Rapid optical characterization method for horizontal array density of carbon nanotubes on substrate
A carbon nanotube and horizontal technology, applied in the field of fast optical characterization, can solve the problems of weak optical signal, small optical cross-section, difficult clear acquisition, etc., and achieve the effect of improving the signal level
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Embodiment 1, optical characterization of carbon nanotube horizontal array density
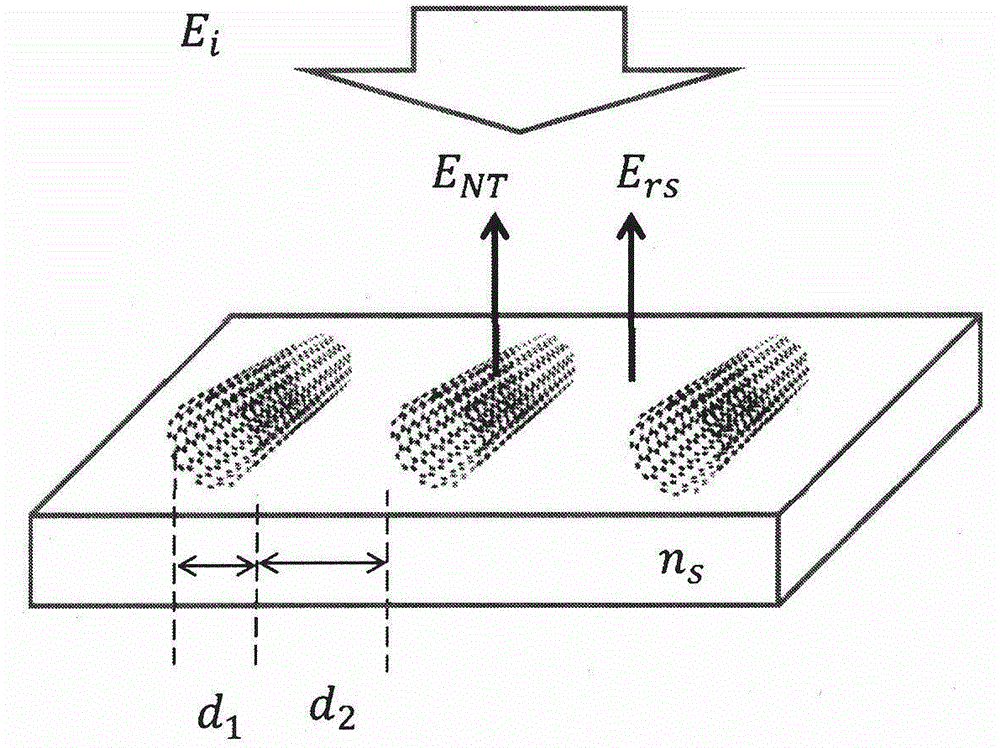
[0027] The Thomas-Reiche-Kuhn summation rule states that for any particle with the same number of electrons, the sum of the oscillator strengths between its various energy levels is equal. Integrating the absorption spectra of different types of carbon nanotubes, the integral values are basically distributed on the same straight line, which is equivalent to the absorption of graphene. Theoretical analysis of the contrast of graphene and carbon nanotube horizontal arrays indicates that the contrast is proportional to the absorption coefficient. That is, we can derive the absorption coefficient of the sample from the optical contrast of the sample, thereby obtaining the density of the horizontal array of carbon nanotubes. Specific principles such as figure 1 shown.
[0028] The invention takes optical photos of carbon nanotube samples under different polarization angles, and uses mat...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Embodiment 2, optical contrast characterization of carbon nanotube type
[0037] Carbon nanotubes can be seen as coiled graphene. Different coiling directions and tube diameters make carbon nanotubes have different chiral indices (n, m), where n and m are both integers. When the polarization direction of the incident light is parallel to the tube axis, the selection rule requires that electrons can only transition between energy levels with the same symmetry. E. ii (i=1, 2, 3...N, where N is a positive integer) marks the transition energy of electrons at different energy levels with the same symmetry, such as E 11 is the transition between the lowest energy levels of carbon nanotubes, E 22 is the transition before the second energy level. for the same E ii , the transition energy of carbon nanotubes with different chirality is different. If (3n+m) is divisible by 3, then the dividing line of the carbon nanotube passes through the K point, and the carbon nanotube i...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Embodiment 3, using the cross polarization method to improve the optical signal level of the carbon nanotube horizontal array
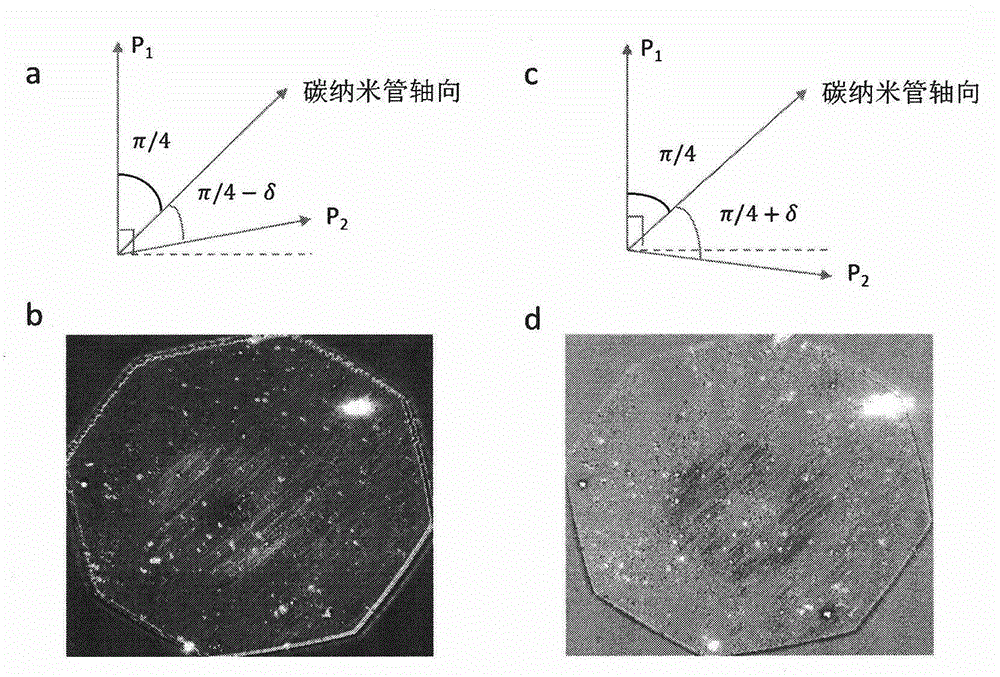
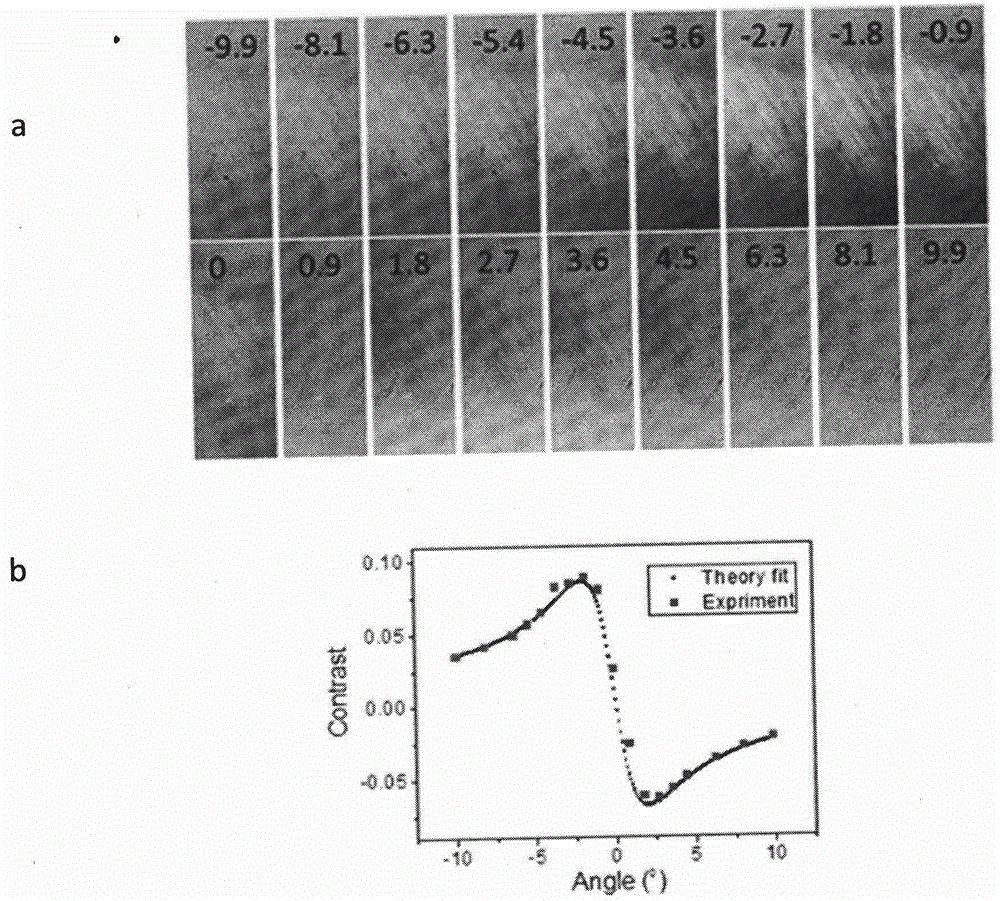
[0039] The signal level of light scattered by carbon nanotubes is usually very weak (the contrast is on the order of 0.1%), much smaller than the signal level of background light or even noise, which brings great difficulties to the optical characterization of carbon nanotubes. The invention remarkably improves the optical signal level of the carbon nanotube through the method of cross polarization, and remarkably weakens the possible error caused by the optical absorption of interference factors such as dirty spots and catalysts on the sample to the experiment.
[0040] A pair of near-vertical polarizers (deviation from perfect vertical: δ radians) are placed on both sides of the sample, and the carbon nanotube growth direction of the carbon nanotube horizontal array is at an angle of 45° to the first polarizer. The incident light passes throu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com