Treatment agent of removing harmful metal elements from surface of catalyst and removal method thereof
A metal element and catalyst technology, applied in the field of removal and regeneration of harmful metal elements on the surface, can solve the problems of insufficient utilization and low catalyst activity, achieve efficient removal, simple and feasible method, and maintain activity and catalytic reforming performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
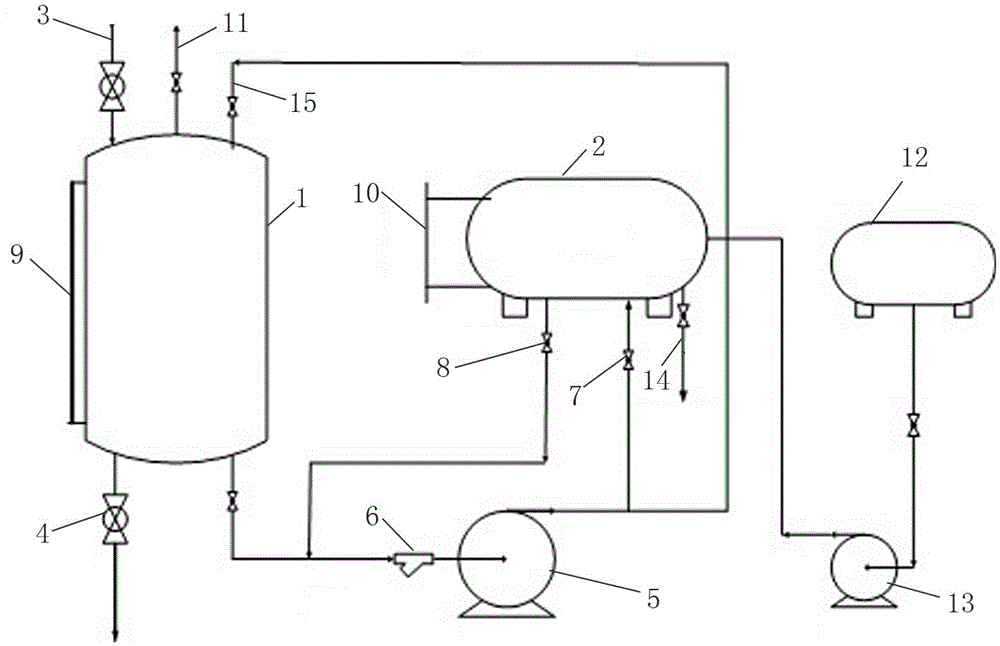
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0060] A treatment agent for removing harmful metal elements on the surface of a catalyst, which consists of the following substances in terms of mass percentage:
[0061] EDTA disodium salt 9%
[0062] Sulfamic acid or / and sulfosalicylic acid 0.5%
[0063] Polyaspartic acid or / and polyepoxysuccinic acid 0.9%
[0064] Surfactant 0.5%
[0065] The balance is water.
[0066] Catalyst iron content analysis is tested by inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer (ICP). The test basis: JY / T 015-1996 standard, the iron content of the catalyst before and after iron removal: 0.42, 0.02%.
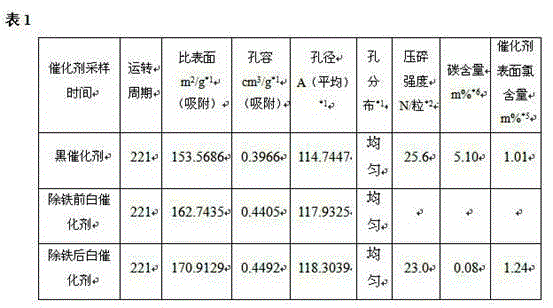
[0067] Table 1 is the performance data before and after the catalyst adopts the treatment agent described in Example 1 to remove harmful metal elements on the surface, wherein the black catalyst refers to the catalyst after deactivation, and "white catalyst before iron removal" refers to the catalyst after deactivation. The burnt treated catalyst, "white catalyst after iron removal" refers...
Embodiment 2
[0071] A treatment agent for removing harmful metal elements on the surface of a catalyst, which consists of the following substances in terms of mass percentage:
[0072] EDTA Disodium Salt 1%
[0073] Sulfamic acid or / and sulfosalicylic acid 5%
[0074] Polyaspartic acid or / and polyepoxysuccinic acid 0.02%
[0075] Surfactant 0.05%
[0076] The balance is water.
[0077] Catalyst iron content (ICP), before and after iron removal: 0.48%, 0.02%.
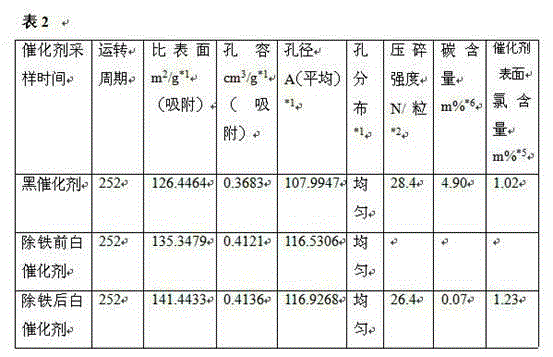
[0078] Table 2 The performance data before and after the catalyst adopts the treatment agent described in Example 2 to remove harmful metal elements on the surface, wherein the black catalyst refers to the catalyst after deactivation, and the "white catalyst before iron removal" refers to the deactivated after burning The treated catalyst, "white catalyst after iron removal" refers to a catalyst that has been deactivated and treated by charring, and a reforming catalyst obtained after removing harmful metal elements on the surface ...
Embodiment 3
[0082] A treatment agent for removing harmful metal elements on the surface of a catalyst, which consists of the following substances in terms of mass percentage:
[0083] Ethylenediammonium tetraacetate disodium salt 0.15%
[0084] Sulfamic acid or / and sulfosalicylic acid 13%
[0085] Polyaspartic acid or / and polyepoxysuccinic acid 0.01%
[0086] Surfactant 0.2%
[0087] The balance is water.
[0088] Table 3 Catalyst surface element content table (mass %)
[0089] element / week new 42 47 52 57 62 69 76 After removal CaO 0.0055 0.0091 0.0095 0.0098 0.01 0.0098 0.0096 0.01 0.0059 Fe 2 o 3 0.02 0.31 0.33 0.35 0.37 0.39 0.40 0.42 0.02 Cr 2 o 3 0.0012 0.0087 0.01 0.01 0.012 0.013 0.012 0.014 0.0031 NiO 0.0015 0.0022 0.0024 0.0027 0.0029 0.0032 0.0037 0.0039 0.0019 Cl 1.36 0.98 1.06 1.01 0.95 1.03 0.94 1.07 1.02 Pt 0.45 0.45 0.44 0.43 0.45 0.43 0.44 0.44 0.44 sn 0....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com