Escherichia coli for detecting lead
A technology of Escherichia coli, escherichiacoli, applied in the direction of bacteria, microorganism-based methods, and microbial determination/inspection, etc. Good performance, stable results and high detection sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
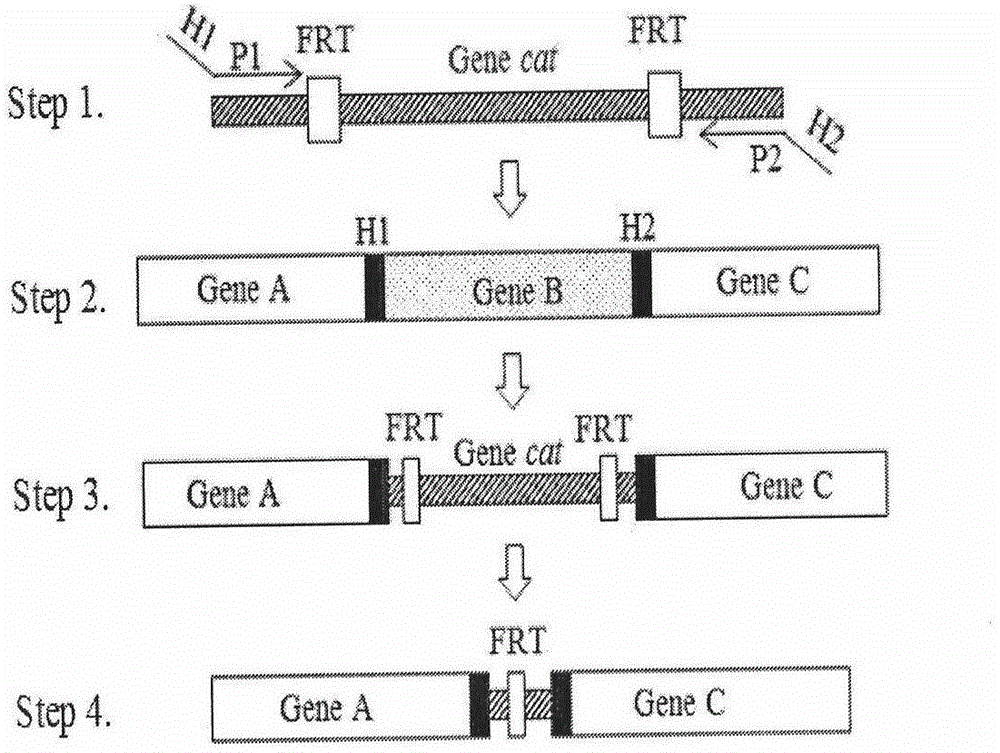
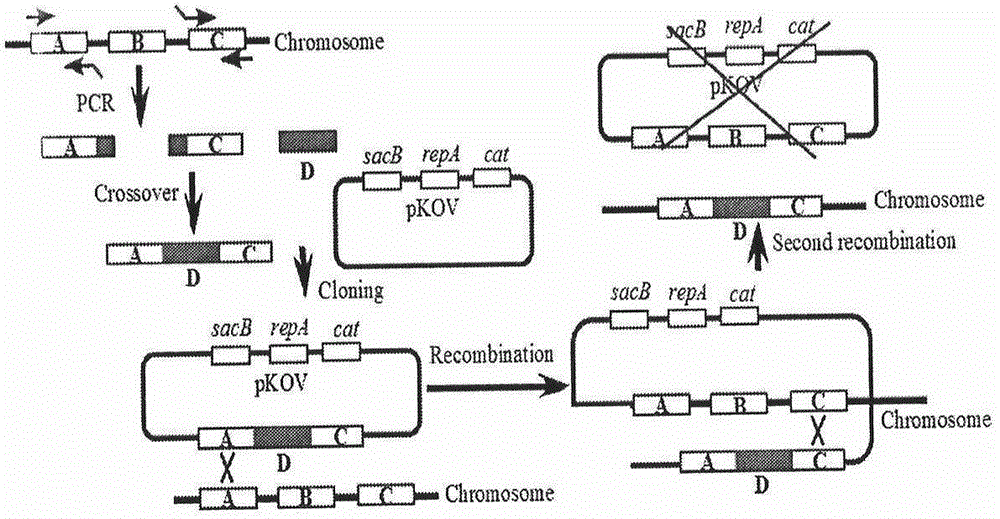
[0049] Example 1. Construction of double knockout sensitive strains, see figure 1
[0050] 1.1 PCR amplification of the chloramphenicol resistance gene containing zntA and zntR upstream and downstream 50bp homologous arms with FRT sites According to the zntA / zntR gene sequence published by http: / / ecogene.org / and the cat gene sequence published by GenBank, design The chloramphenicol resistance gene containing zntA and zntR upstream and downstream 50bp homologous arms with FRT sites and the primers identified were synthesized. The specific information is shown in Table 1. The primers were synthesized by Shanghai Jierui Bioengineering Co., Ltd. with sterile ddH 2 O Dissolve the primers, prepare a storage solution with a concentration of 10 μmol / L, and store at -20°C.
[0051] Table 1. Gene Knockout Primer Details Table
[0052]
[0053] Take 1ml of MC4100 overnight bacterial solution containing plasmid pKD3 in a 1.5ml EP tube, centrifuge at 12,000rpm for 1min, discard the...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Example 2. Fusion of gene knock-in fragments, such as figure 2
[0066] 2.1 Primer information and synthesis
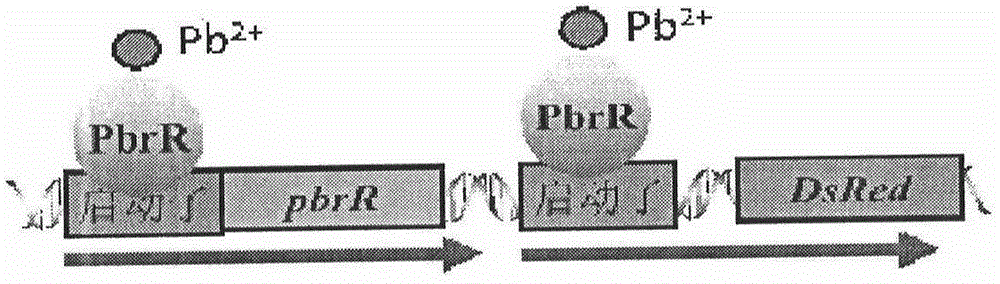
[0067] According to Harvard MoLecuLar TechnoLogy Group&Lipper Center for ComputationaL Genetics website http: / / arep.med.harvard.edu / Labgc / adnan / projects / EcoLiKOprimers / EcoLiKOprimers.htm provided primer sequence knockout zntA gene, http: / / ecogene.org / published zntA gene sequence and GenBank published PpbrA-pbrR-PpbrA::DsRed-express2 gene sequence, design the internal primers (P 2 : zntA-Ni and P 5 : zntA-Ci) and outer primer (P 1 :zntA-No and P 6 :zntA-Co), make P 2 with P 3 , P 4 with P 5 There is a complementary sequence between them, and the two outer primers of gene knockout remain unchanged, P 3 with P 4 A pair of primers for amplifying the PpbrA-pbrR-PpbrA::DsRed-express2 gene. The specific information is shown in Table 2. The primers were synthesized by Shanghai Jierui Bioengineering Co., Ltd. with sterile ddH 2 O Dissolve the primers, pre...
Embodiment 3
[0088] Example 3. Sequencing of gene knock-in fragments
[0089] 3.1 Gene knock-in fragment plus A reaction and purification: The PCR reaction system is as follows
[0090]
[0091] The PCR reaction conditions are as follows: 72°C, 1h, 4°C, 30min. Purify the PCR product with a purification kit, and finally add an appropriate amount of sterile MilliQ H 2 O dissolved and eluted for later use.
[0092] 3.2 The target fragment is connected to the pMD19-T simple vector
[0093] According to the instructions of the pMD19-T simpLe Vector kit from TaKaRa Company, the T vector was connected to the target gene, and the connection reaction system was as follows:
[0094]
[0095] 16°C, ligate overnight.
[0096] 3.3 Conversion
[0097] by cold CaCl 2 The ligation product was transformed into Escherichia coli DH5α competent cells.
[0098] 3.4 Sequencing
[0099] Pick an outer primer P 1 and P 6 The correct monoclonal strains identified by PCR and plasmid digestion were se...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com