Method for producing liquid fuel from biomass waste
A technology of biomass waste and liquid fuel, which is applied in the preparation of biofuel, liquid hydrocarbon mixture, special form of dry distillation, etc. It can solve the problems of increasing the production cost of the device, the inability to guarantee the reaction temperature, and the inability to recycle tail gas.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
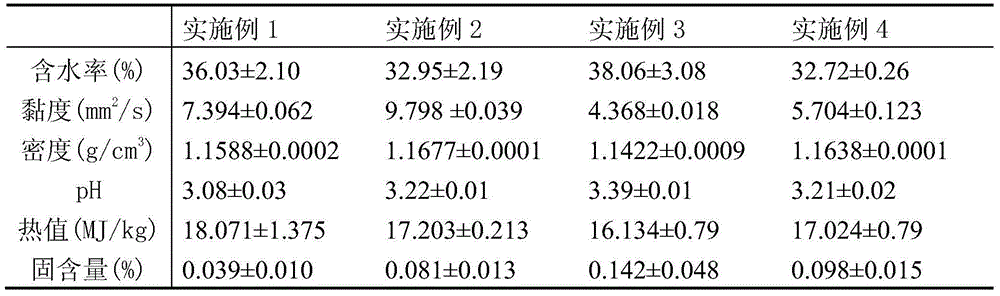
Embodiment 1
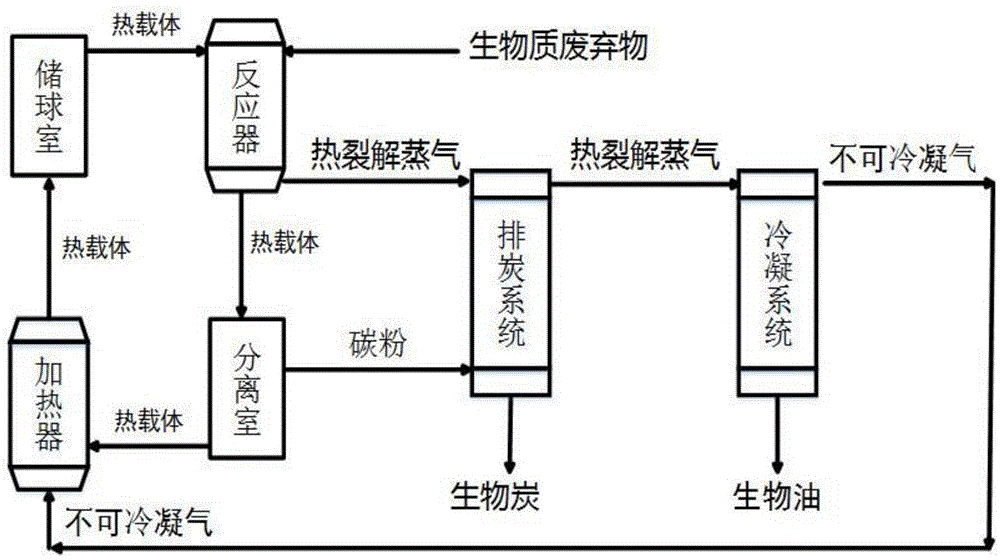
[0038] Start the reaction device, burn bio-oil, heat the heat carrier, and reach the predetermined temperature (560°C), use rice husk powder as the raw material of biomass waste, and transport it to the reaction device through the feeding system. The feeding rate of biomass waste is 2.33t / h.
[0039] The biomass waste and the heat carrier directly contact and exchange heat during the downward process, and the heat carrier and the biomass waste are fully mixed and transfer their heat to the biomass waste. The biomass waste is heated to above 500°C instantaneously (1-2s), and the biomass waste undergoes pyrolysis reaction, and most of the volatile matter and moisture of the biomass waste form pyrolysis steam. Most of the ash and fixed carbon of biomass waste form biochar.
[0040] After the thermal cracking reaction, the heat carrier is separated and transported to the heater. Use one or more sets of cyclone separators to separate the carbon powder in the pyrolysis steam, real...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Start the reaction device, burn bio-oil, heat the heat carrier, and reach the predetermined temperature (560°C), use rice husk powder as the raw material of biomass waste, and transport it to the reaction device through the feeding system, and the feed rate of biomass is 2.17t / h.
[0047] The biomass waste and the heat carrier directly contact and exchange heat during the downward process, and the heat carrier and the biomass waste are fully mixed and transfer their heat to the biomass waste. The biomass waste is heated to above 500°C instantaneously (1-2s), and the biomass waste undergoes pyrolysis reaction, and most of the volatile matter and moisture of the biomass waste form pyrolysis steam. Most of the ash and fixed carbon of biomass waste form biochar.
[0048] After the thermal cracking reaction, the heat carrier is separated and transported to the heater. Use one or more sets of cyclone separators to separate the carbon powder in the pyrolysis steam, realize ...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Start the reaction device, burn bio-oil, heat the heat carrier, and reach the predetermined temperature (560°C), use rice husk powder as the raw material of biomass waste, and transport it to the reaction device through the feeding system, and the feed rate of biomass is 2.19t / h.
[0055] The biomass waste and the heat carrier directly contact and exchange heat during the downward process, and the heat carrier and the biomass waste are fully mixed and transfer their heat to the biomass waste. The biomass waste is heated to above 500°C instantaneously (1-2s), and the biomass waste undergoes pyrolysis reaction, and most of the volatile matter and moisture of the biomass waste form pyrolysis steam. Most of the ash and fixed carbon of biomass waste form biochar.
[0056] After the thermal cracking reaction, the heat carrier is separated and transported to the heater. Use one or more sets of cyclone separators to separate the carbon powder in the pyrolysis steam, realize ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com