Preservative-free herbal composition with antiseptic effect prepared from plant extract and moisturizing agent and its application in daily cosmetics
A plant extract and humectant technology, applied in cosmetic additives, herbal compositions without preservatives and its application in daily cosmetics, can solve the problems of poor antiseptic performance and achieve high reliability and good stability , remarkable anti-corrosion effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
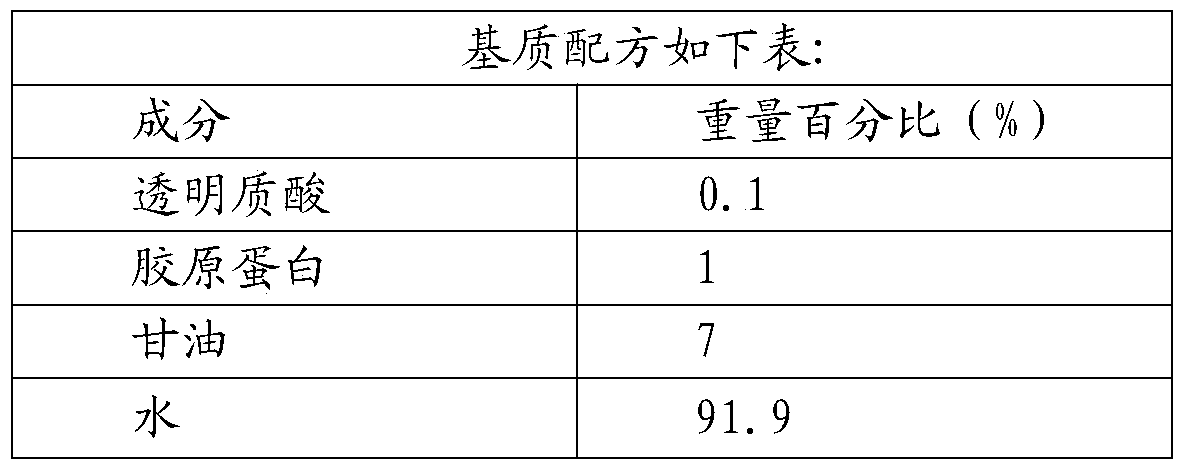
[0056] Example 1 Matrix formulation
[0057] According to the "Compendium of Materia Medica", there are many plants with the function of preventing corruption and killing microorganisms. Sophora flavescens, wild chrysanthemum, honeysuckle, skullcap, mugwort, peony bark, dandelion, purslane, etc. If a reasonable combination is designed, the effect of preservatives can be achieved. Based on years of experience in cosmetic research and development, the following matrix formulations that are very easy to contaminate are designed:
[0058]
[0059] This formula contains hyaluronic acid and collagen, which are nutritional polysaccharides and proteins required for the growth of microorganisms. It is difficult to control the growth of bacteria and molds by adding general preservatives, so the requirements for preservatives are very high and are typical . Preferably, the water is deionized water.
Embodiment 2
[0060] Example 2 Preliminary test 1
[0061] The applicant first conducts preliminary experiments in the microbiology laboratory. The so-called preliminary experiments refer to preliminary experiments. Since the cost of directly conducting a strict microbial anti-corrosion challenge test is too high, a preliminary test is firstly conducted. The test conditions of the preliminary test are not strict. , the experimental results are as follows:
[0062]
[0063]
[0064]Conclusion: The use of plant extracts alone for preservatives is not satisfactory.
Embodiment 3
[0065] Example 3 Stringent Microbiological Challenge Test 1
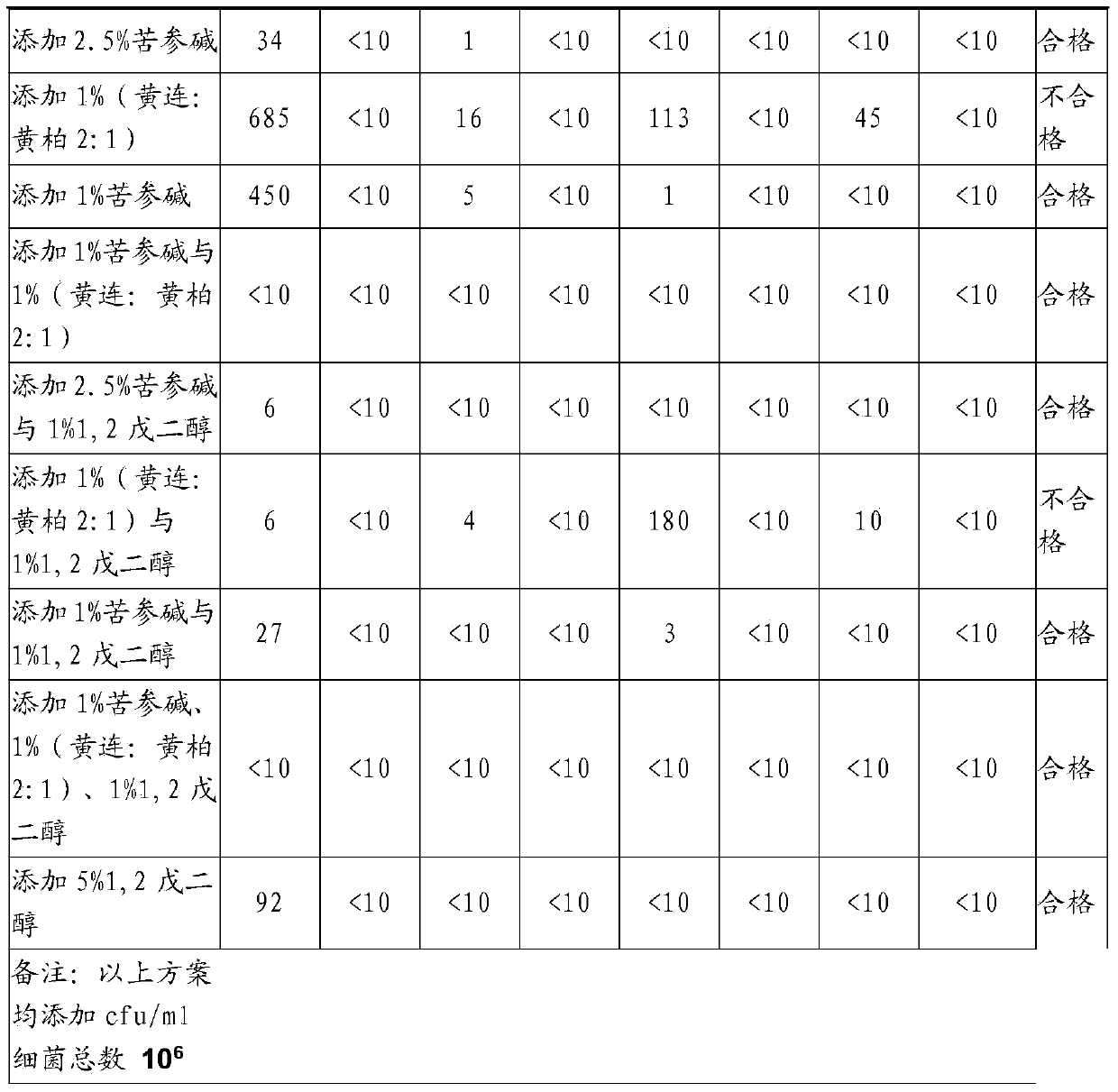
[0066] The microbiological challenge test is the most extensive and classical test method for evaluating the effect of preservatives. In the total of Example 2, the best fourth group was selected to carry out a rigorous antiseptic challenge experiment, wherein the fourth group refers to: adding 1% matrine and 1% (Coptis chinensis: Phellodendron chinensis 2:1). The result is as follows:
[0067]
[0068]
[0069] Extraction source: Matrine is extracted from the dried roots, plants and fruits of the legume Sophora flavescens Ait by ethanol and other organic solvents. It is an alkaloid, generally total alkaloids of Sophora flavescens. Alkali, sophocarpine, oxysophocarpine, sophoridine and other alkaloids, with the highest content of matrine and oxymatrine. Other sources are Sophora subprostrata (shandougen), and the aerial parts of Sophora alopecuroides.
[0070] Conclusion: The microbiological challenge test ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com