Method for treating lignite upgrading wastewater by anaerobic co-metabolism
A co-metabolism and wastewater technology, which is applied in anaerobic digestion treatment, mining wastewater treatment, water treatment parameter control, etc., can solve the problems of unstable operation, low microbial biomass, difficulty in starting, etc., and achieves improved biodegradability and improved treatment. Efficiency, the effect of shortening the start-up time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
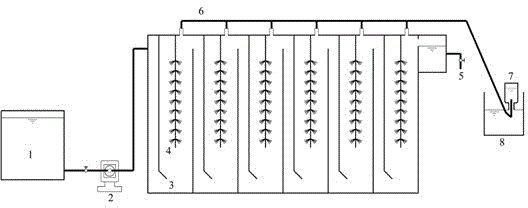
[0009] Specific implementation mode one: this implementation mode is the method for anaerobic co-metabolism treatment of lignite upgrading wastewater, which is specifically completed according to the following steps:
[0010] ① Select lignite upgrading wastewater, which is collected from the lignite upgrading process and then treated by cooling and sedimentation in the intermediate sedimentation tank. The water quality is as follows: COD concentration 2800~3300mg / L, BOD 5 The concentration is 500~600mg / L, the total phenol concentration is 90~110mg / L, the ammonia nitrogen concentration is 70~90mg / L, the total phosphorus concentration is 9~13mg / L, and the cyanide concentration is 0.75~1.25mg / L.
[0011] ②Choose trehalose as the first substrate of co-metabolism, and use it as carbon source to prepare wastewater to start anaerobic reaction. Wastewater preparation method: trehalose is the carbon source, ammonium chloride is the nitrogen source, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate is the...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0019] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that in step ③, the dosage of the initial inoculated sludge in the anaerobic reactor is 9g / L, and the others are the same as Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0020] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that in step ②, the ratio of the total amount of COD added by trehalose to the total amount of COD in the lignite upgrading wastewater to be treated every day is controlled to be 0.8 or 1.0 , and the others are the same as those in Embodiments 1 to 3.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com