Three-dimensional digital imaging method based on generalized S transformation
A technology of three-dimensional digital and imaging methods, which is applied in the fields of electrical digital data processing, image analysis, image data processing, etc., and can solve the problems of poor adaptability of objects, inability to accurately locate fundamental frequency components, and low phase resolution accuracy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
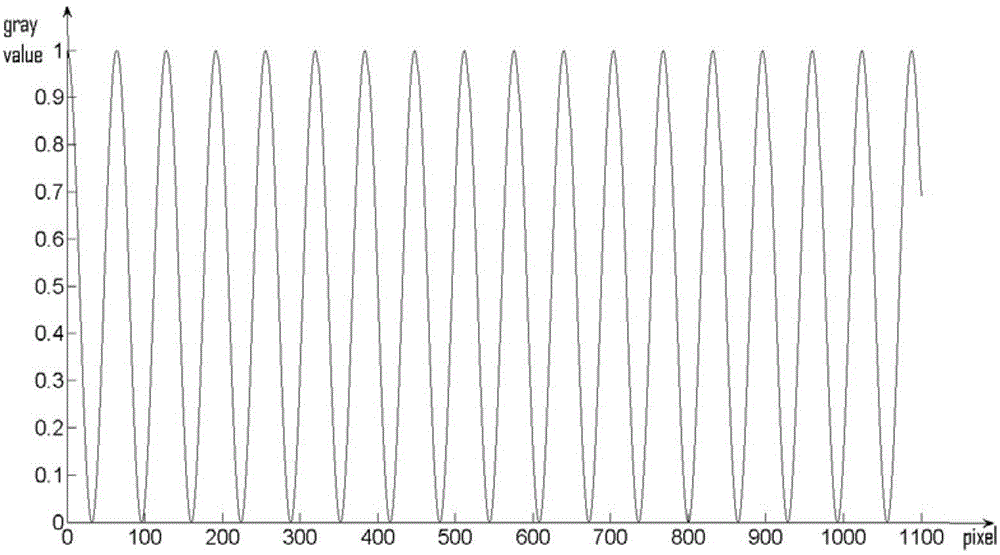
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0088] This embodiment describes the three-dimensional digital imaging device matched with the method of the present invention.
[0089] The three-dimensional digital imaging device matched with the method of the present invention mainly includes a digital projection lighting transmitter, an image sensing receiver and an image processor. Among them, the digital projection lighting transmitter can be a digital liquid crystal projection device (LCD projector), a digital micromirror projection device (DMD projector) or a silicon substrate liquid crystal projection device (LCOS projector), which can be easily generated by a computer image processing system. Grayscale fringe pattern and write to digital projection device. The image sensing receiver includes an optical imaging lens and a photodetector. The optical imaging lens can be an imaging lens or lens group with a fixed focal length or a variable focal length, a binary optical imaging system, a diffraction element imaging syst...
Embodiment 2
[0092] This embodiment illustrates the process of optimizing the energy intensity of a series of S-transform matrices obtained by using the generalized S-transform for each row of the gray-scale fringe image in the present invention.
[0093] The process of energy intensity optimization of the present invention is:
[0094] For the original grayscale fringe image g 1 (x, y) and deformed grayscale fringe image g 2 (x, y) series of S transformation matrices for each row and The energy intensity threshold of the "ridge" is set to optimize the energy intensity of the S-transform matrix to ensure that its energy intensity is sufficient for three-dimensional digital imaging when searching for the best S-transform matrix based on the principle of energy concentration. That is to set a unified energy intensity threshold E, when a certain S transformation matrix S p(b, f) When the ratio of the minimum value of the energy intensity on the "ridge" to the maximum value of the energy...
Embodiment 3
[0099] This embodiment illustrates the principle of energy concentration used when the generalized S-transform is used to piece together the optimal S-transform matrix for each row of the gray-scale fringe image in the present invention.
[0100] The process that the energy concentration principle that the present invention adopts puts together is:
[0101] First, each S transformation matrix S in a series of S transformation matrices optimized for energy intensity for each row of the grayscale fringe image p (b, f) by frequency point f jj Calculate the energy concentration corresponding to that row. Some S transformation matrix S p (b, f) at a certain frequency point f jj The energy concentration at that line is defined as:
[0102] CM ( f jj , p ) = 1 ∫ - ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com