Fully bio-absorbable polymer stent and production method thereof
A vascular stent and polymer technology, applied in the field of fully bioabsorbable polymer vascular stents, can solve the problems of poor mechanical properties, slow degradation speed, high crystallinity, etc., and achieve small residual processing stress, fast degradation speed, and good toughness Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
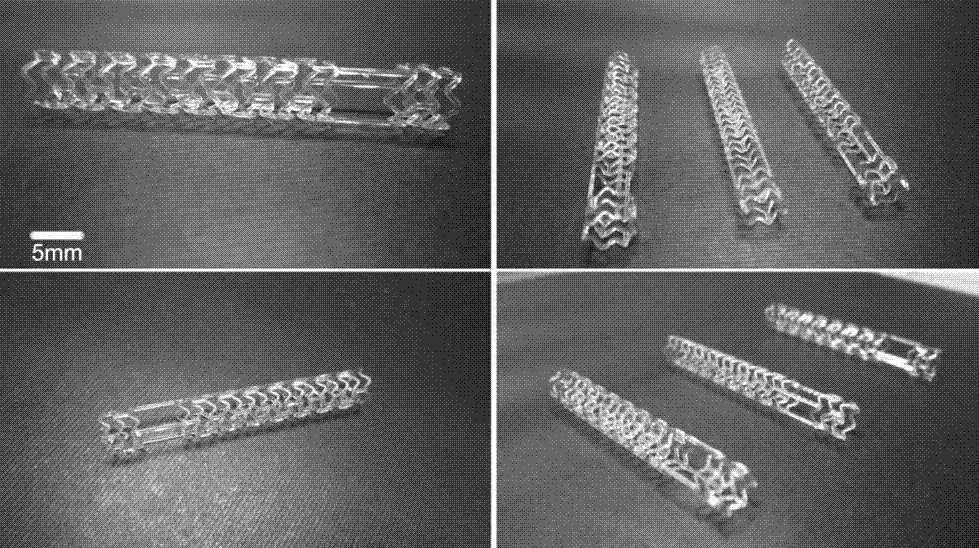
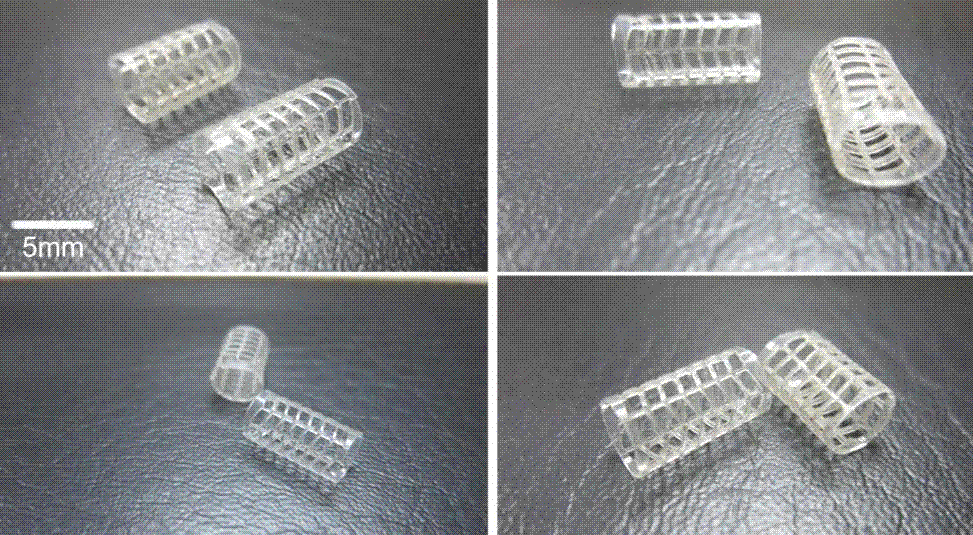
[0031] (1) The molar ratio of LLA / TMC / GA three monomers is 94.7 / 5.3 / 5.1, and the number average molecular weight is 1.53?10 5 g / mol, PLLA-TMC-GA terpolymer with a dispersion coefficient of 2.1, prepared by 3D printing as figure 1 For the fishbone-shaped vascular stent shown, the 3D printing molding layer thickness is 0.02mm, the molding accuracy is 0.02mm, the temperature of the printing head is 170°C, and the temperature of the 3D printing plate is 50°C.
[0032] (2) The radial support force of the vascular stent measured by a universal tensile testing machine is 1.8 bars.
[0033] (3) Put the scaffold in PBS buffer for a week, and observe that there are no obvious microcracks on the surface of the scaffold, indicating that there is no obvious processing residual stress.
[0034] (4) The bending strength of the bracket measured by the 3-point bending method is 93Kpa.
Embodiment 2
[0036] The number average molecular weight is 1.48?10 5 g / mol, the PLLA homopolymer with a dispersion coefficient of 1.7 was printed through the step (1) of Example 1 to obtain a fishbone-shaped vascular stent. The radial support force of the stent is 2.0bars. After soaking in PBS buffer solution for one week, a large number of cracks appear on the surface of the stent, and the bending strength measured by 3-point bending is 32Kpa.
[0037] By comparing the above two embodiments, it is found that the vascular stent of the present invention enhances the toughness of the vascular stent while maintaining a high strength, greatly improves the bending strength of the vascular stent, and the enhancement of toughness also makes the residual stress after processing also decreased significantly.
[0038] In order to better compare the difference in degradation performance between the vascular stent of the present invention and the PLLA-type vascular stent on the market, the following co...
Embodiment 3
[0040] The molar ratio of LLA / TMC / GA three monomers is 94.7 / 5.3 / 5.1, and the number average molecular weight is 1.53?10 5 g / mol, the PLLA-TMC-GA terpolymer with a dispersion coefficient of 2.1 was printed through the step (1) of Example 1 to prepare a fishbone-shaped vascular stent.
[0041] Put the scaffold into PBS buffer solution with pH=7.4 for in vitro degradation. After 6 months of degradation, the sample was taken out from the degradation solution, and then dried in a vacuum oven for one week to constant weight. The molecular weight after 6 months of degradation was measured by GPC to be 21% of the original molecular weight.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flexural strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flexural strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com