Method for recovering gallium from waste gallium nitride-based LEDs
A light-emitting diode, gallium nitride-based technology, applied in the fields of optics, improvement of process efficiency, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as environmental pollution and waste of resources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
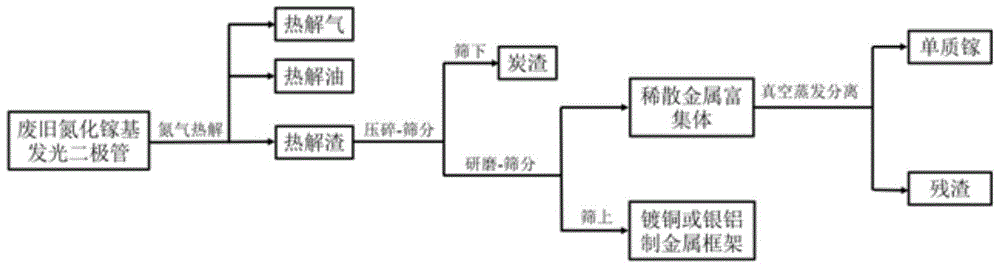
[0035]Firstly, waste GaN-based light-emitting diodes were subjected to nitrogen pyrolysis, the final pyrolysis temperature was 400° C., and the pyrolysis time was 60 minutes. After the pyrolysis is over, the pyrolysis gas, pyrolysis oil and pyrolysis residue are collected respectively, and the pyrolysis gas and pyrolysis oil are recycled for other purposes. After the pyrolysis slag is crushed, the particle size of the charcoal residue is 0.7-1.0mm, and it is sieved through a 18-mesh sieve, and the charcoal residue is recovered under the sieve. The sieved material is ground and then sieved through a 40-mesh sieve. The copper or silver-plated aluminum metal frame is recovered on the sieve, and the light-emitting diode chip enrichment body is formed under the sieve. Put the chip enriched body into the crucible, and then put the crucible into the vacuum furnace. After the vacuum furnace is sealed, start the vacuum system to pump air, so that the vacuum degree of the vacuum furnac...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Firstly, waste gallium nitride-based light-emitting diodes were subjected to nitrogen pyrolysis, the pyrolysis final temperature was 500° C., and the pyrolysis time was 30 minutes. After the pyrolysis is over, the pyrolysis gas, pyrolysis oil and pyrolysis residue are collected respectively, and the pyrolysis gas and pyrolysis oil are recycled for other purposes. After the pyrolysis slag is crushed, the particle size of the charcoal residue is 0.5-0.8mm, and it is sieved through an 18-mesh sieve, and the charcoal residue is recovered under the sieve. The sieved material is ground and then sieved through a 40-mesh sieve. The copper or silver-plated aluminum metal frame is recovered on the sieve, and the light-emitting diode chip enrichment body is formed under the sieve. Put the chip enriched body into the crucible, and then put the crucible into the vacuum furnace. After the vacuum furnace is sealed, start the vacuum system to pump air, so that the vacuum degree of the...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Firstly, waste gallium nitride-based light-emitting diodes were subjected to nitrogen pyrolysis, the pyrolysis final temperature was 600° C., and the pyrolysis time was 10 min. After the pyrolysis is over, the pyrolysis gas, pyrolysis oil and pyrolysis residue are collected respectively, and the pyrolysis gas and pyrolysis oil are recycled for other purposes. After the pyrolysis slag is crushed, the particle size of the charcoal residue is 0.4-0.6mm, and it is sieved through an 18-mesh sieve, and the charcoal residue is recovered under the sieve. The sieved material is ground and then sieved through a 40-mesh sieve. The copper or silver-plated aluminum metal frame is recovered on the sieve, and the light-emitting diode chip enrichment body is formed under the sieve. Put the chip enriched body into the crucible, and then put the crucible into the vacuum furnace. After the vacuum furnace is sealed, start the vacuum system to pump air, so that the vacuum degree of the vac...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com