Corn tissue specificity promoter and applications thereof
A tissue-specific, promoter-based technology, applied in applications, recombinant DNA technology, angiosperms/flowering plants, etc., can solve problems such as unfavorable plant growth, breaking plant metabolic balance, excessive consumption of cell matter and energy, and achieve improved plant traits, quality improvement effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
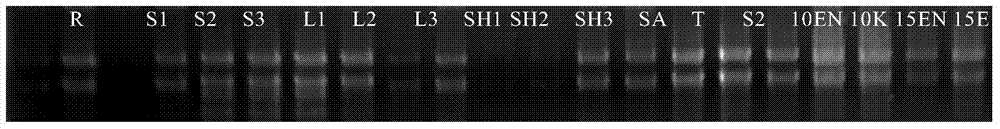
[0065] Example 1 Cloning and sequence analysis of maize tissue-specific promoter
[0066] 1. Using gene chip data to screen promoters that drive specific expression genes in maize seeds
[0067] Preparation of gene chip materials: take the roots, leaves, stems and interstems of maize B73 at the trumpet stage, mature but unpollinated young ears and filaments, embryos and A total of 14 samples, including endosperm, were set up with 3 replicates for each sample type, and the gene expression profiles of 42 samples were analyzed using a gene chip (Maize GenomeArray from Affymetrix).
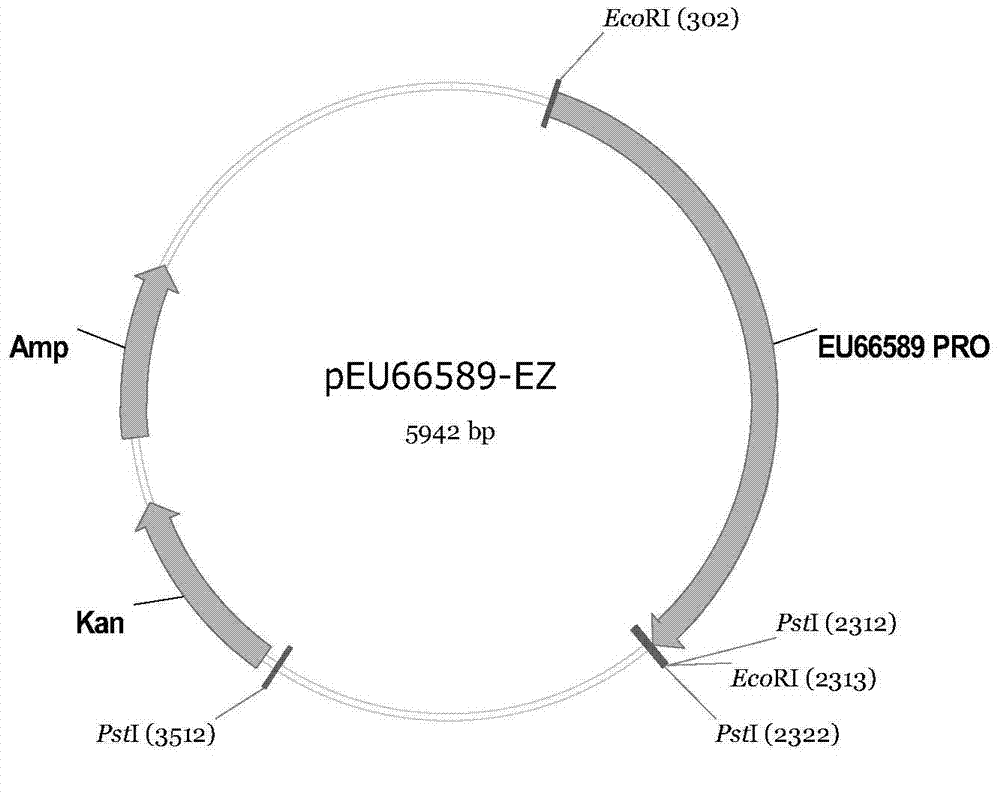
[0068] Bioinformatics analysis: Bioinformatics methods were used to analyze the data of 42 samples, and a gene Zm66589 (the promoter sequence of the gene is shown in SEQ ID NO.1) was found to be specific in the middle and late stages of embryonic development. a large number of expressions.
[0069] Table 1 Analysis of gene expression (its promoter sequence is SEQ ID NO.1) in different tissues by gen...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap