Method for separating hyaluronate tetrasaccharide from hyaluronate hexasaccharide
A hyaluronic acid tetrasaccharide and separation method technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve problems such as unsuitable separation, and achieve the effects of low detection limit, good recovery rate and high purity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] Embodiment 1 is the preparation of hyaluronic acid oligosaccharides with glucuronic acid as the end
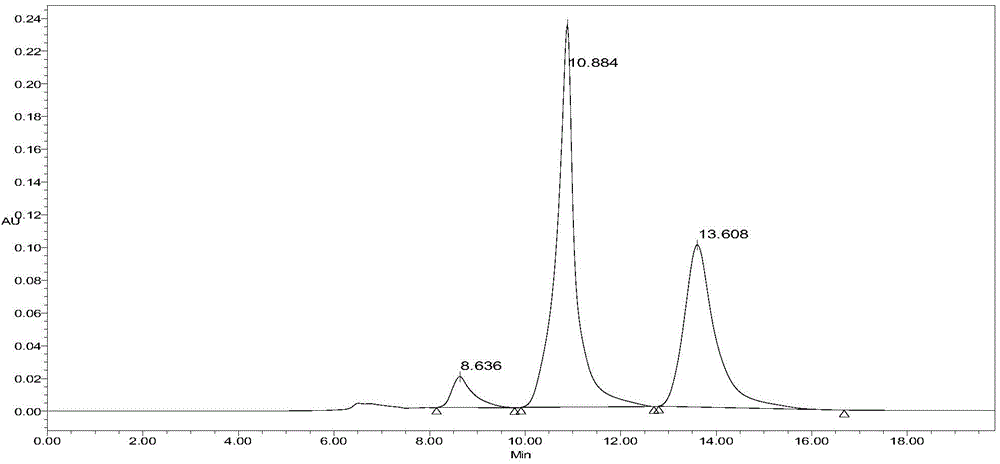
[0018] Add 1g of hyaluronic acid to a 38°C enzyme reactor containing 98ml of deionized water. After incubating at 38°C for 15 minutes, add 2ml of leech hyaluronidase solution with an enzyme activity of 800,000 U / ml, and react for 32 hours. The bath was heated for 10 min. After centrifugation at 8000 rpm for 15 min, the precipitate was discarded and the supernatant was taken. Such as figure 1 As shown, the supernatant is a mixture containing disaccharides, tetrasaccharides and hexasaccharides of hyaluronic acid. The sample with a retention time of 8.636 is hyaluronic acid disaccharide, the sample with a retention time of 10.884 is hyaluronic acid tetraose, and the sample with a retention time of 13.608 is hyaluronic acid hexasaccharide.
Embodiment 2
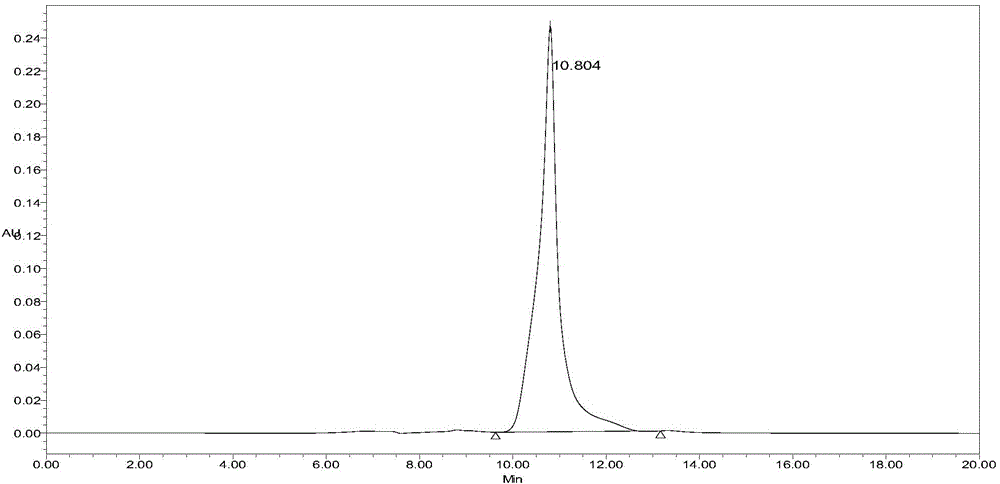
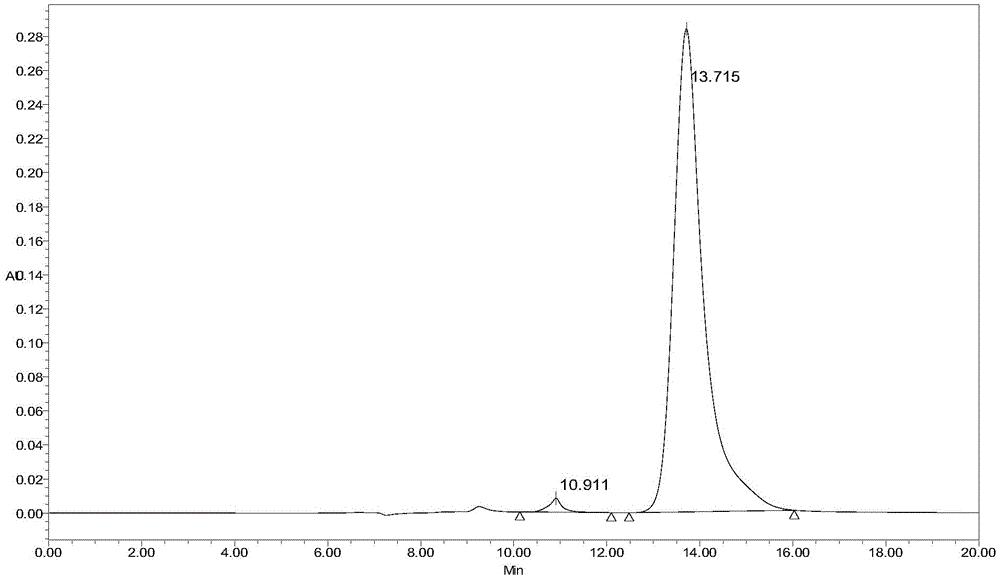
[0019] Example 2 Separation and purity detection of hyaluronic acid tetrasaccharide and hexasaccharide
[0020] Prepare solution A (balance solution): pH 8, 10mM Tris-HCl buffer solution, solution B (elution solution): 0.125M NaCl buffer solution prepared from solution A, and carry out hyaluronic acid tetrasaccharide and hexasaccharide by the following conditions separation.
[0021] (1) Equilibrate the HiPrep 16 / 10Q FF ion exchange column (height diameter 3:1) with 5 column volumes of solution A at a speed of 5ml / min.
[0022] (2) Load the sample (the mixture containing hyaluronic acid tetrasaccharide and hexasaccharide prepared in Example 1) at a flow rate of 1 ml / min until the sample breakthrough point is 5%.
[0023] (3) Wash away the sample with solution A, elute for 5 column volumes, and flow rate is 5ml / min.
[0024] (4) Carry out linear elution with liquid A and liquid B, so that the NaCl concentration in the eluent is 0.000M-0.125M, the elution volume is 15 column v...
Embodiment 3
[0028] Embodiment 3 hyaluronic acid tetrasaccharide and hexasaccharide recovery rate
[0029] Take 0.1000 g of the tetrasaccharides and hexasaccharides separated in Example 2, mix them and dissolve them in 500 μL, follow the operation in Example 2, the sample volume is 500 μL, separate and obtain desalted hyaluronic acid oligosaccharides, and measure after lyophilization The weight of oligosaccharides, including 0.9385g of tetrasaccharides and 0.9061g of hexasaccharides. The recovery rate of tetrasaccharide was 93.85%, and the recovery rate of hexasaccharide was 90.61%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com