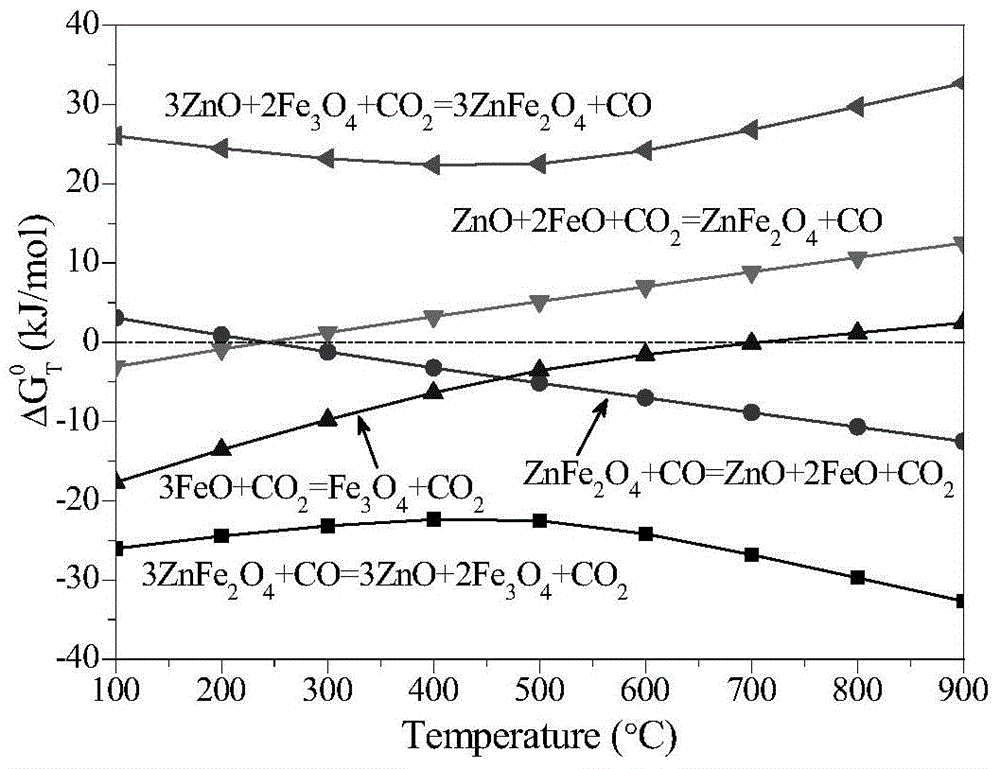
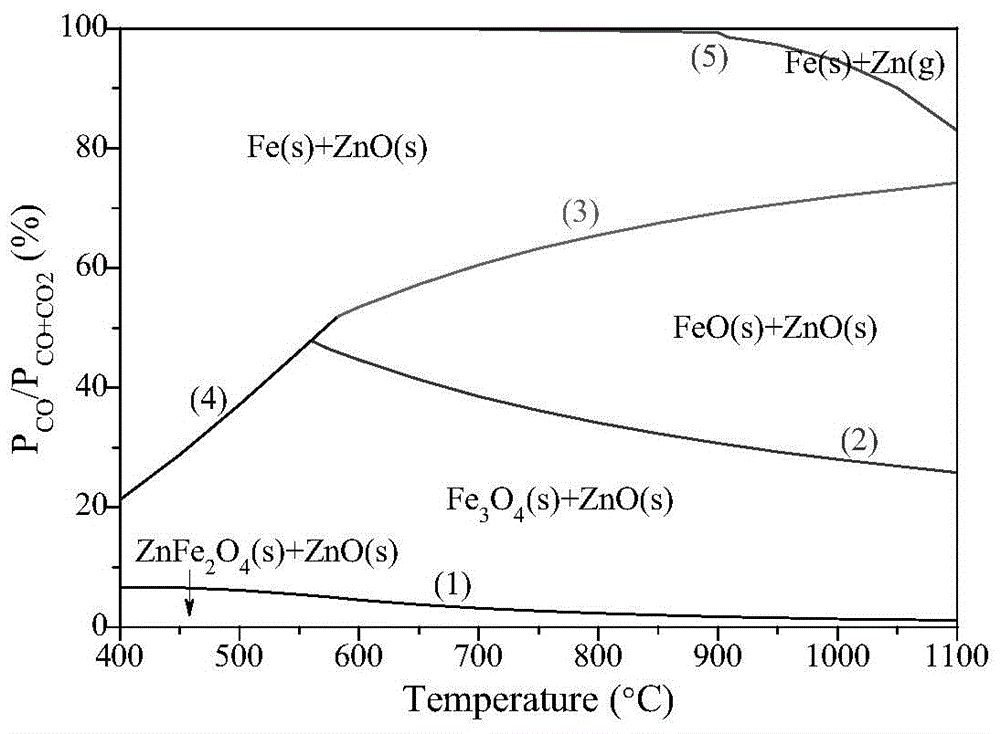
Method for intensifying selective decomposition of zinc ferrite
A selective, zinc ferrite technology, applied in the fields of mineral processing and metallurgical engineering, can solve problems such as inability to guarantee at the same time, high decomposition rate, etc., and achieve the effect of mild conditions, wide temperature range, and favorable industrial production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Zinc calcine with higher zinc ferrite content is used as raw material, the zinc content of the zinc calcine is 57.4%, the iron content is 13.3%, and the iron content in the zinc ferrite accounts for 82.5% of the total iron content. Grind the zinc calcine to be below -75μm, dry it, put it into a small closed rotary kiln in the laboratory, raise the temperature to about 800°C under the condition of nitrogen protection, then stop feeding nitrogen, and feed CO and CO at the same time 2 and mixed gas, so that the total gas flow is controlled at about 1.25L / min, P CO / P (CO+CO2) Control it at about 40%, after reduction roasting for 1.5h, stop heating, lower the temperature in the roasting furnace to about 550°C, keep the temperature constant, and then adjust the roasting atmosphere to ensure the P of the atmosphere. CO / P( CO + CO2 ) is controlled within 5%, after magnetization roasting for 1h, turn off the heating furnace, stop feeding CO and CO 2 Gas, naturally cooled t...
Embodiment 2
[0036] The test uses the zinc leaching slag produced in the conventional hydrometallurgy process as the raw material. The leaching slag has a zinc content of 19.6%, an iron content of 23.9%, and is mainly composed of zinc ferrite. Grind the zinc leaching slag to be below -75μm, dry it, put it into a small closed rotary kiln in the laboratory, raise the temperature to about 750°C under the condition of nitrogen protection, then stop feeding nitrogen, and feed CO and CO at the same time 2 and mixed gas, so that the total gas flow is controlled at about 1.25L / min, P CO / P (CO+CO2) Control it at about 45%. After reduction roasting for 75 minutes, stop heating, lower the temperature in the roasting furnace to about 550°C, keep the temperature constant, and then adjust the roasting atmosphere to ensure the P of the atmosphere. CO / P( CO + CO2 ) within 5%, after 30 minutes of magnetization roasting, turn off the heating furnace, and stop feeding CO and CO 2 The gas was naturally ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com