Patents
Literature
1279 results about "Copper substrate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Copper oxide as a "self-cleaning" substrate for graphene growth. Abstract. Commonly used techniques for cleaning copper substrates before graphene growth via chemical vapor deposition (CVD), such as rinsing with acetone, nitric, and acetic acid, and high temperature hydrogen annealing still leave residual adventitious carbon on the copper surface.
Solar selective coating having higher thermal stability useful for harnessing solar energy and a process for the preparation thereof
InactiveUS20070196670A1Easy to optimizeImprove thermal stabilitySolar heat devicesVacuum evaporation coatingAbsorptanceEngineering
The present invention provides an improved solar selective multilayer coating having higher thermal stability and a process for the preparation thereof. Solar selective coatings having higher thermal stability are useful in solar steam generation, solar steam turbines to produce electricity and also on automobile engine components. In the present invention, a tandem stack of three layers of TiAlN, TiAlON and Si3N4 is deposited on metal and non-metal substrates at room temperature using a planar reactive direct current magnetron sputtering process. The first two layers function as the absorber and the third antireflection layer further enhances the coating's absorptance. The solar selective coatings were annealed in air and vacuum to test the thermal stability at different temperatures and durations. The coatings of the present invention deposited on copper substrates are stable in air up to a temperature of 625° C. for a duration of 2 hours and exhibit higher solar selectivity in the order of 9-10 and these coating also show no change in the absorptance and the emittance values even after vacuum annealing at 600° C. for 3 hours. Coatings deposited on copper substrates showed no significant degradation in the optical properties even after continuous heating in air at 525° C. for 50 hours. The solar selective coatings of the present invention exhibit high hardness, high oxidation resistance, chemical inertness and stable microstructure.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Sulfoxide pyrolid(in)one alkanolamine cleaner composition
InactiveUS6916772B2Organic detergent compounding agentsDetergent mixture composition preparationResistPhotoresist
The present invention relates to, inter alia, a composition for stripping photoresist from substrates comprising: about 5% to about 50% by weight of an alkyl substituted pyrrolidone, an alkyl substituted piperidone, or a mixture thereof, about 0.2% to about 20% of one or more alkanolamines, and about 50% to about 94% of a sulfoxide, sulfoxone, or mixture thereof. Advantageously, the composition can remove copper from a copper substrate at a rate of less than about 10 Å per minute when the substrate is immersed in the composition which is held at 70° C. for 30 minutes and rotated relative to the composition at about 200 revolutions per minute.
Owner:EKC TECH
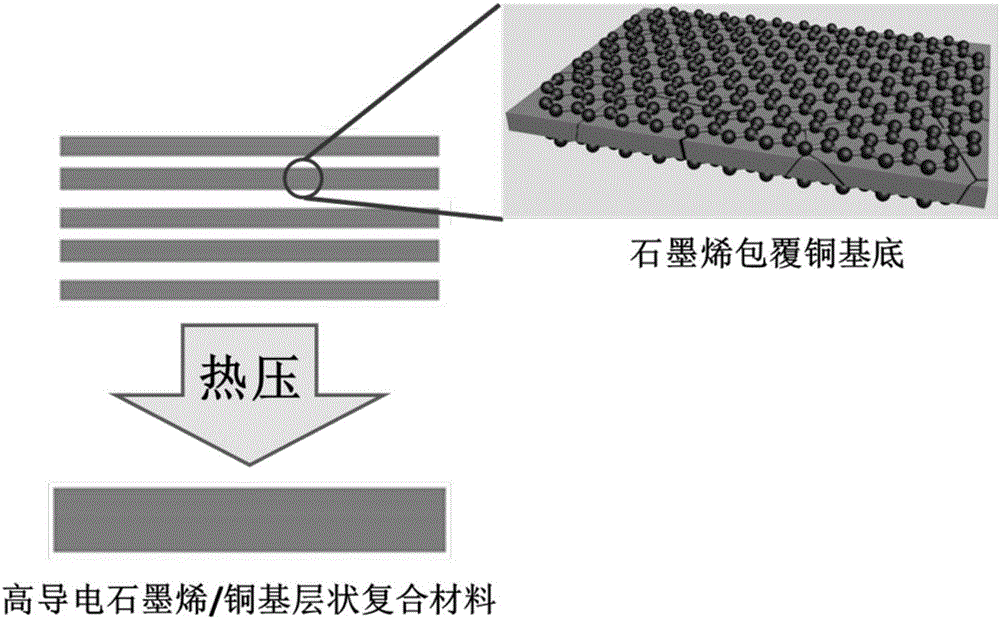
High-conductivity graphene/copper-based layered composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106584976AImprove utilization efficiencyTo overcome the deficiency of reducing resistanceLaminationLamination apparatusSingle crystalCvd graphene
The invention discloses a high-conductivity graphene / copper-based layered composite material and a preparation method thereof. The composite material is characterized in that the composite material is of a layered structure formed by alternate combination of chemical vapor deposition (CVD) graphene and a copper substrate, the copper substrate is in a single-crystal state in the thickness direction in layers, and the (111) crystal face high-orientation effect is achieved. The method includes the following steps that (1) graphene is grown on the upper surface and the lower surface of the platy copper substrate through a CVD technology and the copper substrate is induced to achieve preferred orientation along a (111) crystal face, and the sandwich-shaped graphene-cladding copper substrate is obtained through preparation; and (2) multiple pieces of graphene-cladding copper substrates are subjected to hot pressed sintering densification to form the high-conductivity graphene / copper-based layered composite material. The layered composite material prepared by the method is high in conductivity, higher than pure silver in conduction level and easy to produce and can be used as various conduction materials.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Copper-faced modules, imprinted copper circuits, and their application to supercomputers
InactiveUS20050040513A1Avoid mechanical failureReduce thermal strainInsulating substrate metal adhesion improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSupercomputerElectronic systems
A method for fabricating copper-faced electronic modules is described. These modules are mechanically robust, thermally accessible for cooling purposes, and capable of supporting high power circuits, including operation at 10 GHz and above. An imprinting method is described for patterning the copper layers of the interconnection circuit, including a variation of the imprinting method to create a special assembly layer having wells filled with solder. The flip chip assembly method comprising stud bumps inserted into wells enables unlimited rework of defective chips. The methods can be applied to multi chip modules that may be connected to other electronic systems or subsystems using feeds through the copper substrate, using a new type of module access cable, or by wireless means. The top copper plate can be replaced with a chamber containing circulating cooling fluid for aggressive cooling that may be required for servers and supercomputers. Application of these methods to create a liquid cooled supercomputer is described.
Owner:SALMON TECH
Production method for direct growth of one-dimensional nano cuprous oxide array on metallic copper substrate
InactiveCN101429680AImprove field emission performanceHigh visible light photocatalytic performanceAnodisationPolycrystalline material growthElectrolysisChloride salt
In chloride media, copper anodic dissolution is a mature process for producing cuprous oxide (Cu2O); and based on the preparation process, the invention provides a method for directly growing a one-dimensional nanometer Cu2O array on an anode metal copper substrate through adding a surface active agent to an anode slot, and controlling the concentration of electrolyte chloride salt in the anode slot, the concentration of alkali in a cathode slot, electric quantity of electrolysis and electrolysis temperature. The array has controllable appearance, and consists of a nanometer belt, a nanometer plate and a nanometer line, wherein the top end of the one-dimensional array can be acicular, circular, and the like. The one-dimensional nanometer Cu2O array directly growing on the copper substrate has excellent effect of field emission performance and visible light catalysis, and has wide application prospect in technical fields of vacuum microelectronic devices, panel display, advanced oxidation and other aspects.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
Scalable subsystem architecture having integrated cooling channels
ActiveUS20070025079A1High densitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringBall grid array
A method for building scalable electronic subsystems is described. Stackable modules employ copper substrates with solder connections between modules, and a ball grid array interface is provided at the bottom of the stack. A cooling channel is optionally provided between each pair of modules. Each module is re-workable because all integrated circuit attachments within the module employ re-workable flip chip connectors. Also, defective modules can be removed from the stack by directing hot inert gas at externally accessible solder connections.
Owner:SALMON TECH
Equipment and method for producing nichrome composite plate with vacuum arc ion plating
InactiveCN101294270ACorrosion protectionHigh surface hardnessVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingComposite plateVacuum chamber
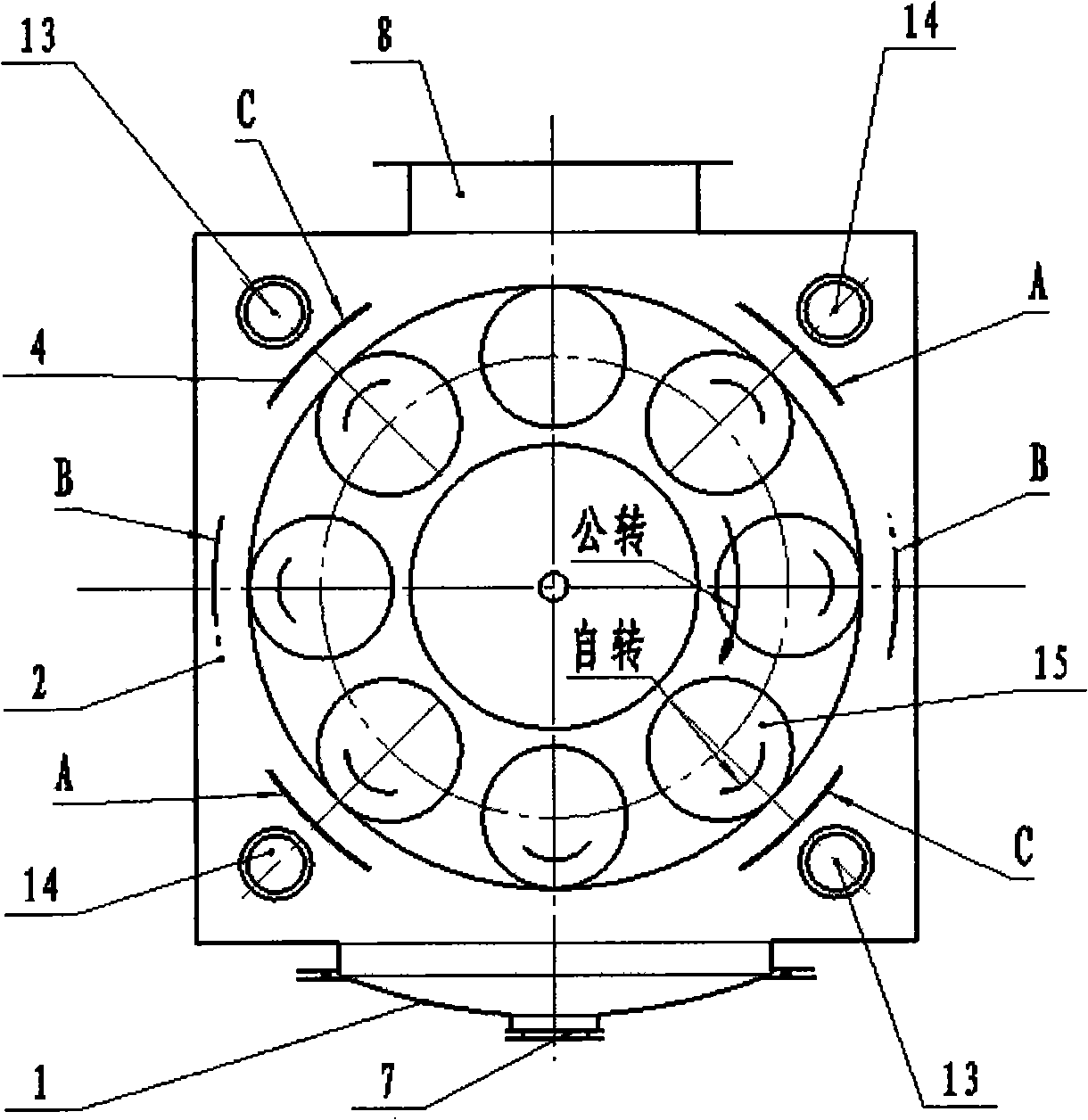
The invention relates to a device for manufacturing a nickel-chromium composite plate by using vacuum arc ion plating to replace electroplating and a method thereof, and is characterized in that the device of the vacuum arc ion plating and the method are utilized to replace water electroplating to sequentially prepare the nickel-chromium composite plate composed of a pure nickel film, a nickel-chromium gradient transition film and a pure chromium film on a copper substrate; the device for manufacturing the nickel-chromium composite plate by using the vacuum arc ion plating is of a vertical cylindrical shape or a regular polygon; arc target sources are evenly distributed around a vacuum chamber wall; a controllable mechanical baffle plate is arranged in front of each target source; a planetary type work rest with rotation and revolution is arranged in the middle part of a vacuum chamber; the technical process of a filming operation comprises three stages that are preliminary treatment, the filming operation and post treatment. The device and the method simplify the process flows and the operation links, increase the work efficiency, fully replace the traditional electroplating technology to coat a wearproof anticorrosion decoration coating on a coppery water heating component, and thoroughly eliminate the environmental pollution problems in the electroplating.
Owner:辽阳市弓长岭区光辉铁矿石加工厂
Copper plating substrate-based method for preparing large-area graphene film
ActiveCN102212794AThe method is simpleEasily damagedVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingCopper platingHydrogen
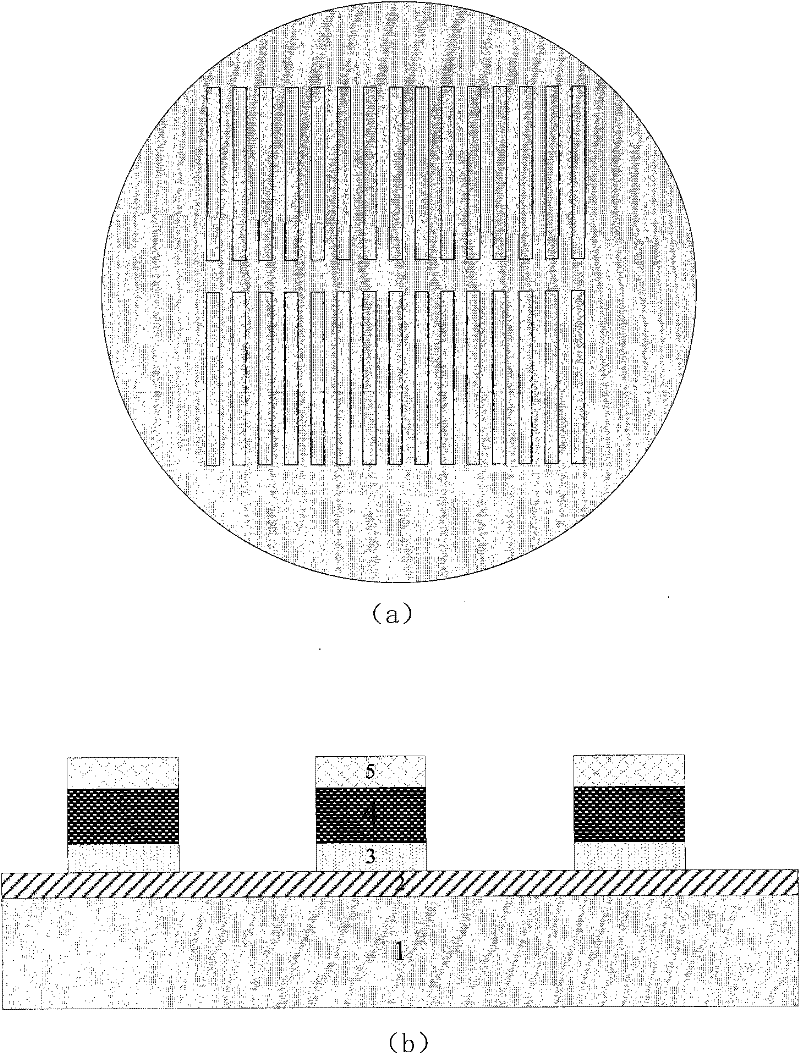
The invention relates to a method for preparing graphene on a copper plating substrate. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: preparing the graphical copper plating substrate on a silicon chip; and growing the graphene on the copper plating substrate for 2 to 5 minutes at the temperature of between 800 and 1,000 DEG C by using a normal pressure chemical vapor deposition method, using methane as a carbon source and using argon and hydrogen as carrier gases. A graphical graphene film can be directly prepared by the method, and the substrate can be compatible with an integrated circuit (IC) process; and the manufacturing method is simple and low in cost, and can be used for large-scale manufacture.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
III-nitride substrate growing method, substrate and LED (light emitting diode)
InactiveCN102201503AWill not introduceSimple growth processSemiconductor devicesCvd grapheneLight-emitting diode
A III-nitride substrate growing method comprises the following steps: providing a copper support substrate; forming a graphene layer on the surface of the support substrate; and forming a III-nitride semiconductor layer on the surface of the graphene layer, wherein the highest growing temperature of the III-nitride semiconductor layer is lower than the melting point of copper. In the method, since graphene and III-nitride are sequentially grown on the conductive metallic copper substrate with high melting point, growth process is simple and impurities cannot be introduced in the production process.
Owner:SUZHOU NANOWIN SCI & TECH +1
Nitride LED epitaxial wafer structure based on copper substrate and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN104538526AImprove crystal qualityNitride Epitaxial Growth of High Crystal QualitySemiconductor devicesOptical propertyNitride
The invention relates to a nitride LED epitaxial wafer structure based on a copper substrate and a manufacturing method of the nitride LED epitaxial wafer structure. The nitride LED epitaxial wafer structure based on the copper substrate comprises the copper substrate, a two-dimensional derived film and a nitride epitaxial layer. The two-dimensional derived film is located between the copper substrate and the nitride epitaxial layer and is attached to the surface of the copper substrate. The nitride epitaxial layer is attached to the two-dimensional derived film. The manufacturing method comprises the steps that one or two layers of two-dimensional derived films are manufactured on the copper substrate, and the nitride epitaxial layer is grown on the copper substrate with the two-dimensional derived films. By the adoption of the nitride LED epitaxial wafer structure based on the copper substrate, high-crystalline-quality nitride epitaxial growth can be conducted on the copper substrate, cost is reduced, and the optical property, the electrical property and the thermal property of a device are improved.
Owner:江苏巨晶新材料科技有限公司
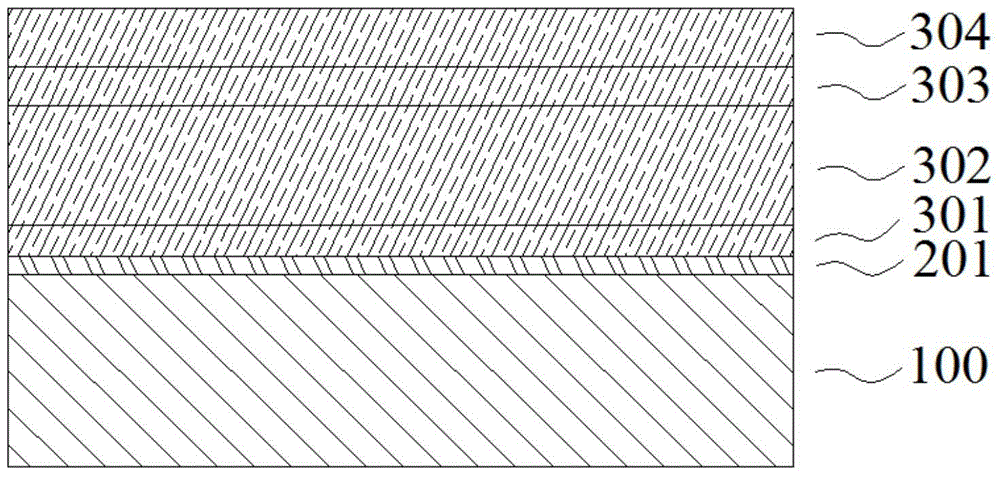
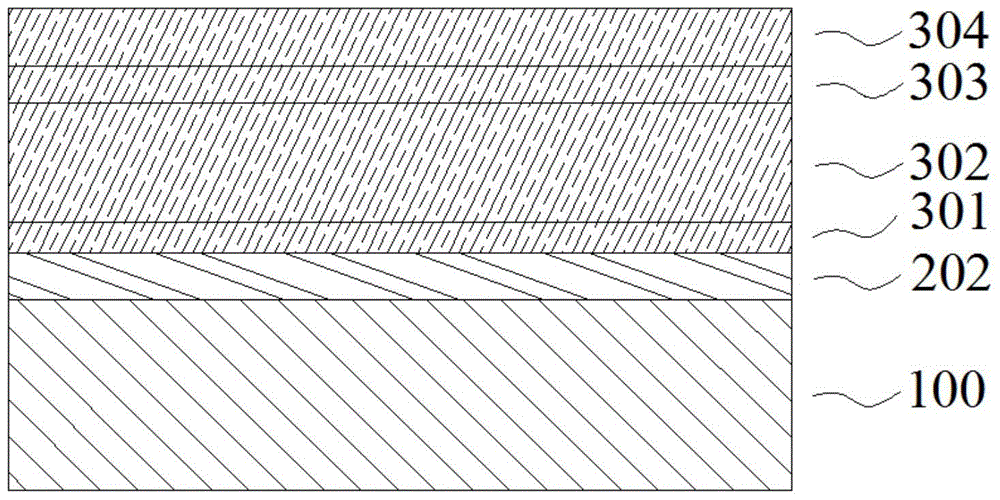
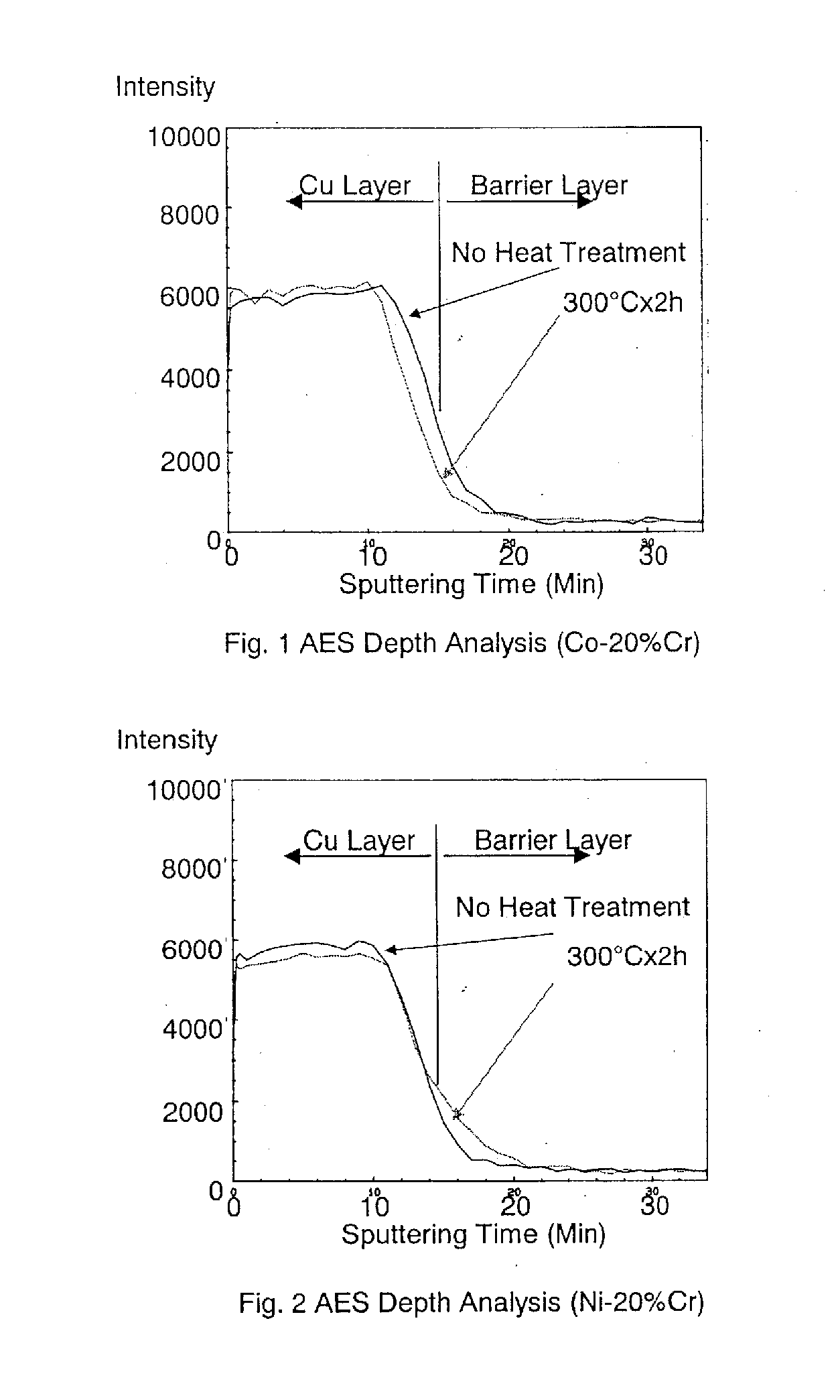
Barrier Film For Flexible Copper Substrate And Sputtering Target For Forming Barrier Film
InactiveUS20070209547A1Prevent peelingSufficient barrier effectVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingIn planeAlloy
Provided are a barrier film for a flexible copper substrate comprising a Co—Cr alloy film containing 5 to 30 wt % of Cr and a balance of unavoidable impurities and Co, having a film thickness of 3 to 150 nm, and film thickness uniformity of 10% or less at 1σ; and a sputtering target for forming a barrier film comprising a Co—Cr alloy containing 5 to 30 wt % of Cr and a balance of unavoidable impurities and Co, wherein the relative magnetic permeability in the in-plane direction of the sputtered face is 100 or less. The barrier film for a flexible copper substrate and the sputtering target for forming such barrier film have a film thickness that is thin enough to prevent film peeling in inhibiting the diffusion of copper to a resin film such as polyimide, is capable of obtaining a sufficient barrier effect even in a minute wiring pitch, and have barrier characteristics that will not change even when the temperature rises due to heat treatment or the like.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
Method for synthesizing graphene film material
ActiveCN102020263AQuality improvementEasy to prepareChemical vapor deposition coatingHydrogenGas phase
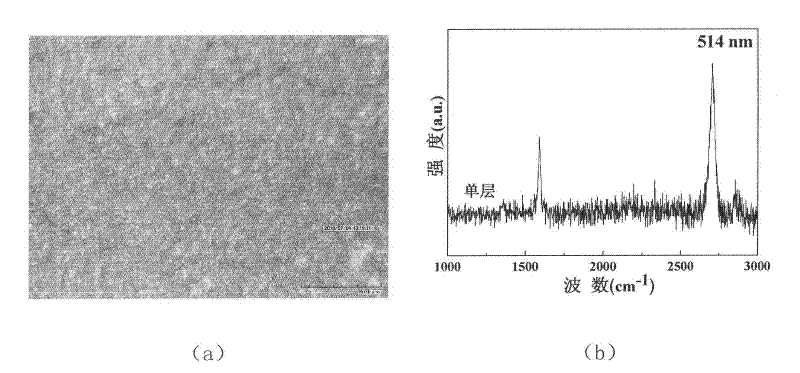
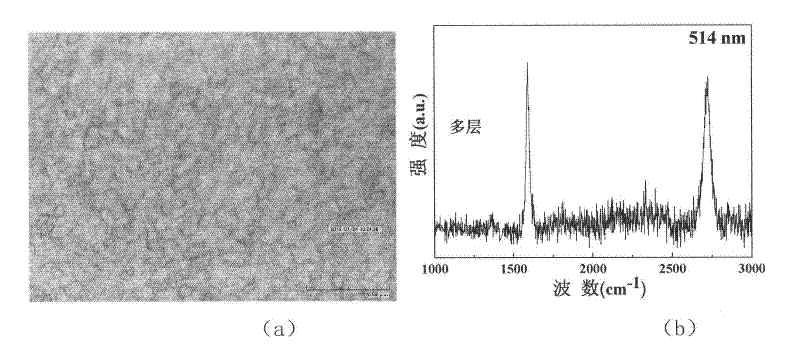
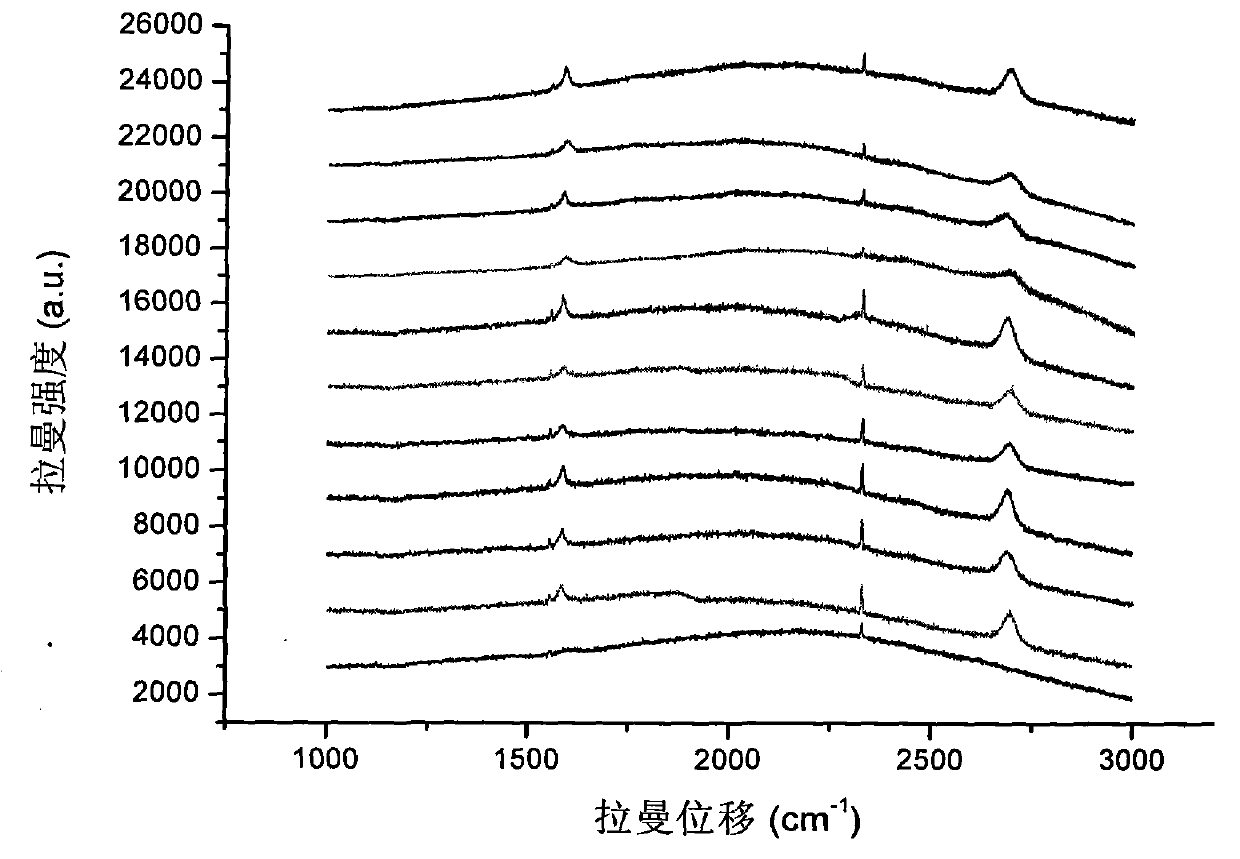
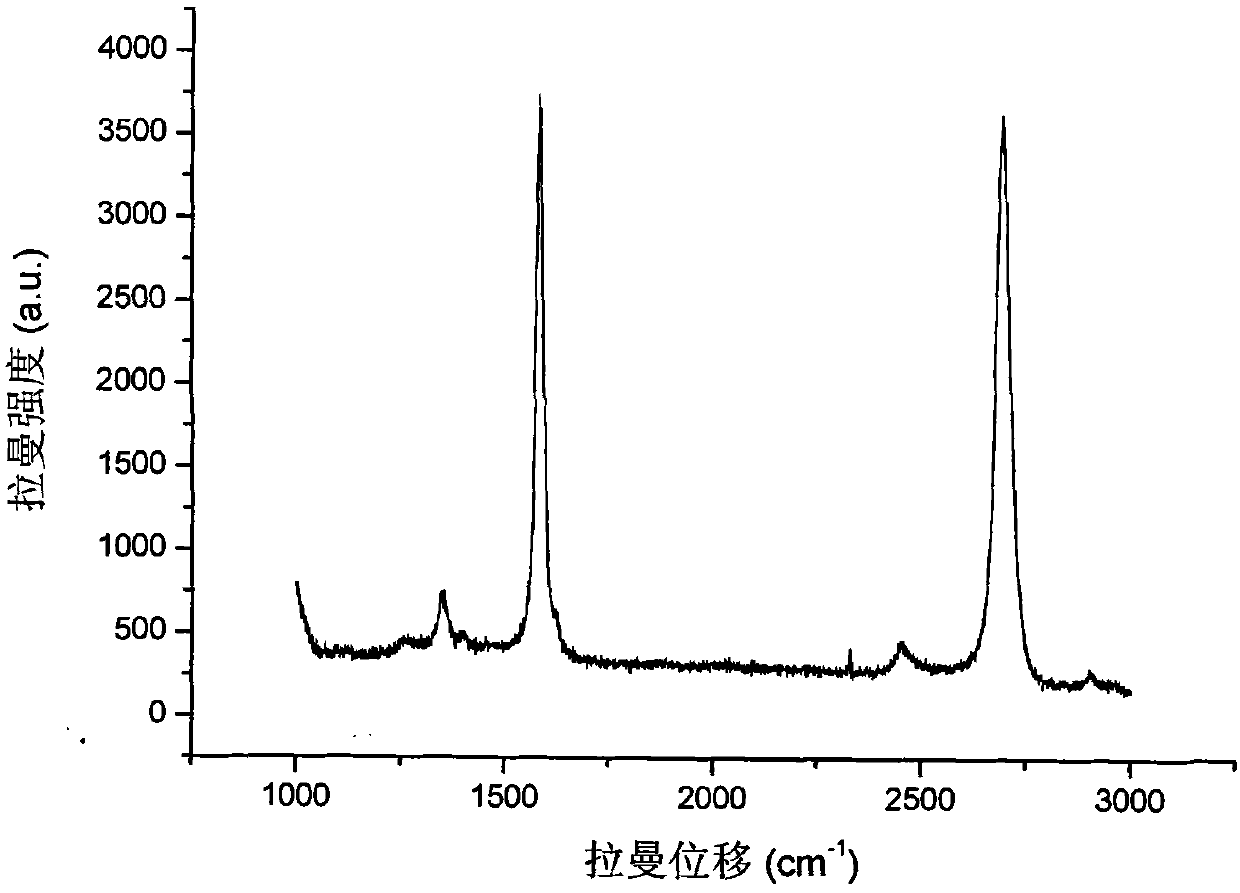
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing a graphene film material, comprising the following steps: a grapheme film is grown on a copper substrate under mixed atmosphere of hydrogen and methane by using a chemical vapor deposition method; then the copper substrate grown with the grapheme film is placed flatly on a silicon substrate with the oxidized surface, the obtained silicon substrateis placed into a ferric nitrate solution, the copper substrate is dissolved, and at the moment, the graphene film is deposited on the silicon substrate; then, the solution is diluted, then the silicon substrate deposited with the grapheme is taken out of the solution, and is dried in a vacuum drying oven; and after ultrasonic cleaning is carried out on the silicon substrate deposited with the graphene, and the obtained silicon substrate is placed in an annealing furnace communicated with argon for protection to anneal, thus a high-quality grapheme sample is prepared. By utilizing the method for synthesizing the graphene film material, the original complex steps needed for preparing the graphene film are simplified, a toxic agent needed by a chemical method is avoided, and the production efficiency of the graphene film is improved, thus by measurement of a Raman spectrometer, the prepared graphene film is proved to have good performances and excellent reliability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Self assembled molecules on immersion silver coatings
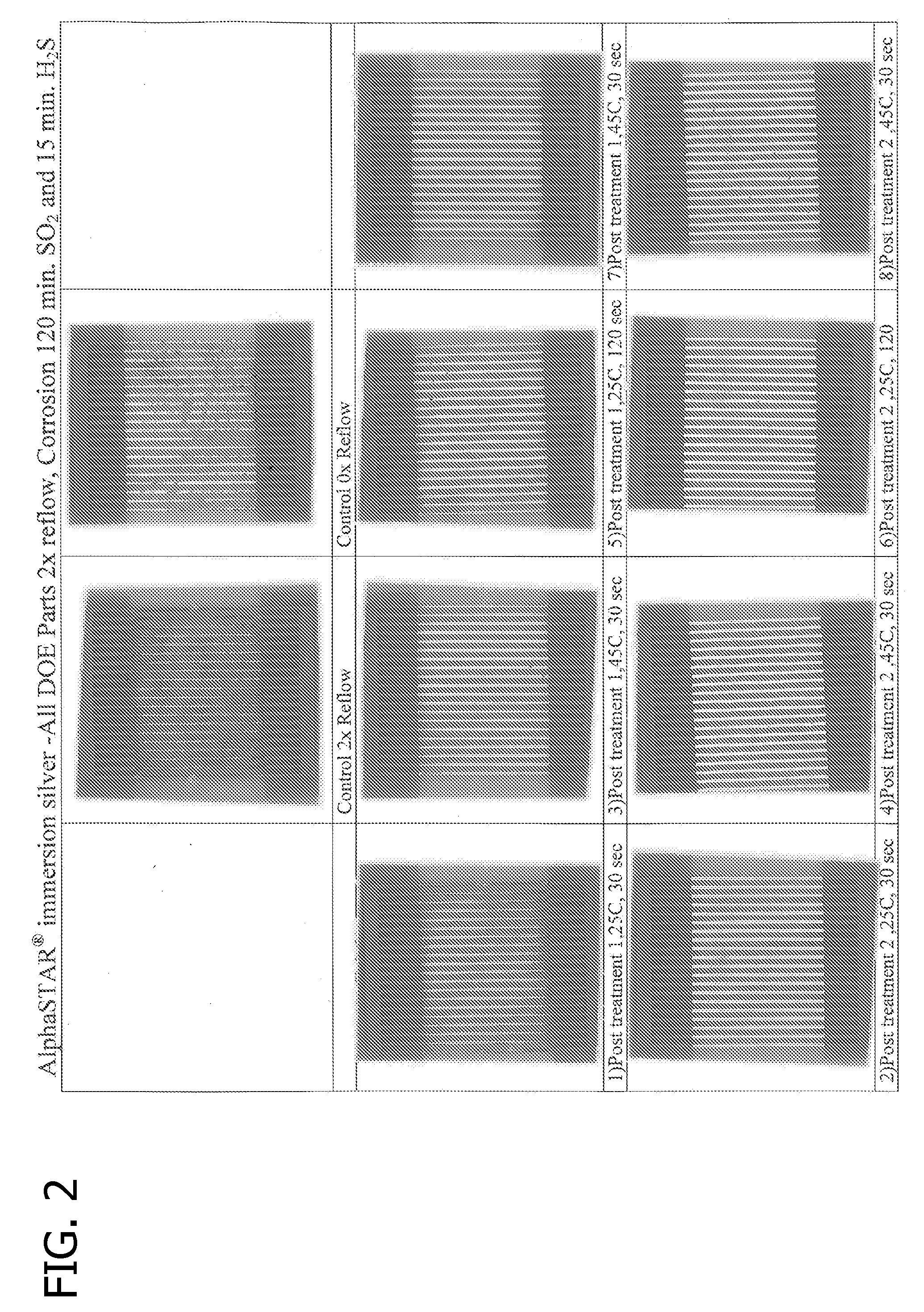
ActiveUS20090121192A1Improve corrosion resistanceOther chemical processesPretreated surfacesAlcoholSilver coating
A method for enhancing the corrosion resistance of an article comprising a silver coating deposited on a solderable copper substrate is provided. The method comprises exposing the copper substrate having the immersion-plated silver coating thereon to an anti-corrosion composition comprising: a) a multi-functional molecule comprising at least one organic functional group that interacts with and protects copper surfaces and at least one organic functional group that interacts with and protects silver surfaces; b) an alcohol; and c) a surfactant.
Owner:MACDERMID ENTHONE INC
Package structure
ActiveUS20150303164A1Improve electrical performanceAvoid parasitic effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesInsulation layerElectronic component
A package structure includes a first insulation layer, a first conductive layer, a direct bond copper substrate, and a first electronic component. A first conductive via is formed in the first insulation layer. The first conductive layer is disposed on a top surface of the first insulation layer and in contact with the first conductive via. The direct bond copper substrate includes a second conductive layer, a third conductive layer and a ceramic base. The ceramic base is disposed on a bottom surface of the first insulation layer and exposed to the first insulation layer by press-fit operation. The first electronic component is embedded within the first insulation layer and disposed on the second conductive layer. The first electronic component includes a first conducting terminal. The first conducting terminal is electrically connected with the second conductive layer and / or electrically connected with the first conductive layer through the first conductive via.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INTL SINGAPORE
Solid electrolytic capacitor, circuit board having built-in solid electrolytic capacitor and methods for manufacturing them
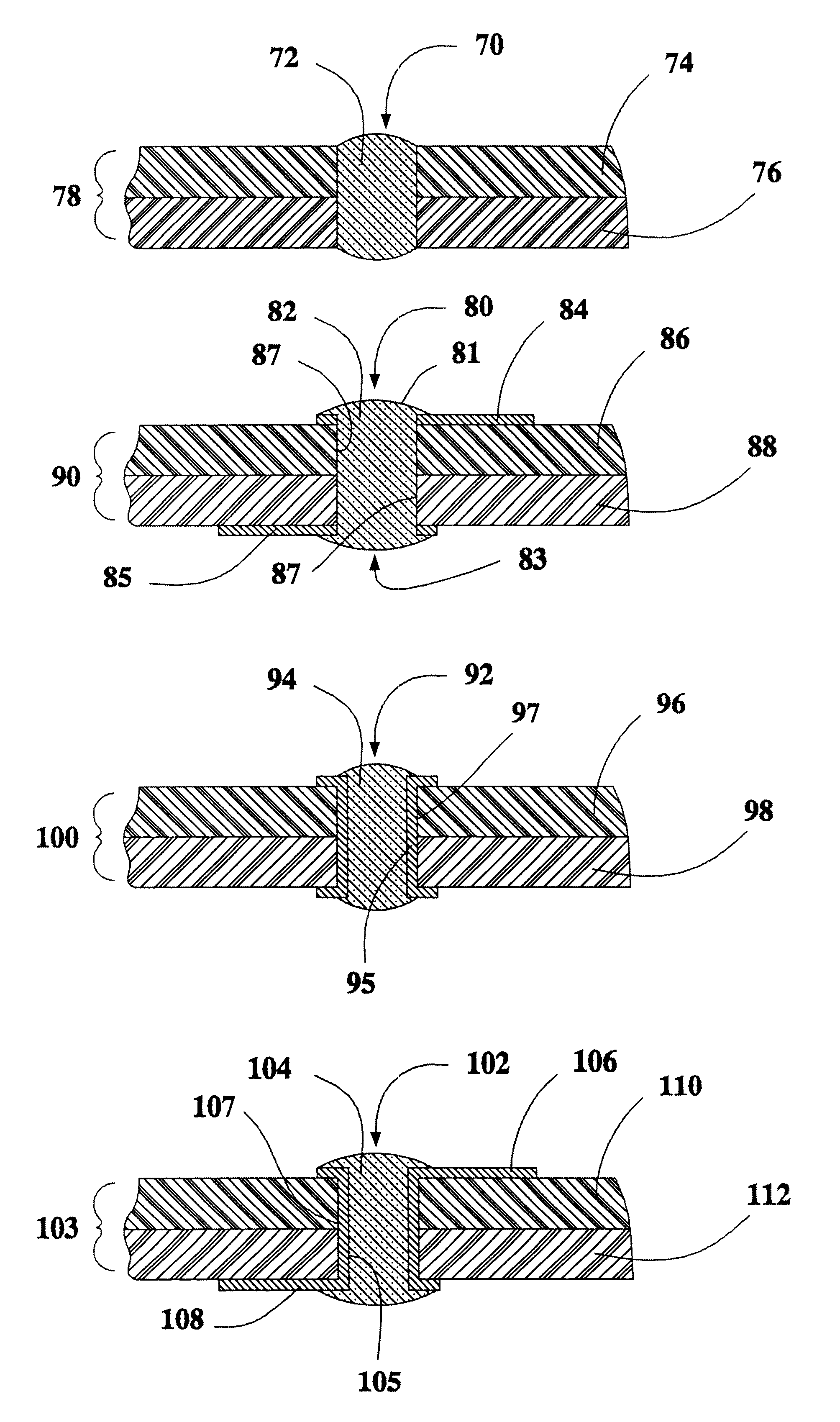
InactiveUS6989982B2Prevented from reachingIncrease capacitanceLiquid electrolytic capacitorsHybrid capacitor electrodesElectrolysisElectrolytic capacitor
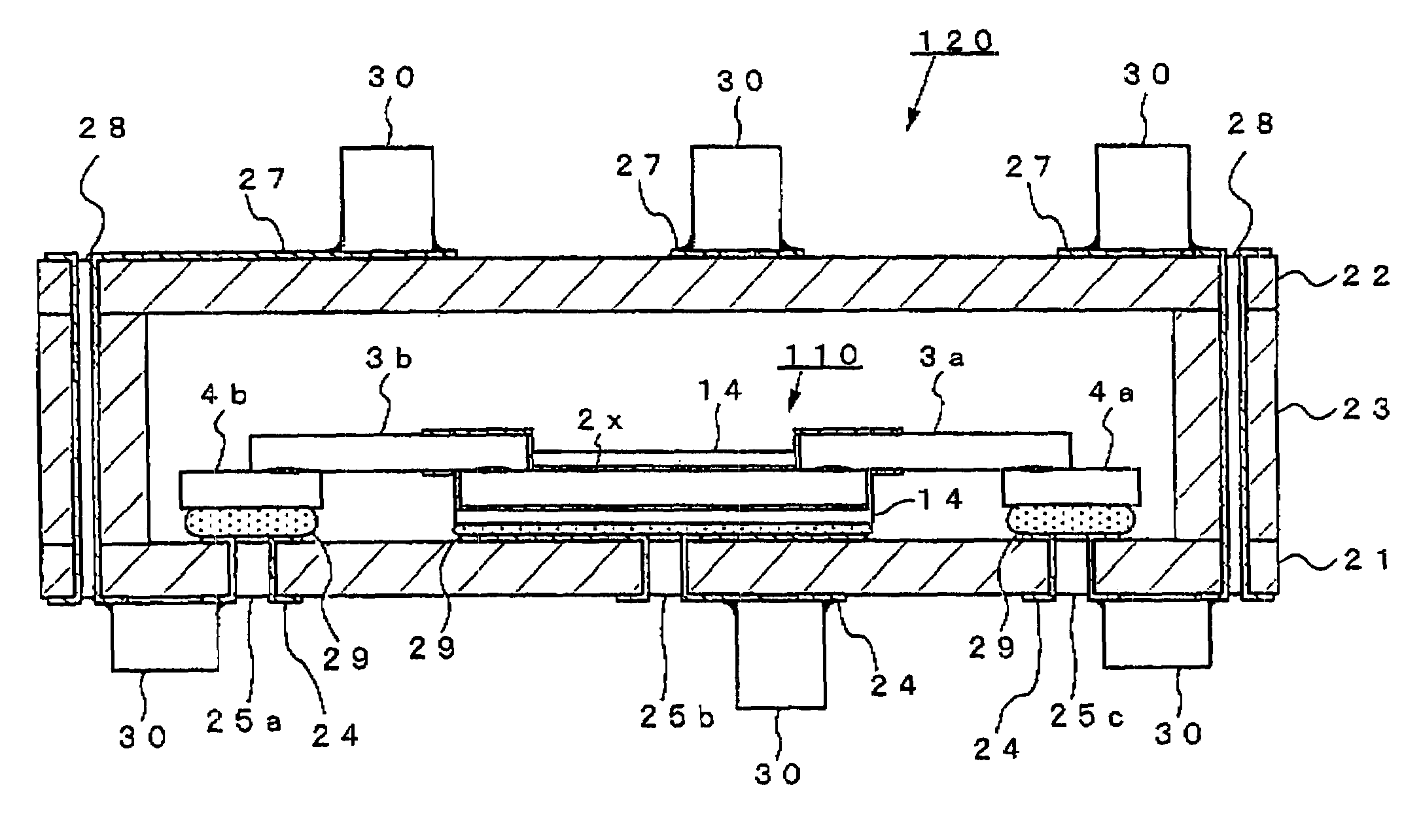
An electrode body 100 of a solid electrolytic capacitor component includes a foil-like aluminum substrate 2 whose surface is roughened or enlarged and which is formed with an aluminum oxide film the surface thereof as an insulating oxide film, two foil-like aluminum substrates 3a,3b whose surfaces are not roughened, and two foil-like copper substrates 4a,4b as a metal electric conductor for constituting a lead electrode. On the whole surface of the foil-like aluminum substrate 2, an anode electrode 14 including a solid high molecular polymer electrolyte layer 11, a graphite paste layer 12 and a silver paste layer 13 is formed. The thus constituted solid electrolytic capacitor component 110 is accommodated in a substantially closed space defined by a first insulating substrate 21 and a second insulating substrate 22, thereby fabricating a three-terminal type solid electrolytic capacitor.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Method of separating an atomically thin material from a substrate
InactiveUS20140261999A1Semi-permeable membranesLamination ancillary operationsAcoustic waveCvd graphene
A method of separating an atomically thin material, such as graphene, from a substrate, such as copper, is disclosed. The method provides a composite sheet, such as a graphene-copper sheet, and then applies hypersonic waves to the composite sheet so as to break the bonds therebetween and separate a graphene sheet from the copper substrate. A system to implement the separation is also disclosed.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
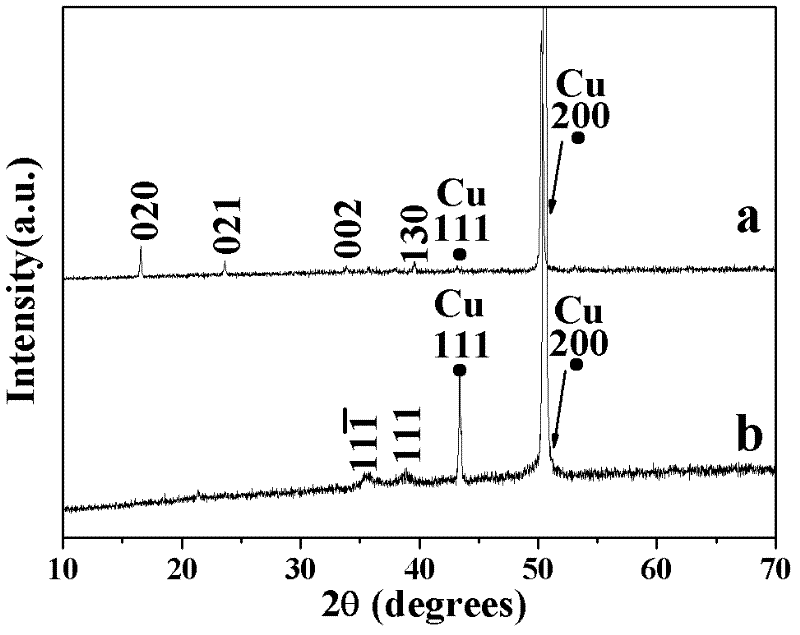
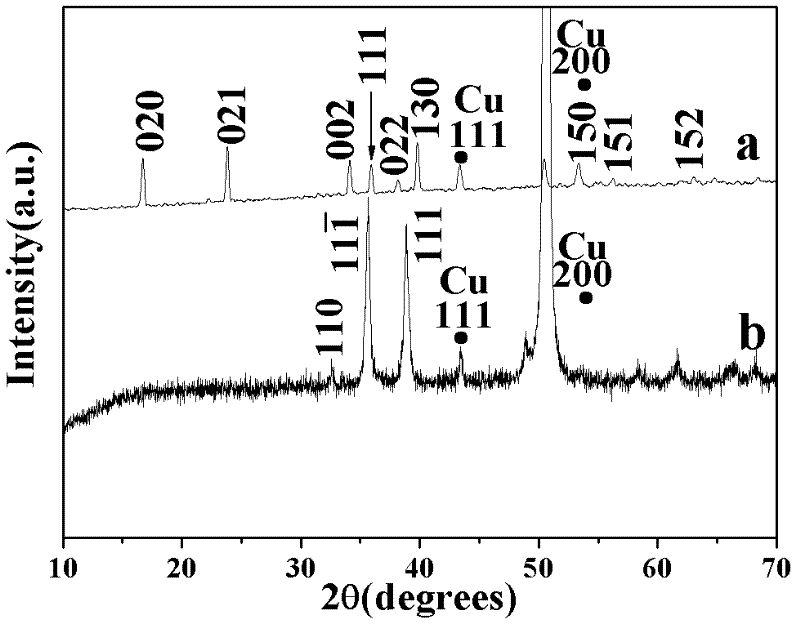
AlN ceramic bonded copper substrate and preparation method thereof
The invention provides an AlN ceramic bonded copper substrate which comprises an AlN ceramic substrate and copper foil bonded and connected onto the AlN ceramic substrate and is characterized in that a spinel structure compound modification layer is formed between the AlN ceramic substrate and the copper foil and comprises one or two of CuAlO2, CuAl2O4, Cu2O and CuO. The invention further provides a preparation method of the AlN ceramic bonded copper substrate. The method comprises the steps of spraying nano Cu2O on the surface of the AlN substrate, sintering in inert gas with a micro oxygen content and air sequentially, and then removing a surface oxide by a pickling manner. The prepared modification layer is tightly combined with matrix ceramic, and also has good affinity characteristic with the Cu foil. A uniform oxidation layer can be formed on the surface of the Cu foil by putting the Cu foil in a prepared solution at a certain temperature for specified time and more facilitates an AlN-DBC (direct bonded copper) technology.
Owner:NANJING ZHONGJIANG NEW MATERIAL TECH
Plain copper foodware and metal articles with durable and tarnish free multiplayer ceramic coating and method of making
ActiveUS20100255340A1Cooking-vessel materialsVacuum evaporation coatingCeramic coatingThermal stability
Soft and porous material is coated with a multilayer ceramic coating by physical vapor deposition. The coated material is suitable for use as foodware, particularly, a copper foodware article including a plain copper substrate, a base coating, and a ceramic coating. The base coating is deposited by sputtering and cathodic arc in combination, providing the good corrosion resistance and adhesion to the substrate. The ceramic coating includes a PVD nitride or carbonitride layer, providing a tarnish-free surface, good durability, and thermal stability. The coated copper foodware article has the same heat conductivity as pure copper, good corrosion resistance, high durability, excellent cooking, and ease of cleaning.A metal article having a multilayer coating and a method of making a metal article are also described.
Owner:MEYER INTPROP
Maskless femtosecond laser manufacturing method for super-hydrophobic and anti-reflective surface
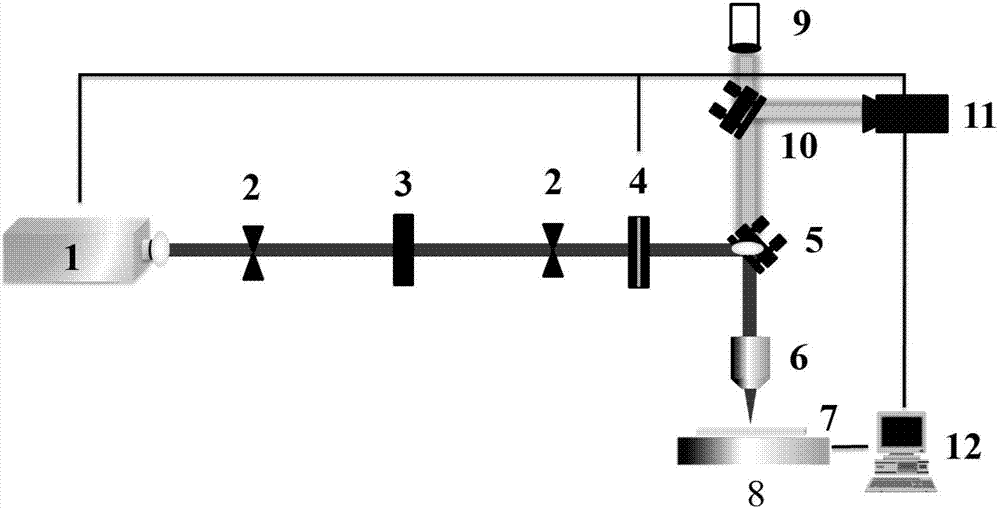
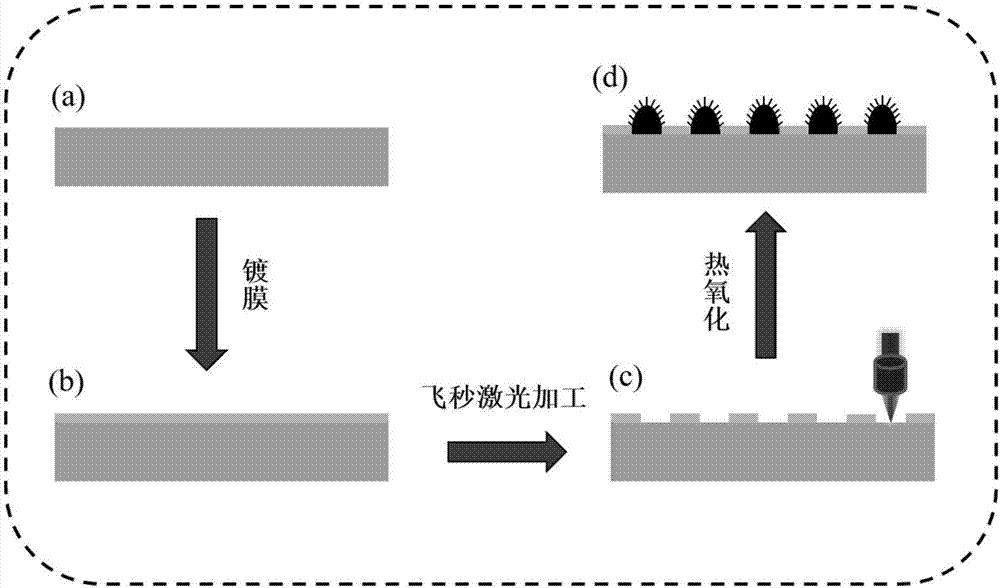
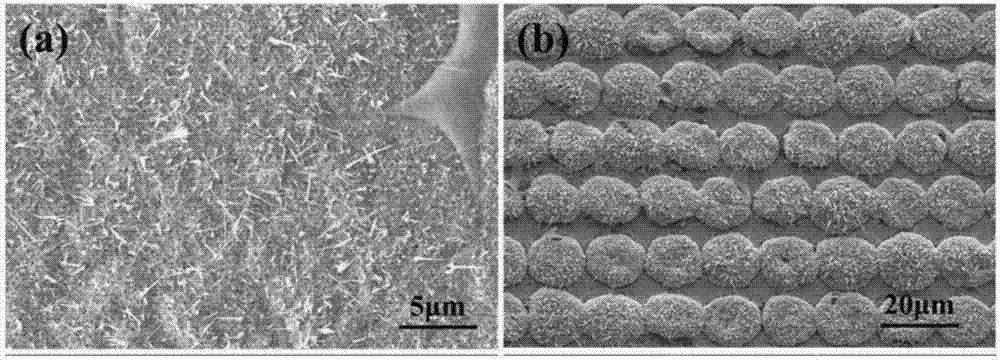
ActiveCN107243697ALow costExcellent superhydrophobicityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingFemto second laserEvaporation
The invention relates to a maskless femtosecond laser manufacturing method for a super-hydrophobic and anti-reflective surface and belongs to the field of preparation of super-hydrophobic and anti-reflective materials. The maskless femtosecond laser manufacturing method for the super-hydrophobic and anti-reflective surface comprises the following steps that (1) a copper substrate is plated with a film of a nanometer thickness through electron beam evaporation or a magnetron sputtering coating method; (2) through a femtosecond laser direct writing method, patterning is conducted on the copper substrate plated with the film of the nanometer thickness, and the shape of patterning can be controlled through a program; (3) a heating device is used for conducting thermal oxidation treatment on the substrate obtained after femtosecond laser patterning, and then a micro-nanometer composite structure is prepared. Compared with the prior art, the maskless femtosecond laser manufacturing method for the super-hydrophobic and anti-reflective surface has the advantages that the manufacturing process does not need a vacuum device or an optical mask, and the manufactured substrate is controllable in shape and has the super-hydrophobic performance, the self-cleaning performance, the anti-reflective performance and other performances.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
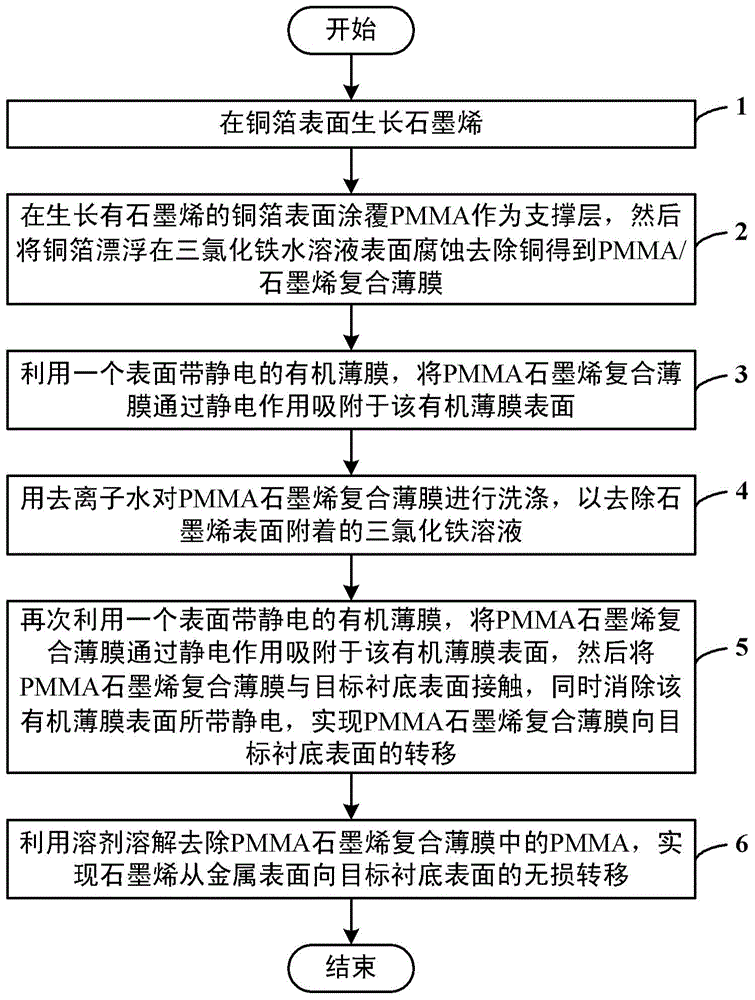
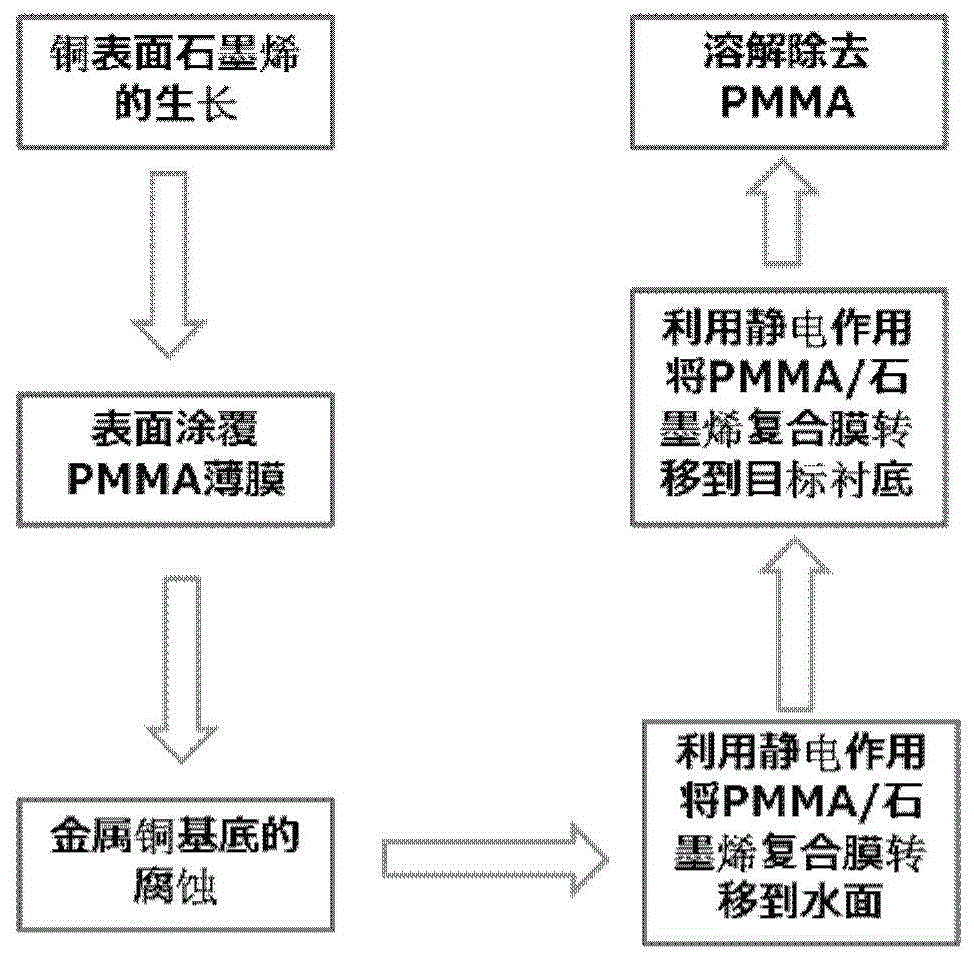
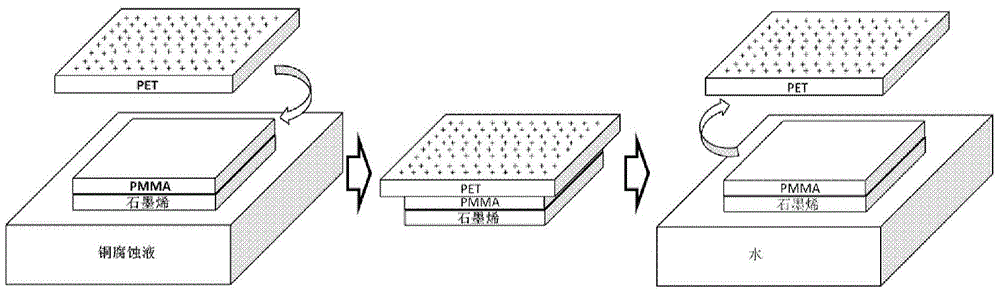
Method for nondestructively transferring graphene from metal surface to surface of target substrate
ActiveCN104451592AEfficient transferReduce breakageGrapheneChemical vapor deposition coatingComposite filmGraphene
The invention discloses a method for nondestructively transferring graphene from a metal surface to the surface of a target substrate. The method comprises the steps of enabling graphene to grow on the surface of metal copper; coating the surface of graphene with a PMMA film, floating a copper substrate in an etching agent solution to corrode and remove the copper to obtain a PMMA / graphene composite film; enabling a PET film with static electricity in a friction manner to approach the PMMA / graphene composite film which is floated on the liquid surface, and adsorbing the graphene / PMMA composite film on the surface of the PET film by utilizing the electrostatic effect, contacting the graphene / PMMA composite film with the deionized water, meanwhile, releasing static electricity on the surface of the PET film, separating the PMMA / graphene composite film from the PET film, and floating the PMMA / graphene composite film on the water surface; repeating the steps, washing graphene, and completely removing the copper etching agent attached to the surface of the graphene; and finally transferring the PMMA / graphene composite film to the surface of the target substrate, and dissolving and removing the PMMA on the surface. By utilizing the method, not only can the location transfer of the large-sized graphene be realized, but also the damage rate of the graphene can be greatly reduced.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Laser fusion welding method of abrasion-proof heat-proof composite coating on surface of tuyeres of blast furnace port sleeve
InactiveCN101109026AImprove wear resistanceImprove corrosion resistanceMolten spray coatingTuyeresHigh power lasersWear resistant
The invention relates to a wear-resistant and heat-resistant complex coating laser fusion approach on the tuyere surface of a blast furnace. The high power laser quickly scans and welds the tuyere surface of the blast furnace and metallurgically combines with the substrate materials to form a good nickel-based toughness transition layer. The laser bandwidth clads the nickel-based toughness transition layer to produce a cobalt-based alloy with excellent effects of wear-resistant and heat-resistant. The technology process comprises the following steps: firstly the blast furnace tuyere is pre-treated; secondly the pre-deposited nickel-base alloy is coated with plasma; thirdly the nickel-based alloy is welded quickly by the high power laser; fourthly the cobalt-based alloy is clad by the high power laser bandwidth; finally is the following heat treatment. The invention can avoid the structure stress caused by the difference between the substrate material and the cladding material in the laser cladding process. In addition, the treatment to the copper substrate before and after laser cladding can decrease temperature gradient so as to prevent the cladding layer from cracking to a certain degree.
Owner:SHENYANG DALU LASER COMPLETE EQUIP
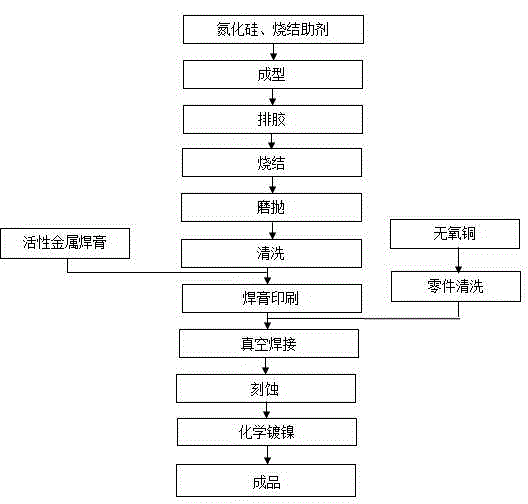
High-thermal-conductivity silicon nitride ceramic copper-clad plate and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN104409425AHigh strengthImprove impact resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesManufacturing technologyFlexural strength
The invention discloses a high-thermal-conductivity silicon nitride ceramic copper-clad plate and a manufacturing method thereof and relates to the field of the copper-clad plate manufacturing technology. The high-thermal-conductivity silicon nitride ceramic copper-clad plate comprises a high-thermal-conductivity silicon nitride ceramic substrate and oxygen-free copper layers; the upper and lower surfaces of the high-thermal-conductivity silicon nitride ceramic substrate are respectively welded with the oxygen-free copper layers; and the welding is a high-temperature welding in a vacuum brazing furnace by using an active metal welding paste. The bending strength of the high-strength and high-thermal-conductivity silicon nitride ceramic substrate is 2-3 times that of an aluminum nitride ceramic substrate, and the cladding of the high-thermal-conductivity silicon nitride ceramic substrate and a thick copper substrate can be realized; the thermal conductivity is 3-4 times that of the aluminum nitride ceramic substrate, so that the heat dissipation performance of the substrate can be improved greatly; compared with a direct copper-cladding process, the active copper-welding process has higher interface bonding strength, less cavities and higher reliability. Therefore, the high-thermal-conductivity silicon nitride ceramic copper-clad plate has the features of high strength, high conductivity and high reliability.
Owner:HEBEI SINOPACK ELECTRONICS TECH
Method for preparing electrode material CuO (cupric oxide) film of lithium ion battery on copper substrate
InactiveCN102231435AUniform shapeThe synthesis method is simple and controllableCell electrodesMicro nanoLevel structure
The invention provides a method for preparing electrode material CuO (cupric oxide) film of a lithium ion battery on a copper substrate. The method comprises the following steps of: reacting a pretreated copper substrate with a microemulsion for 2-96 hours at room temperature or reacting the pretreated copper substrate with an alkaline aqueoussolution for 40-90 minutes at room temperature; takingout the copper substrate, and washing and drying the copper substrate to obtain a Cu(OH)2 micro-nano multi-level structure film or Cu(OH)2 nano-rod array film; and processing the dried film in an inert atmosphere fro 4-6 hours at a temperature of 150-200 DEG C to obtain a CuO micro-nano multi-level structure film or CuO nano-rod array film with the similar shape. The film is uniform in shape and stable in structure and can be used as an electrode of a lithium ion battery directly; in addition, by using the film, the preparing processes of the electrode can be simplified, the initial dischargespecific capacity of the battery can be improved obviously, the initial irreversible capacity loss can be reduced and the cycle performance and the multiplying power performance can be improved further.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Flat cable
InactiveUS7482540B2AmountReduce formationStrip/foil conductorsFlat/ribbon cablesElectrical conductorTin plating
A flat cable includes a plurality of flat conductors each including a copper substrate, the flat conductors being aligned in a plane, and an insulating resin that covers the flat conductors. At least a terminal part of each of the flat conductors has a tin-copper alloy layer on the copper substrate, and a zinc-containing tin plating layer on the tin-copper alloy layers. The thickness of the tin-copper alloy layer is at least 0.2 μm and not greater than 1.0 μm. The thickness of the zinc-containing tin plating layer is at least 0.2 μm and not greater than 1.5 μm. The total thickness of the tin-copper alloy layer and the zinc-containing tin plating layers is at least 0.4 μm and not greater than 1.7 μm.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Method for manufacturing pure copper/copper chromium alloy composite contact material
InactiveCN101834077AOvercome the serious problem of macro segregationDense tissueElectric switchesMetallic material coating processesMelting tankWear resistance
The invention provides a method for manufacturing pure copper / copper chromium alloy composite contact material, comprising the following steps of: first, carrying out surface pretreatment on pure copper substrate; second, mixing 60-85 percent of copper powder and 15-40 percent of chromium powder evenly according to weight percentage , mixing binder and Cu-Cr powder according to the volume ratio of 1: 1.6-2, adding acetone for dilution and stirring into paste, and coating a Cu-Cr layer with the thickness of 1.2-1.8mm on the surface of the pure copper and drying at 80-100 DEG C in an oven; third, carrying out laser cladding by adopting a 5KW multifunctional CO2 crossflow laser, wherein the process parameters are that the output power is 1.5-2.5KW, the scanning speed is 6-15mm / s, the light spot diameter is 3mm, and single track cladding and overlapping rate of multi-track cladding is 30-45 percent, and protecting a molten pool with argon gas; and fourth, carrying out leveling and polishing treatment on the surface. In the method, a Cu-Cr alloy layer with good wear resistance and electrical erosion resistance can be obtained on the surface of the pure copper, so that the core part can remain the excellent conductivity of the pure copper.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
NiCrOxNy solar spectrum selective absorbing thin-membrane and preparing method thereof
Selective solar spectrum-absorbing films of NiCrOxNy are produced by magnetic sputtering process on copper substrate. The films have high absorbing rate and low reflecting rate, and strong adhering ability, and can be colored for decoration and be used as functional materials of construction.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Printed wiring board conductive via hole filler having metal oxide reducing capability
InactiveUS6337037B1Low costImprove efficiencyConductive materialPrinted circuit aspectsCopper oxideEngineering
A conductive via filler for printed wiring boards capable of reducing copper oxides and thereby eliminating a cleaning step in printed wiring board construction, the conductive via filler consisting essentially of silver flake, a resin, a hardener, and a titanate coupling compound. The filler or paste may further include one or more of a flexibilizer, a solvent, and / or an accelerator. It is a feature of the invention that extensive pre-cleaning of copper substrates is obviated.
Owner:METHODE ELETRONICS INC
Cantilever-type piezoelectric diaphragm pump
InactiveCN103334907AAdjustable lengthDifferent vibration characteristicsPositive displacement pump componentsFlexible member pumpsDiaphragm pumpEngineering
The invention discloses a cantilever-type piezoelectric diaphragm pump. The cantilever-type piezoelectric diaphragm pump is composed of a vibration excitation unit, a pump cavity body and a flow channel structure. The vibration excitation unit is composed of a pump body, an adjustable pressing mechanism, a piezoelectric vibrator, a vibration transmission piston and a PET diaphragm. The piezoelectric vibrator is composed of a copper substrate and a piezoelectric ceramic piece. Compared with the traditional method of periphery fixing or wave joint supporting of a circular oscillator, the method of cantilever supporting of the rectangular piezoelectric vibrator has the advantages that deflection is large, tail end output amplitude is large, and simple harmonic frequency is low. Meanwhile, the length of a cantilever of the rectangular piezoelectric vibrator is adjustable, and therefore a vibration system has different vibration characteristics so as to meet different requirements for output performance. The adopted PET diaphragm material has the advantages of being good in abrasive resistance, dimensional stability and electrical insulation, nontoxic, impermeable, light in weight and the like, and further has the advantages of being safe and reliable, free of pollution and the like as a pump cavity vibrating diaphragm for conveying chemical and medical liquid. The piezoelectric vibrator is not contacted with the conveyed liquid directly, and therefore the piezoelectric pump can work at high working voltage and is good in output performance.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for processing copper surface, method for forming copper pattern wiring and semiconductor device manufactured using such method
InactiveUS20070187812A1Easy to removeClean copper surfaceNanotechNitrogen-metal/silicon/boron binary compoundsChemical speciesDevice material
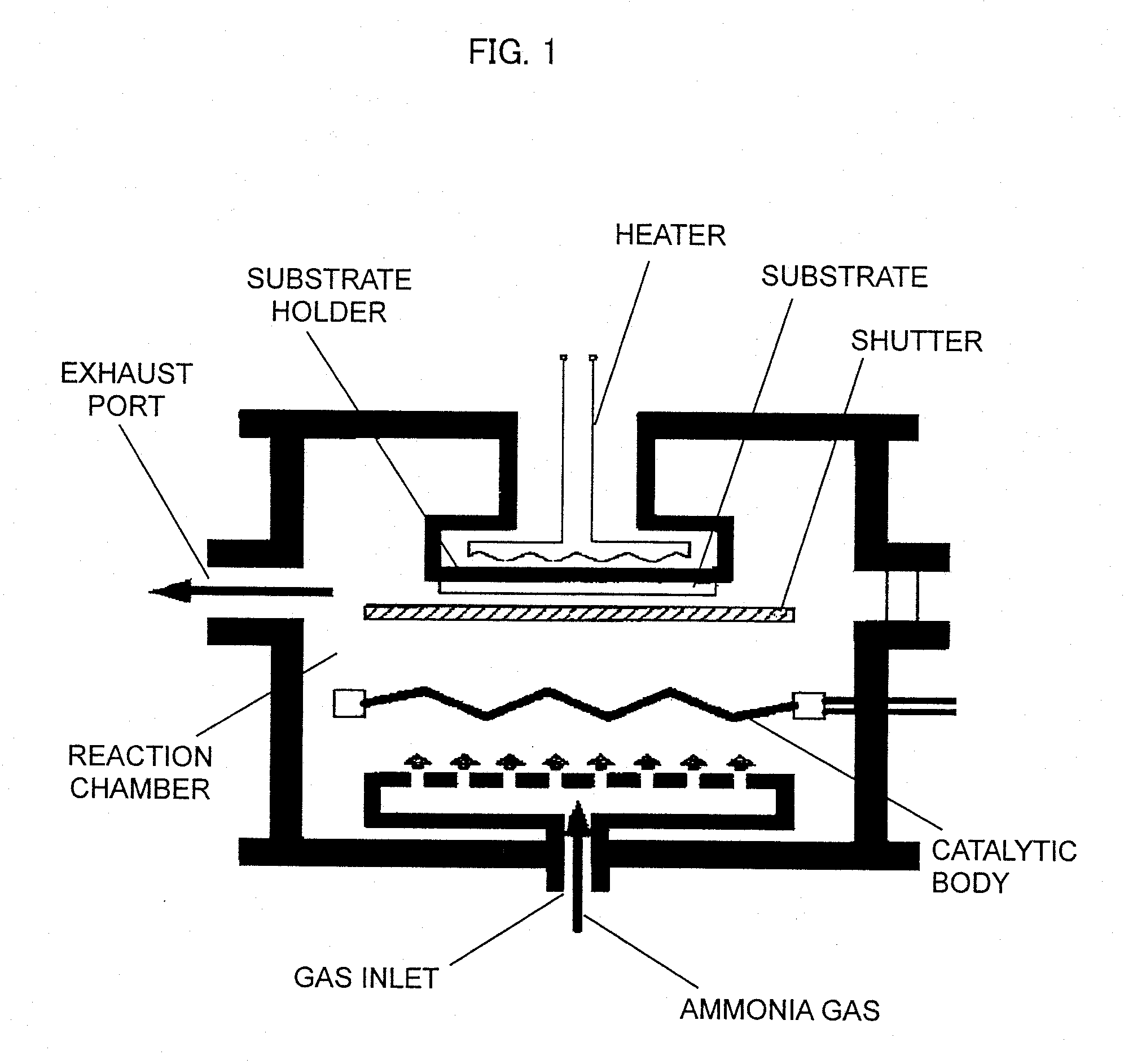
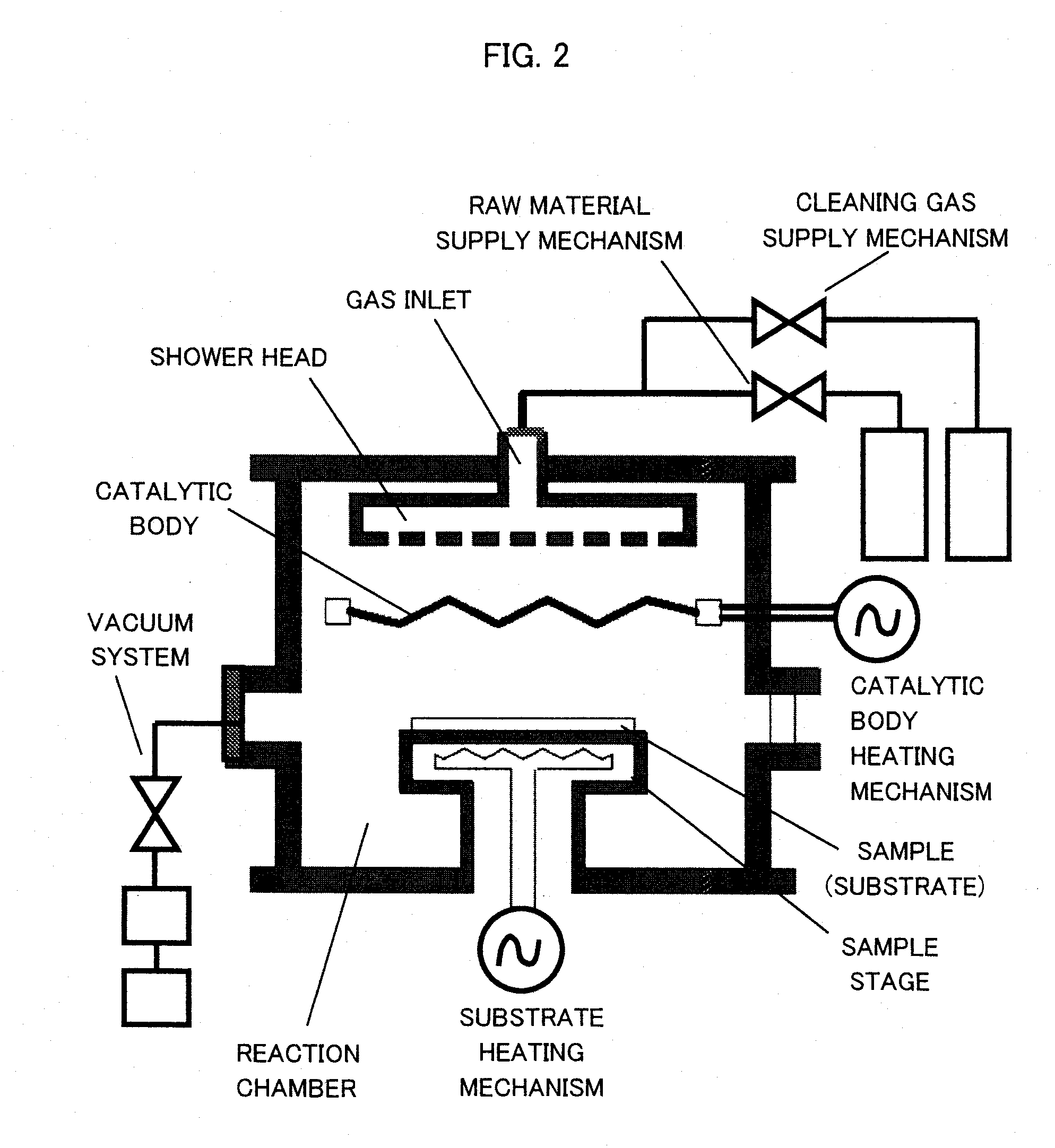
A gas inlet is disposed in a lower portion of a reaction chamber, a copper substrate is disposed in an upper portion thereof, and a tungsten catalytic body heated to 1600° C. is disposed midway between the two. Ammonia gas introduced from the gas inlet is decomposed by the tungsten catalytic body, a chemical species generated by the decomposition reacts with a surface of the copper substrate, and reduces and removes a contaminant on the copper surface, and a Cu3N thin film is formed on the copper substrate surface. This Cu3N film has the action of a film which prevents the oxidation of copper. This Cu3N film is thermally decomposed and removed when heated to temperatures of not less than 300° C., leaving a clean copper surface behind.
Owner:INVENSAS CORP
Method for manufacturing ceramic filled polytetrafluoroethylene glass fiber copper-clad substrate
InactiveCN102555349AHigh peel strengthGood electrical conductivityGlass/slag layered productsMetal layered productsFiberGlass fiber
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a ceramic filled polytetrafluoroethylene glass fiber copper-clad substrate. The method sequentially comprises the following processes of: 1) preparing a polytetrafluoroethylene solution; 2) stirring the prepared polytetrafluoroethylene solution, ceramic powder and a dispersing agent with high-speed stirring equipment to form a solvent; 3) immersing a glass fiber fabric in the solvent to form an impregnated fabric; and 4) sequentially paving a pure polytetrafluoroethylene thin film and the impregnated fabric between copper foil layers, wherein the copper foil layers are connected with the pure polytetrafluoroethylene thin film. According to the method, the ceramic powder, the polytetrafluoroethylene solution and the dispersing agent are mixed and blended together to form common excellent waveguide medium substrates with low dielectric loss and different dielectric constants. The high conductivity of copper foils can be greatly improved through the ceramic filled copper-clad substrate, the copper-clad substrate also has high heat conductivity, and the stripping strength of the substrate can be greatly improved.
Owner:珠海国能复合材料科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com