Sn-Ag-Cu-based solder powder, and solder paste using said powder
A solder powder and solder technology, applied in the field of SnAgCu solder powder, can solve the problems of powder surface oxidation, poor wettability, time-consuming, etc., and achieve rapid melting, good wettability, excellent melting and wettability effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
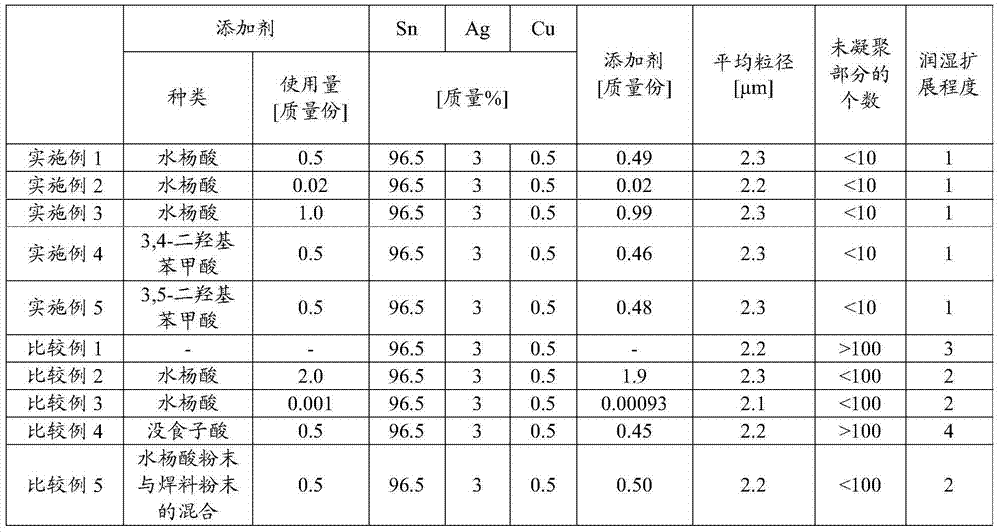
[0048] First, add 1.59×10 to 50mL of water -4 mol of copper(II) sulfate, 4.10×10 -4 mol of silver (I) sulfate, 2.62×10 -2 mol of tin(II) sulfide was stirred with a stirrer at 300 rpm for 5 minutes to prepare a solution. After adjusting the pH of the solution to 0.5 with sulfuric acid, 0.5 g of polyvinyl alcohol 500 (polyvinyl alcohol having an average molecular weight of 500) was added as a dispersant, and stirred at 300 rpm for 10 minutes.
[0049] Next, 50 mL of a 1.58 mol / L divalent chromium ion aqueous solution adjusted to a pH of 0.5 was added to the solution at an addition rate of 50 mL / sec, and stirred at a rotation speed of 500 rpm for 10 minutes to reduce each metal ion to obtain a solution dispersed in the solution. Dispersions of metal powders. After the dispersion was allowed to stand for 60 minutes to precipitate the produced metal powder, the supernatant was removed, and the operation of adding 100 mL of water and stirring at 300 rpm for 10 minutes was repeate...
Embodiment 2
[0053] A solder powder was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1 except that 0.80 mg of salicylic acid was used as an additive. On the surface of the solder powder, 0.02 parts by mass of salicylic acid was adhered to 100 parts by mass of the total components of tin, silver, and copper contained in the solder powder.
Embodiment 3
[0055] A solder powder was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1 except that 40 mg of salicylic acid was used as an additive. On the surface of the solder powder, 0.99 parts by mass of salicylic acid was adhered to 100 parts by mass of the total components of tin, silver, and copper contained in the solder powder.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com