Zinc ferrite-loaded carbon nano tube catalyst prepared by microwave-hydrothermal method and application of catalyst in degrading organic pollutants in water
A microwave hydrothermal method, a technology of organic pollutants, applied in physical/chemical process catalysts, metal/metal oxide/metal hydroxide catalysts, chemical/physical processes, etc., can solve the problem of low bisphenol A concentration and high cost , difficult to degrade and other problems, to achieve the effect of enhanced absorbing performance, fast preparation speed and fast degradation speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] Example 1 Zinc ferrite supported carbon nanotube catalyst
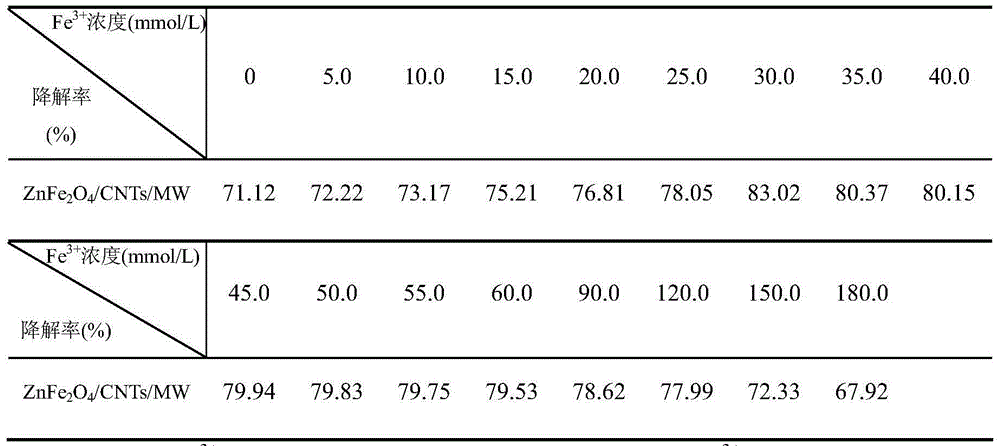
[0018] (1) Fe 3+ The effect of the concentration on the degradation rate
[0019] 1. Preparation method
[0020] Pretreatment of carbon nanotubes: adding carbon nanotubes (particle size 10-20nm) into nitric acid, boiling for 30min, cooling to room temperature, washing the suspension with deionized water to neutrality, filtering, and the obtained carbon nanotube particles in Dry in a constant temperature drying oven at 105°C for 5-7 hours, cool, grind, and pass through a 100-mesh sieve;
[0021] Preparation of zinc ferrite-supported carbon nanotube catalyst (ZnFe 2 o 4 / CNTs) Catalyst: Weigh FeCl respectively as in Table 1 3 Make Fe 3+ The concentration is 0.03~0.18mol / L, according to Fe 3+ with Zn 2+ The molar ratio is 2:1, weigh ZnCl 2 The solids were then dissolved together in 15.0 mL of deionized water to obtain a solution, and then 0.5 g of pretreated carbon nanotubes (CNTs, 10-20 nm) were added in...
Embodiment 2
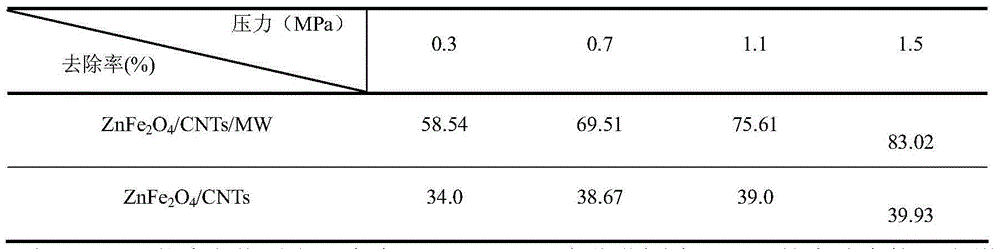
[0049] Example 2 Application of Zinc Ferrite Supported Carbon Nanotube Catalyst in Degradation of Organic Pollutants
[0050] (1) Preparation of Zinc Ferrite Supported Carbon Nanotube Catalyst
[0051] Pretreatment of carbon nanotubes: adding carbon nanotubes (particle size 10-20nm) into nitric acid, boiling for 30min, cooling to room temperature, washing the suspension with deionized water to neutrality, filtering, and the obtained carbon nanotube particles in Dry in a constant temperature drying oven at 105°C for 5-7 hours, cool, grind, and pass through a 100-mesh sieve;
[0052] Preparation of zinc ferrite-supported carbon nanotube catalyst (ZnFe 2 o 4 / CNT s ) Catalyst: according to Fe in the mixed solution 3+ Concentration is 0.03mol / L, Fe 3+ with Zn 2+ The molar ratio of FeCl is 2:1, and FeCl 3 and ZnCl 2 Dissolve in 15.0 mL of deionized water, then add 0.5 g of pretreated carbon nanotubes (CNTs, 10-20 nm) into the mixture, and ultrasonicate for 1.0 min. Stir, a...
Embodiment 3
[0080] Example 3 Degradation of different organic pollutants by zinc ferrite-supported carbon nanotube catalysts
[0081] (1) Preparation of zinc ferrite supported carbon nanotube catalyst: same as Example 2
[0082] (2) Microwave degradation
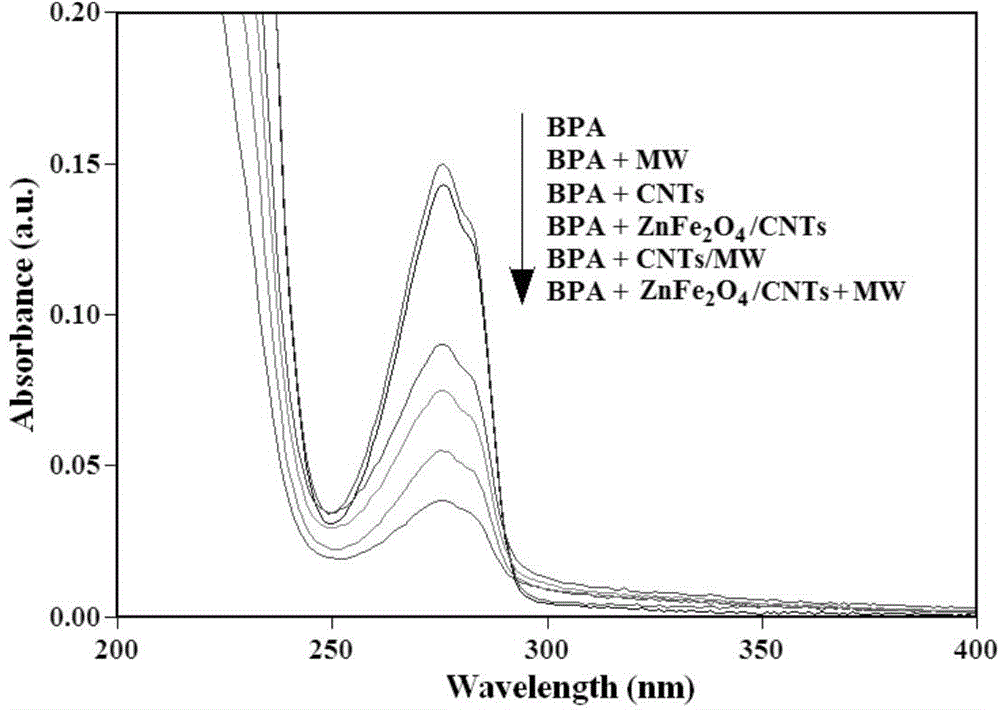
[0083] Measure 25.0mL of 10.0mg / L solution containing different organic pollutants into the reactor, add 0.02g of zinc ferrite-supported carbon nanotube catalyst, put it in a microwave oven (750W) for 0-5.5min, cool to room temperature, filter, Its UV-vis spectrum was measured at 200-800 nm. Calculate the degradation rate. The results are shown in Table 10.
[0084] Table 10 ZnFe 2 o 4 Comparison of Degradation Performance of Different Organic Pollutants by / CNTs / MW
[0085]
[0086] Table 10 compares the degradation of five organic pollutants with different compositions and molecular structures in the system. It can be seen that ZnFe 2 o 4 In the / CNTs / MW system, the degradation rate of organic pollutants increased with the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com