Fluorometric analysis based detection method for acrylamide in fried food
A technology for acrylamide and fluorescence analysis, which is applied in the direction of fluorescence/phosphorescence, material excitation analysis, etc., can solve the problems of unsafe test conditions, high derivation temperature, and complicated process, so as to improve safety and stability, avoid high temperature reaction, The effect of increasing the fluorescence intensity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] Embodiment 1: the establishment of standard method:
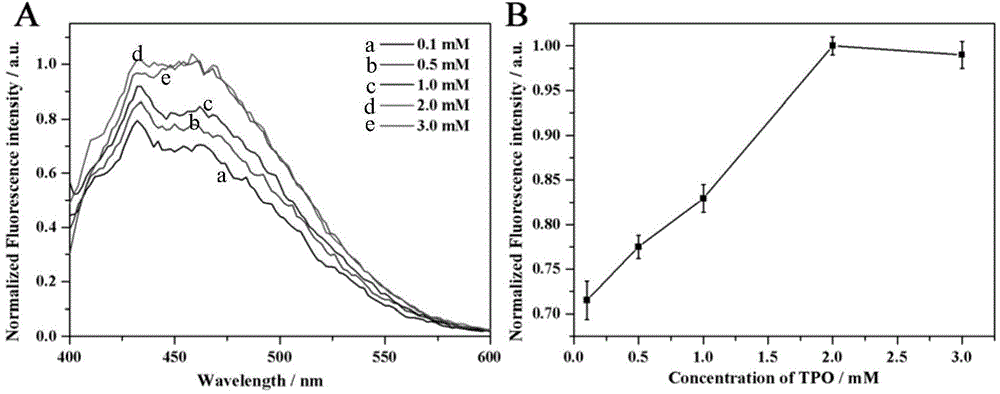
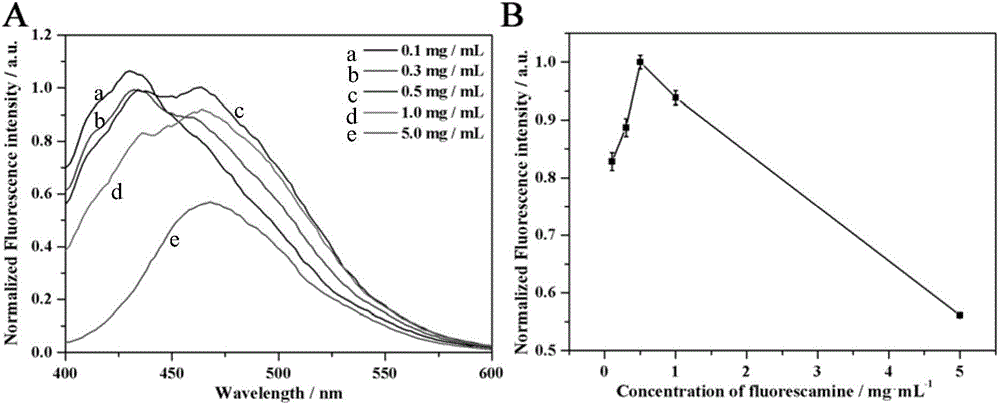
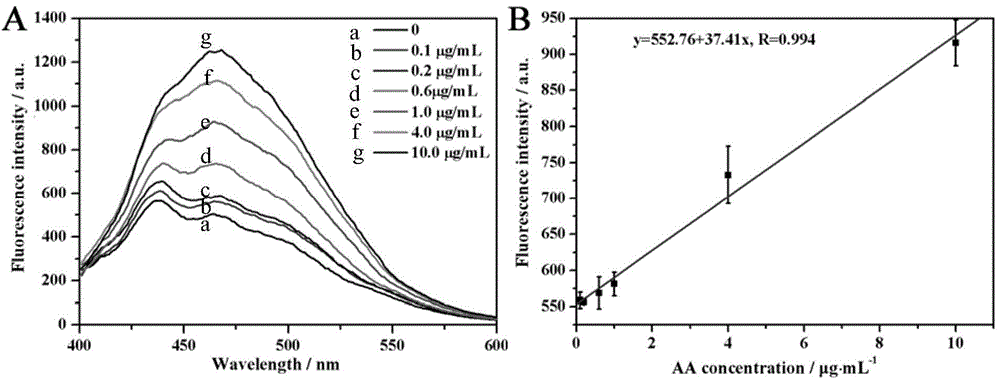
[0056] Add 500 μL of AA solution with a concentration of (0.1, 0.2, 0.6, 1, 4, 10 μg / mL) into 10 μL of KPS solution, add 100 μL of TPO solution at the same time, mix well and put it into a UV lamp (wavelength 365nm and 254nm UV are turned on at the same time ) under irradiation for 1h. Then add 200 μL phosphate buffer solution (PBS, pH 8), then add 200 μL fluorescamine solution and 480 μL Tx-100 solution, mix well, and measure the fluorescence intensity of the system at 465 nm under the condition of excitation wavelength 375 nm. A good linear relationship between fluorescence intensity and AA can be obtained, such as Figure 6 As shown, the linear equation of the working curve can be obtained as y=552.76+37.41x, the correlation coefficient R=0.994, the linear range is 0.2–10 μg / mL, and the lowest detection limit calculated by triple noise is 0.15 μg / mL.
Embodiment 2
[0057] Embodiment 2: the detection of actual sample:
[0058] The sample pretreatment step in the method of the present invention.
[0059] 1) Degreasing: Select six kinds of fried samples to pulverize and dry at 60°C. Weigh 1.0g of the reagent sample into a 50mL centrifuge tube, add 10mL of distilled n-hexane to degrease, oscillate, sonicate for 10min, then place it for 10min, filter to take the filter residue, then add 10mL of n-hexane to the filter residue, repeat the above experimental steps.
[0060] 2) Extraction: extract the filter residue in operation 1) with ultrapure water, add 10 mL of ultrapure water to the filter residue, ultrasonicate for 10 minutes, centrifuge (10000 rpm) for 10 minutes, and filter to obtain the supernatant. Add 10 mL of ultrapure water to the filter residue, repeat the above operation, and combine the extracts.
[0061] 3) Polymerization and detection of acrylamide: add 500 μL of extraction solution containing 10 μg / mL standard AA solution to...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| correlation coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com