Method for regulating volatile oil content of plant by using MicroRNA156 and its target gene
A technology of plant volatile oil and transgenic plants, which is applied in the fields of biotechnology and botany, and can solve the problems of few studies on the transcriptional regulation of volatile oil
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0097] Example 1, Isolation of Arabidopsis miR156 and SPL10 Genes
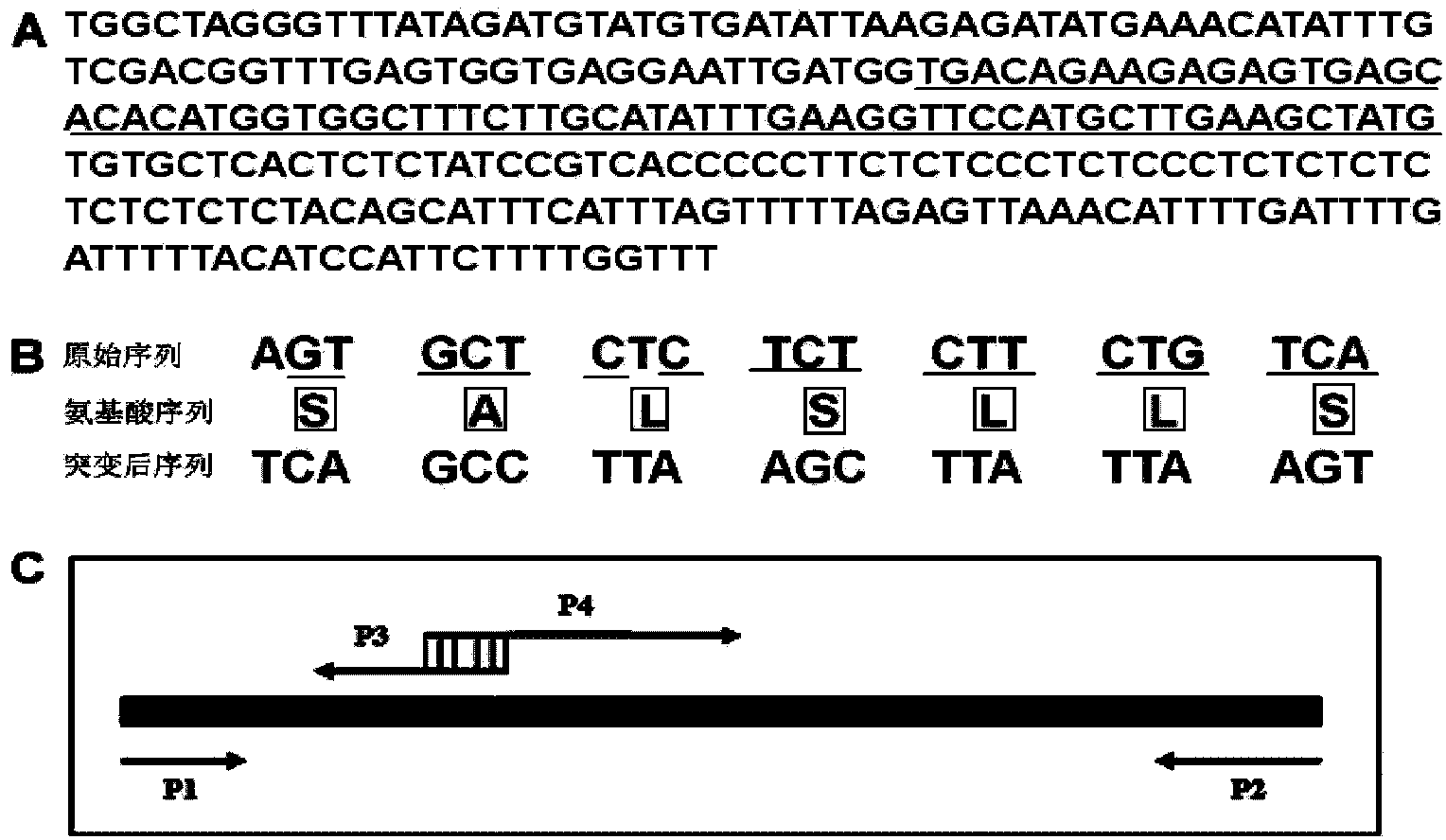
[0098] According to the genome sequence information of AT5G26147 (miR156f) on the Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR) website, the sequence is (SEQ ID NO: 1): TGGCTAGGGTTTATAGATGTATGTGTATTAAGAGATATGAAACATATTTGTCGACGGTTTGAGTGGTGAGGAATTGATGG TGACAGAAGAGAGTGAG CACACATGGTGGCTTTCTTGCATATTTGAAGGTTCCATGCTTGAAGCTAT GTGTGCTCACTCTCTATCCGTCA CCCCCTTCTCCCCTCTCCCTTCTCTCTCTCTCTCTACAAGCATTTCATTTAGTTTTTAGAGTTAAAACATTTTGATTTTGATTTTTACATCCATTCTTTTGGTTT.
[0099] The primers miR156-F-BamHI and miR156-R-SacI were synthesized, and the Arabidopsis miR156f genome partial sequence was amplified by PCR ( figure 1 A); According to the sequence information of AT1G27370 (SPL10), primers SPL10-F and SPL10-R were synthesized, and the sequence of SPL10 encoding Arabidopsis SQUMOSA PROMOTER BINDING PROTEIN LIKE gene was obtained by PCR amplification. The PCR amplified fragments of miR156f and SPL10 were TA cloned into the pMD18-T v...
Embodiment 2
[0103] The binary vector construction of embodiment 2, miR156f and SPL10 gene
[0104] Firstly, the CaMV35S promoter was amplified with a high-fidelity enzyme, HindIII / PstI sites were introduced at both ends, and then ligated into the corresponding sites of pCAMBIA2301 (Cambia Company) by enzyme digestion to construct pCAMBIA2301-35S. Then the gene fragment of miR156f in the sequenced pMD18-T vector was digested with BamHI and SacI, and then introduced between the multiple cloning sites BamHI and SacI of pCAMBIA2301-35S, thereby obtaining the Pro35S:MIR156f binary vector.
[0105] The miR156 cleavage sequence in SPL10 was mutated (without changing the encoded amino acid species) by two rounds of PCR to form rSPL10 resistant to miR156 cleavage ( figure 1 B and C): The first round of PCR uses high-fidelity enzymes to amplify the fragments on both sides of the mutation site, using the gene fragment of SPL10 in the pMD18-T vector as a template, and the primers are SPL10-F and SPL1...
Embodiment 3
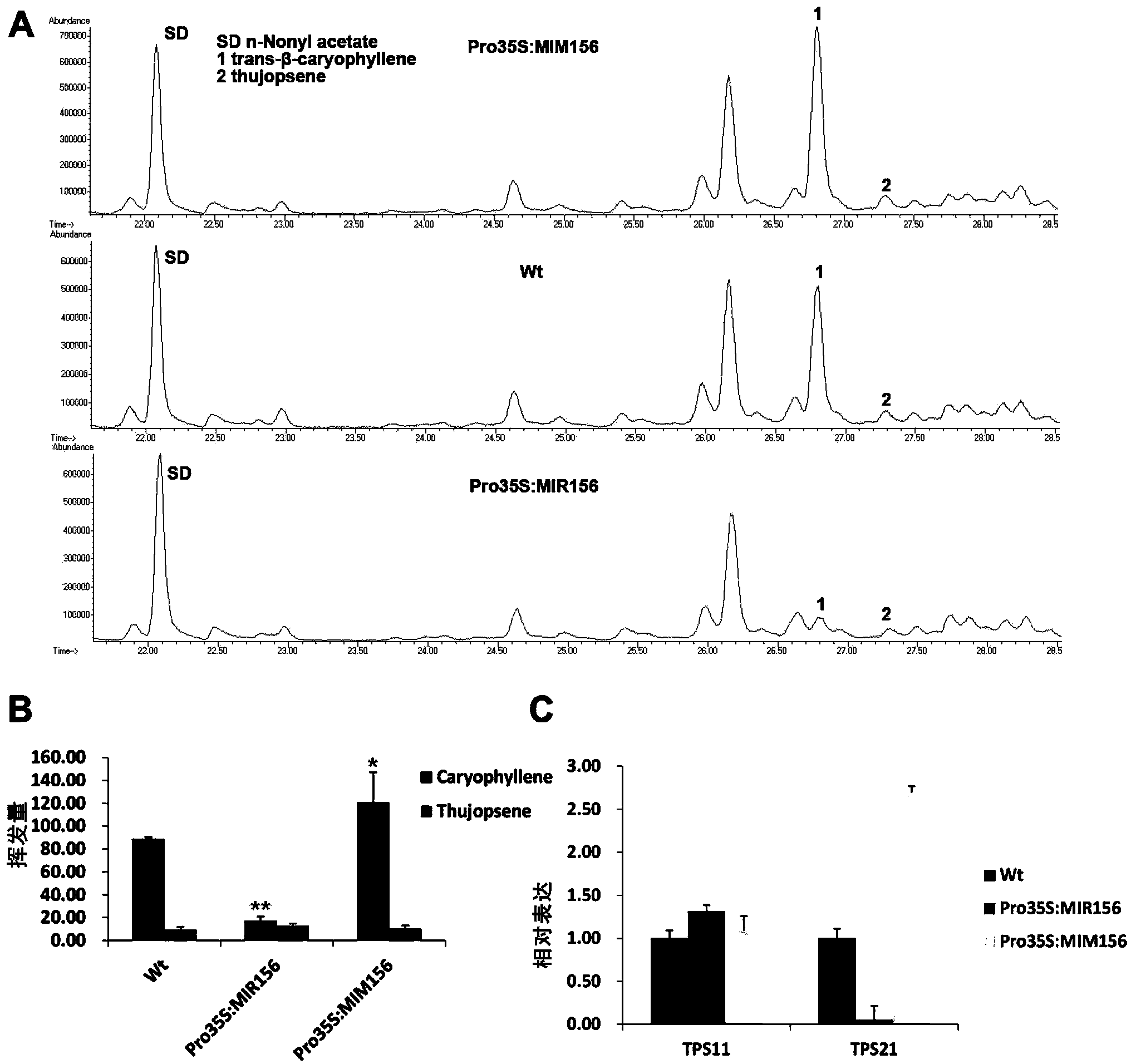
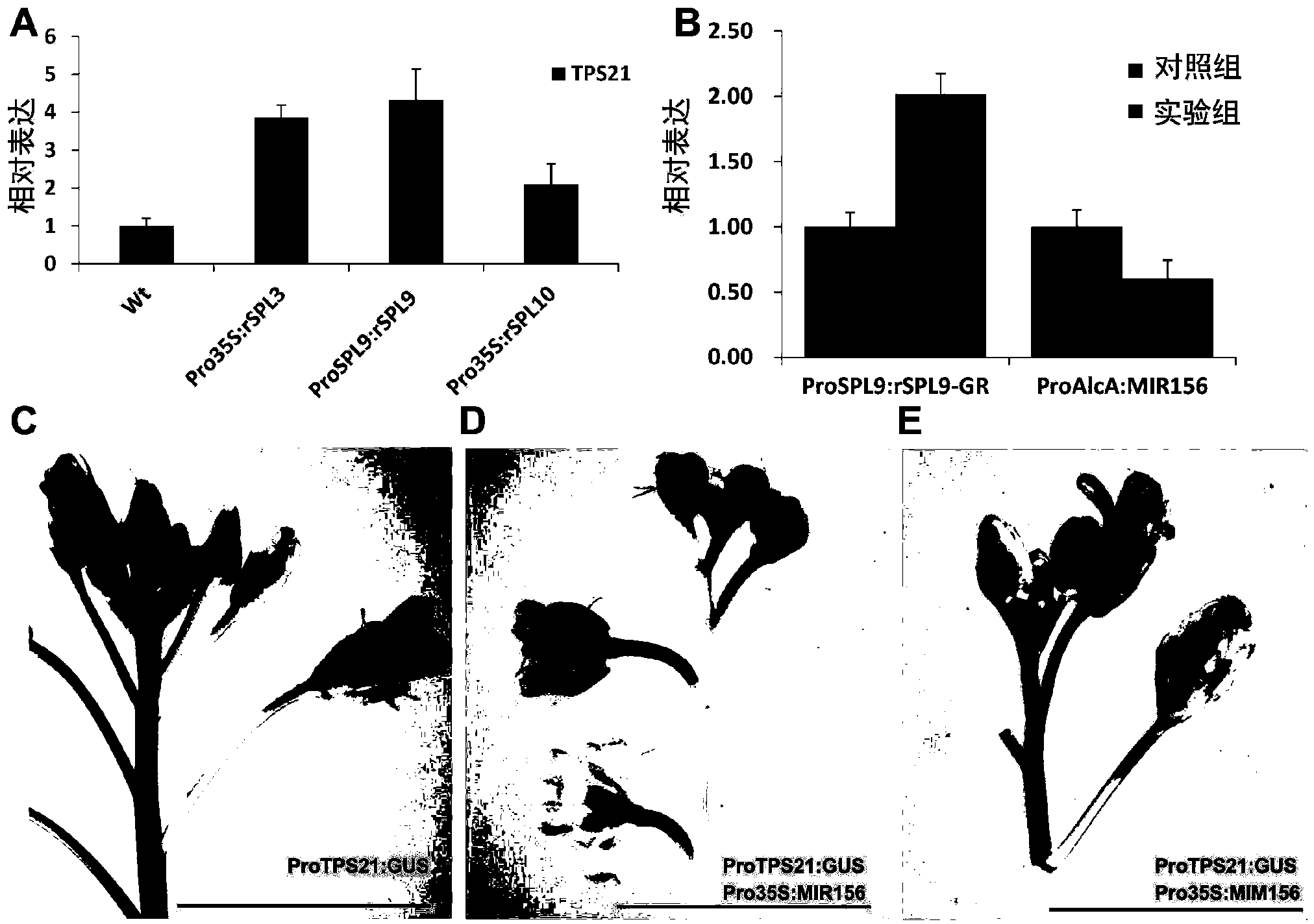
[0113] Example 3, miR156 regulates the synthesis of sesquiterpene in Arabidopsis inflorescence
[0114] Arabidopsis inflorescences release volatile substances, 60% of which are monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes, and sesquiterpenes account for 95% of the volatile terpenes in inflorescences. The synthesis of many terpenoids has time-space specificity. Since miR156 plays an important role in plant growth and development and time-phase transition, the inventors first analyzed the expression of miR156 (Pro35S:MIR156f) by GC-MS (gas chromatography-mass spectrum). ) and simulated miR156 (Pro35S:MIM156) volatile sesquiterpene content in inflorescences.
[0115] Take about 100 inflorescences of Arabidopsis thaliana about 5 weeks old, put them into the micro-pool thermal extraction instrument μ-CTE (pre-balanced temperature and carrier gas) of Markes, UK, and insert the sample collection adsorption tube (Tenax TA, C-T9TNX-2S ), at 42°C, the helium flow rate was 50ml / min, and the extracti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com