may include a graphene monolayer having a plurality of discrete pores that may be chemically perforated into the graphene monolayer. The discrete pores may be of substantially uniform pore size. The pore size may be characterized by one or more carbon vacancy defects in the graphene monolayer. The graphene monolayer may have substantially uniform pore sizes throughout. In some examples, the membrane may include a permeable substrate that contacts the graphene monolayer and which may support the graphene monolayer. Such perforated graphene monolayers, and membranes comprising such perforated graphene monolayers may exhibit improved properties compared to conventional polymeric membranes for gas separations, e.g., greater selectivity, greater gas permeation rates, or the like.
Owner:EMPIRE TECH DEV LLC
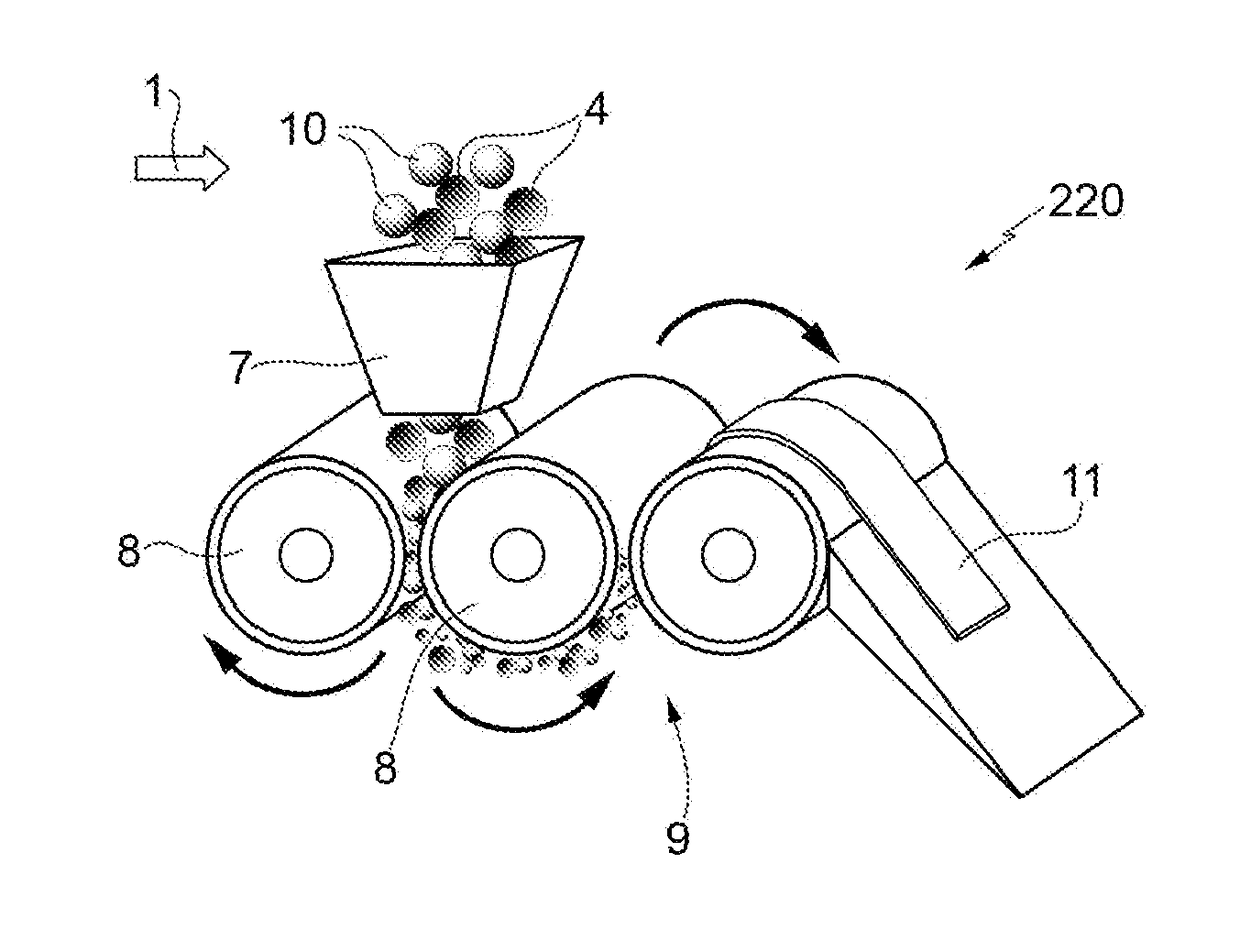
Dry type stripping production process of graphene nano powder
The invention relates to the technical field of graphene production methods, in particular to a dry type stripping production process of graphene nano powder. The dry type stripping production processincludes the steps of firstly, heating to expand expandable graphite with high expansion times under inert or reduction atmosphere to obtain graphite worms; secondly, subjecting the collected graphite worms to ultrahigh-speed rotary shearing in a crushing cavity to obtain graphite micro-sheets; thirdly, processing the graphite micro-sheets in a high-pressure container on a vibration platform; fourthly, subjecting the graphite micro-sheets flowing out of the high-pressure container to continuous stripping in an ultrasonic stripping cavity to obtain the graphene nano powder. The obtained graphene nano powder is large in single-layer sheet diameter, few in layers, good in universality, high in conductivity, low in resistance, high in specific surface area and low in production cost.
Owner:苏州鼎烯聚材纳米科技有限公司
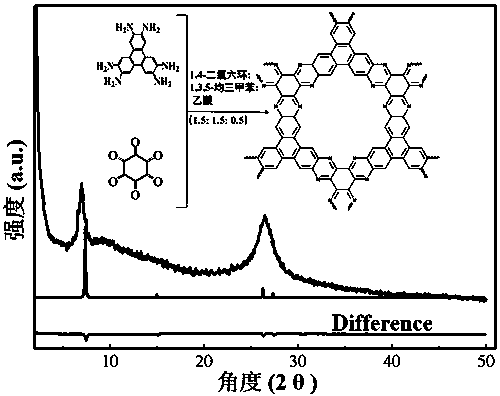
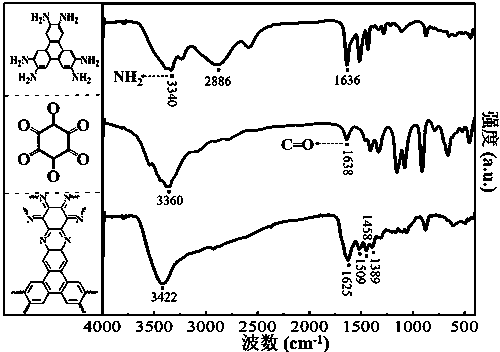
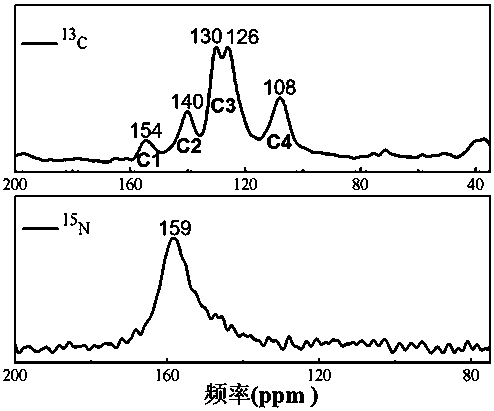
Preparation of phenazine-connecting two-dimensional covalent organic framework material of novel structure
The invention discloses a preparation method of a phenazine-connecting two-dimensional covalent organic framework material of a novel structure. The synthesized phenazine-connecting two-dimensional covalent organic framework material of the novel structure has a highly planar rigid structure in a graphene-like single layer, and is also highly conjugated between layers. A synthesis method is a solvothermal method and is easy and safe to operate, the reaction is a molecular level reaction, and the synthesized product is more ordered and more stable. According to the method, triphenylene-2,3,6,7,10,11-hexaaminotriphenylene and hexaketocyclohexane octahydrate serve as raw materials, 1,4-dioxane and 1,3,5-mesitylene serve as organic solvents, and the phenazine-connecting two-dimensional covalent organic framework material of the novel structure is successfully prepared through the solvothermal method under the condition that acetic acid is used for adjusting the acid environment.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Infrared radiation detectors using bundled-vxoy or amorphous silicon nanoparticles nanostructures and methods of constructing the same
ActiveUS9945720B1Improve stabilityIncrease temperature coefficientPhotometry electrical circuitsPyrometry using electric radation detectorsReadout integrated circuitVanadium oxide
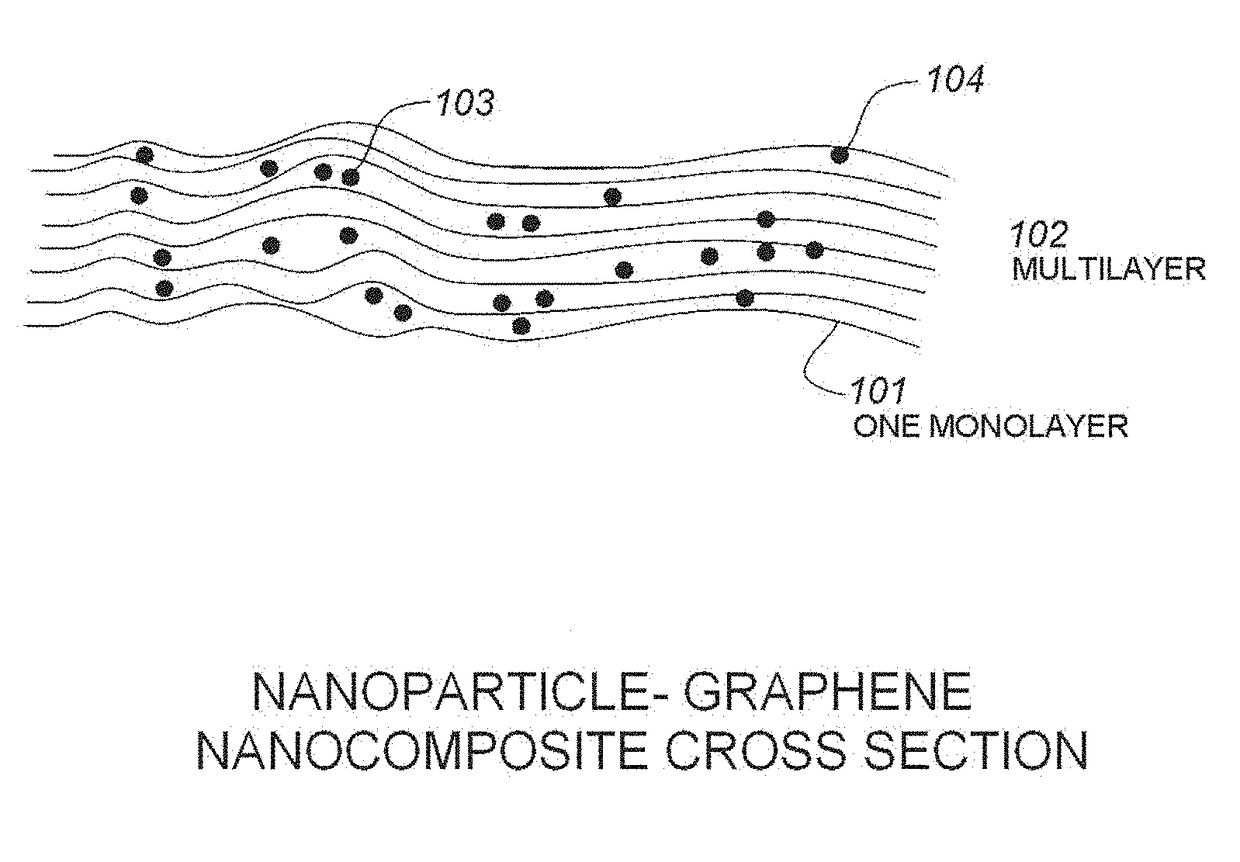
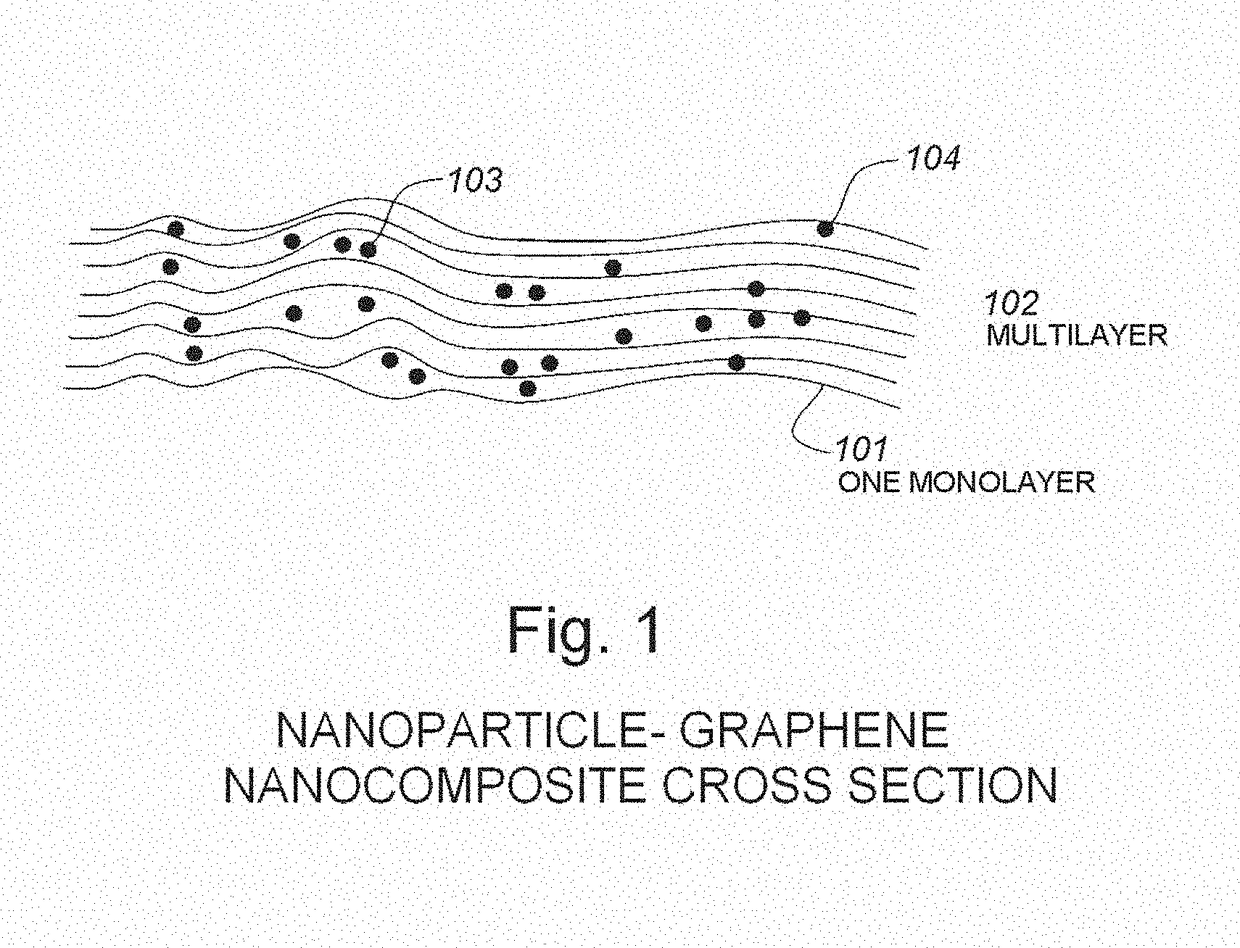
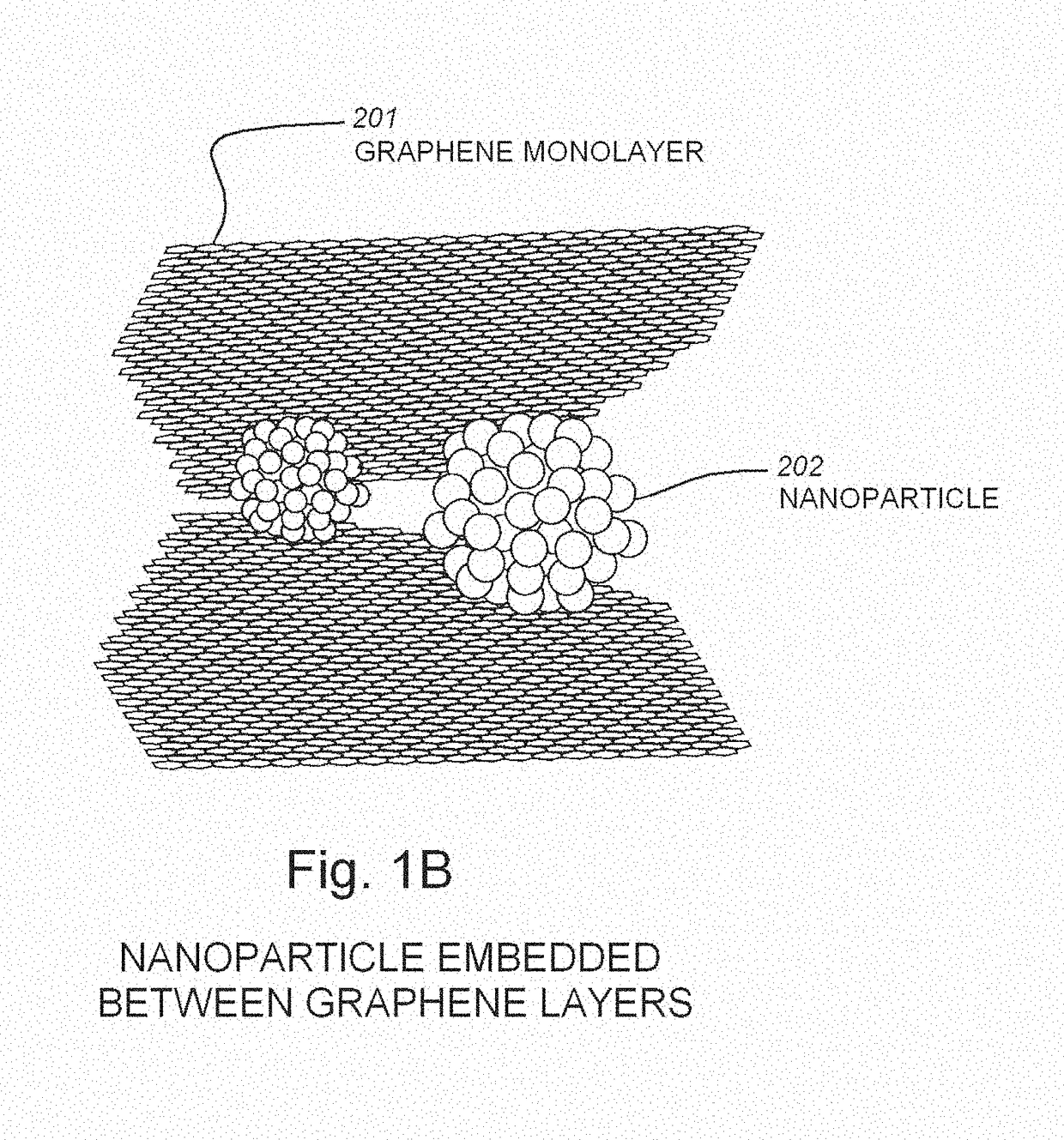
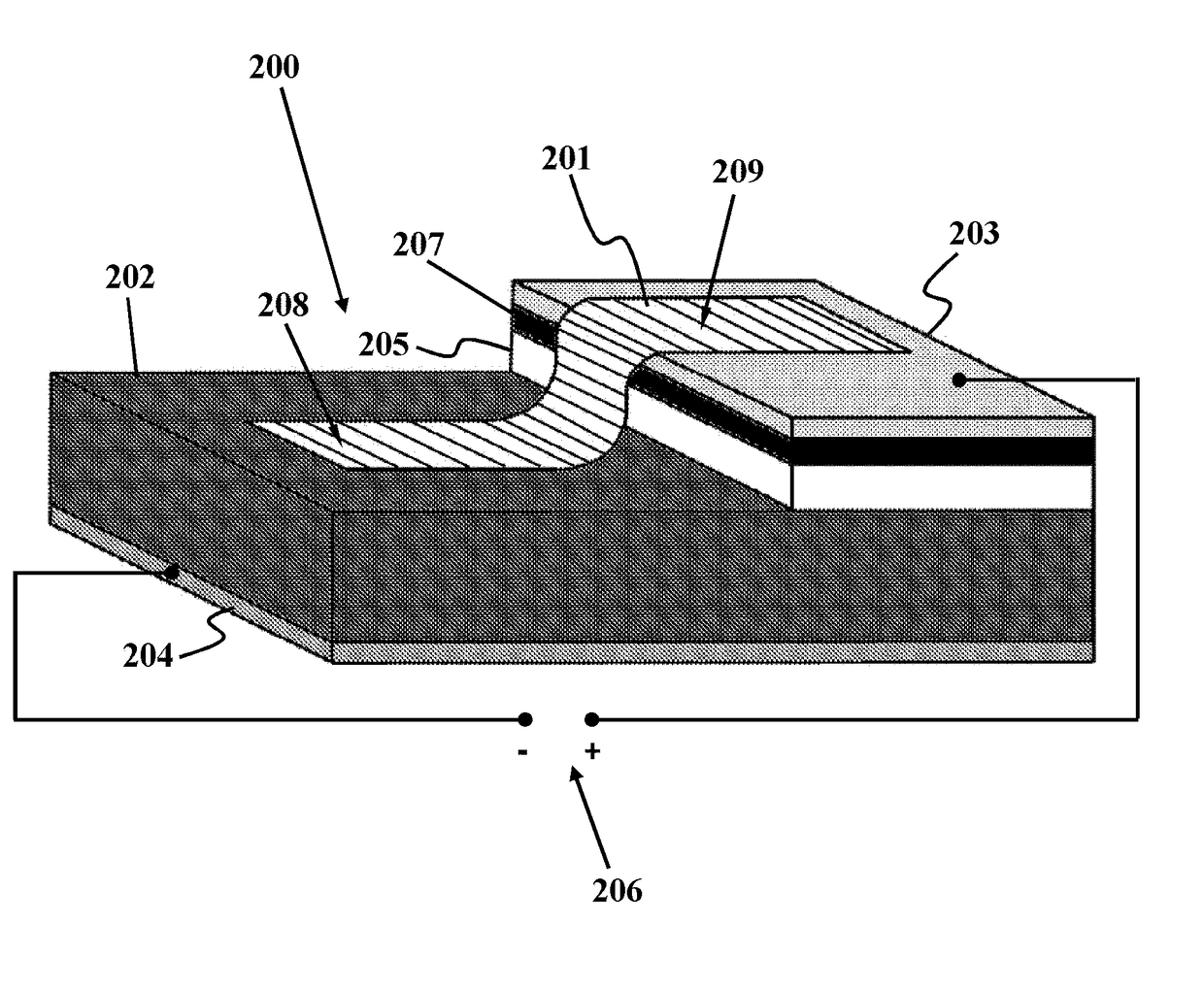
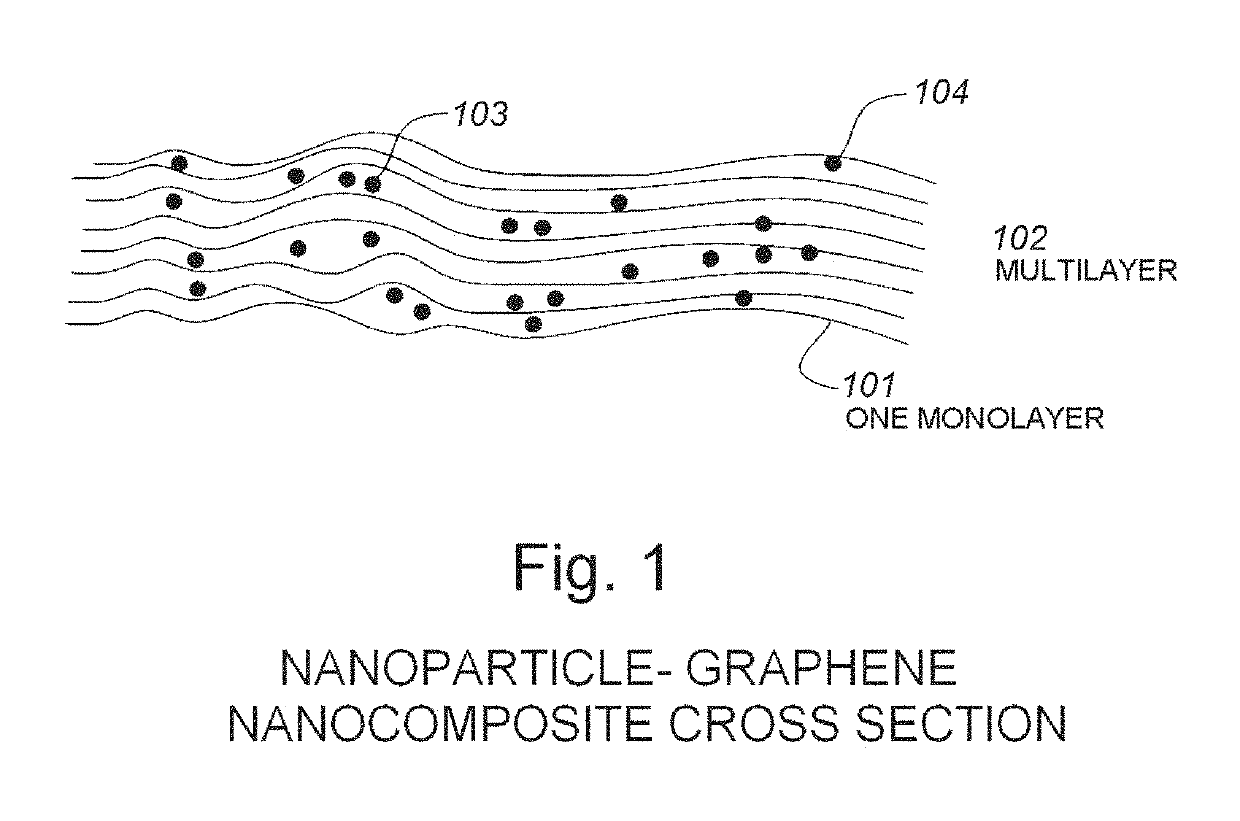
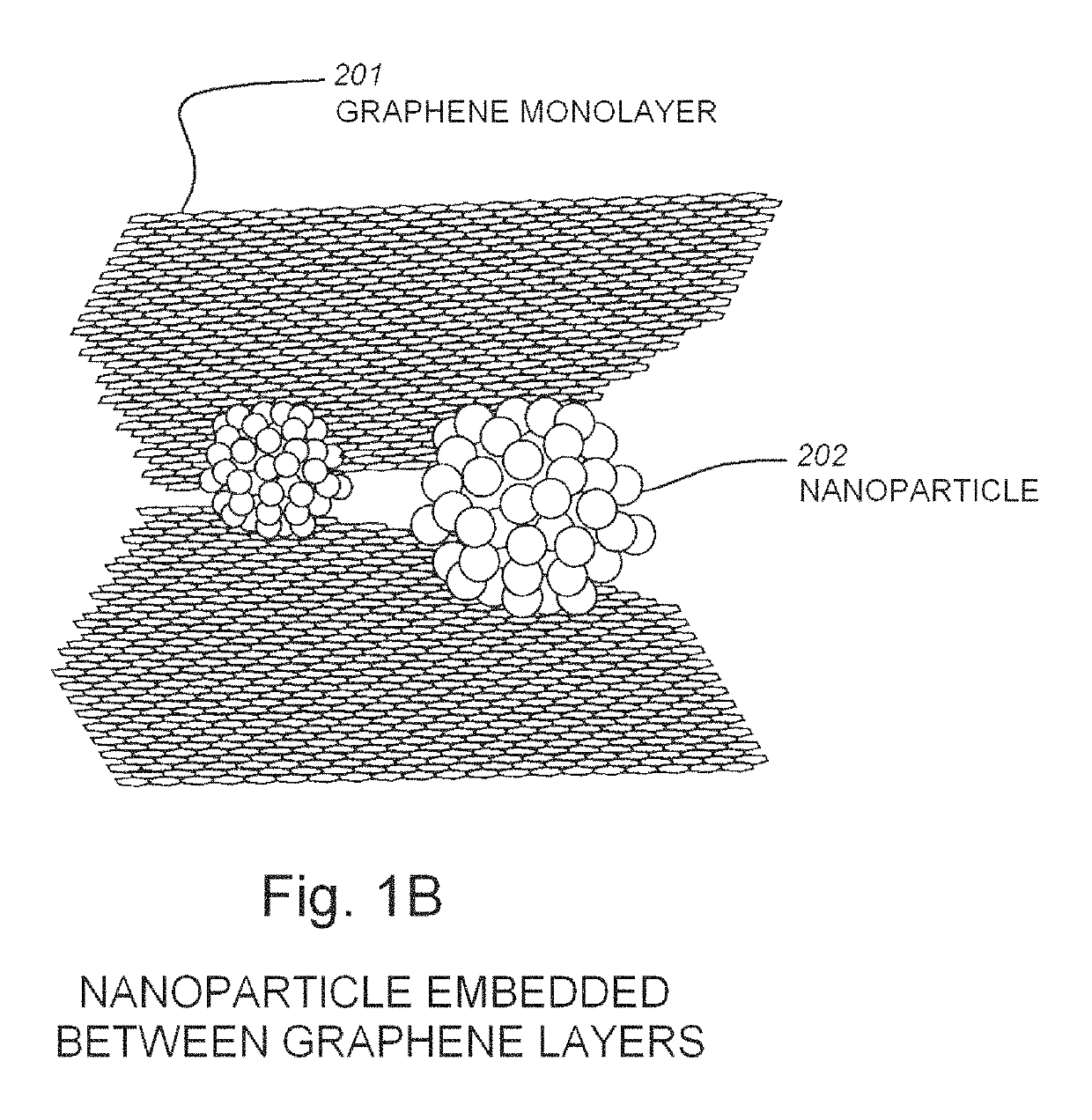
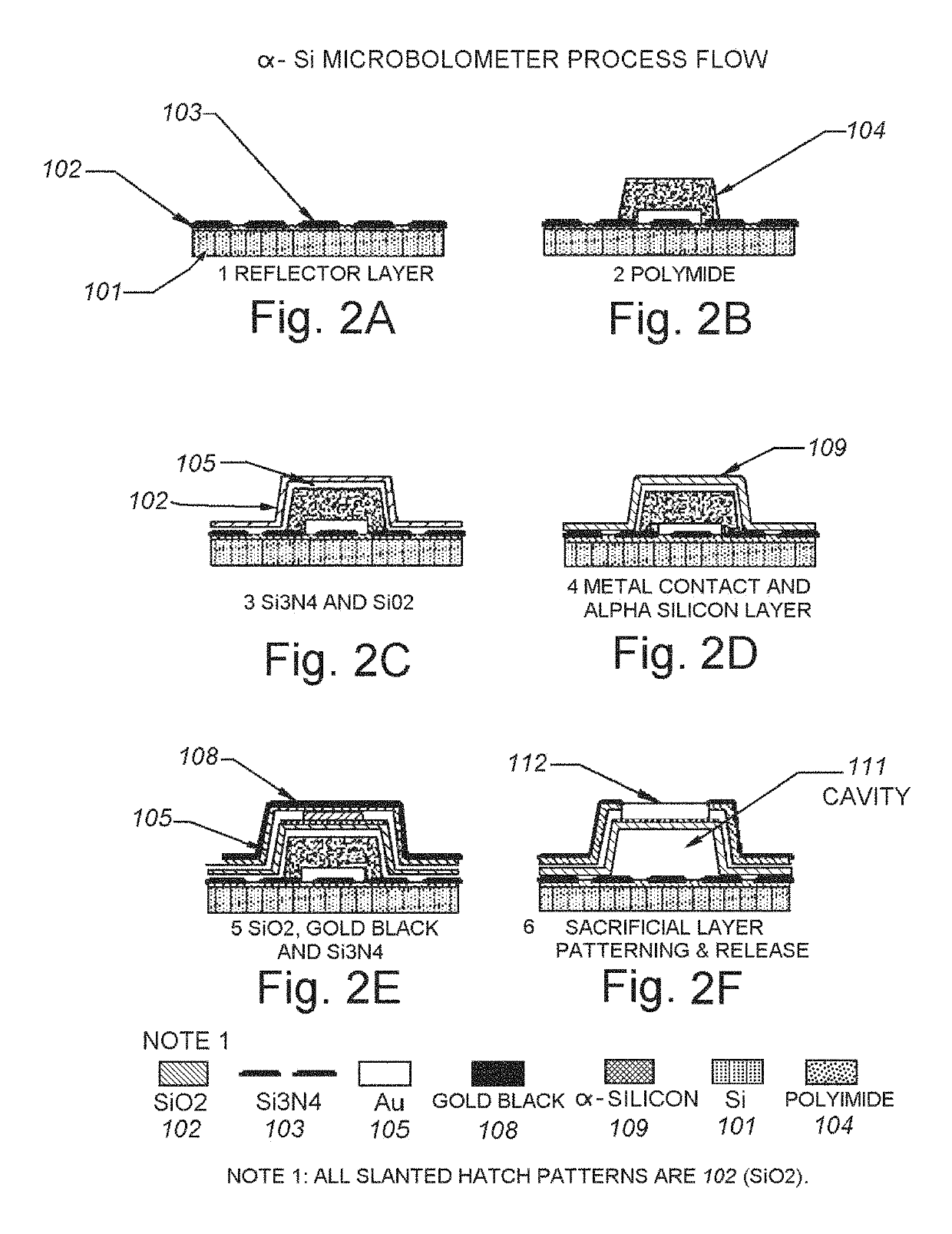
The use of silicon or vanadium oxide nanocomposite consisting of graphene deposited on top of an existing amorphous silicon or vanadium oxide microbolometer can result in a higher sensitivity IR detector. An IR bolometer type detector consisting of a thermally isolated nano-sized (<one micron feature size) electro-mechanical structure comprised of Si3N4, SiO2 thins films, suspended over a cavity with a copper thin film reflecting surface is described. On top of the suspended thin film is a nanostructure composite comprised of graphene monolayers, covered with various surface densities of VoXy or amorphous nanoparticles, followed by another graphene layer. The two conducting legs are connected to a readout integrated circuit (ROIC) fabricated on a CMOS wafer underneath. The nanostructure is fabricated after the completion of the ROIC process and is integrate able with the CMOS process.
Owner:MAGNOLIA OPTICAL TECH
Graphene-based detector for w-band and terahertz radiations
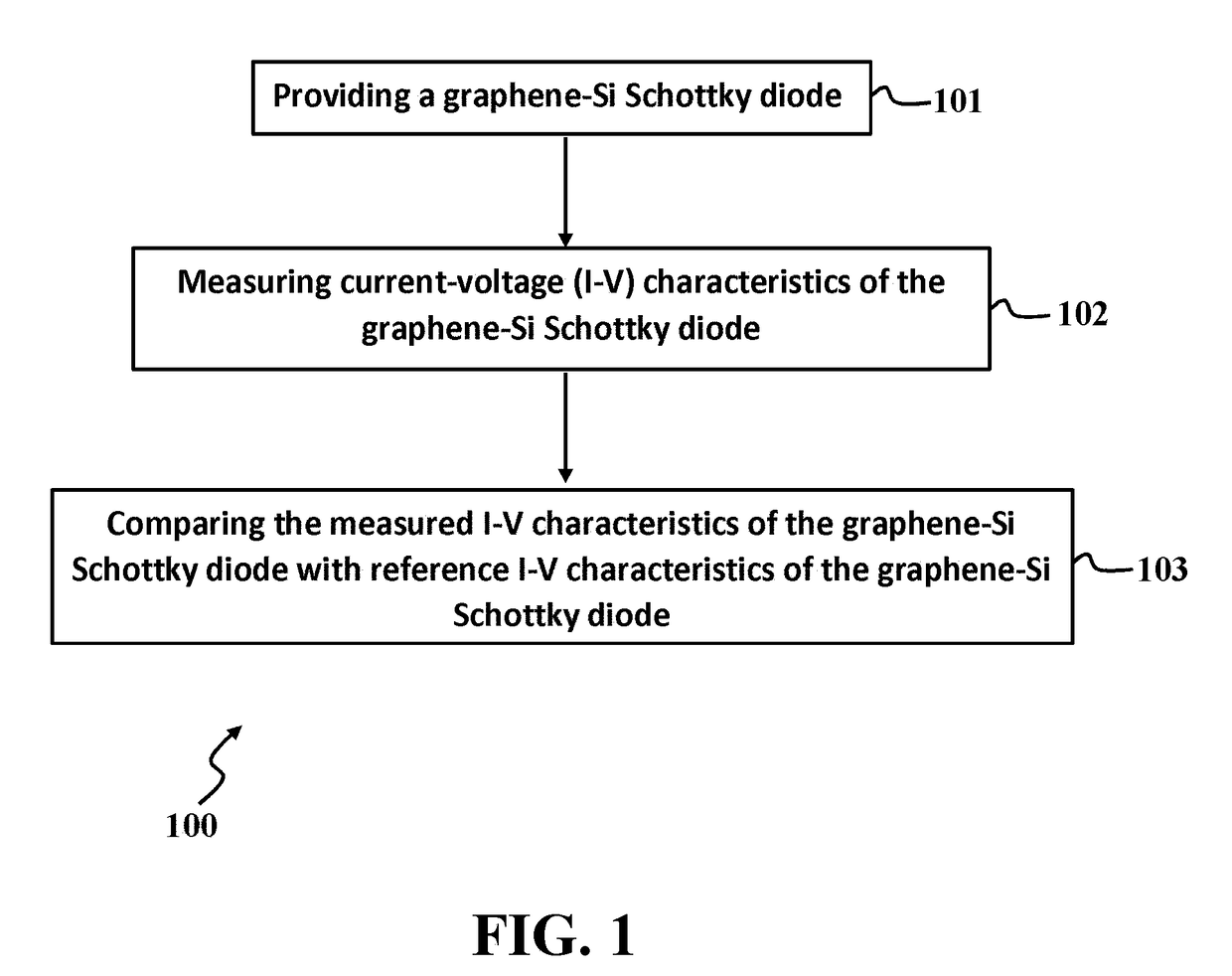
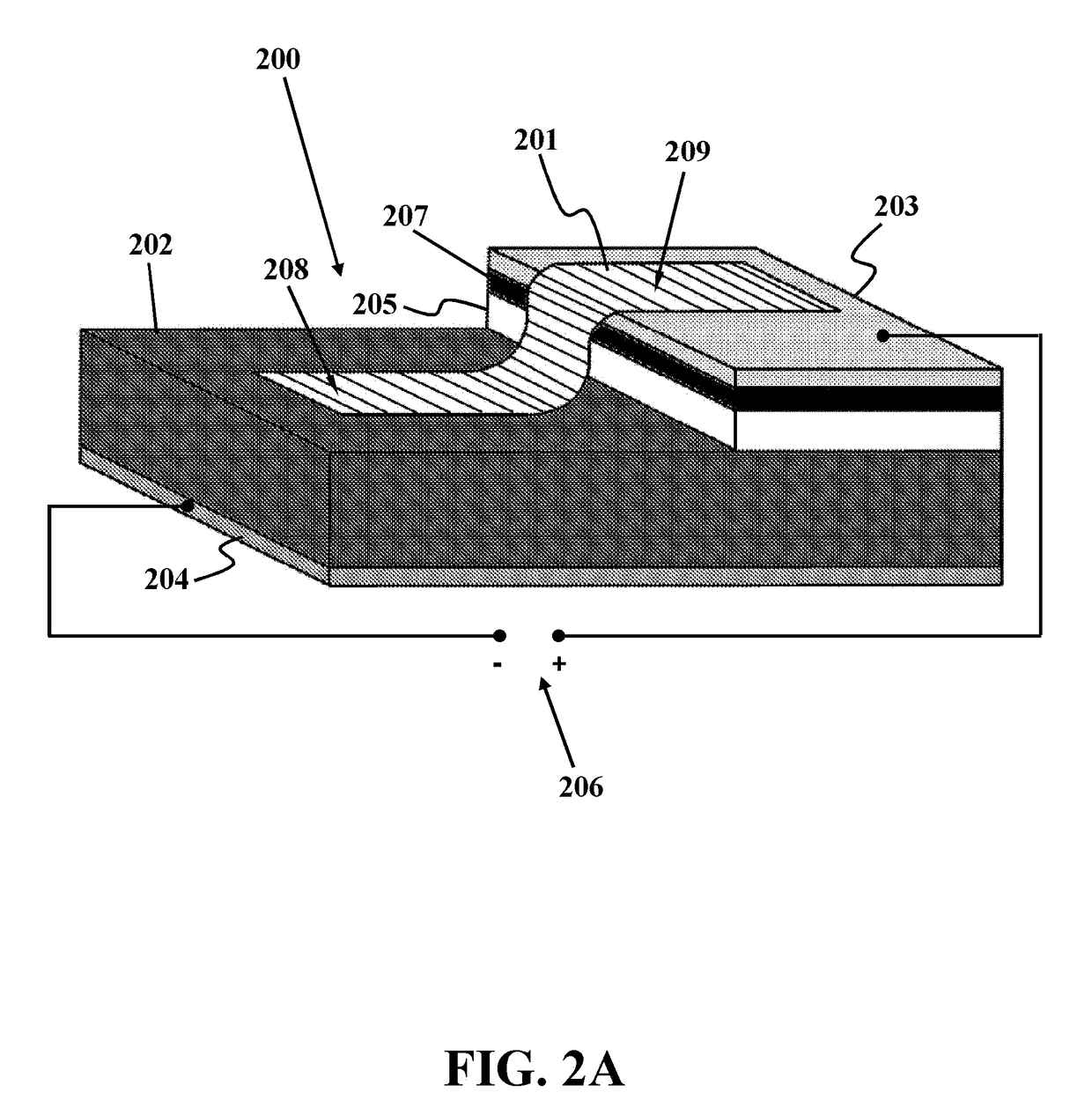
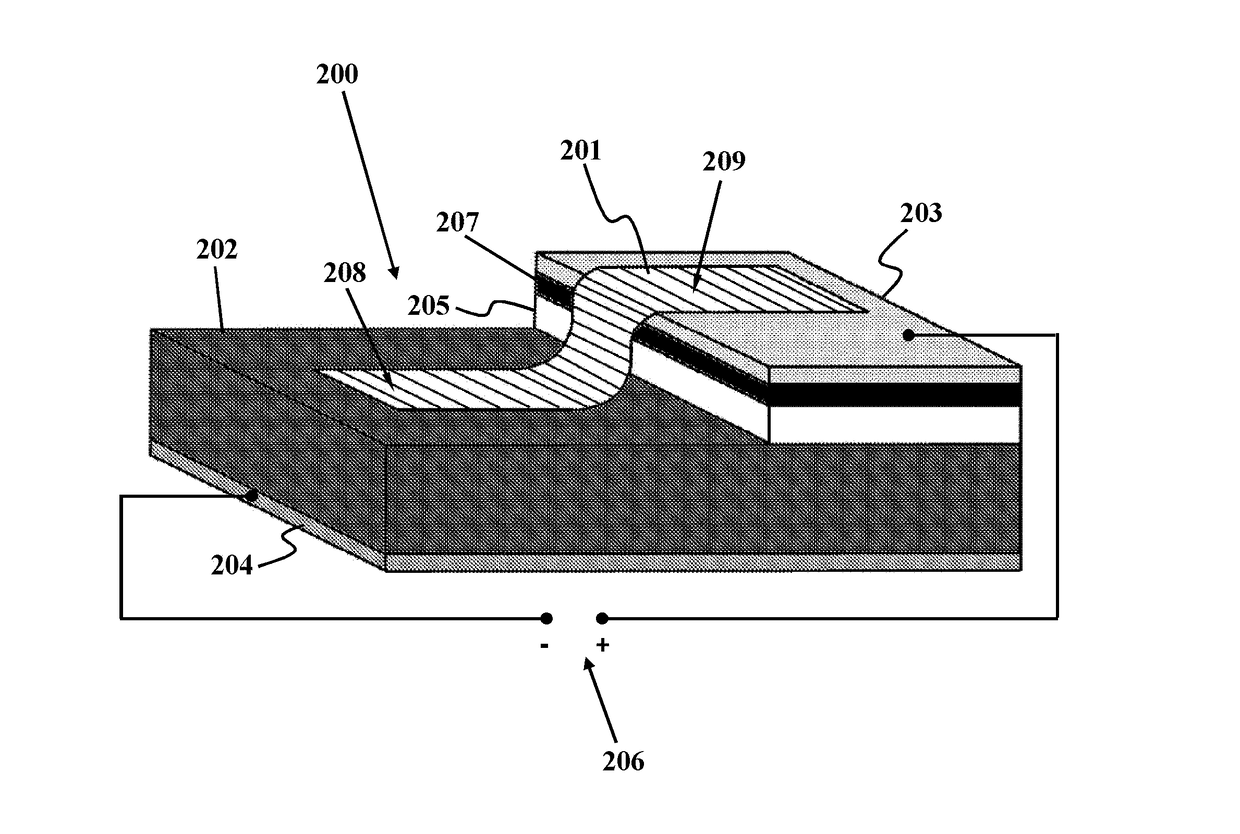
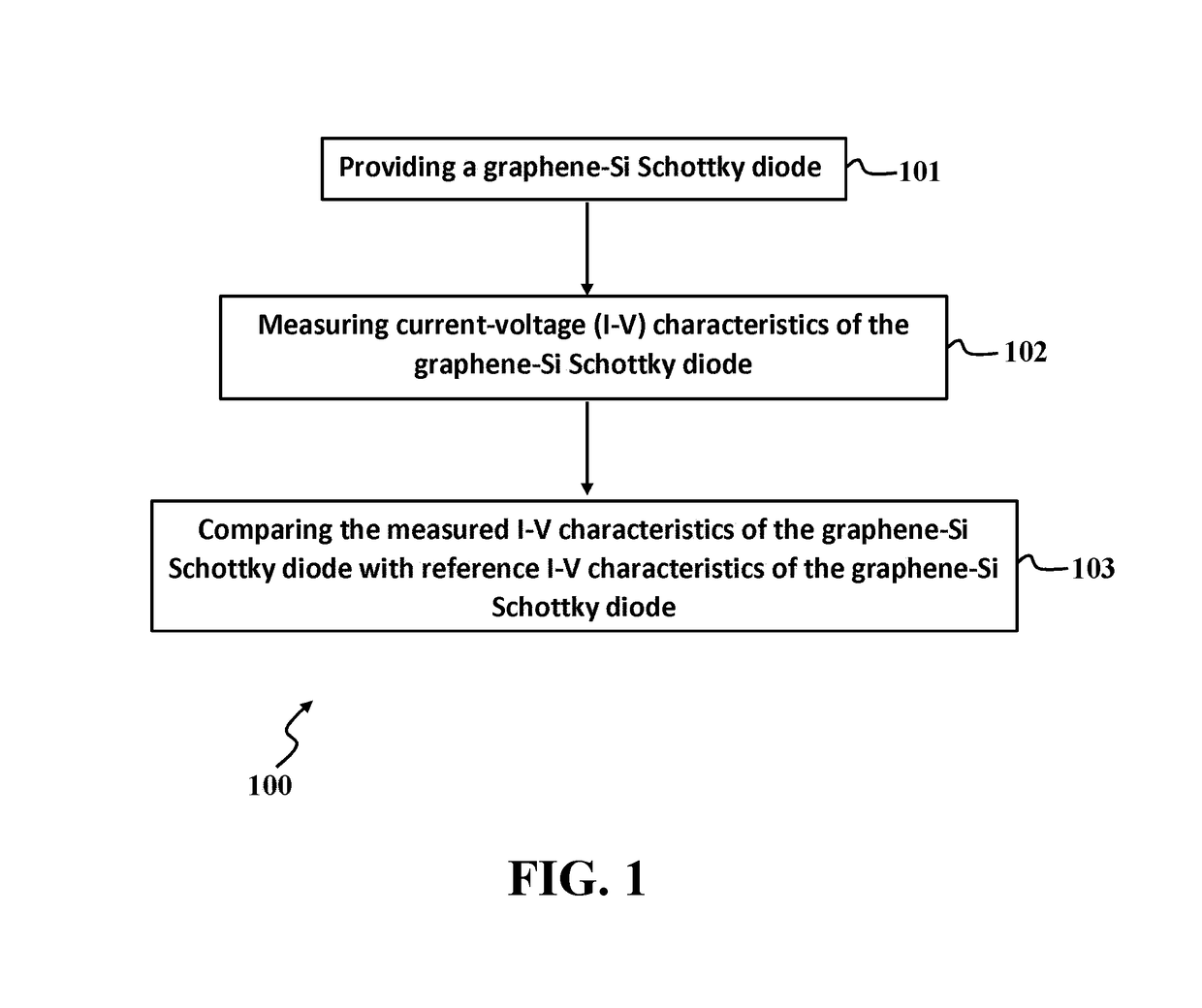
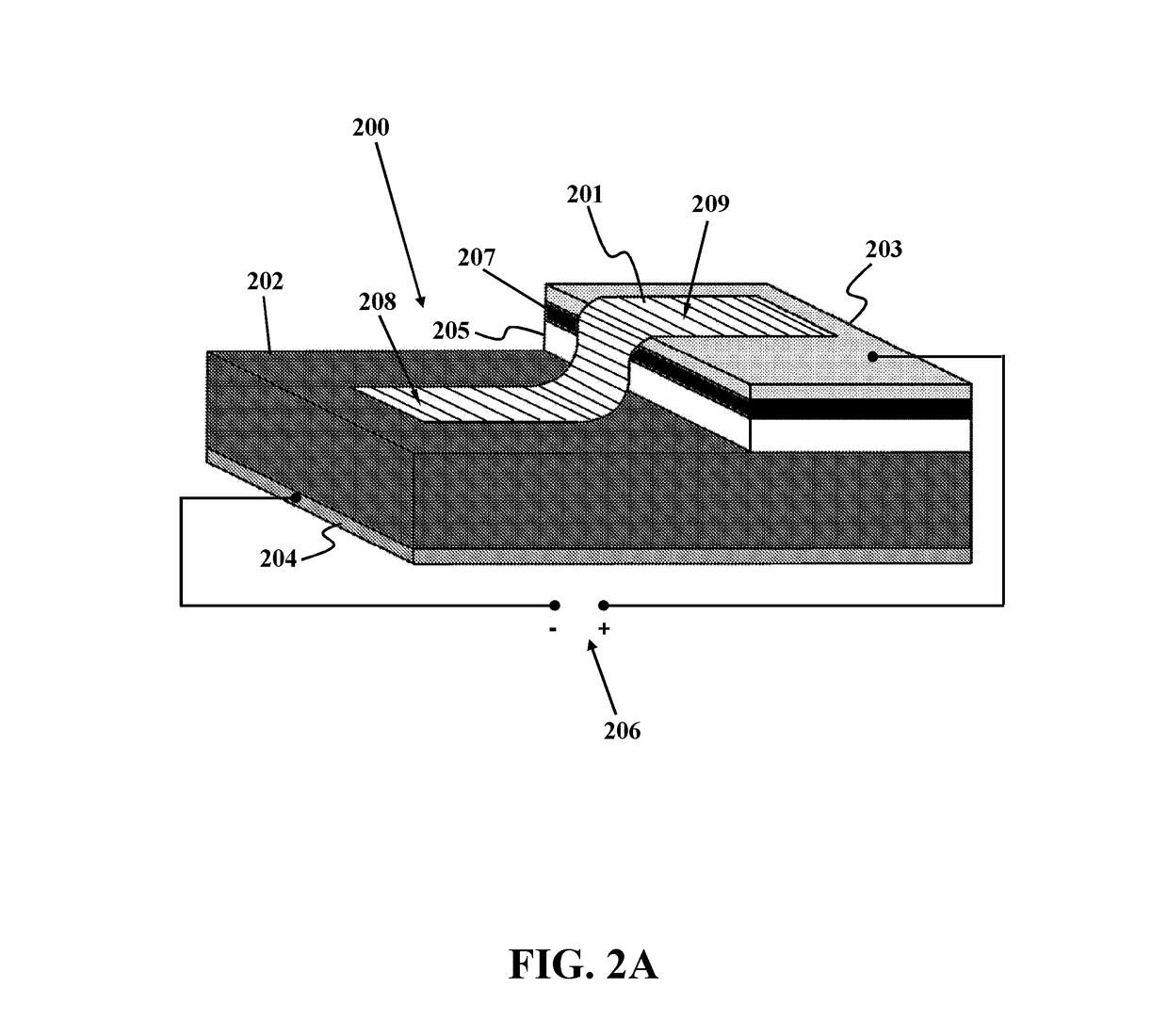
A method for detecting W-band and terahertz radiations is disclosed. The method provides a graphene-Si Schottky diode that includes a graphene monolayer having an Ohmic contact with a source electrode supported on a top surface of a doped silicon substrate by an insulating layer, and extends over an edge of the source electrode and contacts the top surface, in a manner forming a Schottky junction. The method stores reference current-voltage (I-V) characteristics of the Schottky junction in a reverse biased mode, then measures I-V characteristics of the Schottky junction in the reverse biased mode, and detects W-band and terahertz radiation by comparing the measured I-V characteristics of the Schottky junction to the stored reference I-V characteristics.
Owner:SHAHID RAJAEE TEACHER TRAINING UNIVERSITY +2
Graphene growth on a carbon-containing semiconductor layer
ActiveUS8187955B2Material nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsCvd graphene
A semiconductor-carbon alloy layer is formed on the surface of a semiconductor substrate, which may be a commercially available semiconductor substrate such as a silicon substrate. The semiconductor-carbon alloy layer is converted into at least one graphene layer during a high temperature anneal, during which the semiconductor material on the surface of the semiconductor-carbon alloy layer is evaporated selective to the carbon atoms. As the semiconductor atoms are selectively removed and the carbon concentration on the surface of the semiconductor-carbon alloy layer increases, the remaining carbon atoms in the top layers of the semiconductor-carbon alloy layer coalesce to form a graphene layer having at least one graphene monolayer. Thus, a graphene layer may be provided on a commercially available semiconductor substrate having a diameter of 200 mm or 300 mm.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Method for preparing monolayer graphene with controllable stripe width by laser heating
The invention relates to a method for preparing monolayer graphene with controllable stripe width on a substrate by utilizing laser beam heating through a grating, belonging to the technical field of semiconductor novel materials. Graphene has higher electron transport properties, good response frequency and wider light band transparency, and can achieve the optimization of high-speed electronic device fabrication. Therefore, the realization of growth of high-quality stripe-shaped graphene materials is important for the development of electronic technology. Through the method, stripe-shaped monolayer graphene is prepared by heating the substrate with lasers through the grating, the lithography step is omitted, the method is performed by one step and is simple and feasible, and the growth materials are not polluted by additional materials; and at the same time, the laser beams can be quickly removed, the method has the characteristics of rapid temperature reduction and the like, the unnecessary multi-layer graphene growth can be reduced, the graphene monolayer growth is effectively realized, and the method is characterized by acquiring the discrete beams through the grating, thus obtaining the discrete stripe-shaped monolayer graphene.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
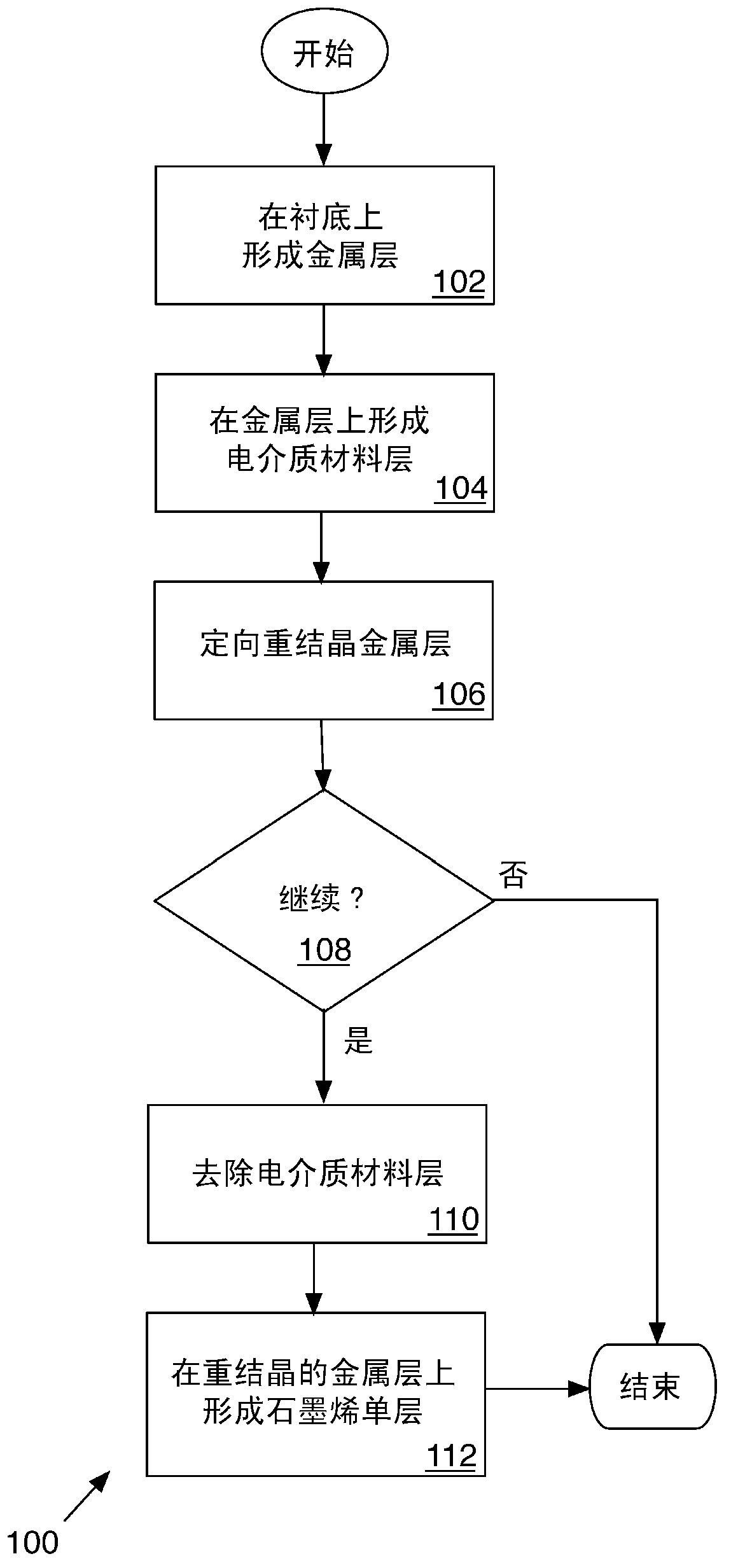
Directionally recrystallized graphene growth substrates
InactiveCN103124691AMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCvd grapheneBiology
Implementations and techniques for producing substrates suitable for growing graphene monolayers are generally disclosed.
Owner:EMPIRE TECH DEV LLC
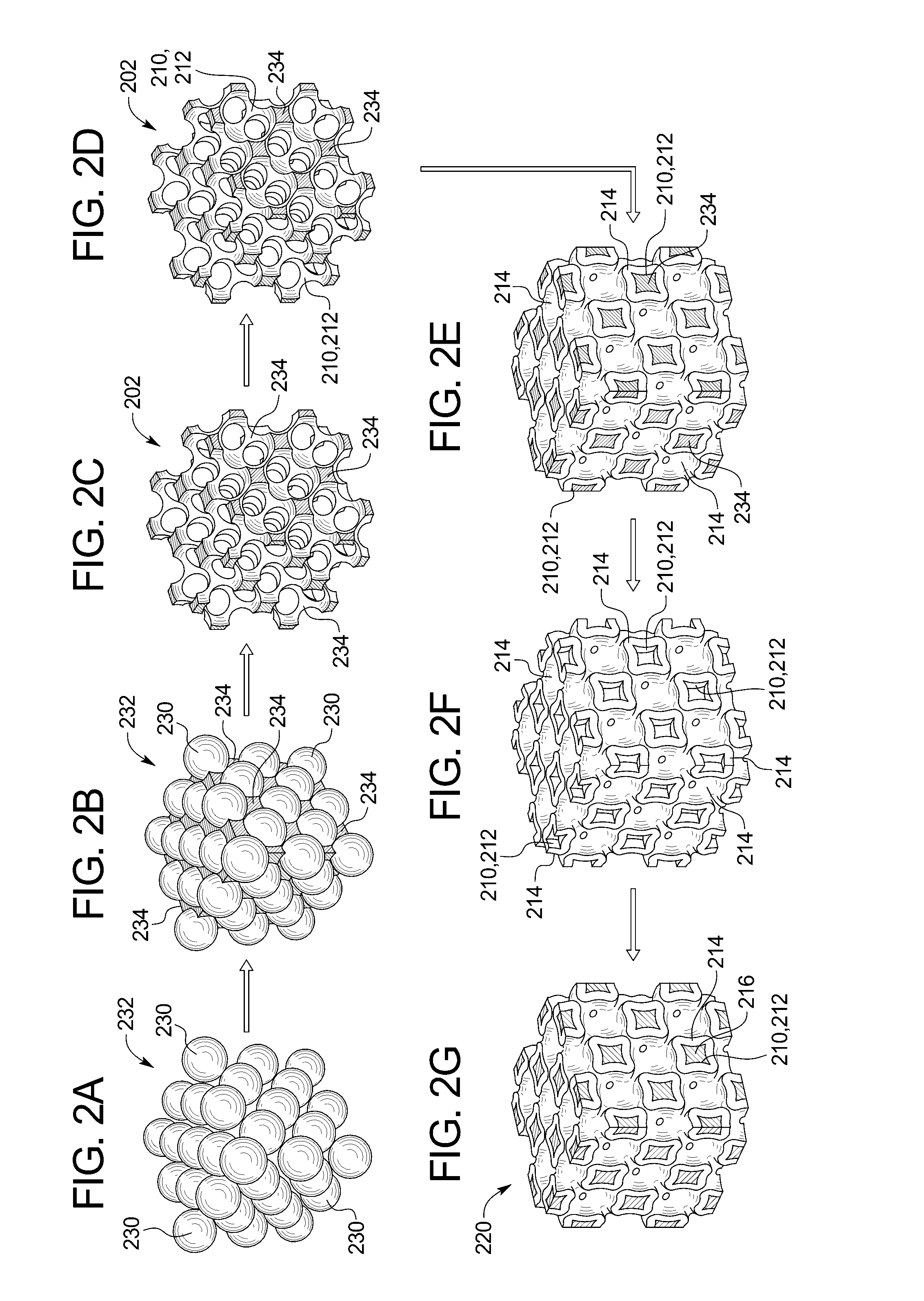
Scaffold-free 3D porous electrode and method of making a scaffold-free 3D porous electrode
A scaffold-free 3D porous electrode comprises a network of interconnected pores, where each pore is surrounded by a multilayer film including a first layer of electrochemically active material, one or more monolayers of graphene on the first layer of electrochemically active material, and a second layer of electrochemically active material on the one or more monolayers of graphene. A method of making a scaffold-free 3D porous electrode includes depositing one or more monolayers of graphene onto a porous scaffold to form a graphene coating on the porous scaffold, and depositing a first layer of an electrochemically active material onto the graphene coating. The porous scaffold is removed to expose an underside of the graphene coating, and a second layer of the electrochemically active material is deposited onto the underside of the graphene coating, thereby forming the scaffold-free 3D porous electrode.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Graphene-based detector for W-band and terahertz radiations
InactiveUS10121926B2Solid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesTerahertz radiationReference current
A method for detecting W-band and terahertz radiations is disclosed. The method provides a graphene-Si Schottky diode that includes a graphene monolayer having an Ohmic contact with a source electrode supported on a top surface of a doped silicon substrate by an insulating layer, and extends over an edge of the source electrode and contacts the top surface, in a manner forming a Schottky junction. The method stores reference current-voltage (I-V) characteristics of the Schottky junction in a reverse biased mode, then measures I-V characteristics of the Schottky junction in the reverse biased mode, and detects W-band and terahertz radiation by comparing the measured I-V characteristics of the Schottky junction to the stored reference I-V characteristics.
Owner:SHAHID RAJAEE TEACHER TRAINING UNIVERSITY +2
Method for preparing graphene heat dissipation film by using self-propagating stripping technology
ActiveCN111137879AEvenly heatedAvoid bubblingSingle layer grapheneChemical industryChemical physicsThin membrane
The invention relates to the technical field of graphene, and aims to provide a method for preparing a graphene heat dissipation film by using a self-propagating stripping technology. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out chemical modification on a graphite oxide dispersion liquid by using hydrogen peroxide or ammonia water, and carrying out homogenizing and defoaming under vacuum; coating water-permeable nylon cloth with modified graphite oxide slurry obtained in the previous step to form a graphite oxide film; drying the graphite oxide film and stripping a substrate to obtain a modified graphite oxide film; after heating, carrying out self-propagating stripping to obtain a few-layer stripped graphene film; carrying out firing in an inert atmosphere, and performing cooling to obtain graphene foam; and conducting rolling to form a film, and carrying out trimming post-treatment to obtain the graphene heat dissipation film. The graphite oxide film is uniformly heated, uneven decomposition of functional groups can be avoided, and pretreatment efficiency is improved. The graphene is high in single-layer rate and large in size; the graphene film is excellent in heat conduction performance, high in strength and better in heat dissipation effect. Any toxic and harmful chemical reagent is not adopted, the preparation process is simple, and efficient and high-quality reduction of the graphite oxide film is realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Adjustable perfect wave absorber based on graphene photonic crystal structure
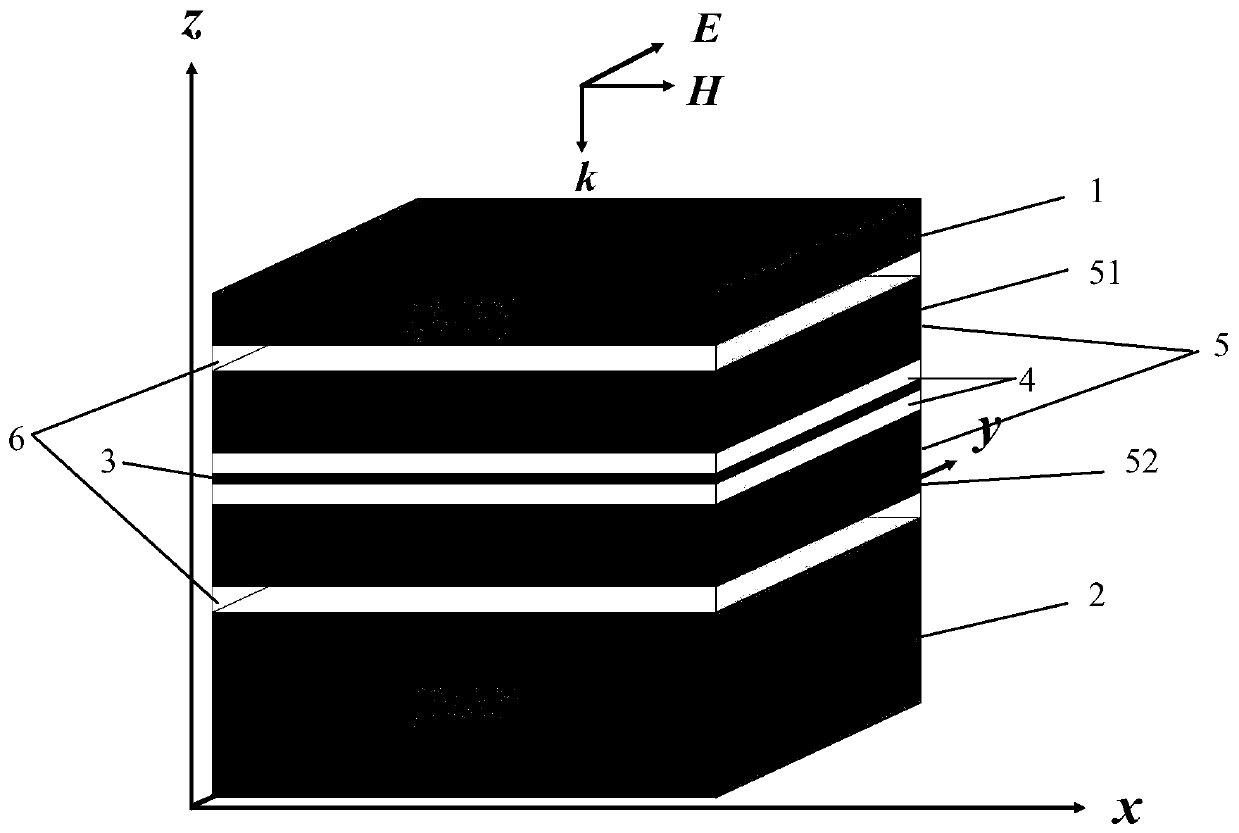
ActiveCN110927843AFlexible regulationReduce manufacturing costOptical elementsResonant cavityPhotonic crystal structure
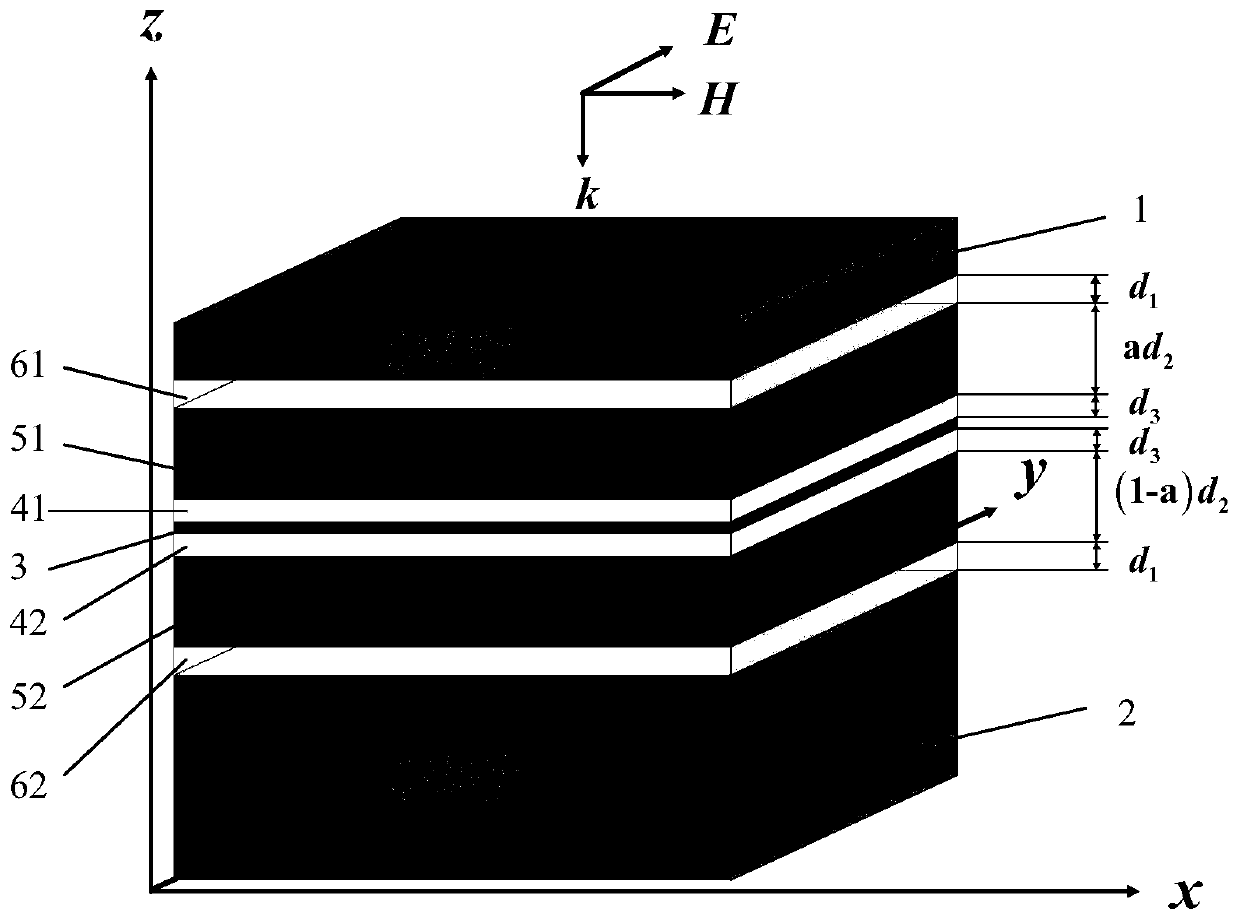
The invention belongs to the technical field of wave absorber materials, and particularly relates to an adjustable perfect wave absorber based on a graphene photonic crystal structure. The adjustableperfect wave absorber comprises a top mirror 1, a bottom mirror 2 and a triple nested FP resonant cavity located between the top mirror and the bottom mirror. The specific structure of the triple nested FP resonant cavity is as follows: a graphene single layer 3, a first layer cavity 4 attached to the upper and lower surfaces of the graphene single layer, a second layer cavity 5 attached to the outer surface of the first layer cavity, and a third layer cavity 6 attached to the outer surface of the second layer cavity. By changing the chemical potential of graphene and the angle of incident waves, the resonant frequency of a perfect absorption mode can be adjusted without changing the geometric structure of the wave absorber.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Preparation method of in-situ-polymerization graphene microemulsion
ActiveCN104176730AGuaranteed decentralizationFor long-term storageIn situ polymerizationNanoscopic scale
The invention discloses a preparation method of an in-situ-polymerization graphene microemulsion. The method comprises the following steps: 1. adding 400mL of deionized water into a flask; 2. adding 1-10g of intercalation agent, and sufficiently dissolving; 3. adding 4-50g of graphene, and stirring and dispersing for 15 minutes; 4. treating with an ultrasonic treatment device for 15-30 minutes, wherein the ultrasonic power is greater than 500 watts; 5. heating to 70 DEG C, and adding 2.4-30g of emulsifying micelle protective agent; 6. adding 200mL of 2% hydroxypropyl methylcellulose ether water solution, and sufficiently stirring; and 7. treating in the ultrasonic treatment device for 60-120 minutes, wherein the ultrasonic power is greater than 500 watts. Under the high-power ultrasonic action, the intercalation agent is intercalated into the graphene laminae to obtain the monolayer graphene; the micelle protective agent protects the graphene monolayer to form a nano microscopic micelle; and the graphene is dispersed in the nano monolayer in the microemulsion, can be stored stably, and can be used for in-situ polymerization.
Owner:XINJIANG ZHONGTAI CHEM CO LTD +1
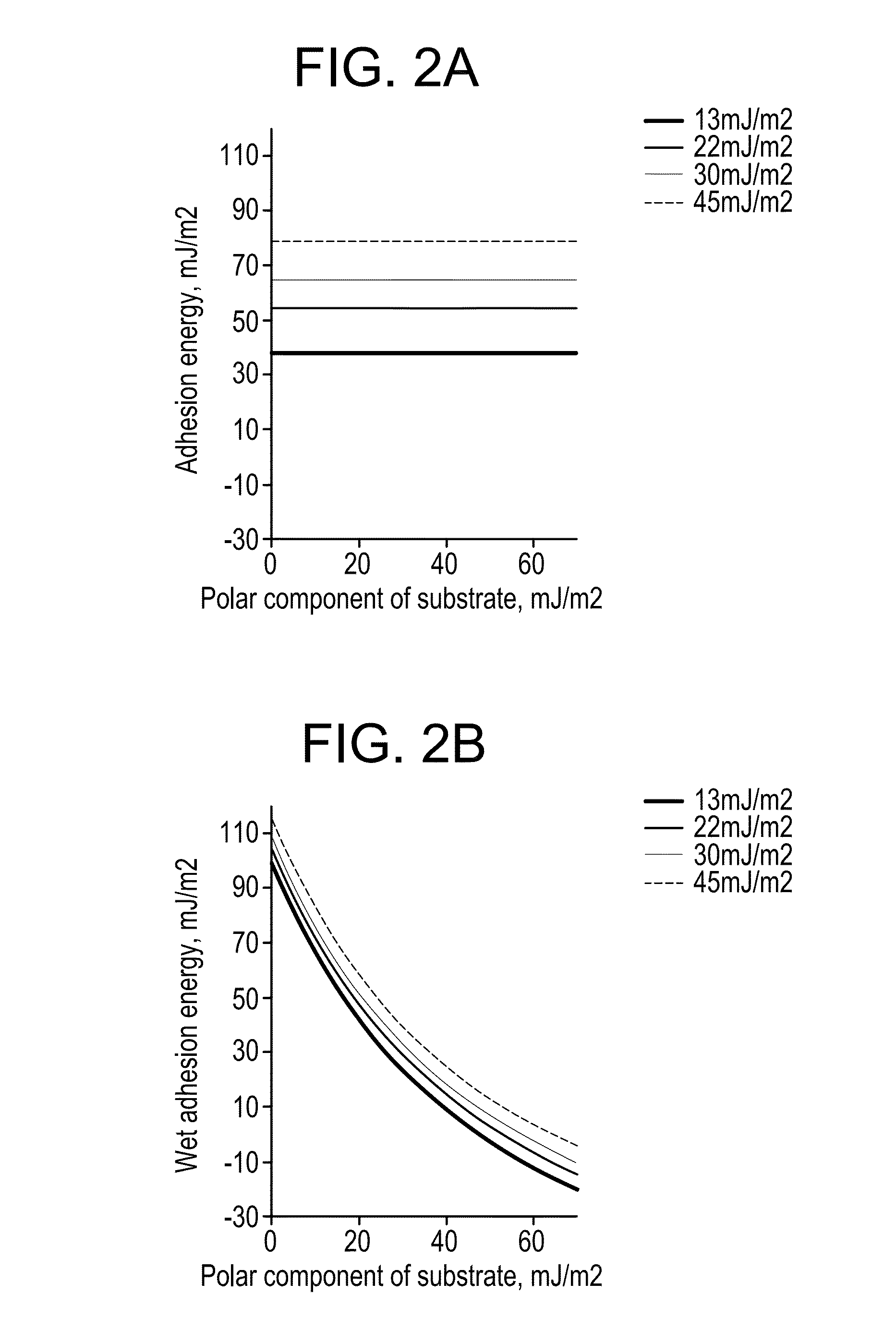
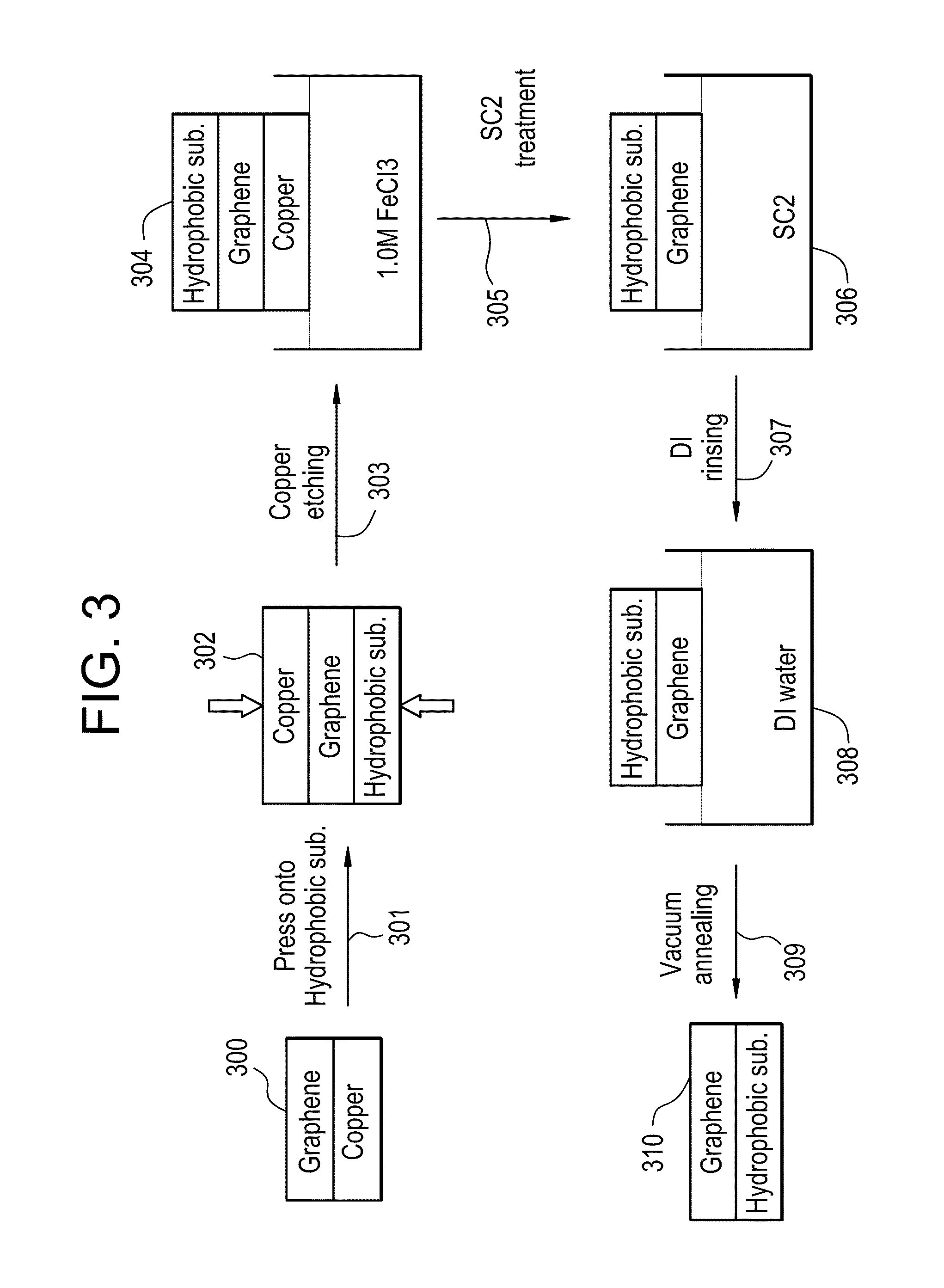
Graphene and polymer-free method for transferring CVD grown graphene onto hydrophobic substrates
Described herein are methods for improved transfer of graphene from formation substrates to target substrates. In particular, the methods described herein are useful in the transfer of high-quality chemical vapor deposition-grown monolayers of graphene from metal, e.g., copper, formation substrates via non-polymeric methods. The improved processes provide graphene materials with less defects in the structure.
Owner:CORNING INC
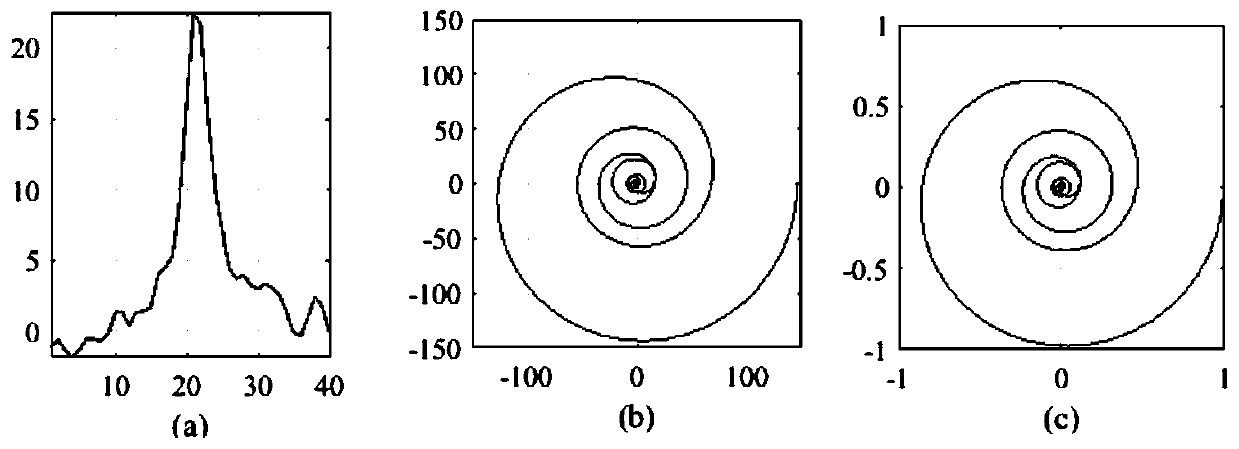
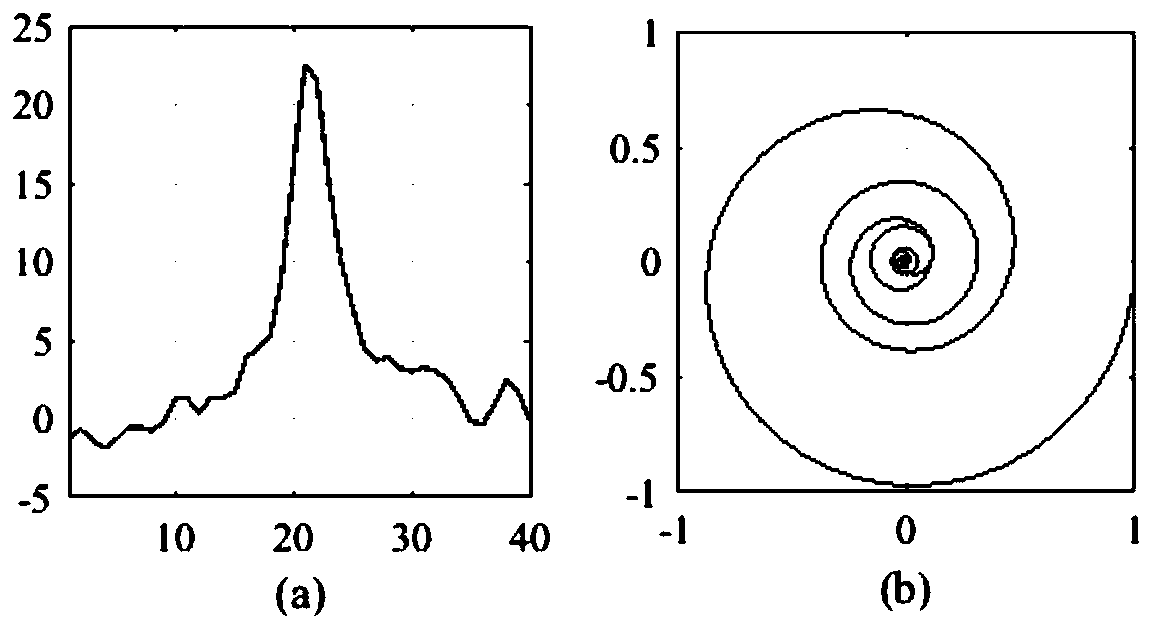
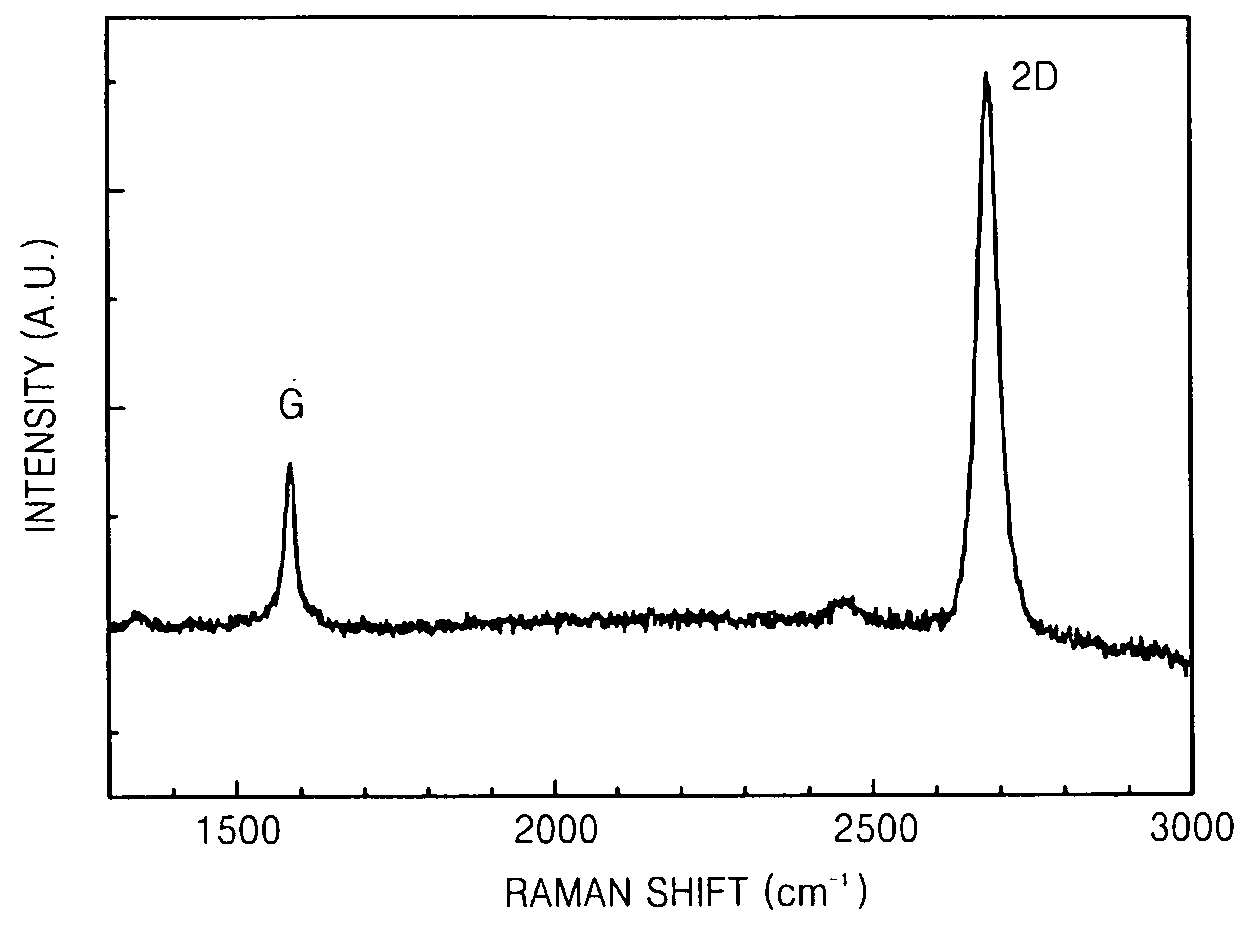
Graphene fingerprint peak analysis method based on big data analysis
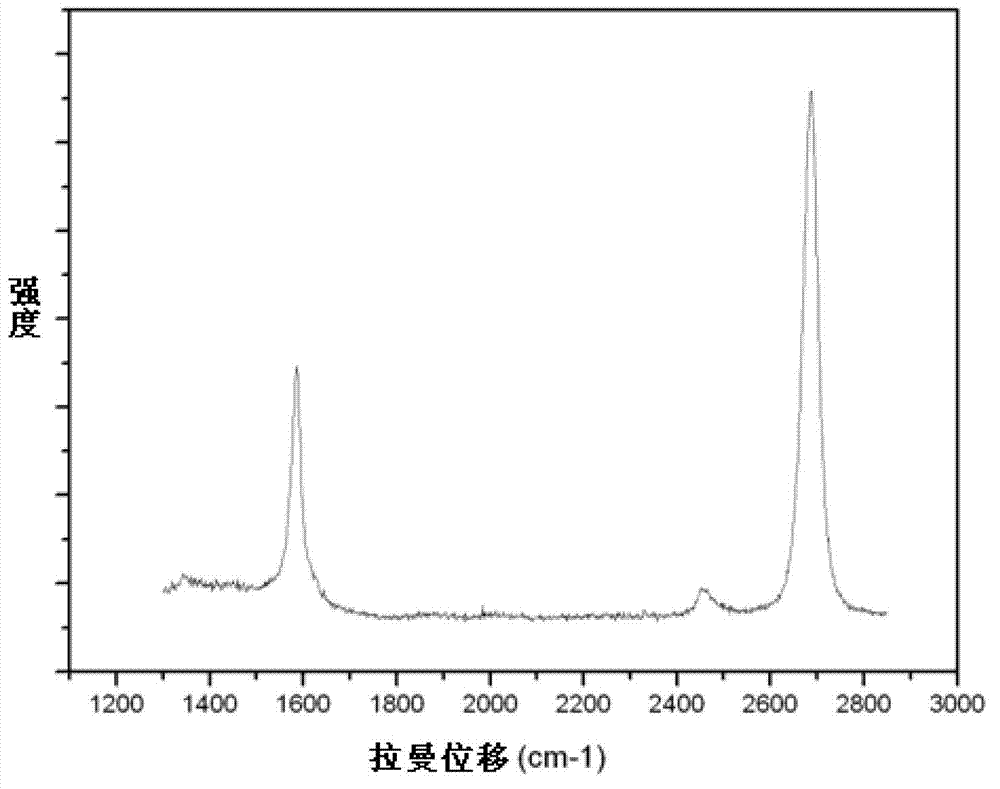
ActiveCN110197481AImprove recognition efficiencyImprove recognition accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisFeature setFourier transform on finite groups
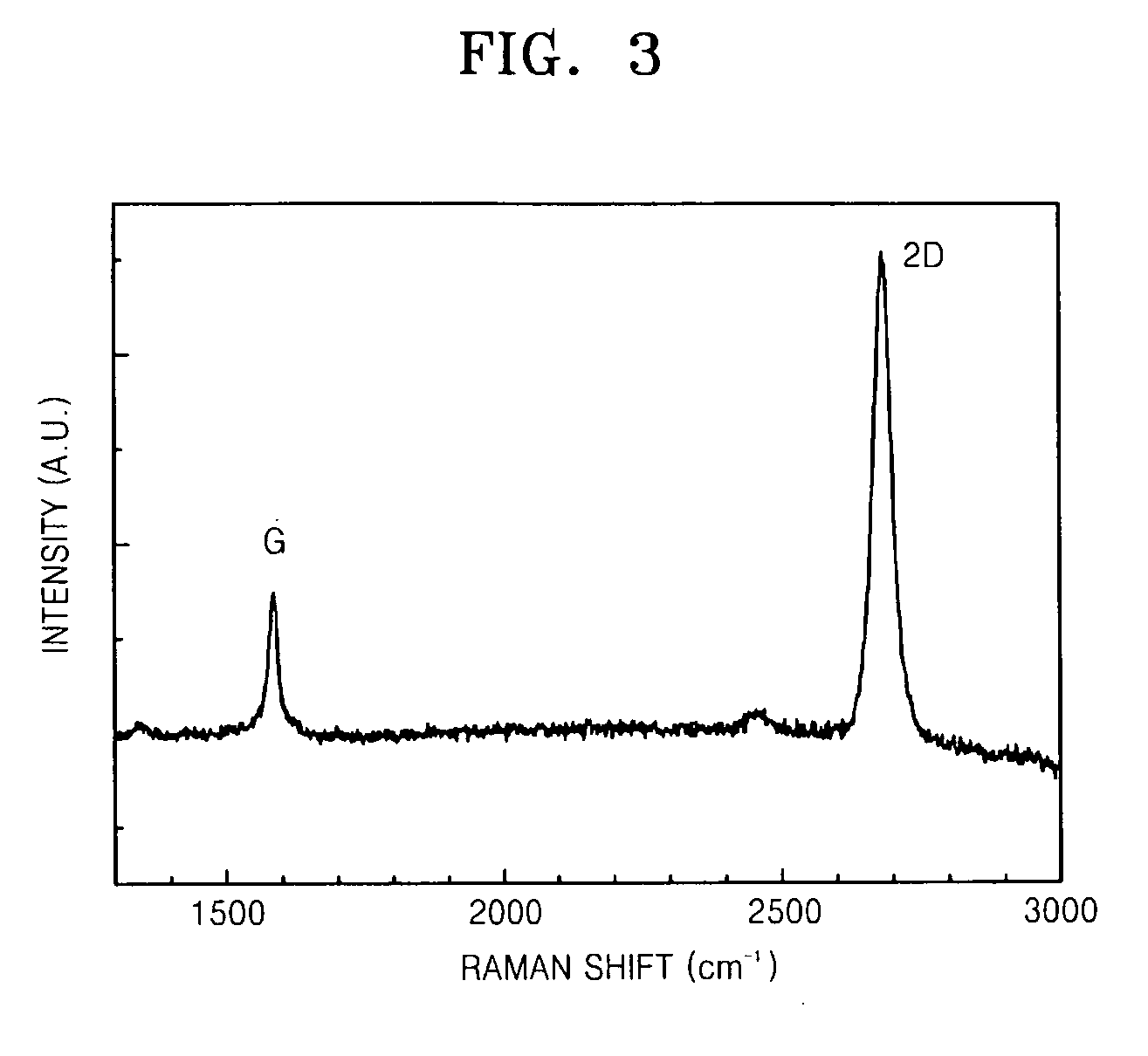
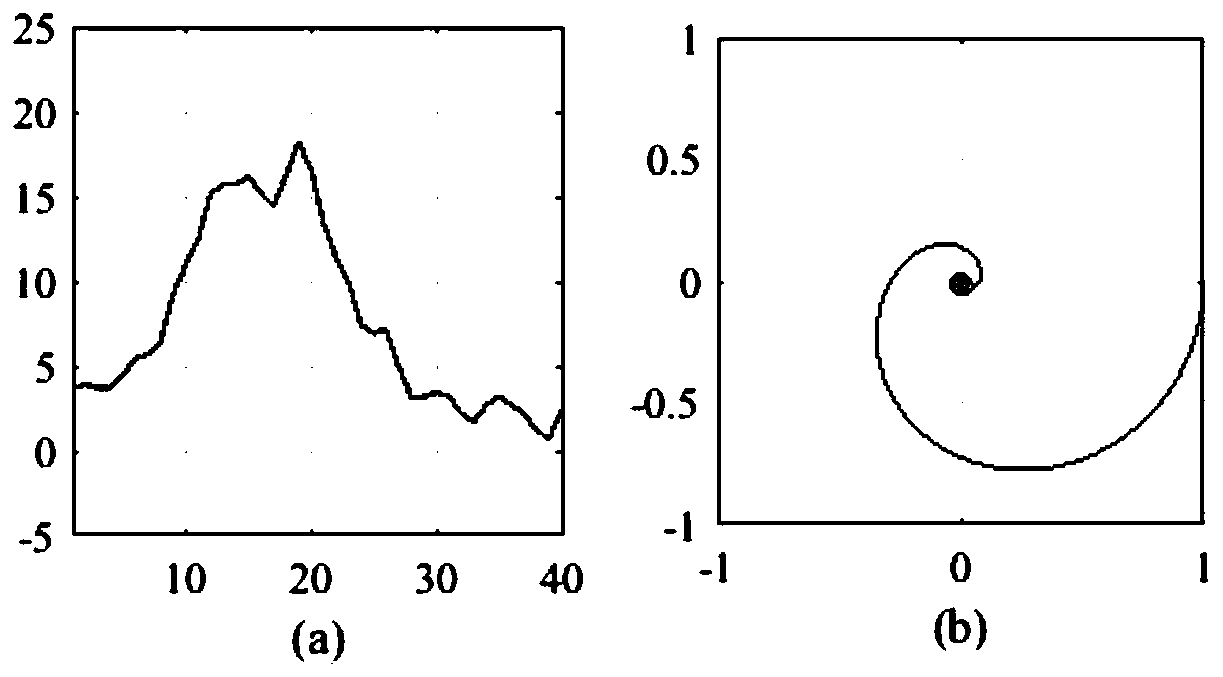
The invention discloses a graphene fingerprint peak analysis method based on big data analysis. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, resampling m points in any region in q characteristicpeak neighborhoods on a graphene Raman spectrum; step 2, performing p-point fast Fourier transform on the resampled m point characteristic peak neighborhood characteristic spectrums to obtain a characteristic peak neighborhood complex track; step 3, normalizing the amplitude of each obtained complex track according to the maximum amplitude of the complex track; 4, dividing the complex track into aplurality of circles from outside to inside, and defining an identification feature set; 5, establishing a graphene Raman spectrum automatic identification model based on big data; and 6, automatically identifying the graphene Raman spectrum to be identified, and performing defect judgment and layer number judgment according to an identification result. Under the background of big data, graphenesingle-layer / multi-layer or defect-free automatic identification is carried out according to the Raman characteristic spectrum of graphene, so that the identification accuracy and efficiency are improved.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
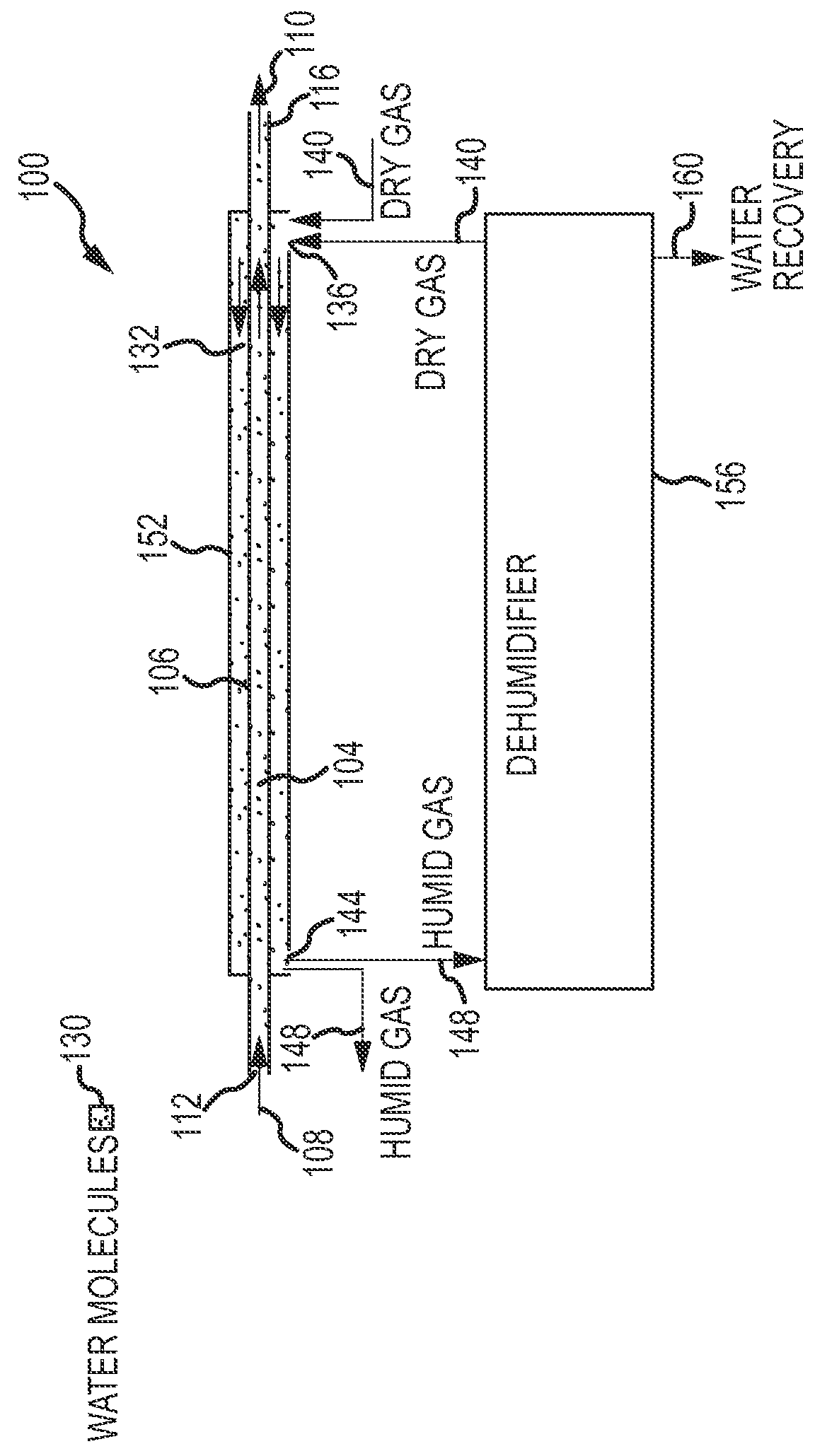
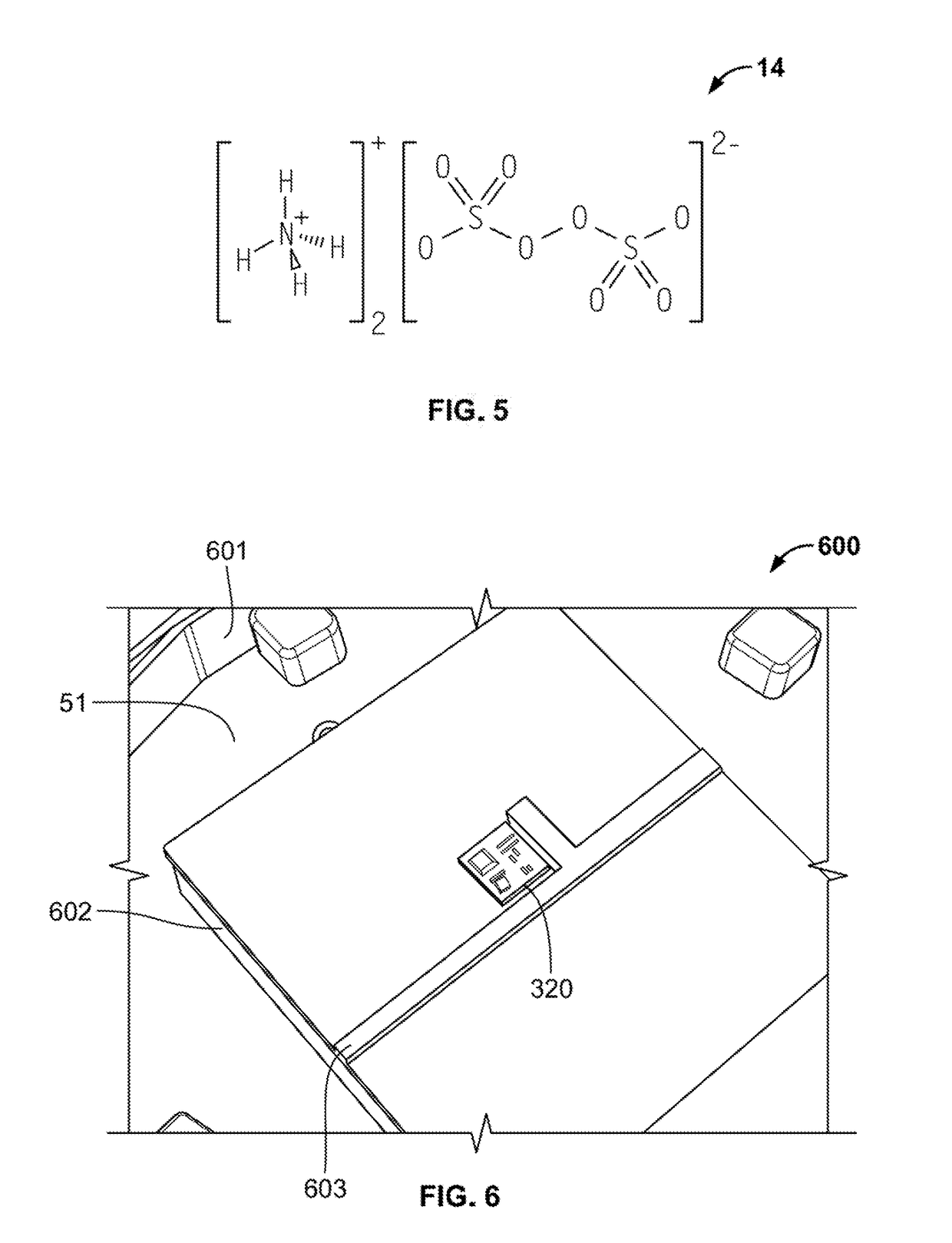
Dryer and water recovery/purification unit employing graphene oxide or perforated graphene monolayer membranes
InactiveUS9358508B2Reduce the amount of waterIncrease concentrationMembranesSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningLiquid waterWater vapor
Apparatuses and systems for removing water vapor from a gas stream and for providing water purification, recovery and / or concentration. The apparatuses and systems employ a graphene oxide or a perforated graphene monolayer membrane to separate liquid water molecules and / or water vapor molecules from gasses, liquids, and other substances such as a wet muck or an aqueous sample. In one embodiment, an apparatus for removing water from a gas or liquid stream includes a first lumen, a second lumen, and a graphene oxide membrane separating the first lumen from the second lumen. Water molecules within a humid gas or liquid stream introduced into the first lumen pass through the graphene oxide membrane into a dry gas stream introduced into the second lumen.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
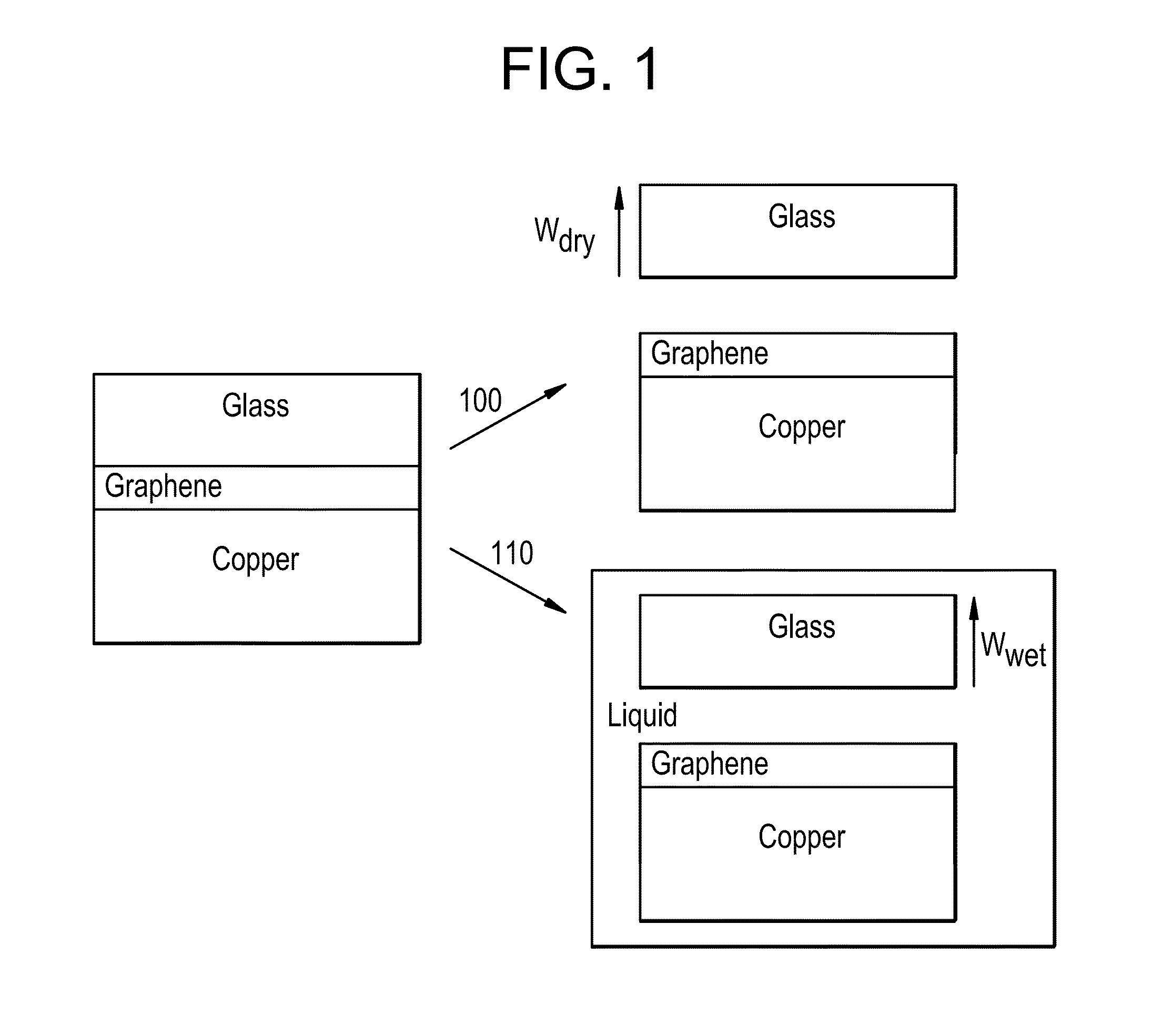
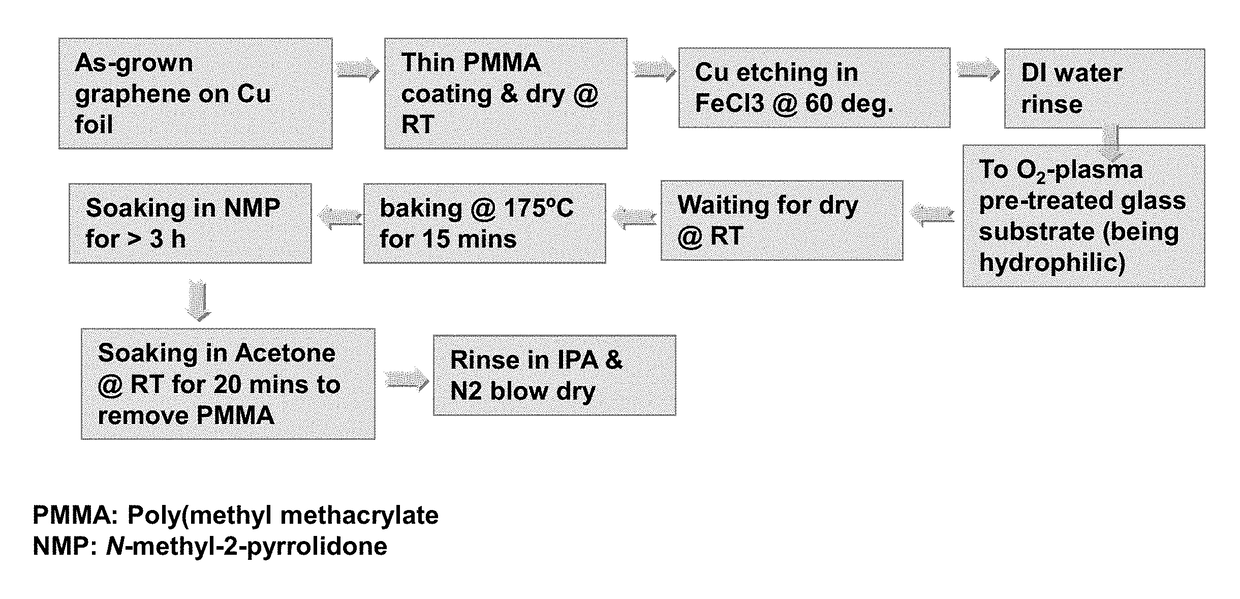
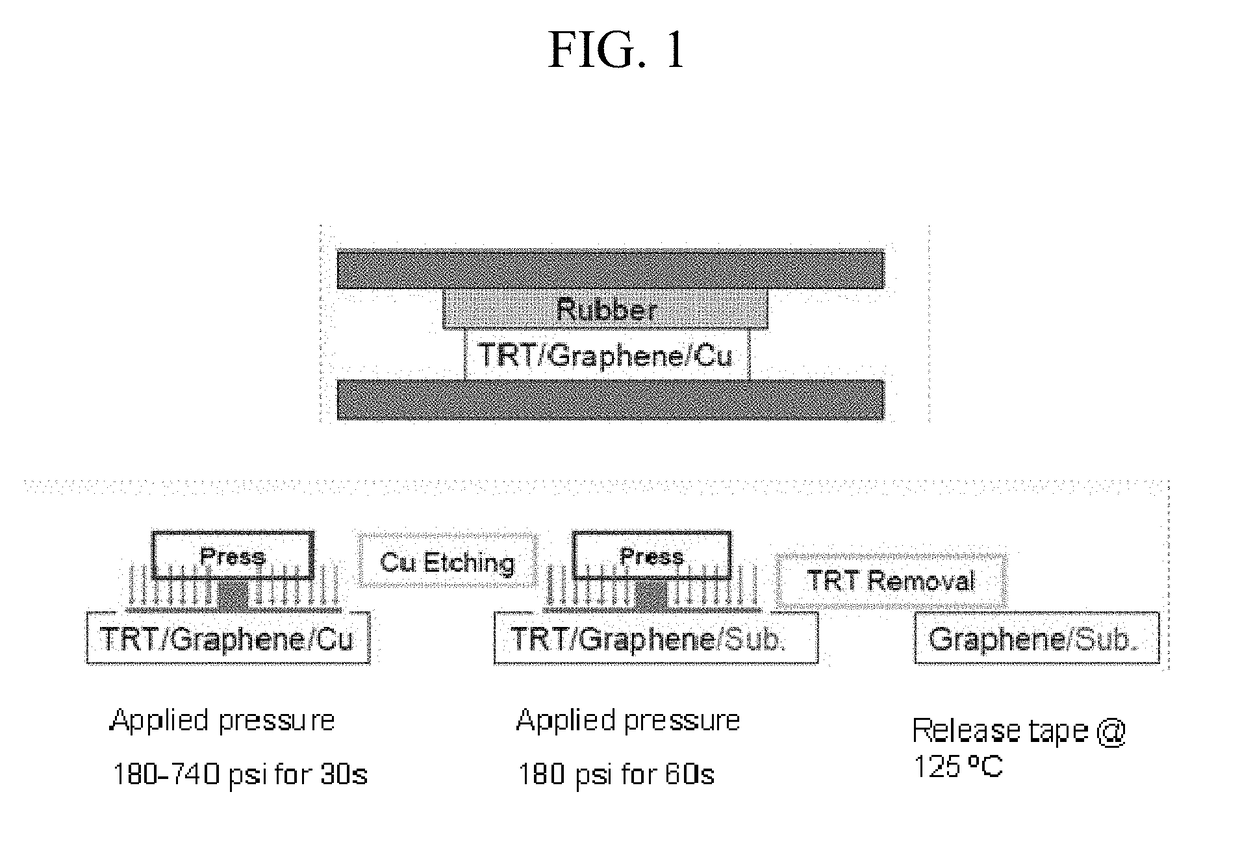
Transfer of monolayer graphene onto flexible glass substrates
ActiveUS9828285B2Carbon compoundsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseMonolayer graphene
Described herein are methods for improved transfer of graphene from formation substrates to target substrates. In particular, the methods described herein are useful in the transfer of high-quality chemical vapor deposition-grown monolayers of graphene from metal, e.g., copper, formation substrates to ultrathin, flexible glass targets. The improved processes provide graphene materials with less defects in the structure.
Owner:ICFO THE INST OF PHOTONIC SCI +2
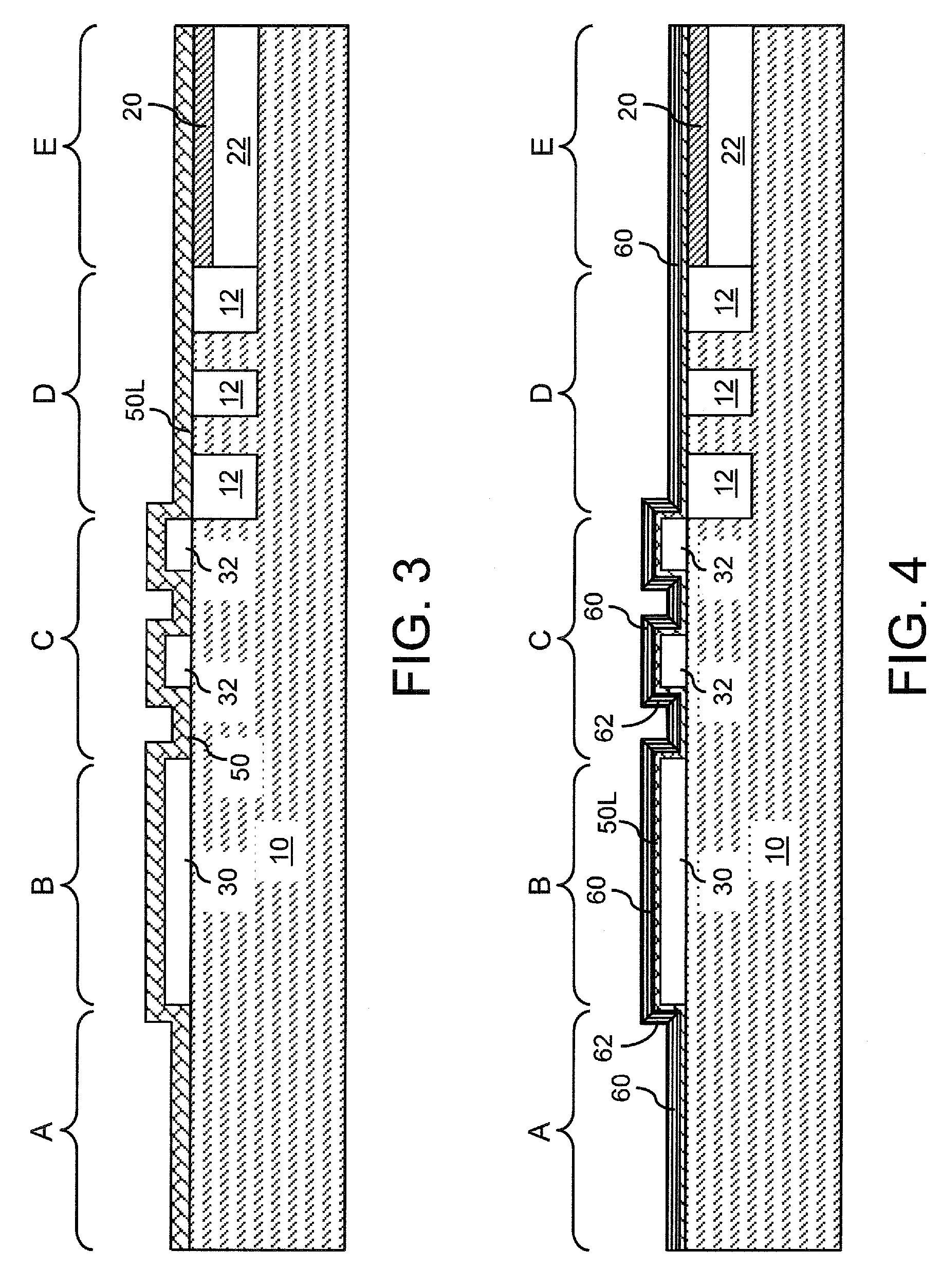
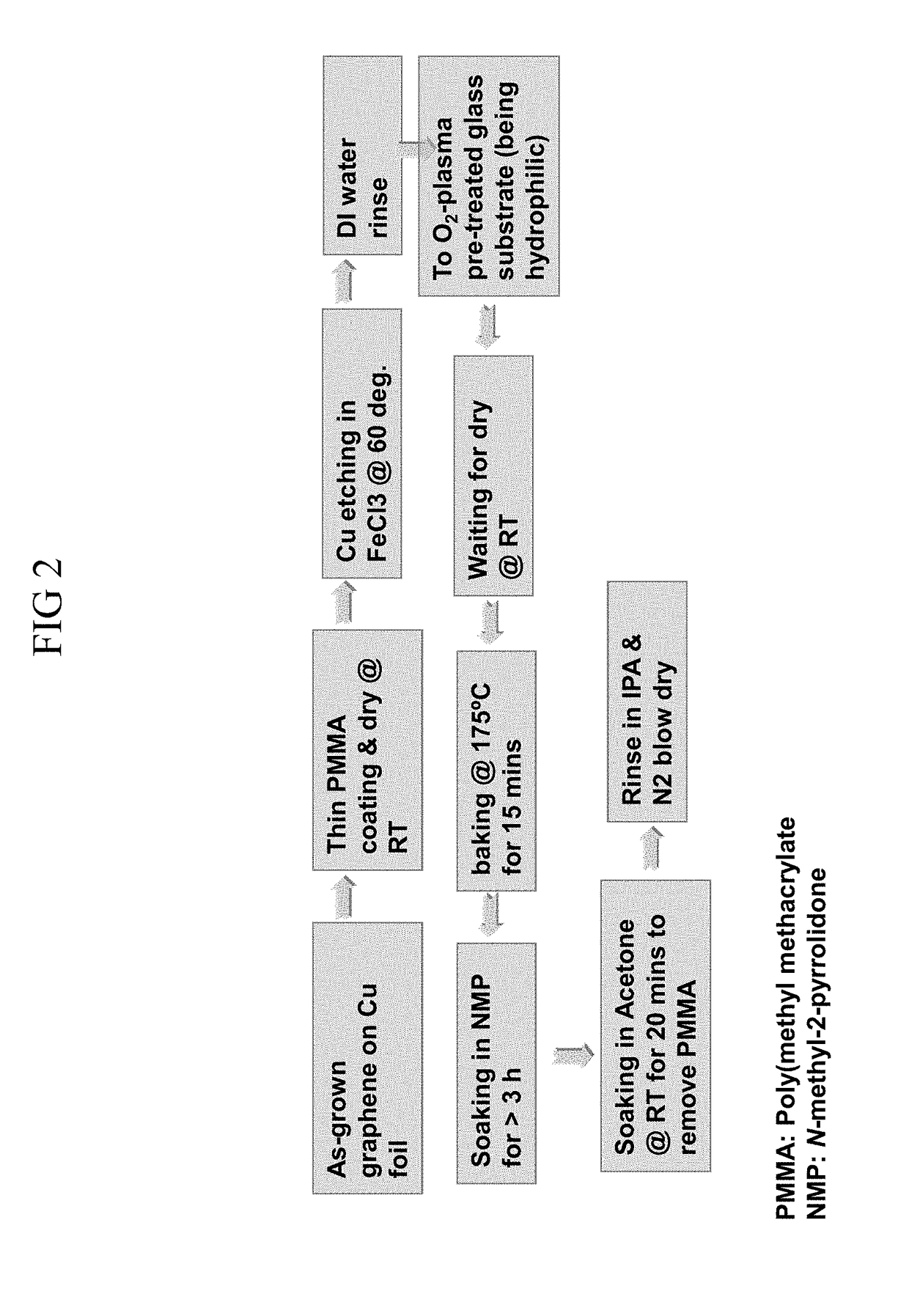
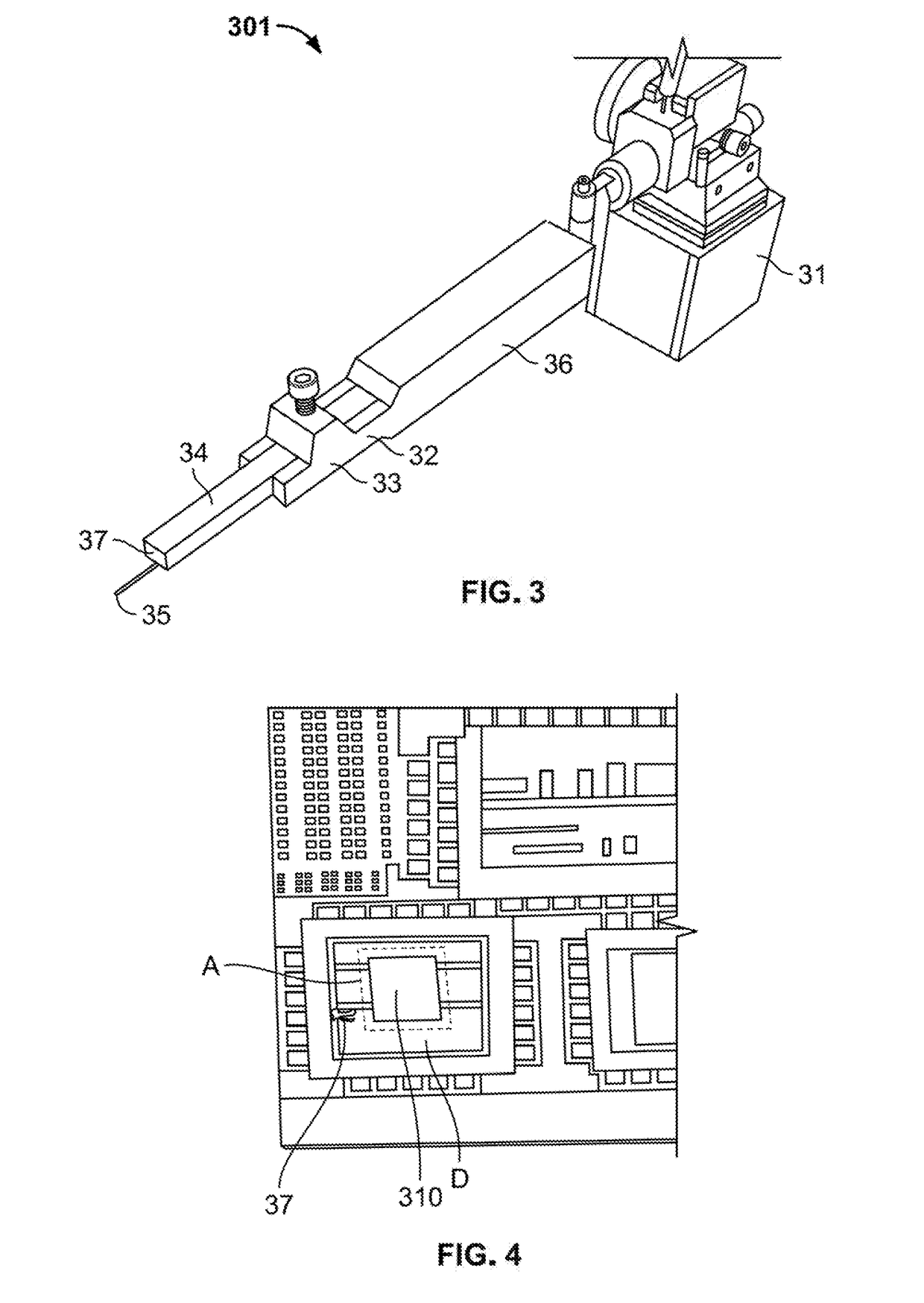
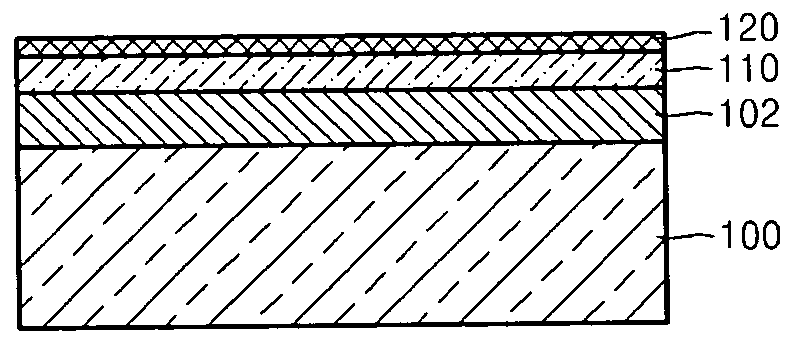
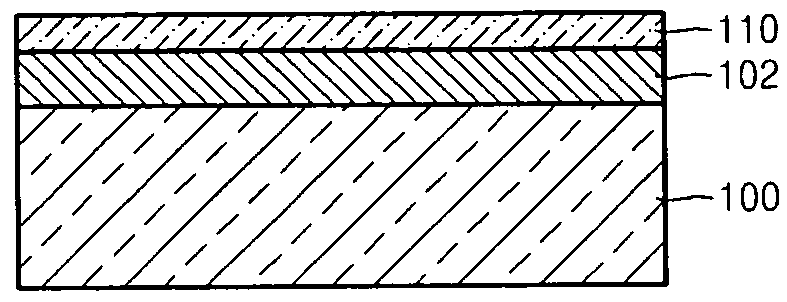
Methods of Transferring a Graphene Monolayer via a Stacked Structure and Devices Fabricated Thereby
InactiveUS20190051553A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal catalystOptoelectronics
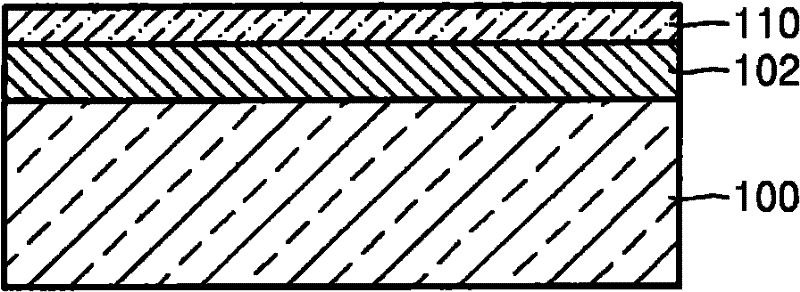
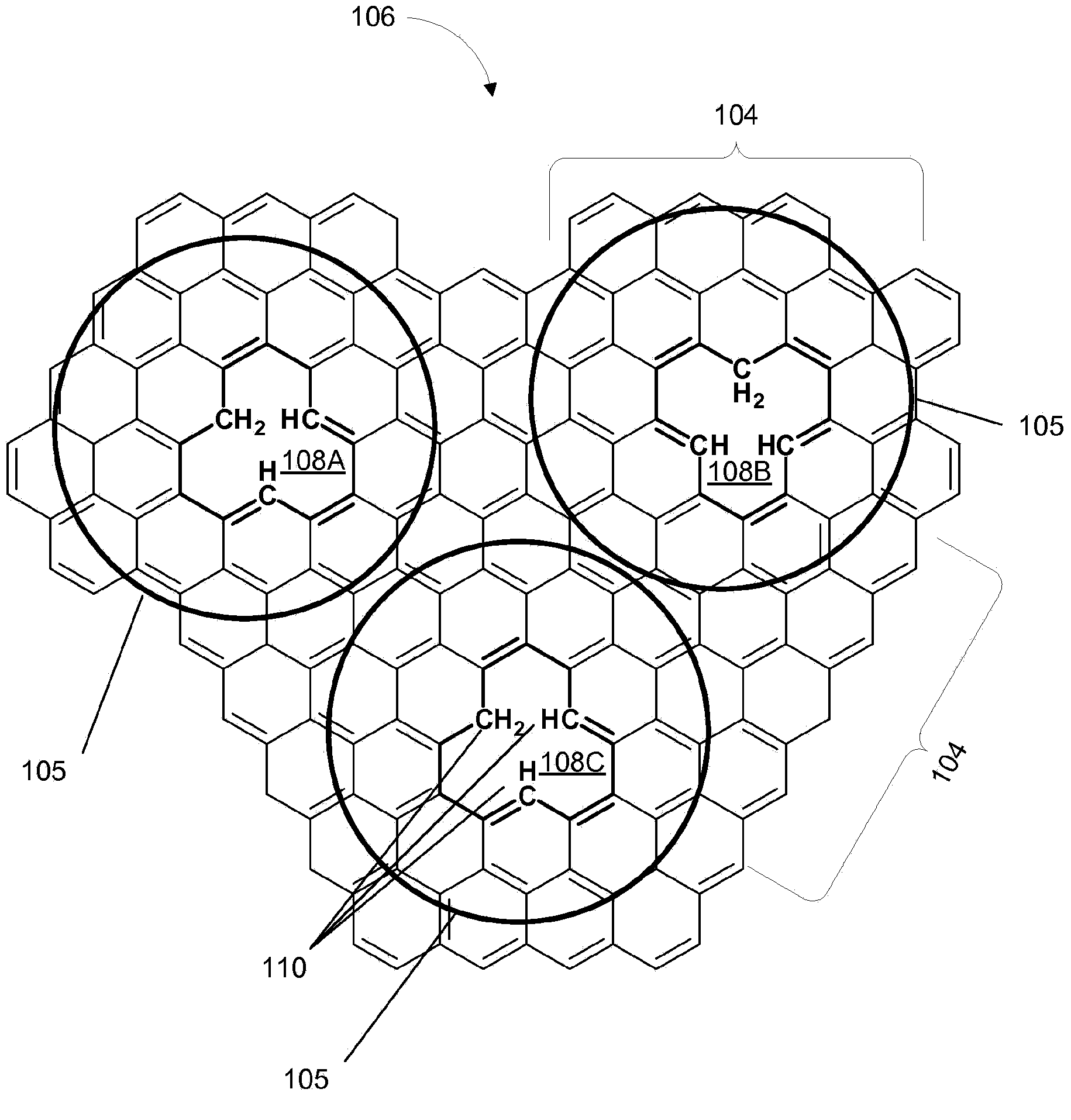
A method of fabricating a graphene device generally involving depositing a graphene monolayer from a carbon source on a metal catalyst layer; depositing a transfer substrate on the graphene monolayer by way of casting, thereby forming a transfer-substrate / graphene / metal-catalyst structure; annealing the transfer-substrate / graphene / metal-catalyst structure, thereby forming an annealed transfer-substrate / graphene / metal-catalyst structure; coupling a thermal adhesive with the transfer-substrate / graphene / metal-catalyst structure; moving the annealed transfer-substrate / graphene / metal-catalyst structure to a target area of a target device, by using a probe assembly or the like, thereby forming an annealed transfer-substrate / graphene / metal-catalyst / thermal-adhesive / target-device structure; releasing the slip of thermal adhesive from the annealed transfer-substrate / graphene / metal-catalyst thermal-adhesive / target-device structure by applying heat, thereby forming an annealed transfer-substrate / graphene / metal-catalyst / target-device structure; etching away the metal catalyst layer from the annealed transfer-substrate / graphene / metal-catalyst / target-device structure in an etching solution, thereby forming a graphene / transfer-substrate / target-device structure; rinsing the graphene / transfer-substrate / target-device structure with DI water, thereby removing any excess etching solution; and drying the graphene / transfer-substrate / target-device structure, thereby providing the graphene device.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
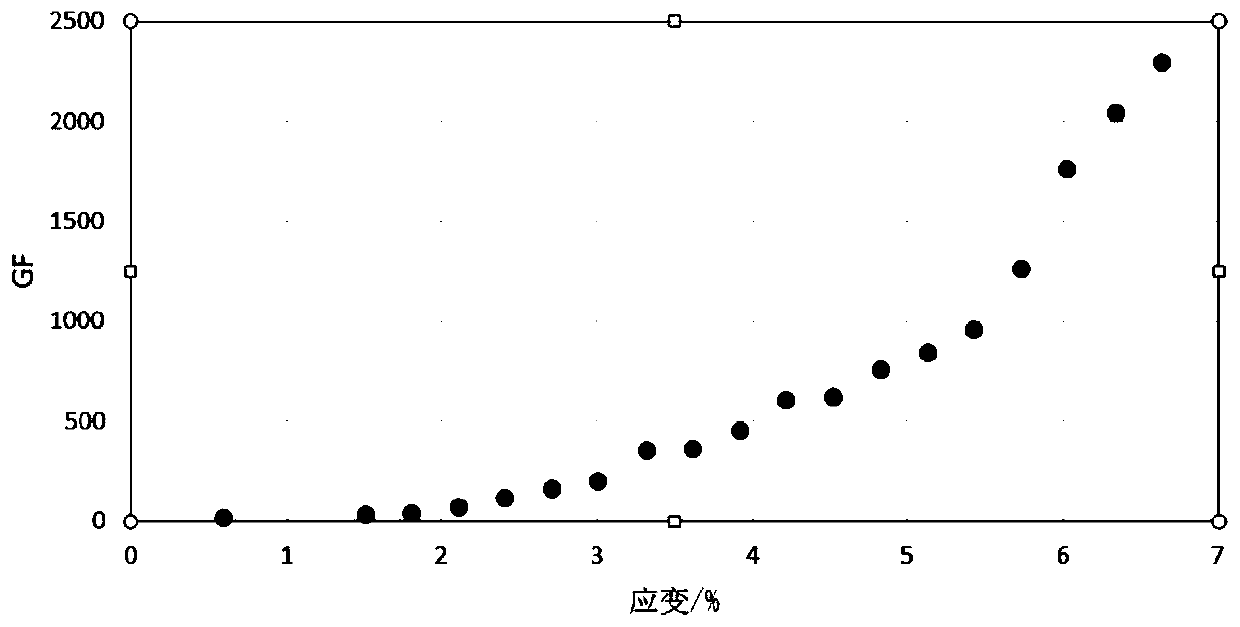
Strain detection sensor based on graphene film and method of fabricating the same
ActiveCN110044251AHigh gauge factorEasy to controlGrapheneElectrical/magnetic solid deformation measurementCvd grapheneBilayer graphene
The invention provides a strain detection sensor based on a graphene film with large strain coefficient and high detection sensitivity and a method of fabricating the same. The strain detection sensorcomprises a graphene film, wherein the graphene film comprises two layers of graphene monolayer films, which are overlapped with each other; and the graphene on the graphene monolayer films is distributed in an island shape. The method of fabricating the strain detection sensor based on the graphene film comprises the following steps of growing graphene monolayer films on a copper substrate; applying a binder to the surface of the graphene monolayer films to obtain a copper substrate-graphene monolayer films-adhesive film; etching the copper substrate in the copper substrate-graphene monolayer films-adhesive film to obtain a graphene monolayer films-adhesive film; lifting up the graphene monolayer films-adhesive film with the other copper substrate-graphene monolayer film to obtain a copper substrate-dual-layer graphene films-adhesive film; and finally completely etching the copper substrate in the copper substrate-dual-layer graphene films-adhesive film to obtain a dual-layer graphene films-adhesive film.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Infrared radiation detectors using bundled-VXOY or amorphous silicon nanoparticles nanostructures and methods of constructing the same
ActiveUS10345143B1Increase temperature coefficientImprove stabilityRadiation pyrometryPhotometry electrical circuitsReadout integrated circuitNanostructure
Owner:MAGNOLIA OPTICAL TECH
Methods of fabricating graphene using alloy catalyst
Methods of fabricating graphene using an alloy catalyst may include forming an alloy catalyst layer including nickel on a substrate and forming a graphene layer by supplying hydrocarbon gas onto the alloy catalyst layer. The alloy catalyst layer may include nickel and at least one selected from the group consisting of copper, platinum, iron and gold. When the graphene is fabricated, a catalyst metal that reduces solubility of carbon in Ni may be used together with Ni in the alloy catalyst layer. An amount of carbon that is dissolved may be adjusted and a uniform graphene monolayer may be fabricated.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
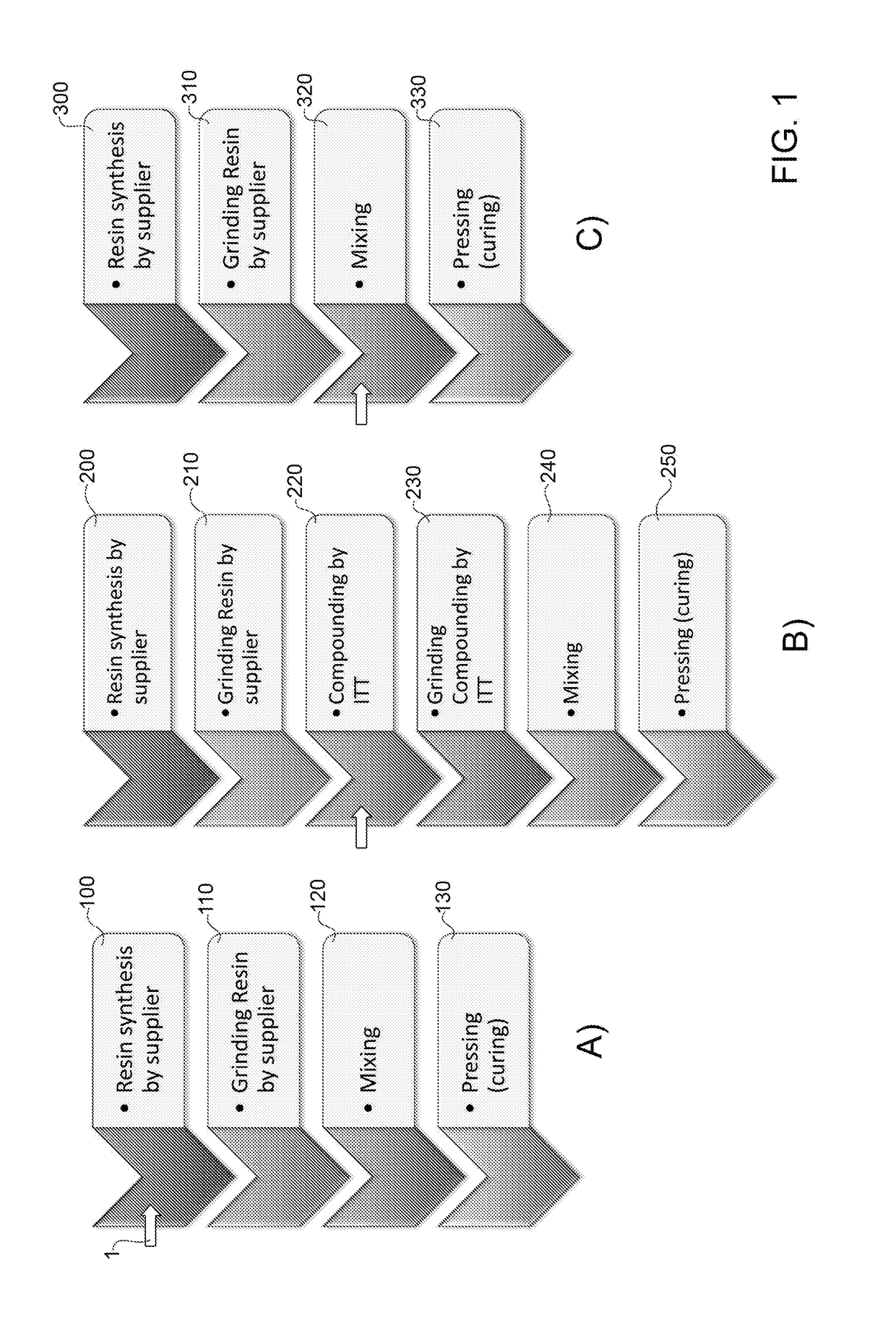
Friction material, in particular for the manufacturing of a brake pad, and associated preparation method
ActiveUS20180128335A1Easy to mergeOther chemical processesFriction liningMetal fibersFriction modifier
An asbestos-free friction material includes inorganic and / or organic and / or metallic fibers, at least one binder, at least one friction modifier or lubricant, at least one filler or abrasive and a carbonaceous material constituted by a microstructure. The microstructure is in the form of flakes or scales of micrometric planar dimensions and of nanometric thickness consisting of a substantially pure graphene mono- or multilayers, preferably pre-blended with at least part of the organic binder.
Owner:ITT ITAL SRL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com