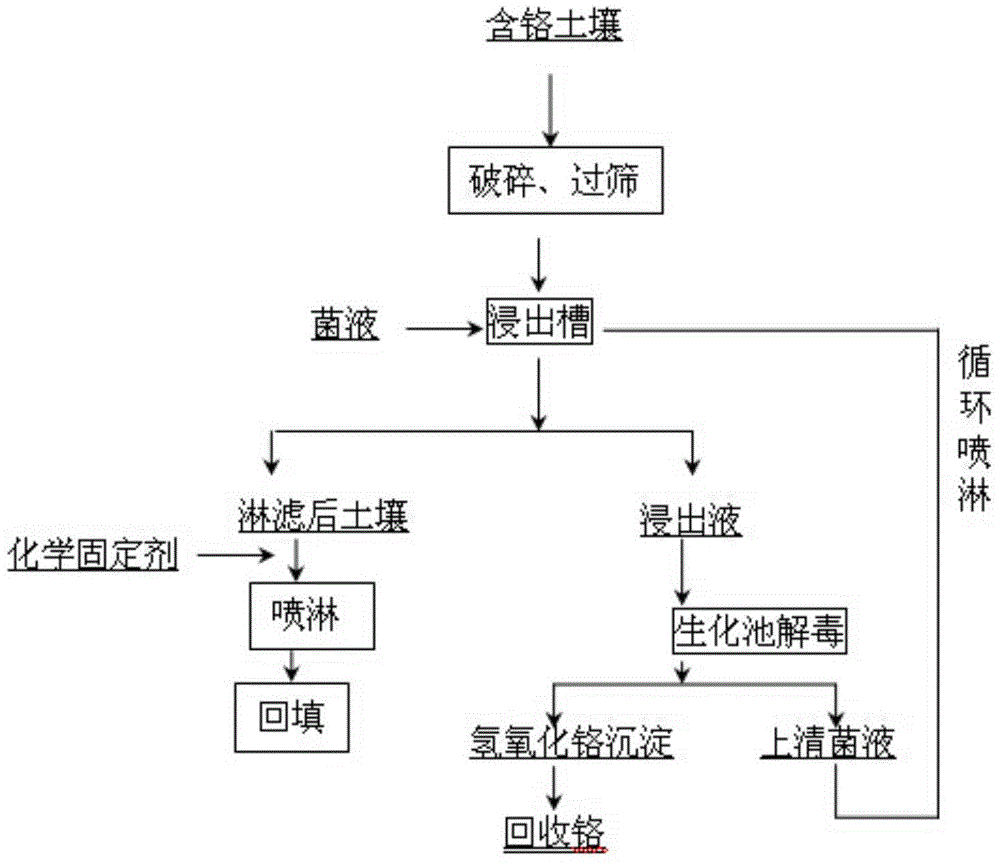
Microbial leaching and chemical fixing joint repairing method for heavily polluted soil of chromium slag yard
A soil microorganism and chromium slag storage yard technology, which is applied in the field of remediation of contaminated soil in chromium slag storage yard, can solve the problem of unstable microbial Cr(VI) reduction efficiency, harsh soil conditions for electrodynamic remediation, and chromium slag storage yard pollution, etc. It can reduce the acid-base adjustment process, solve the problems of treatment and discharge, and solve the environmental risk problem.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
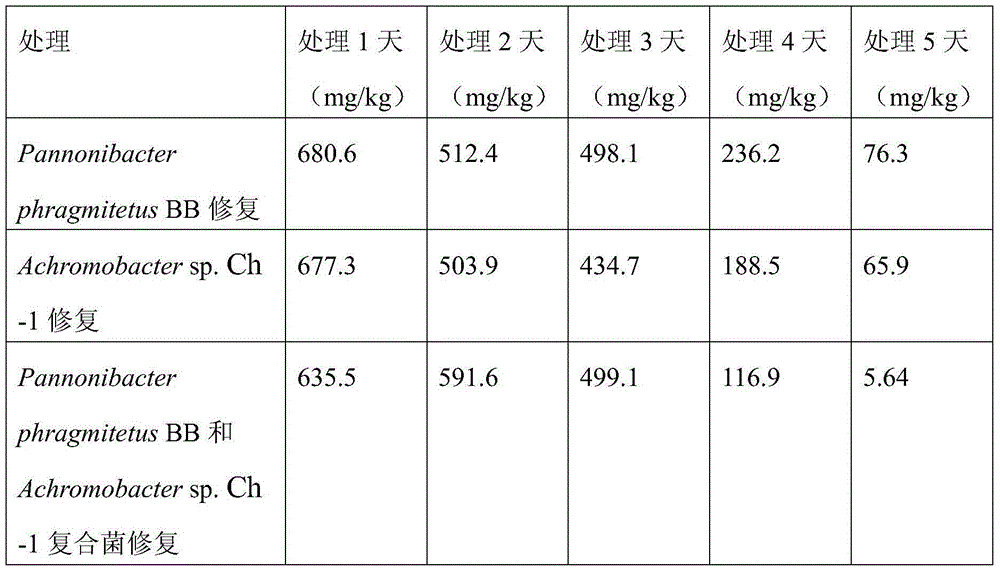
[0030] Example 1: Small-scale test effect of single strain and composite strain on the restoration of a chromium salt factory muck mixture in Changsha
[0031] At present, the pollution of chromium slag stockpiles in my country is complicated, and some single strains may have a good treatment effect on pure chromium-contaminated soil, but the treatment effect on chromium-contaminated slag-soil mixture is not so ideal, because chromium slag contains a part of acid-soluble For hexavalent chromium, the bacterial strain used for the remediation of chromium-contaminated soil is not necessarily suitable for the remediation of chromium slag, which is the case for the bacterial strain of the present invention. Moreover, the coexistence of dregs and soils is common in the upper soil of the dregs field, which leads to difficulties in treatment, and it is difficult for a single strain to meet the restoration requirements. Therefore, the present invention compares the remediation effects of...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Example 2: Remediation effect of high-concentration Cr(VI) contaminated slag from a chromium salt factory in Changsha, Hunan
[0037] Pick a single colony of Pannonibacter phragmitetus BB and Achromobacter sp.Ch-1 and inoculate it in a sterilized medium (3g yeast extract, 5g glucose, 3g sodium chloride, adjust pH=9.0-10.0 with 5mol / L NaOH; add water to 1L) Cultivate for 3 days to obtain a composite bacterial solution; inoculate 5% of the inoculum into a newly prepared non-sterile medium with 300mg / LCr(VI) added (pH value is 9.0-10.0), and culture at 28-32°C Until Cr(VI) is completely reduced, that is, culture until no hexavalent chromium is detected in the culture medium, and the concentration of bacteria is 3-5×10 9 CFU / mL. Then use the bacterial solution to continue to expand the culture in the same manner.
[0038] The former Changsha Chromium Salt Factory muck mixture is passed through a jaw crusher and a 1cm vibrating sieve, and the dregs are transferred into a 1...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Example 3 Remediation effect of slag contaminated by concentration Cr(VI) in a chromium salt factory in Changsha, Hunan
[0042] According to the same method as in Example 1, 25 tons of slag polluted by concentration Cr(VI) in a smelting waste slag yard of a certain chromium salt factory in Changsha was repaired.
[0043] After microbial spray repair, the contents of total chromium, water-soluble Cr(VI) and leached toxic Cr(VI) in the muck were reduced from 5533.5 mg / kg, 317.0 mg / kg and 34.5 mg / L to 3860.8 mg / L, respectively. kg, 27.4mg / kg and 3.7mg / L; after further chemical fixation with hydrazine hydrate, the leaching toxicity concentrations of water-soluble Cr(VI) and Cr(VI) in the slag soil were reduced to 1.74mg / kg and 0.35mg / L, respectively.
[0044] Table 2 Remediation effect of medium concentration Cr(VI) contaminated muck
[0045] Total Chromium (mg / kg) Water-soluble Cr(VI)(mg / kg) Leaching toxicity (mg / L) Raw muck 5533.5 317.0 34.5 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com