Efficient transgenic method for maize skeleton inbred lines
A backbone inbred line and transgenic technology, which is applied in the field of genetic engineering and crop breeding, can solve the problems of long transformation cycle, low positive rate, and low transformation efficiency, and achieve high positive rate, simple and convenient operation, and high transformation efficiency. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Embodiment 1 Preparation of Agrobacterium tumefaciens containing target gene
[0035] The Agrobacterium strains used in this specific embodiment are EHA105 and LBA4404. The herbicide-resistant gene Bar (gene sequence such as SEQ ID NO: 1) and the green fluorescent protein coding gene GFP (gene sequence such as SEQ ID NO: 2) were transformed into Agrobacterium by the Agrobacterium transformation method commonly used in the art. It should be understood that this specific embodiment uses the gene encoding green fluorescent protein as an example of the exogenous gene, but the present invention is not limited to a specific exogenous gene. The Agrobacterium-introduced gene used in this embodiment, the vector construction method and the plasmid used are only well known to those skilled in the art.
[0036] One week before infection, take 20 μL of glycerol bacteria from the -80°C refrigerator, and streak on the YEP medium plate with the corresponding antibiotics (EHA105 corres...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Example 2 Preparation of transgenic corn
[0038] The maize inbred line used in this example is 'Xiang 249', provided by China Seed Group Co., Ltd.
[0039] 1. Selection of ears and separation of immature embryos
[0040] (1) Select corn cobs whose young embryos have grown to 0.5-2.0 mm in 6-15 days after pollination, and the number of samples shall not be less than 500;
[0041] (2) Mix the sodium hypochlorite with a concentration of 6.15% with sterilized water at a concentration of 15% by volume, and add 1 drop (20ul) of Tween-20 to make a sterilant;
[0042] (3) Soak the cobs of corn in a sterilizing agent for 15 minutes, and then rinse them with sterile water for 3-5 times;
[0043] (4) Peel off the immature embryos, and put the immature embryos into the suspension.
[0044] 2. Infection and co-cultivation
[0045] (1) Put the stripped immature corn embryos into a 2ml EP tube containing 1.8mL of suspension, treat about 150 immature embryos within 30min, and then...
Embodiment 3
[0080] Example 3 Detection of transgenic corn
[0081] 1. Observation on the expression of exogenous gene GFP in tissues of transgenic maize
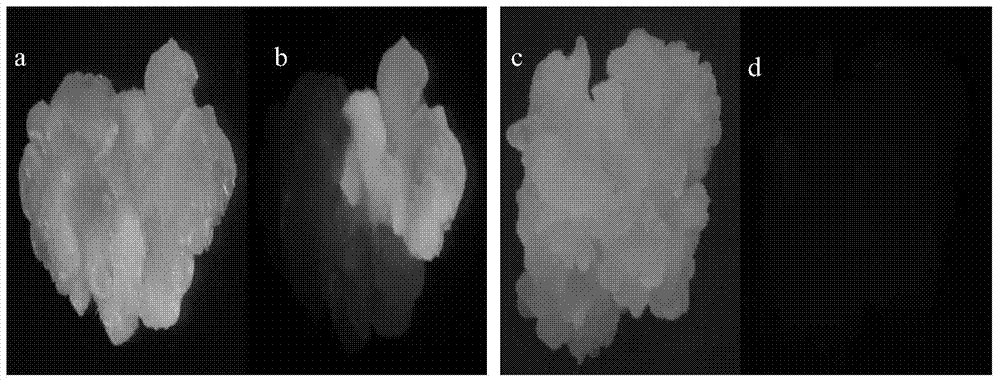
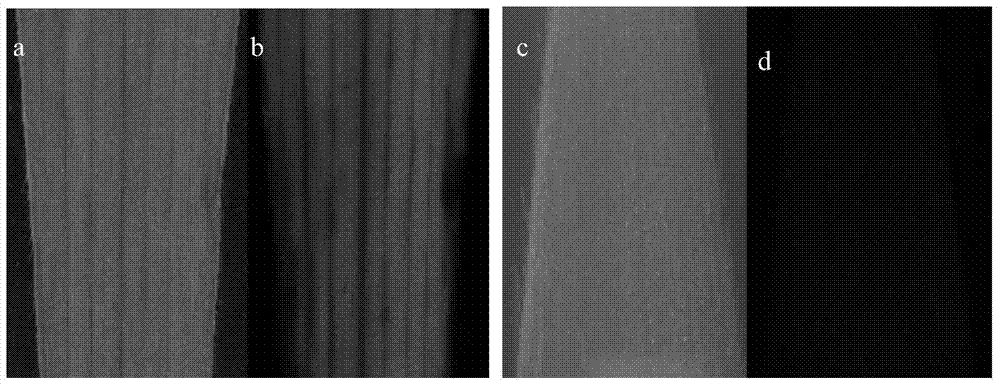
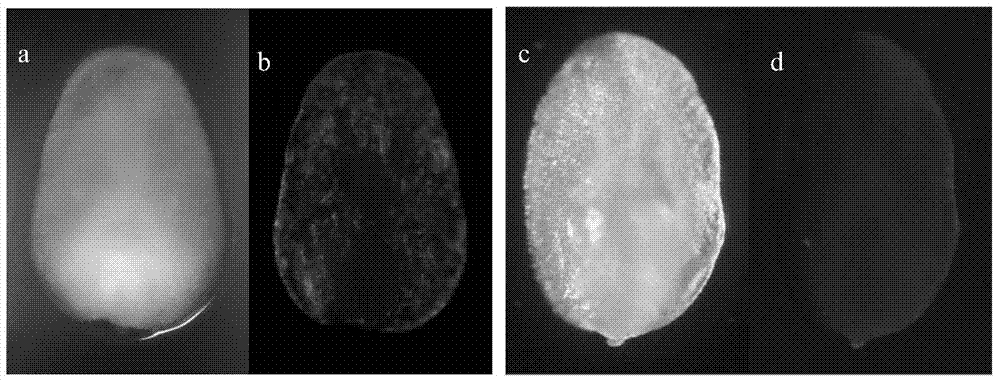
[0082] Take the 'Xiang 249' transformed immature embryos, callus and leaves of Example 2 to observe the expression of the exogenous gene (GFP) in the tissue. It turns green under fluorescence, indicating that the exogenous gene is successfully expressed, otherwise it is a negative material. Compared with the positive material, the negative material is darker under the fluorescence, the immature embryo and callus are yellow, and the leaves are red. see results Figure 1A , Figure 1B , Figure 1C . 2. PCR detection
[0083] (1) DNA extraction: Genomic DNA of the T0 transgenic maize obtained in Example 2 was extracted with a DNA extraction kit purchased from Tiangen Biochemical Technology (Beijing) Co., Ltd.
[0084] (2) PCR detection
[0085] Thaw the following reagents from the -20°C refrigerator: 10×PCR reaction buffer (Takara), ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com