A method for hydrophilic modification of the surface of a porous hydrophobic material
A technology of hydrophobic material and porous material, applied in fiber processing, textile and papermaking, fiber type, etc., can solve the problem of poor blood compatibility of hydrophobicity, and achieve obvious hydrophilic effect, firm modified layer, and hydrophilic effect. boosted effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Hydrophilic modification of polypropylene non-woven fabrics using quaternized polyethyleneimine: The polypropylene non-woven fabric was completely immersed in ethanol for 1 hour, during which time it was sonicated for 10 minutes every 20 minutes; 2 g of dopamine was dissolved in 1 L In tris-hydrochloric acid buffer solution (pH=8.5), the polypropylene non-woven fabric soaked in ethanol was immersed in the above dopamine solution for 12 hours; then it was taken out and rinsed with deionized water. Immerse the polypropylene non-woven fabric coated with dopamine in concentration once again in the phosphate buffered saline solution (pH=8.5) of quaternized polyethylenimine (molecular weight is 25000) of 5g / L, put The reaction was placed in an incubator at 37°C for 24 hours; after the reaction, the polypropylene non-woven fabric was taken out, washed 5 times with deionized water, and dried to obtain a polypropylene non-woven fabric with hydrophilic surfaces and pores. After m...
Embodiment 2
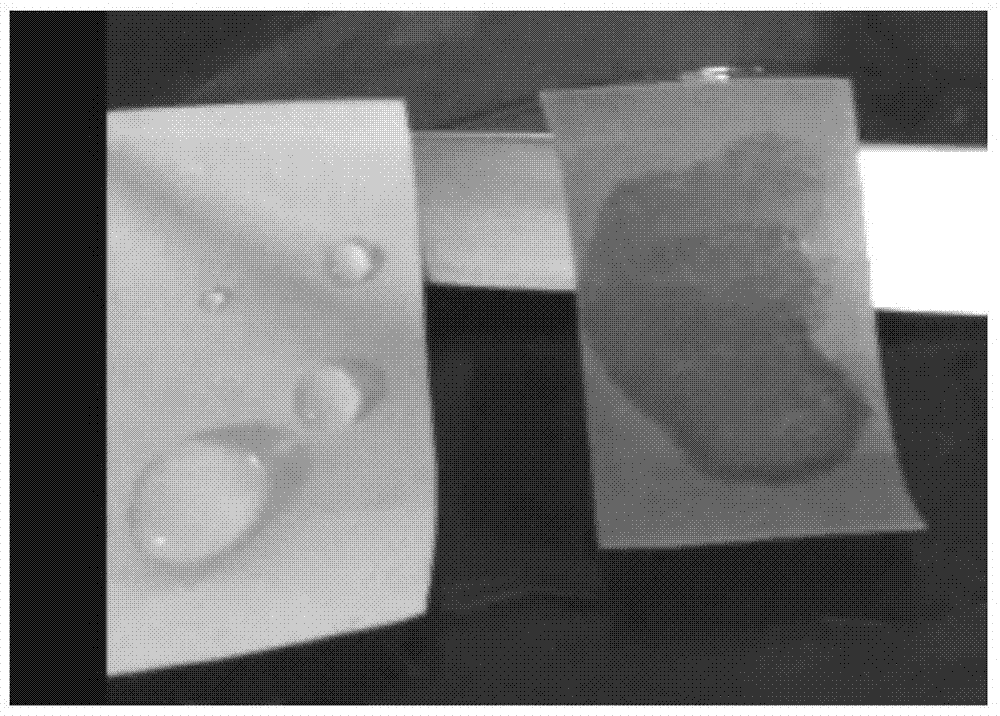
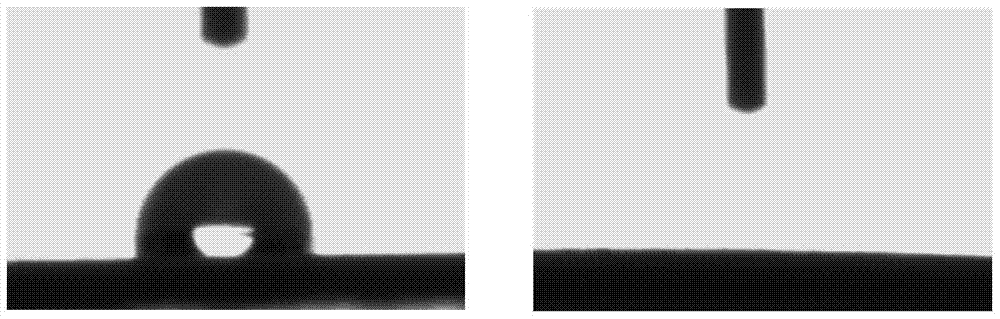
[0029] Hydrophilic modification of polypropylene non-woven fabrics using activated polyethylene glycol: replace the quaternized polyethyleneimine in Example 1 with amino polyethylene glycol, and the other experimental conditions are the same as in Example 1, and prepare A polypropylene nonwoven fabric with hydrophilic surface and pore interior was obtained. The water contact angle was measured, and the water contact angle of the unmodified polypropylene non-woven fabric was 144°, and the water contact angle after modification was 34°.
Embodiment 3
[0031] Hydrophilic modification of polypropylene non-woven fabrics using chitosan: replace the quaternized polyethyleneimine in Example 1 with chitosan, other experimental conditions are the same as in Example 1, and the surface and pores are prepared Hydrophilic polypropylene non-woven fabric inside. The water contact angle was measured, and the water contact angle of the unmodified polypropylene non-woven fabric was 144°, and the water contact angle after modification was 44°.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| water contact angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| water contact angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com