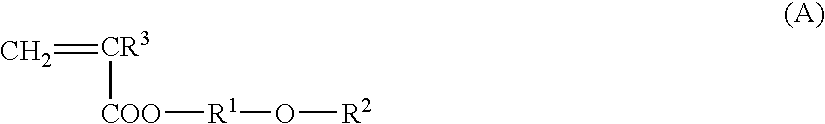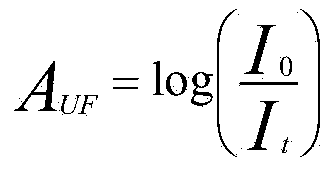Patents
Literature
115 results about "Blood filtration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Blood Filtration in the Kidney. The kidneys filter about one-quarter (750-1000 pints) of the blood that is output by the heart daily. This blood is sent to the body’s filter treatment plant, where it is purified by the kidneys and circulated on to the rest of the body.
High convection home hemodialysis/hemofiltration and sorbent system
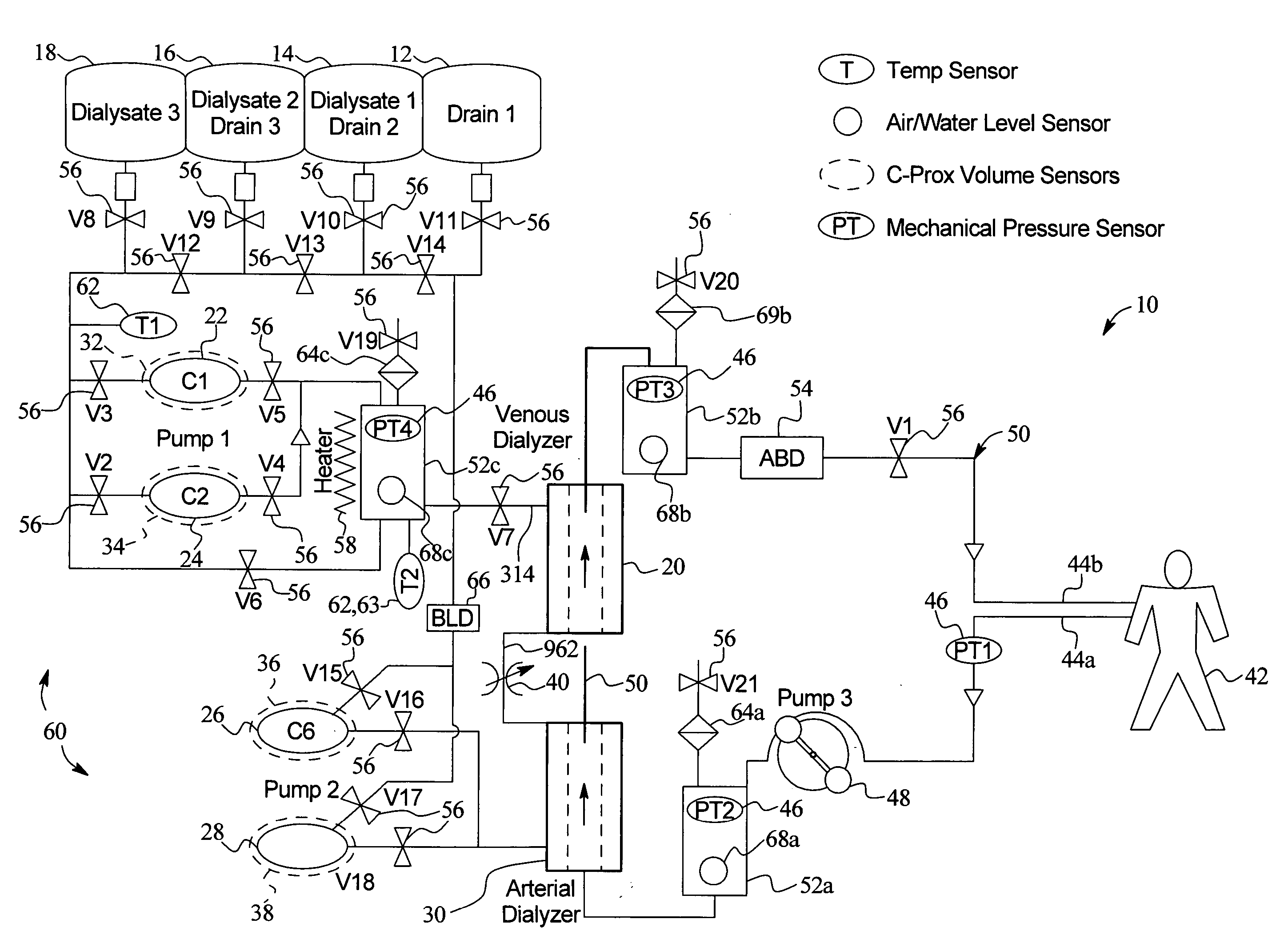
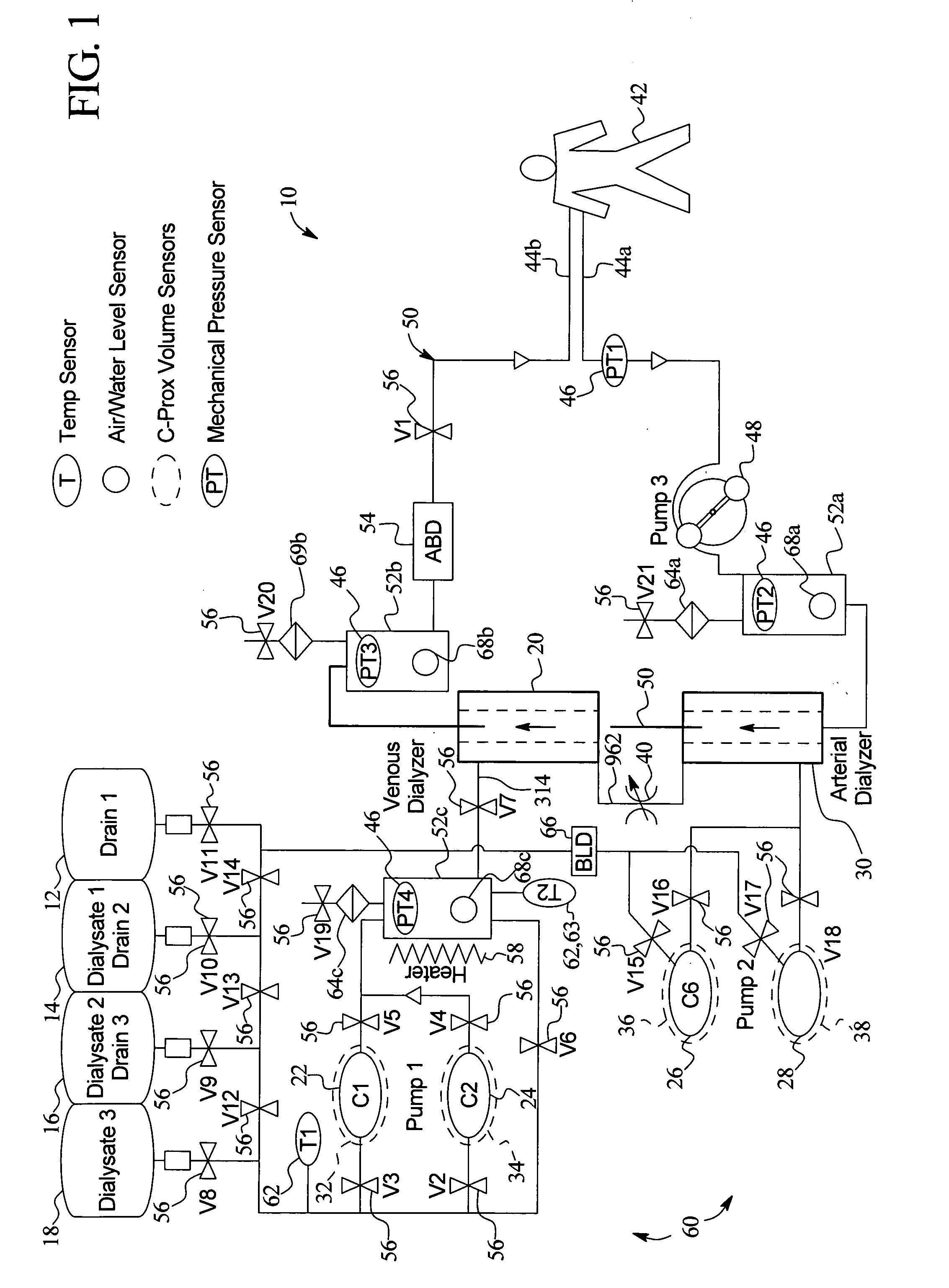
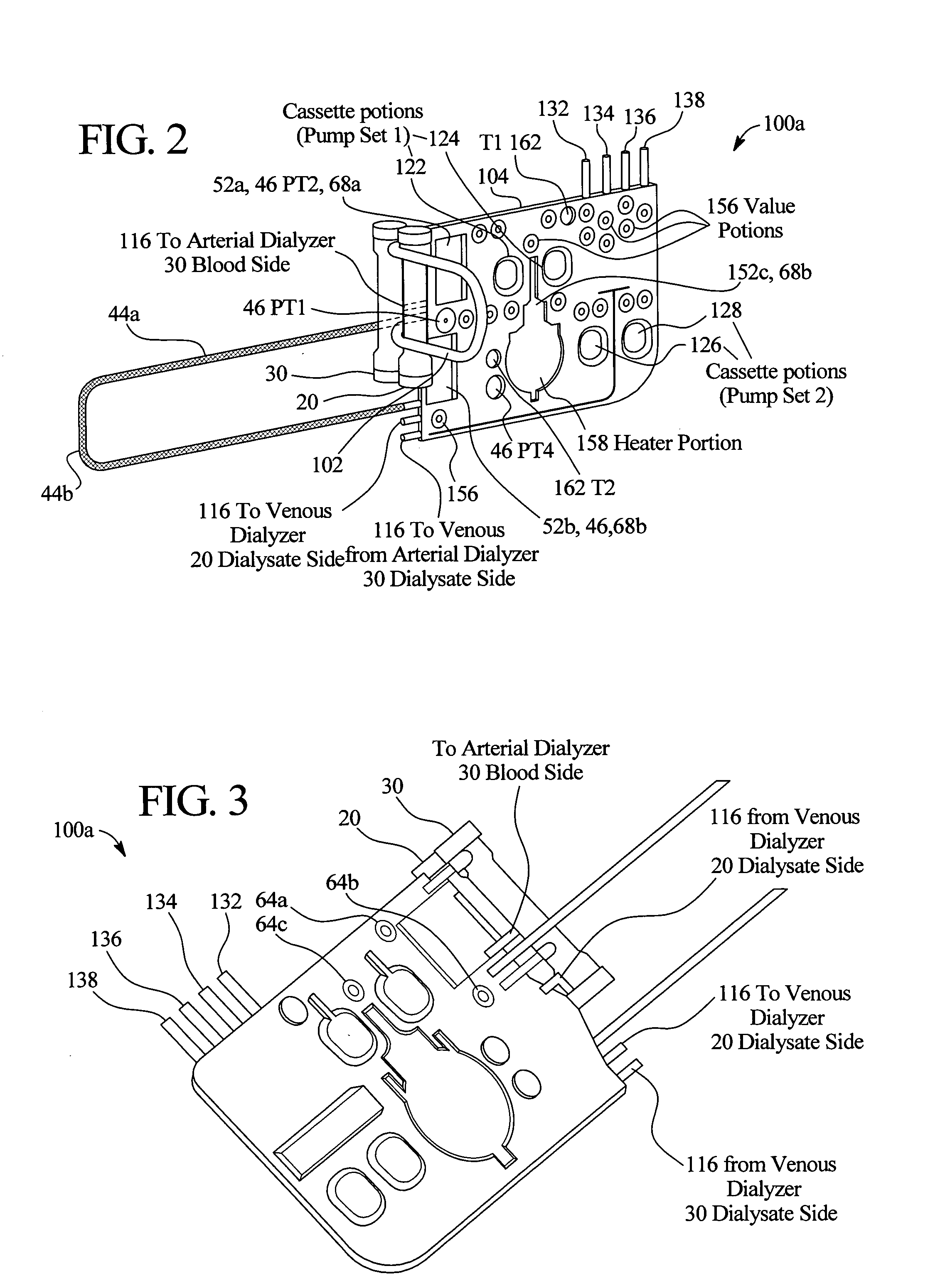
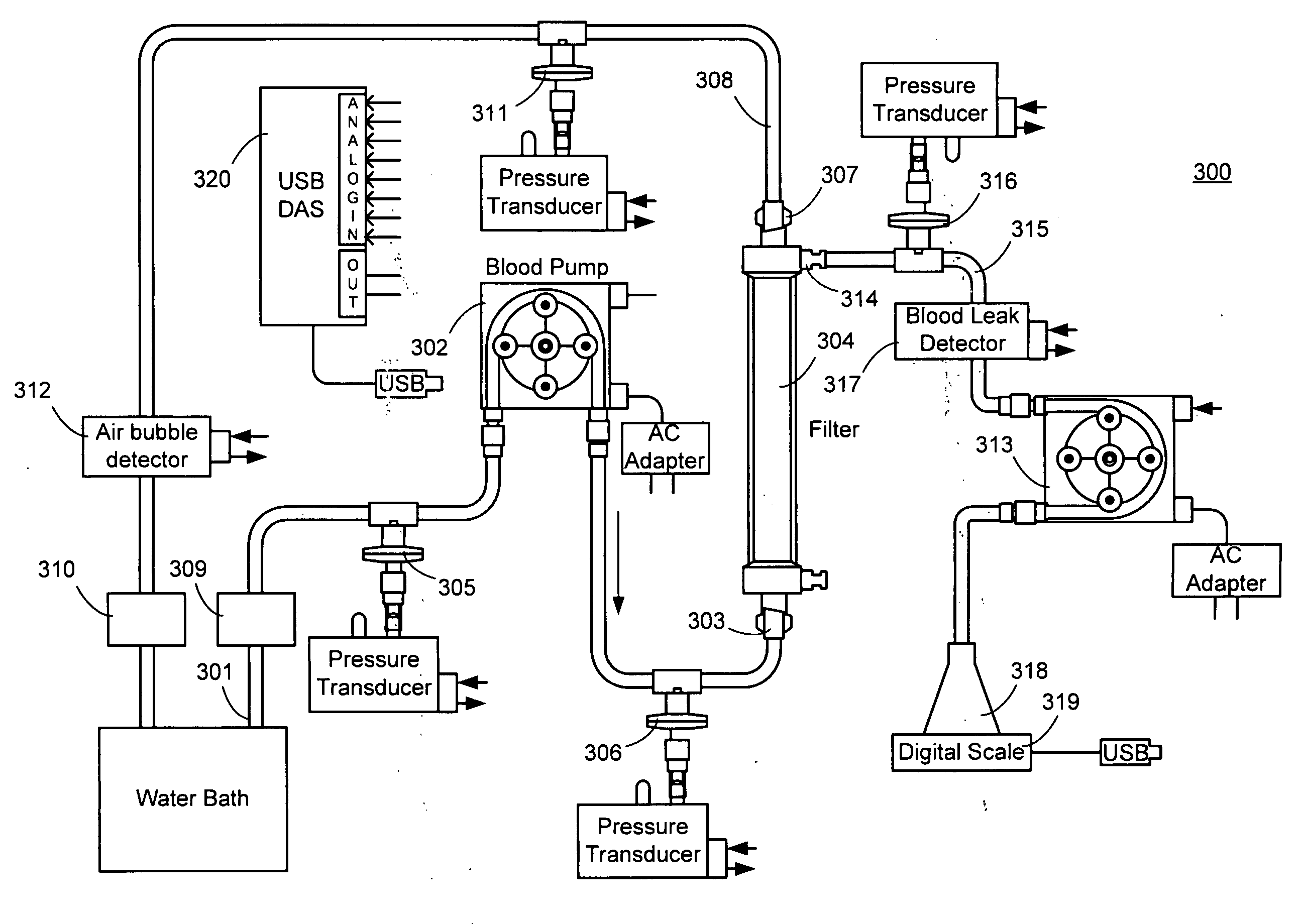
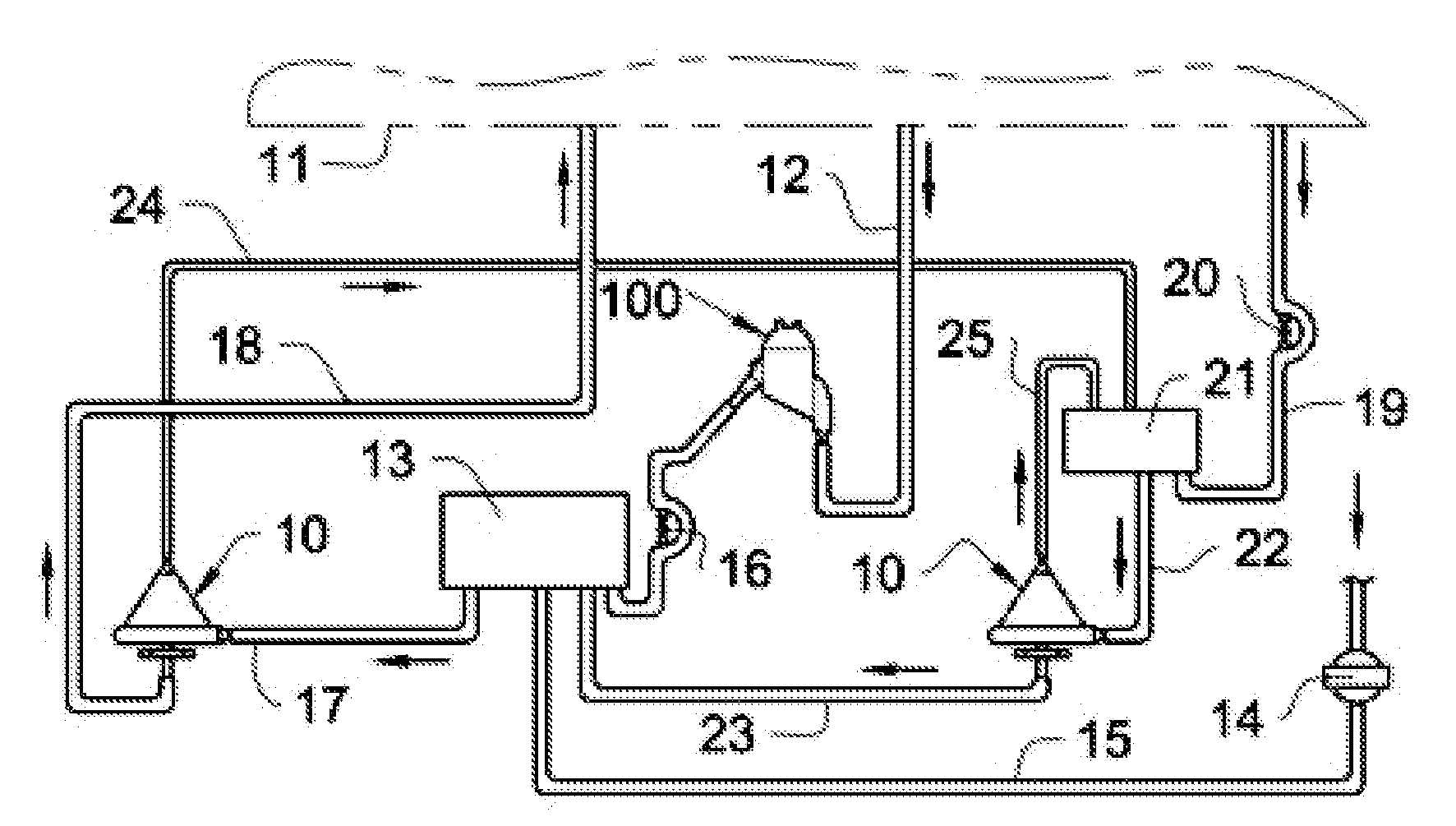
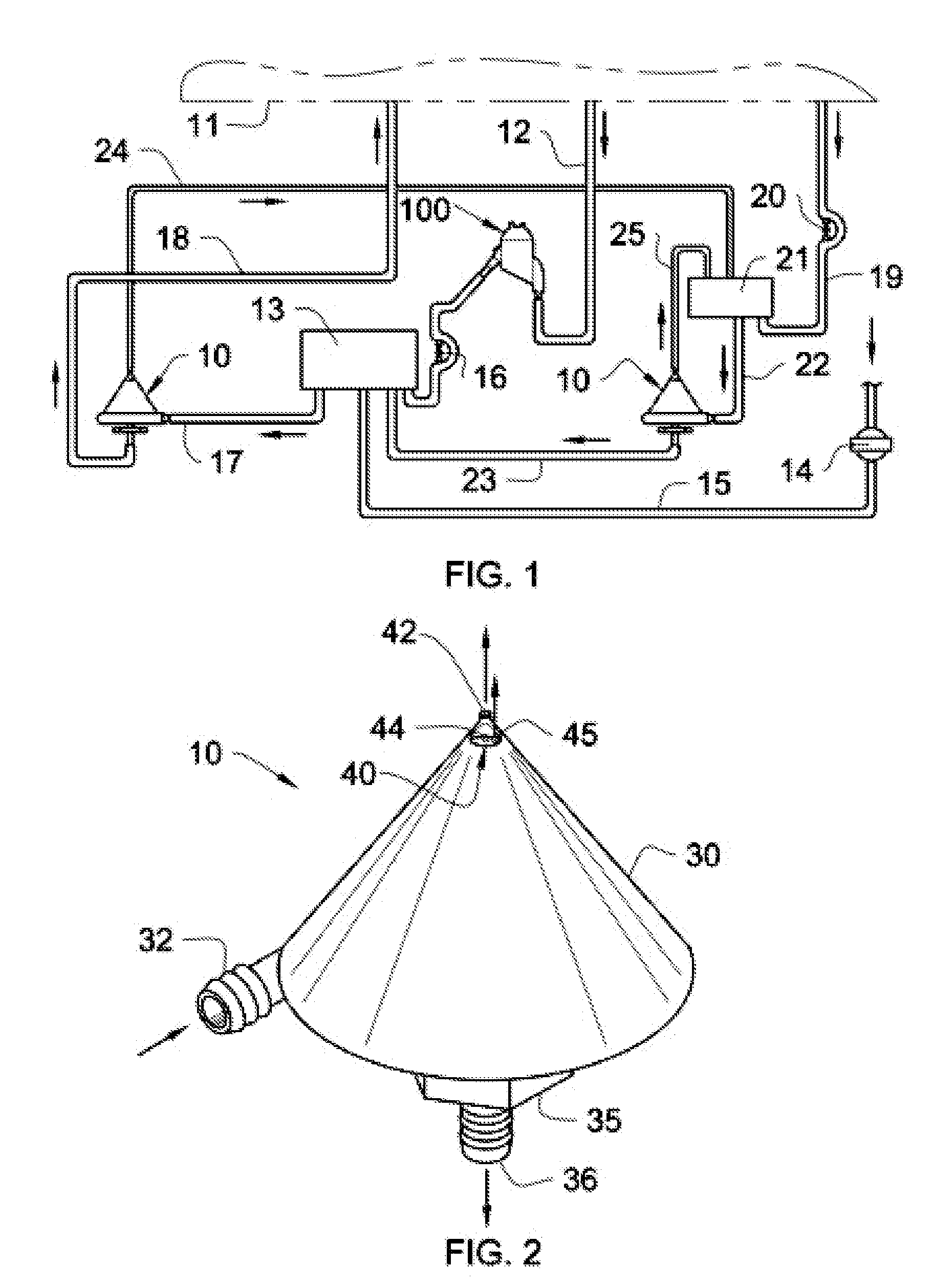
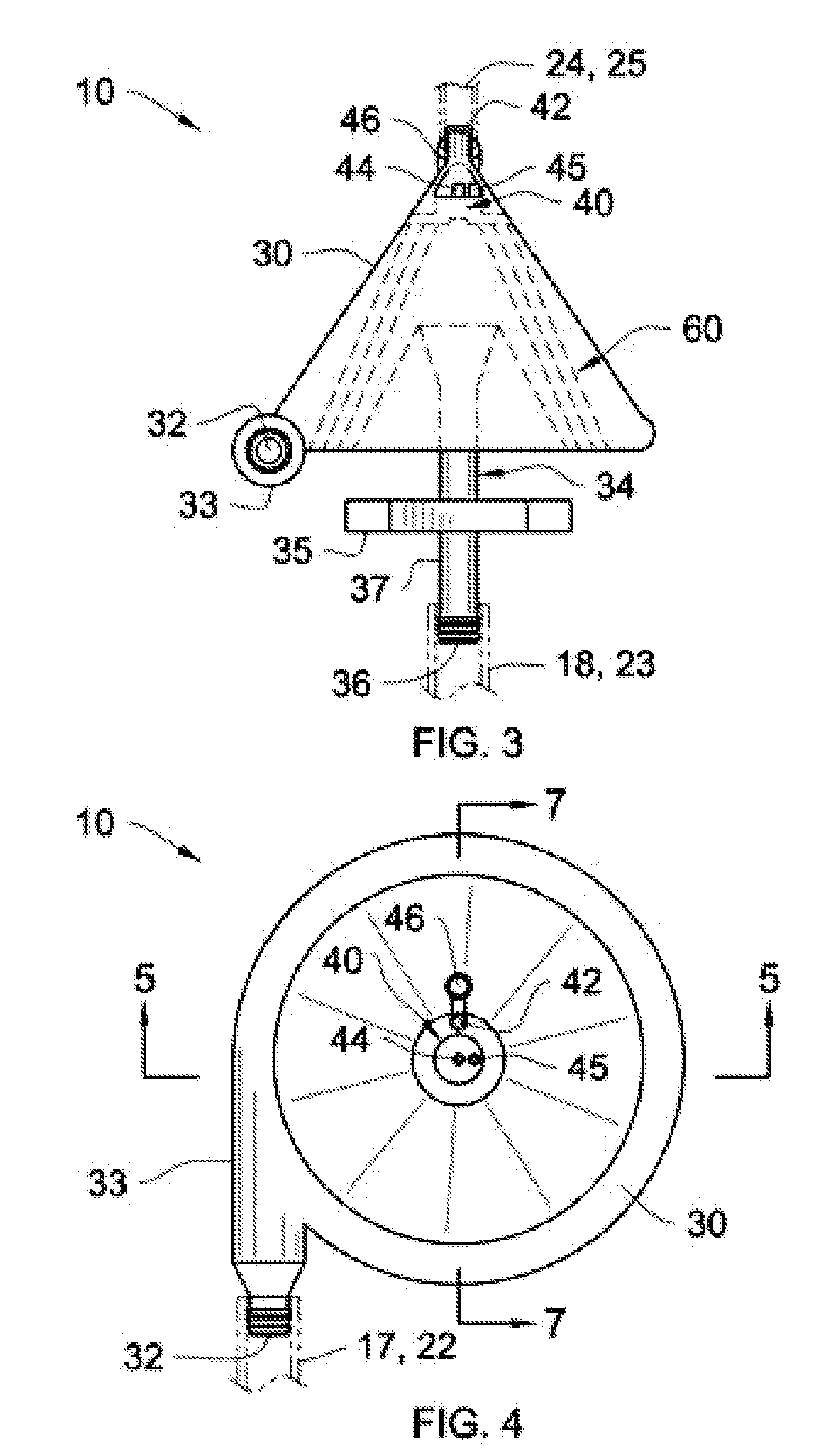
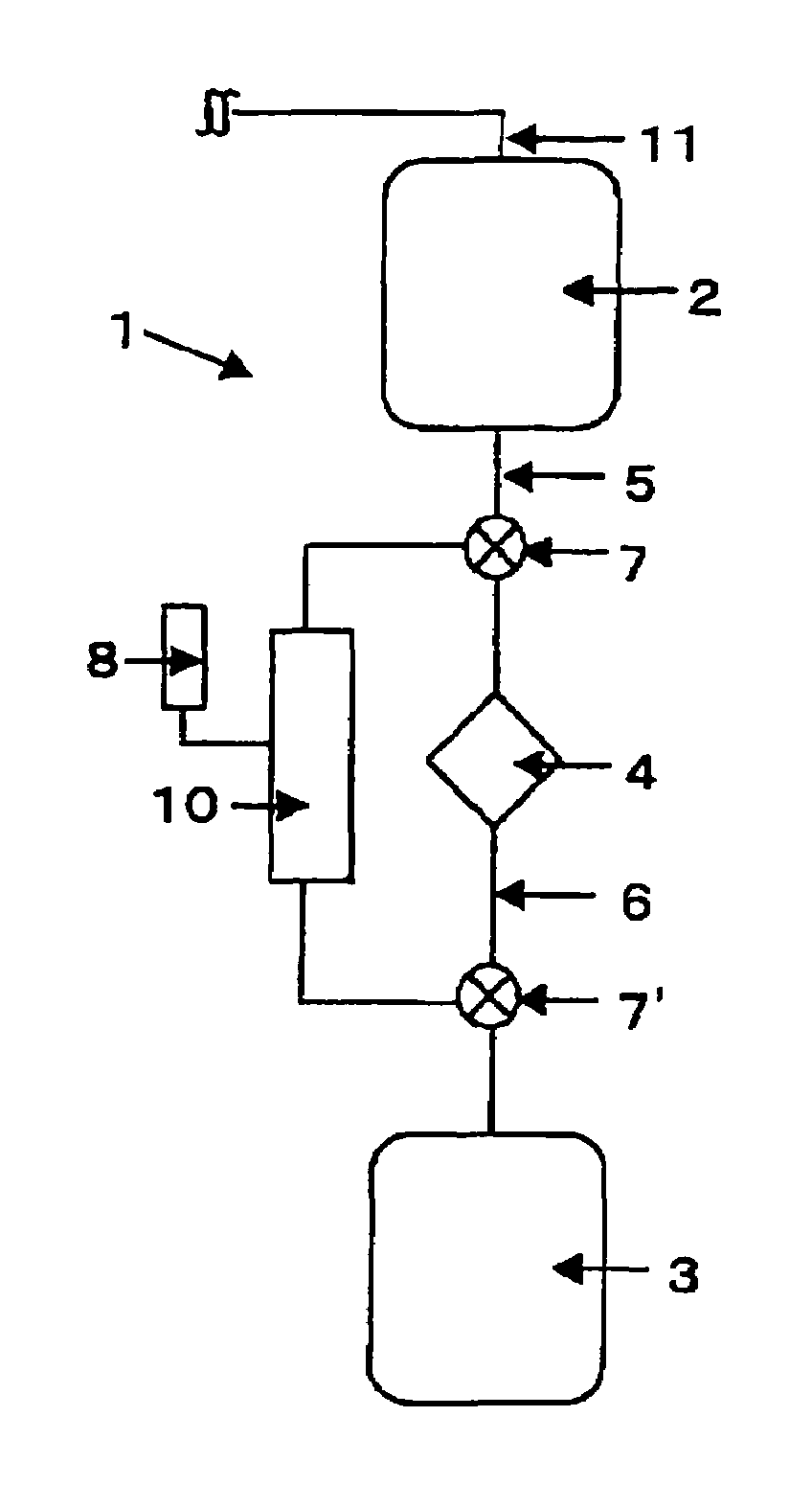
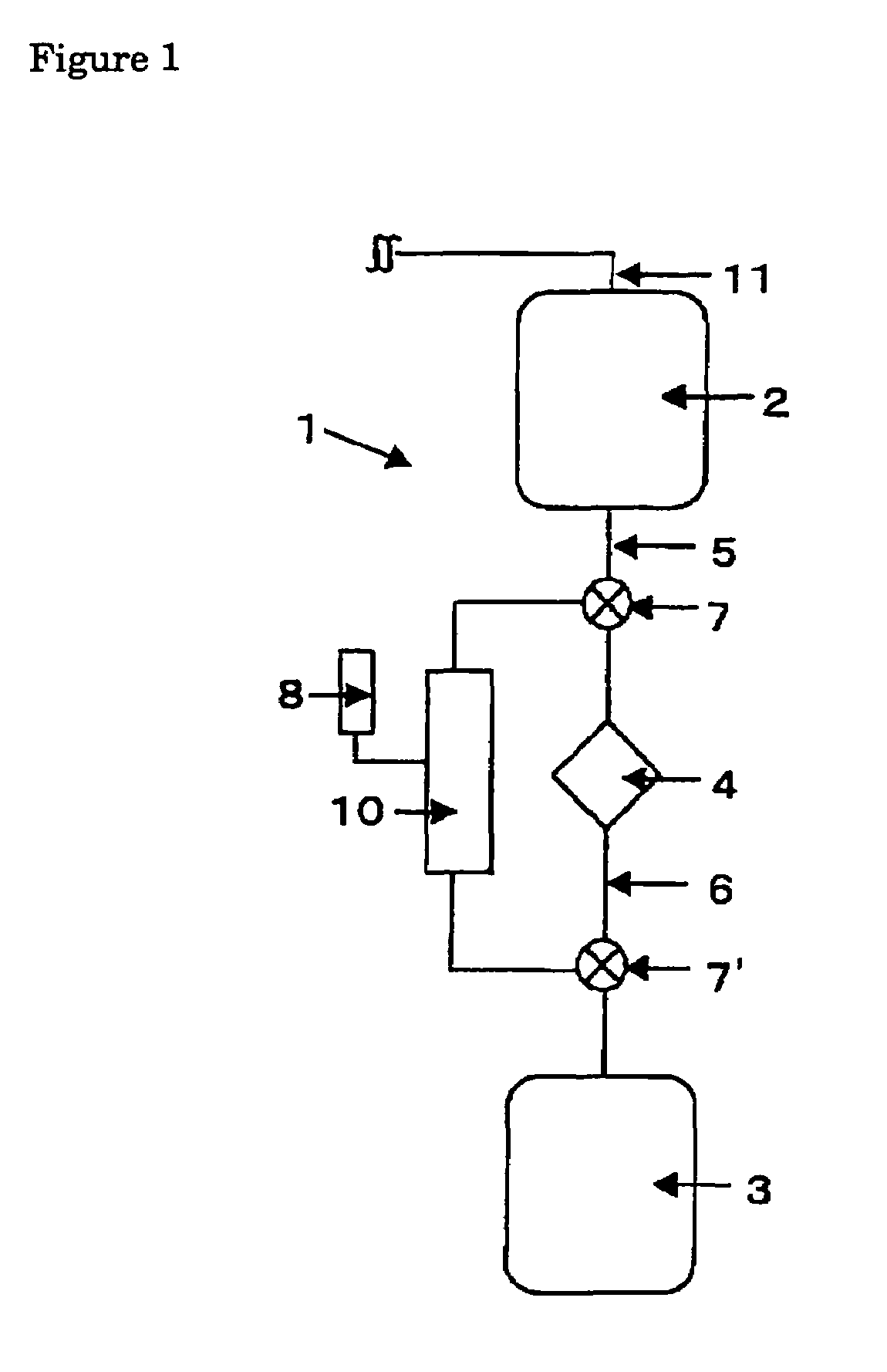
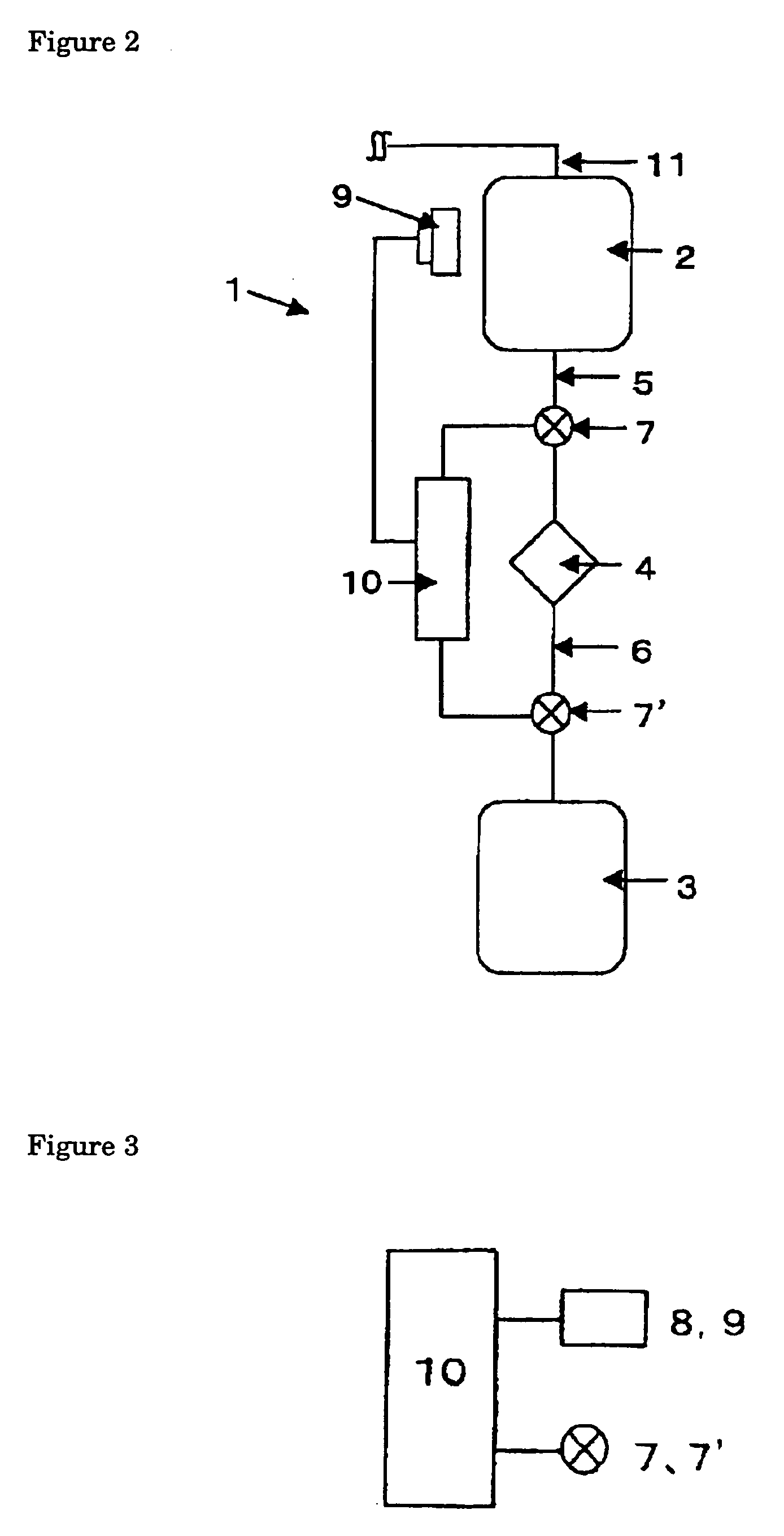
InactiveUS20050131332A1Easily set up sterile blood therapy systemImprove efficiencySemi-permeable membranesHaemofiltrationPositive pressureSorbent
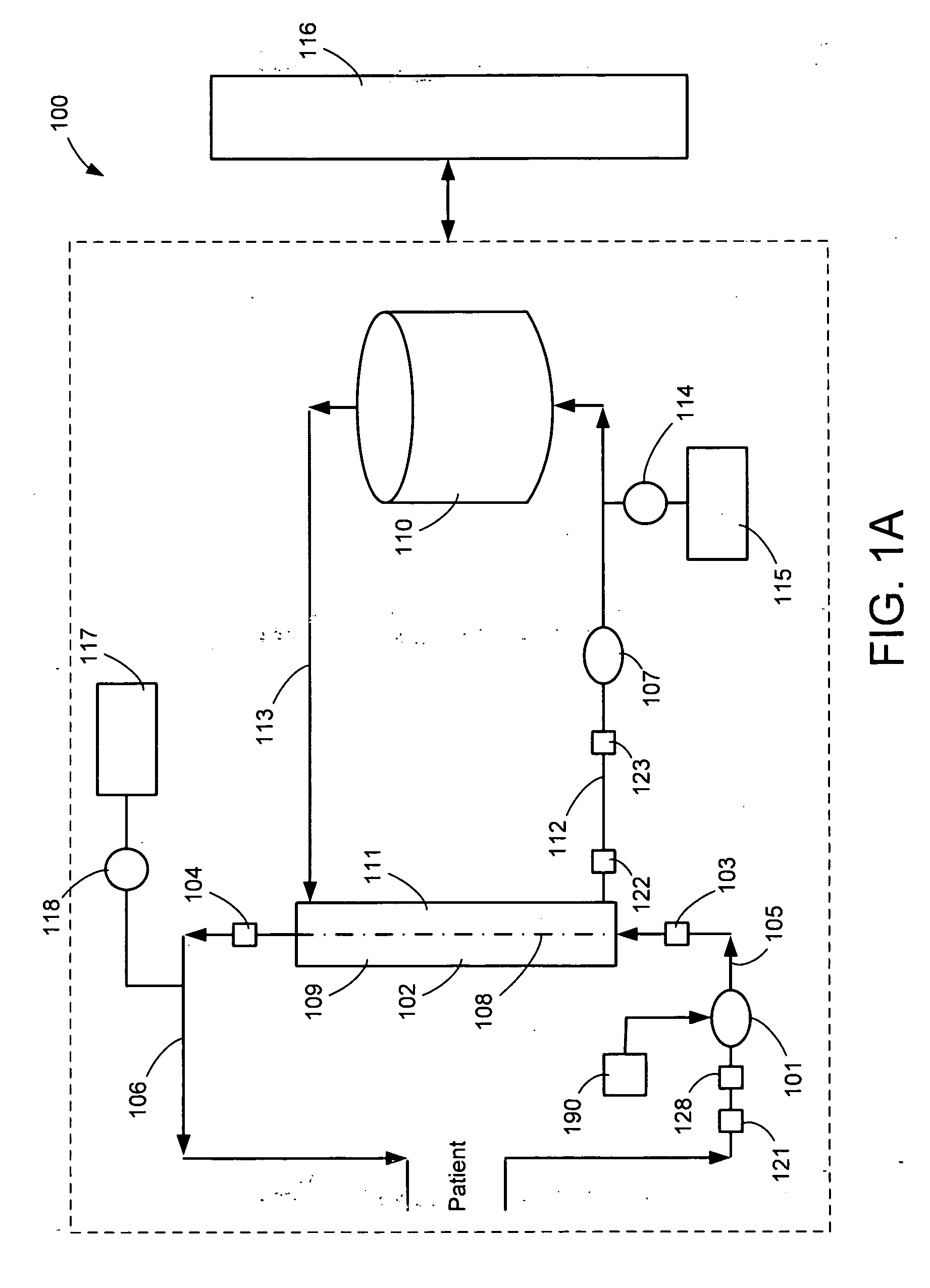
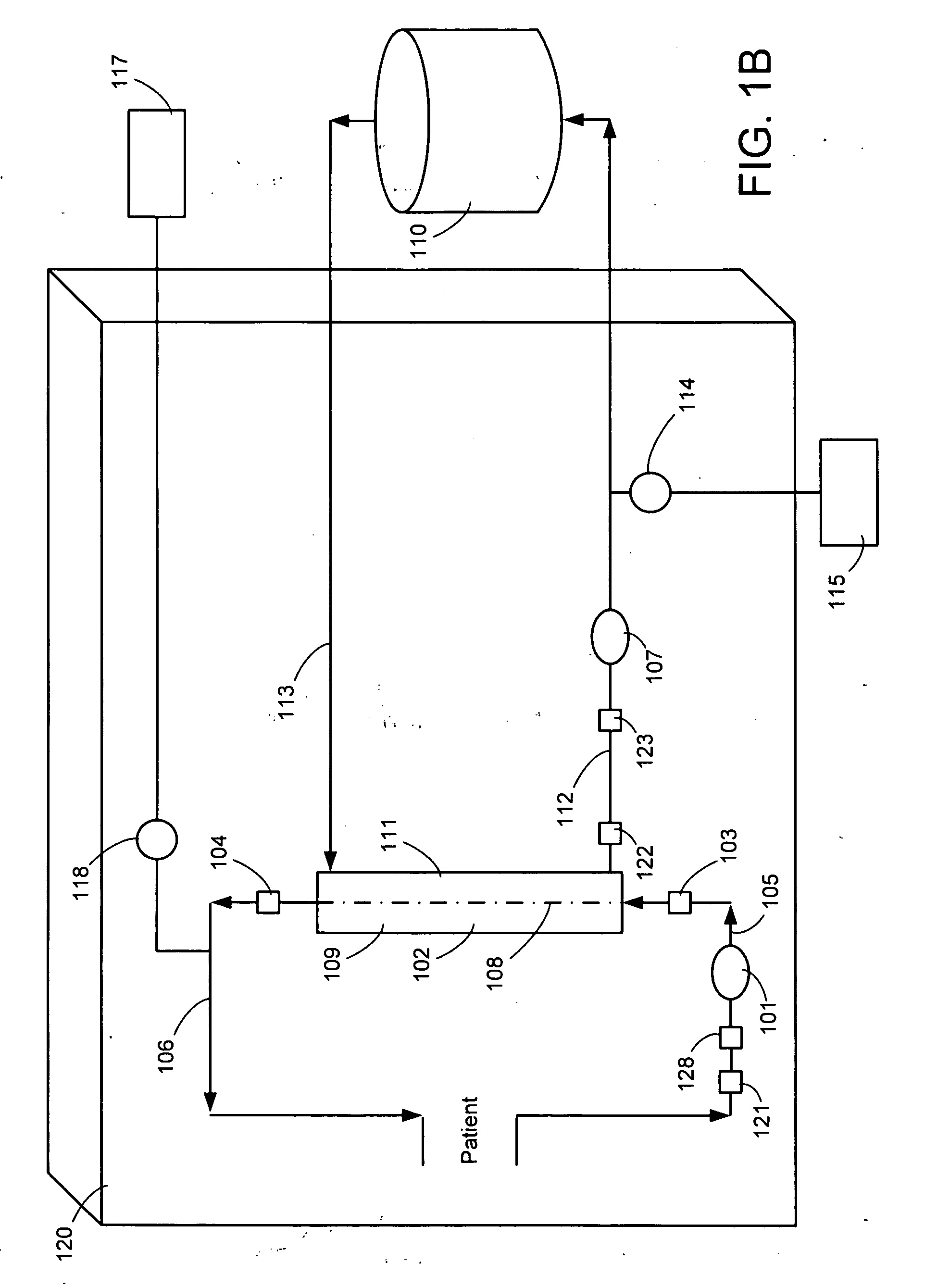
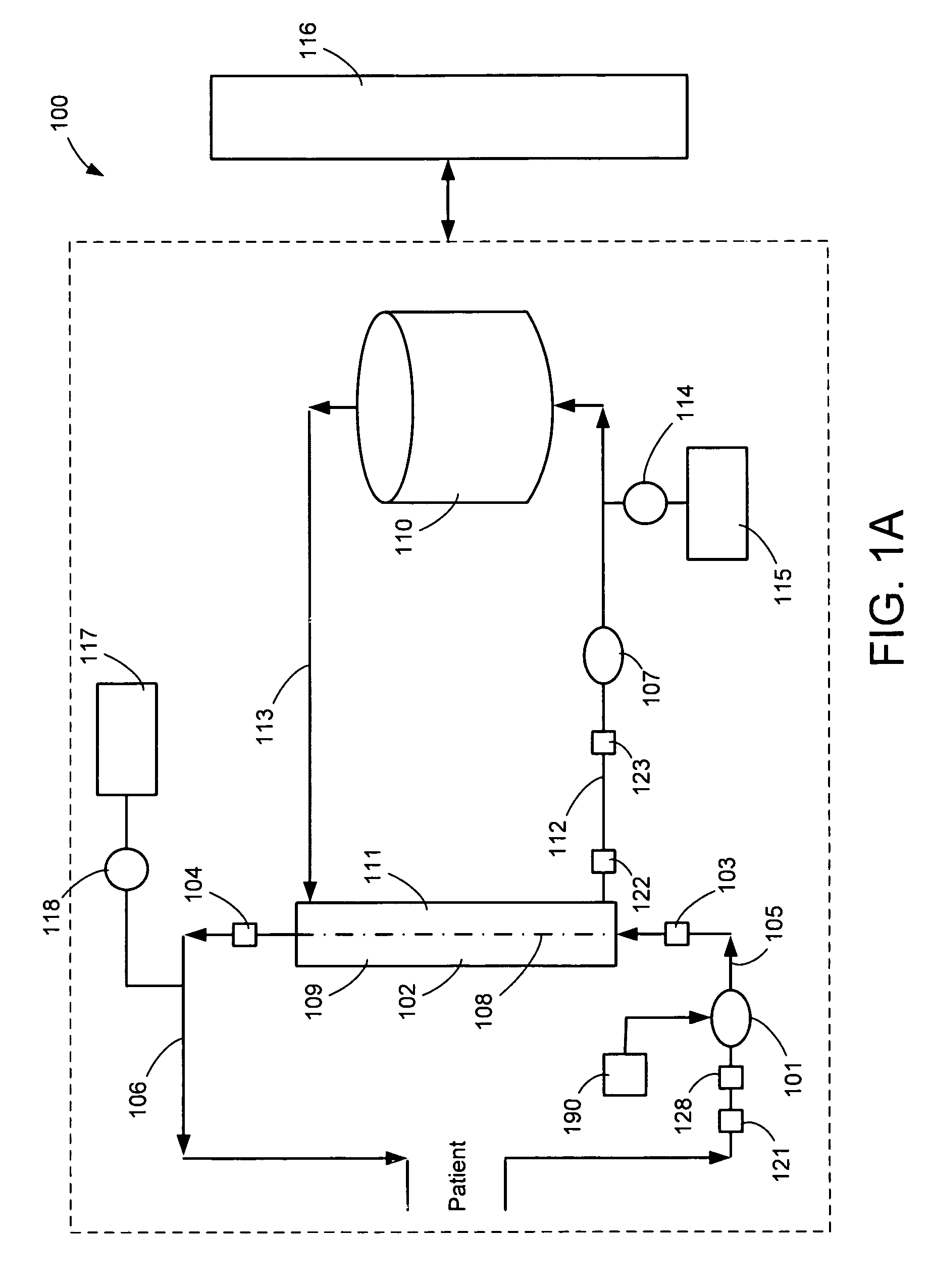
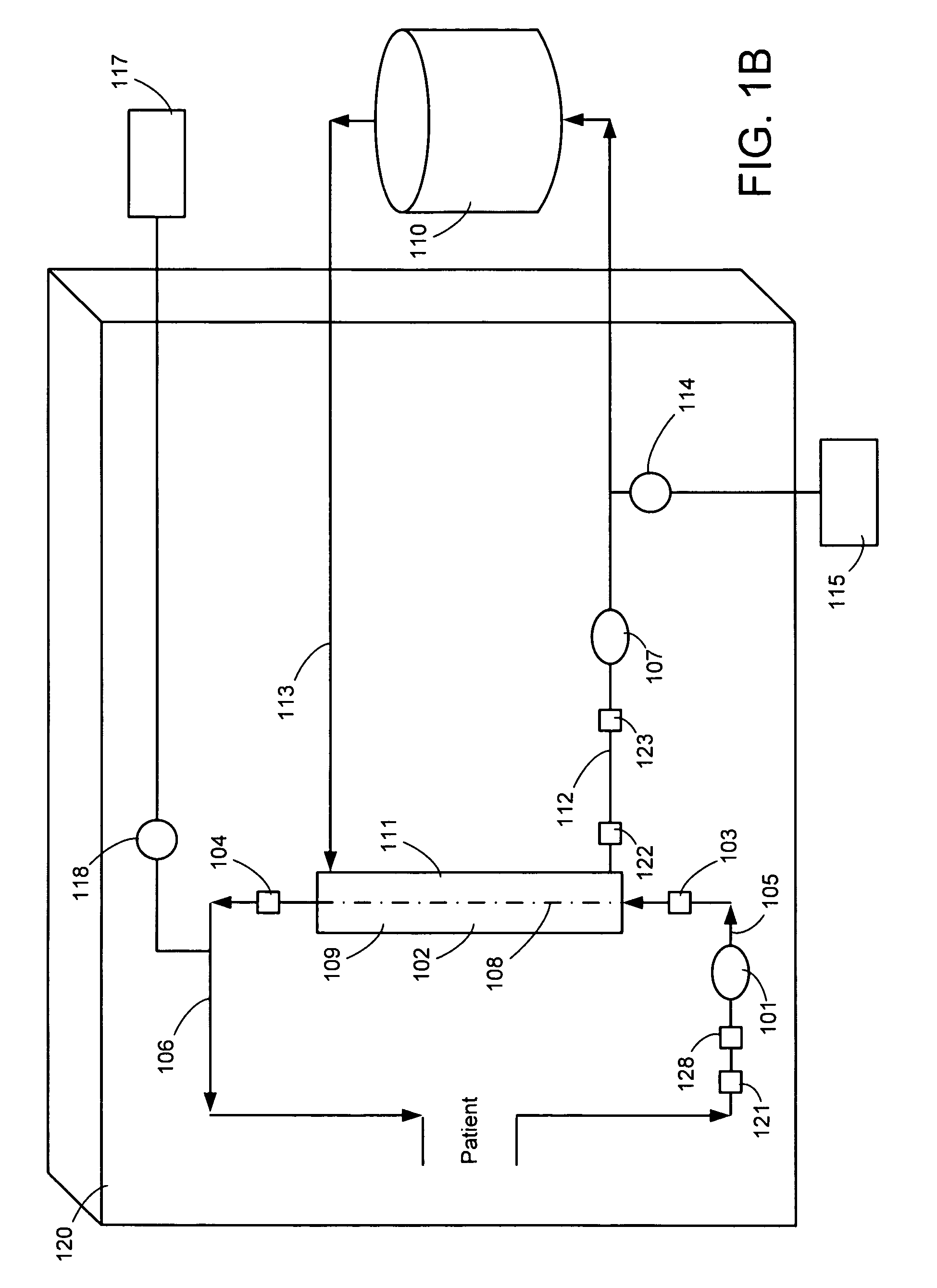
A system, method and apparatus for performing a renal replacement therapy is provided. In one embodiment, two small high flux dialyzers are connected in series. A restriction is placed between the two dialyzers in the dialysate flow path. The restriction is variable and adjustable in one preferred embodiment. The restriction builds a positive pressure in the venous dialyzer, causing a high degree of intentional backfiltration. That backfiltration causes a significant flow of dialysate through the high flux venous membrane directly into the patient's blood. That backfiltered solution is subsequently ultrafiltered from the patient from the arterial dialyzer. The diffusion of dialysate into the venous filter and removal of dialysate from the arterial dialyzer causes a convective transport of toxins from the patient. Additionally, the dialysate that does not diffuse directly into the patient but instead flows across the membranes of both dialyzers provides a diffusive clearance of waste products.
Owner:BAXTER HEALTHCARE SA +1
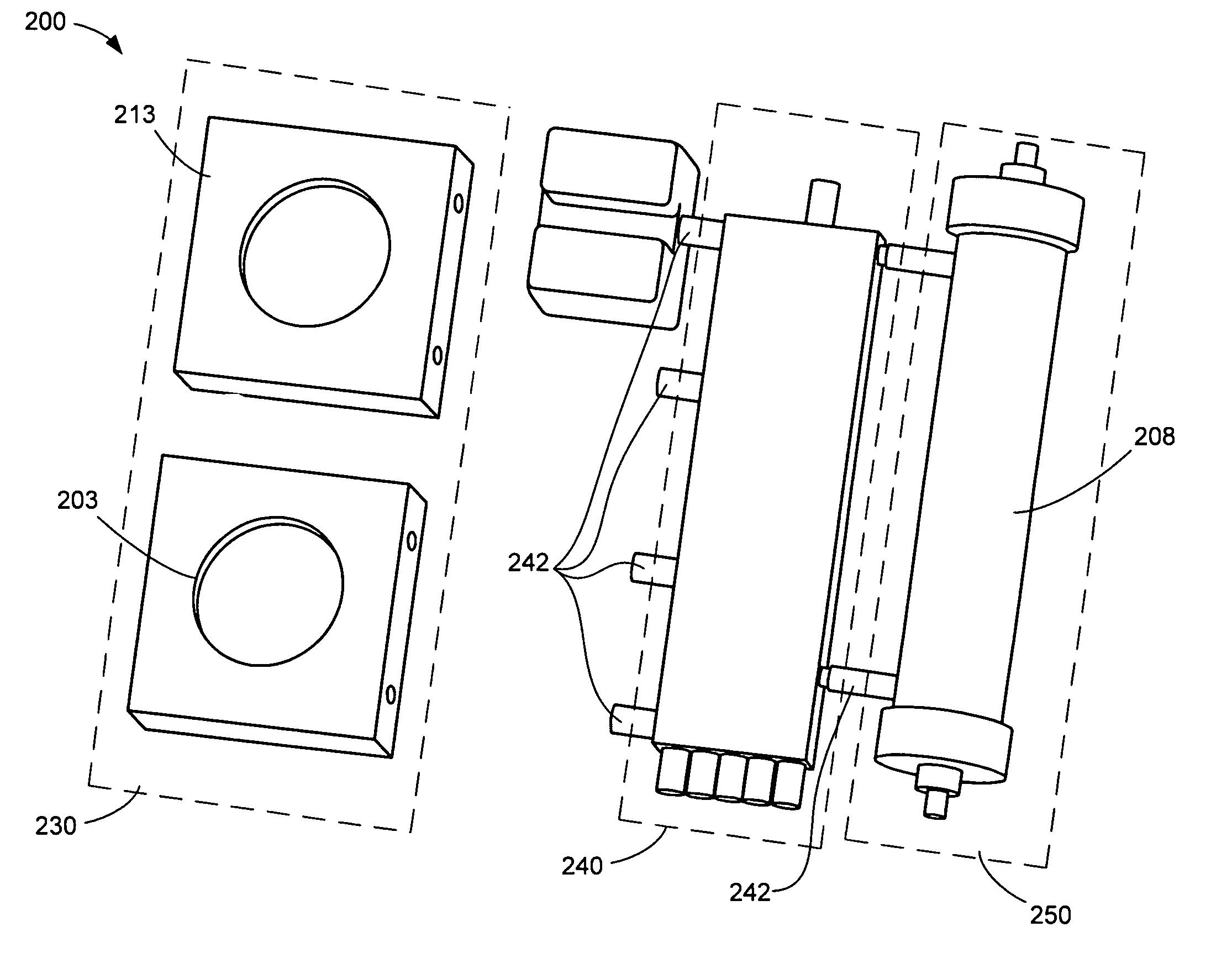
Manifolds for Use in Conducting Dialysis
The present invention is directed to novel systems for conducting the filtration of blood using manifolds. The manifolds integrate various sensors and have fluid pathways formed therein to direct fluids from various sources through the requisite blood filtration or ultrafiltration system steps.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
Manifolds for use in conducting dialysis
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
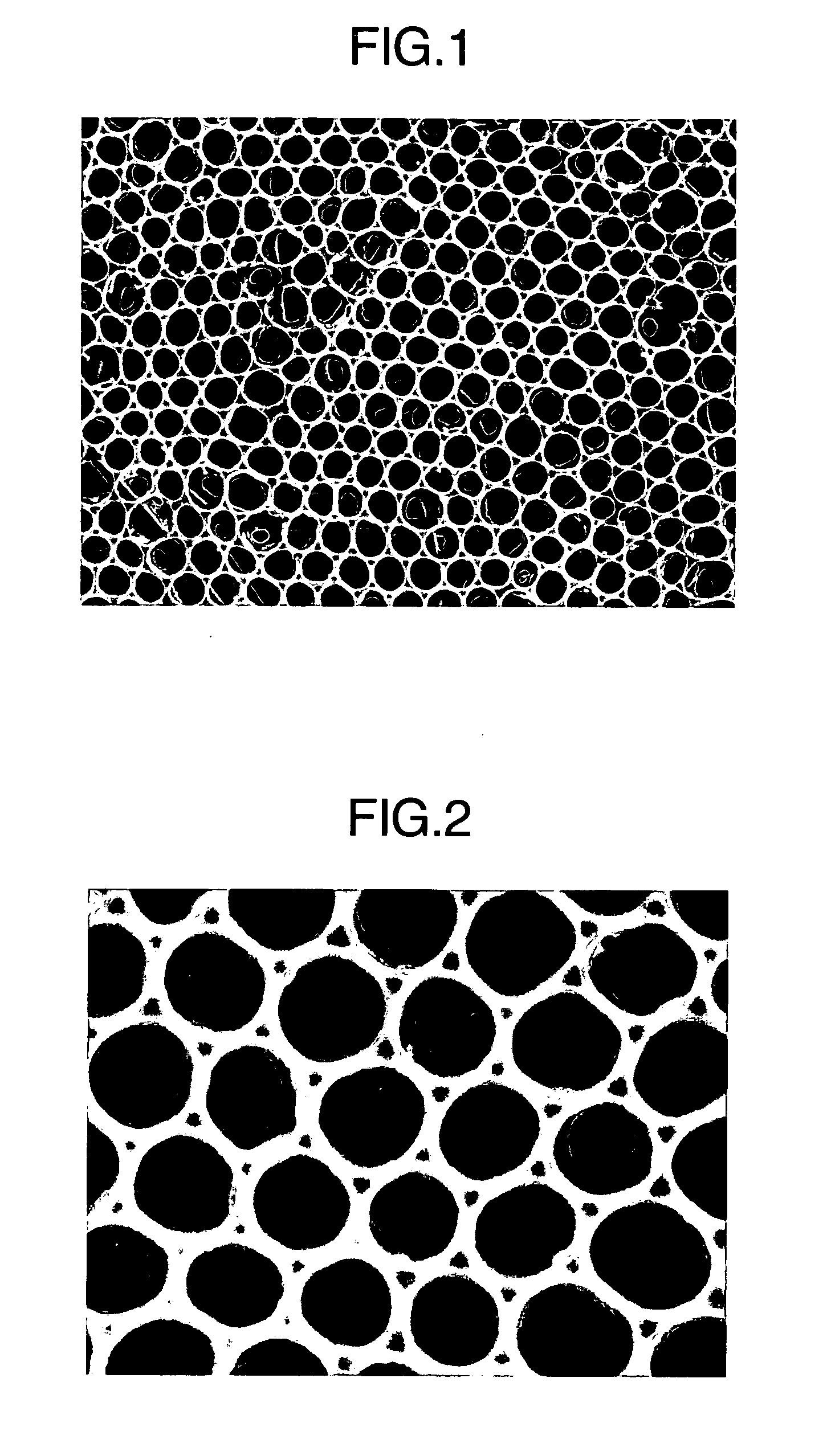
Composite porous membrane and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20070029256A1Good size uniformityLow filtration resistanceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWhite blood cellMicron size
[Problems]To provide a membrane material that realizes effective and efficient separation of a target substance of micron size, being easy to handle and that can be worked into various forms; a blood filtration membrane and a leukocyte removing filter unit that realizes a substantial reduction of filter material volume while retaining high capability of removing leukocytes, thereby reducing the loss of hemocyte suspension; and a cell culturing diaphragm suitable for co-culturing and a relevant method of cell culturing. [Means for Solving Problems]There is provided a composite porous membrane comprising a porous membrane comprised of an organic polymeric compound, and a supporting porous membrane adjacent to the porous membrane, characterized in that the organic polymeric compound constituting the porous membrane penetrates in at least part of a surface adjacent to porous membrane of the supporting porous membrane, the porous membrane having specified opening ratio, average pore diameter, standard deviation of pore diameter, ratio of through pore, average membrane thickness, standard deviation of membrane thickness and internal structure, and that the supporting porous membrane has communicating pores of 0.5D μm or greater average pore diameter. Further, there are provided a blood filtration membrane comprising the composite porous membrane; a leukocyte removing filter unit comprising the composite porous membrane as a second filter; and, utilizing the composite porous membrane, a cell culturing diaphragm and method of cell culturing.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI MEDICAL CO LTD
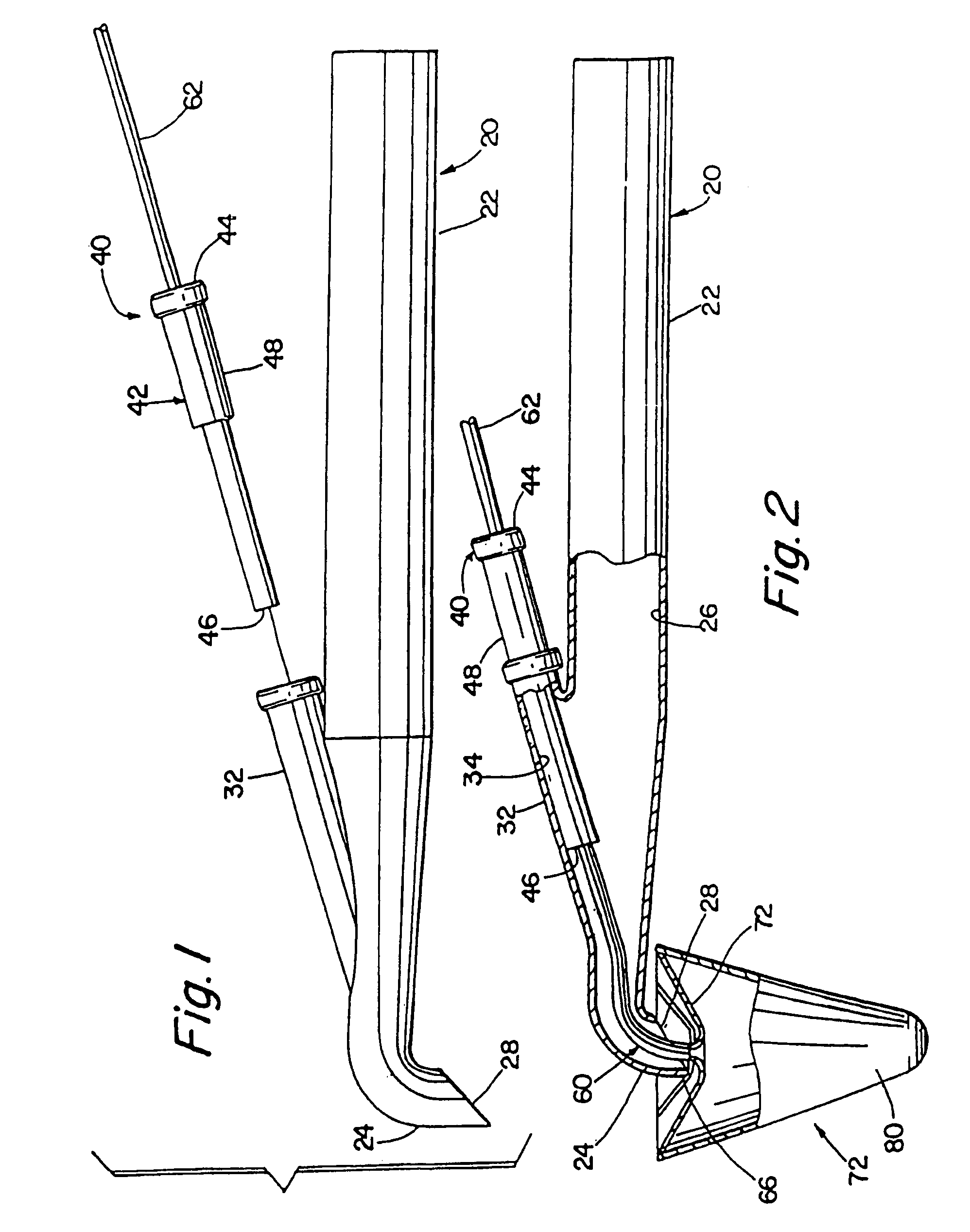
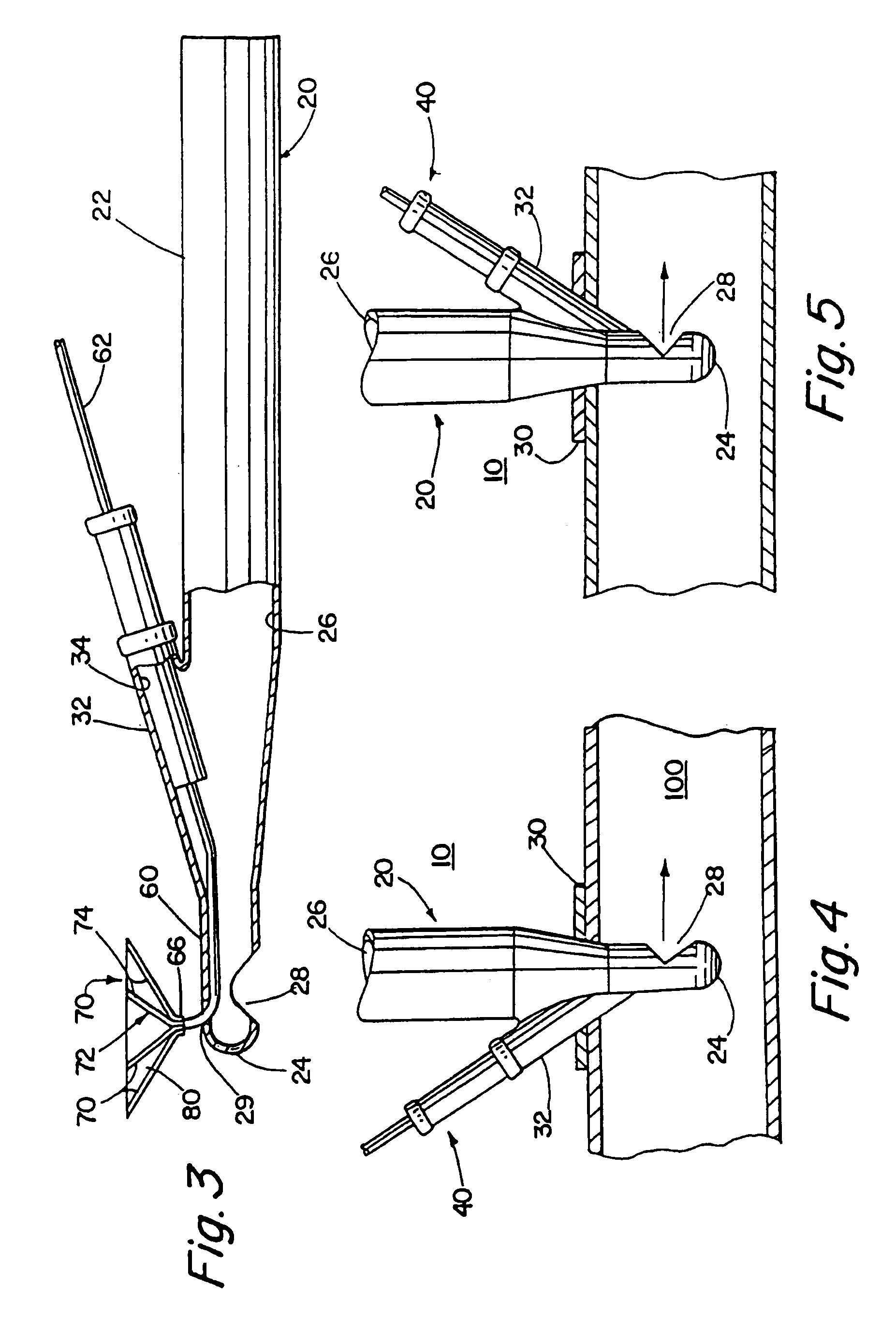
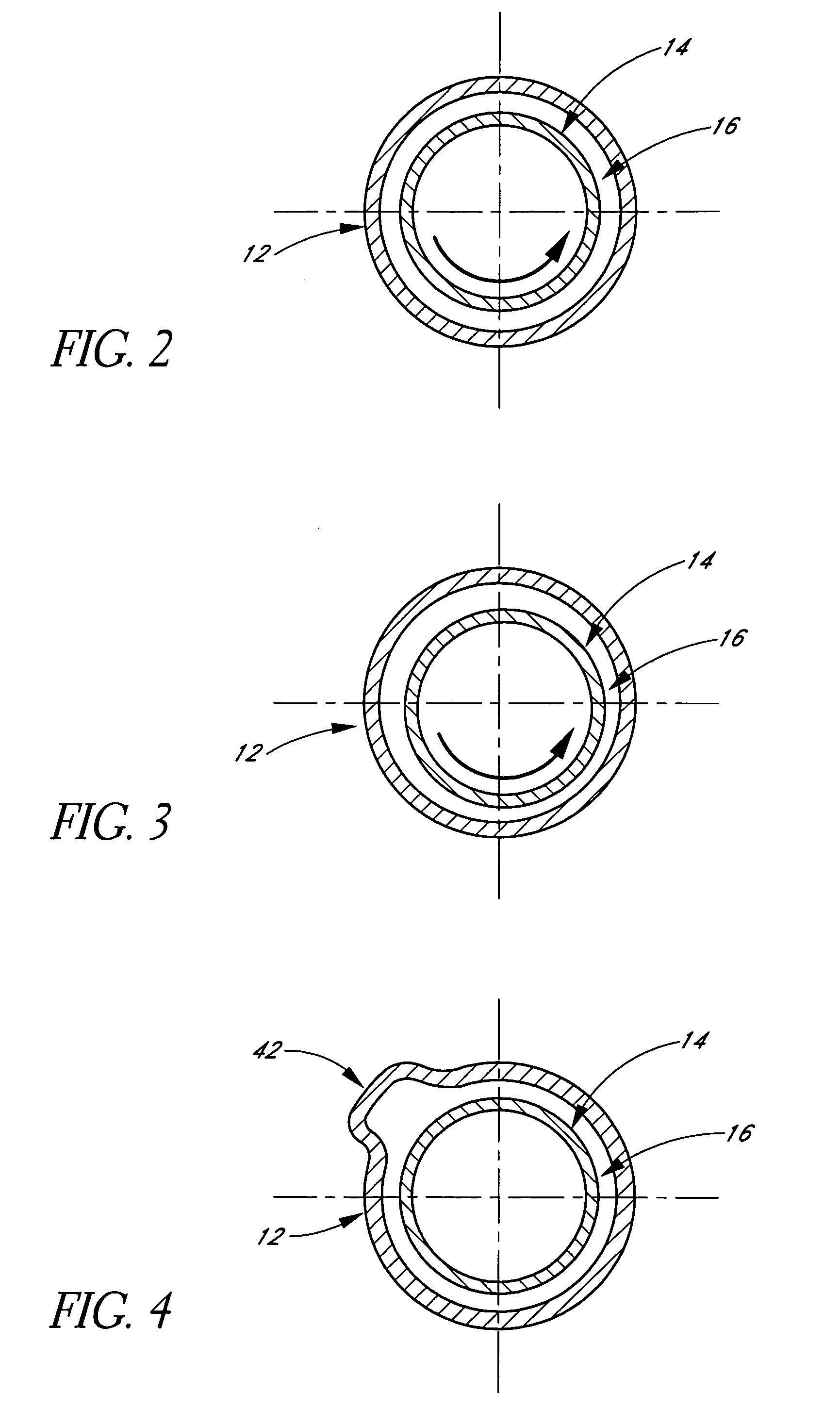
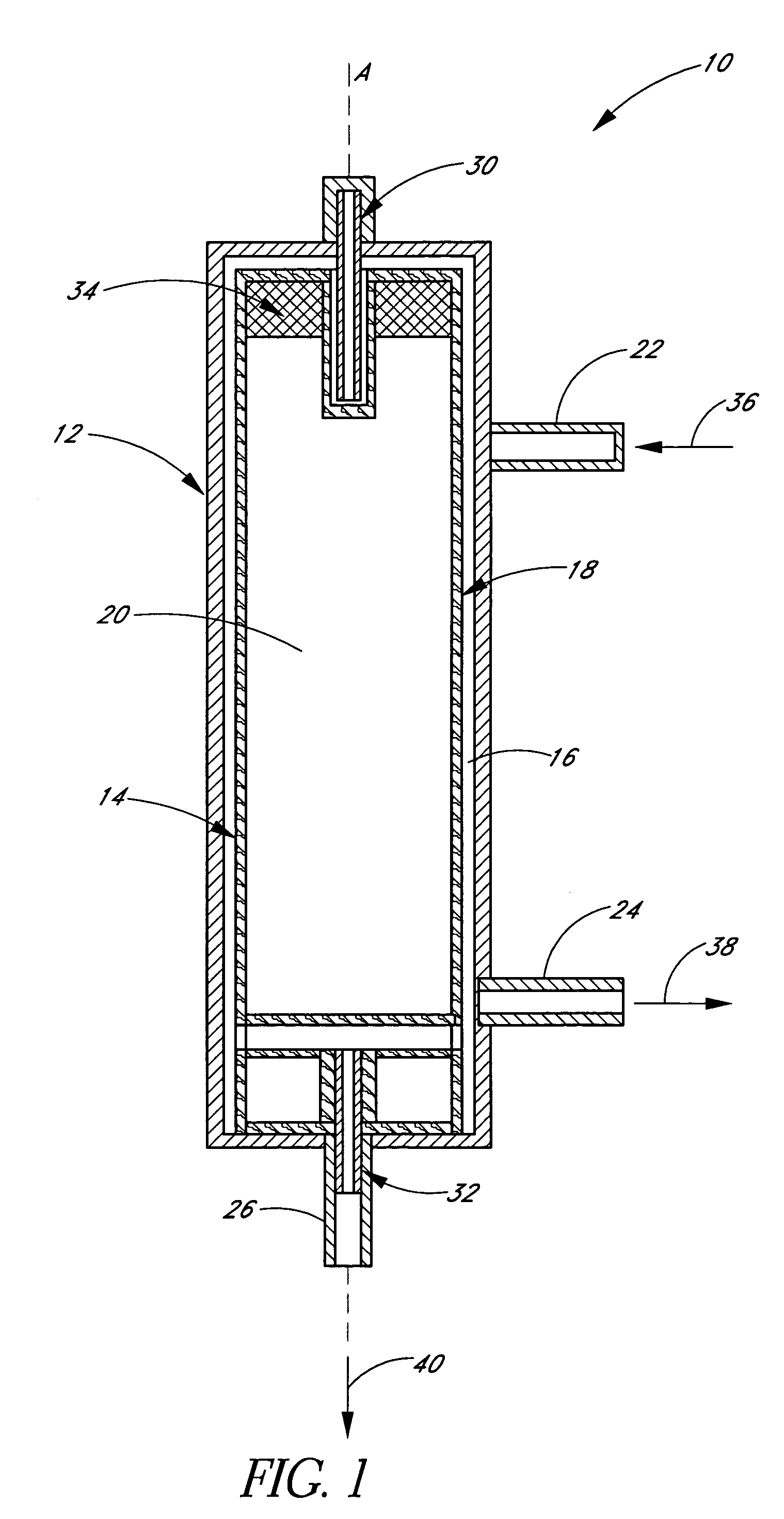
Adjustable blood filtration device
InactiveUS7014648B2Convenient commandPrevent escapeDiagnosticsSurgeryMedical deviceBiomedical engineering
A medical device comprising a tubular member having a proximal end, a distal end, and a lumen extending therebetween. An adjustable filter is provided having a frame and a mesh disposed about the frame. The frame is generally circular when deployed and has a first point, a first arc extending 180° from the first point to a second point on the circular frame that is opposite the first point, and a second arc extending 180° from the first point to the second point. The filter is deployed by advancing the frame distally through the tubular member with the second point leading and the first point trailing.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Haemodialfiltration method and apparatus
InactiveUS20100187176A1Extended service lifeAvoid performance degradationSolvent extractionMixing methodsBlood pumpToxic material
Device for haemodiafiltration, which comprises a first circuit for a dialysis solution and a second circuit for blood, so that the toxic substances from the blood flow pass into the dialysis liquid within a haemofilter (11), a liquid pump (20) located upstream of the haemofilter (11) in the first dialysis liquid circuit, is adapted for injecting replacement liquid into the dialysis solution flow after a blood pump (15) finishes pumping blood to the interior of the haemofilter (11).
Owner:FUNDACION PARA LA INVESTIGACION BIOMEDICA DEL HOSPITAL GREGORIO MARANON
Two stage hemofiltration that generates replacement fluid
The present invention relates to a system for two-stage blood dialysis of a patient. In one embodiment, the system comprises a first filtration device for receiving the blood from the patient and for producing a first filtrate and processed blood. The system further comprises a second filtration device for receiving the first filtrate and producing replacement fluid and waste product. At least one of the first and second filtration devices preferably comprises a Taylor vortex-enhanced blood filtration device.
Owner:MCLAUGHLIN TRUSTEE OF THE JENNIFER MCLAUGHLIN TRUST JENNIFER K
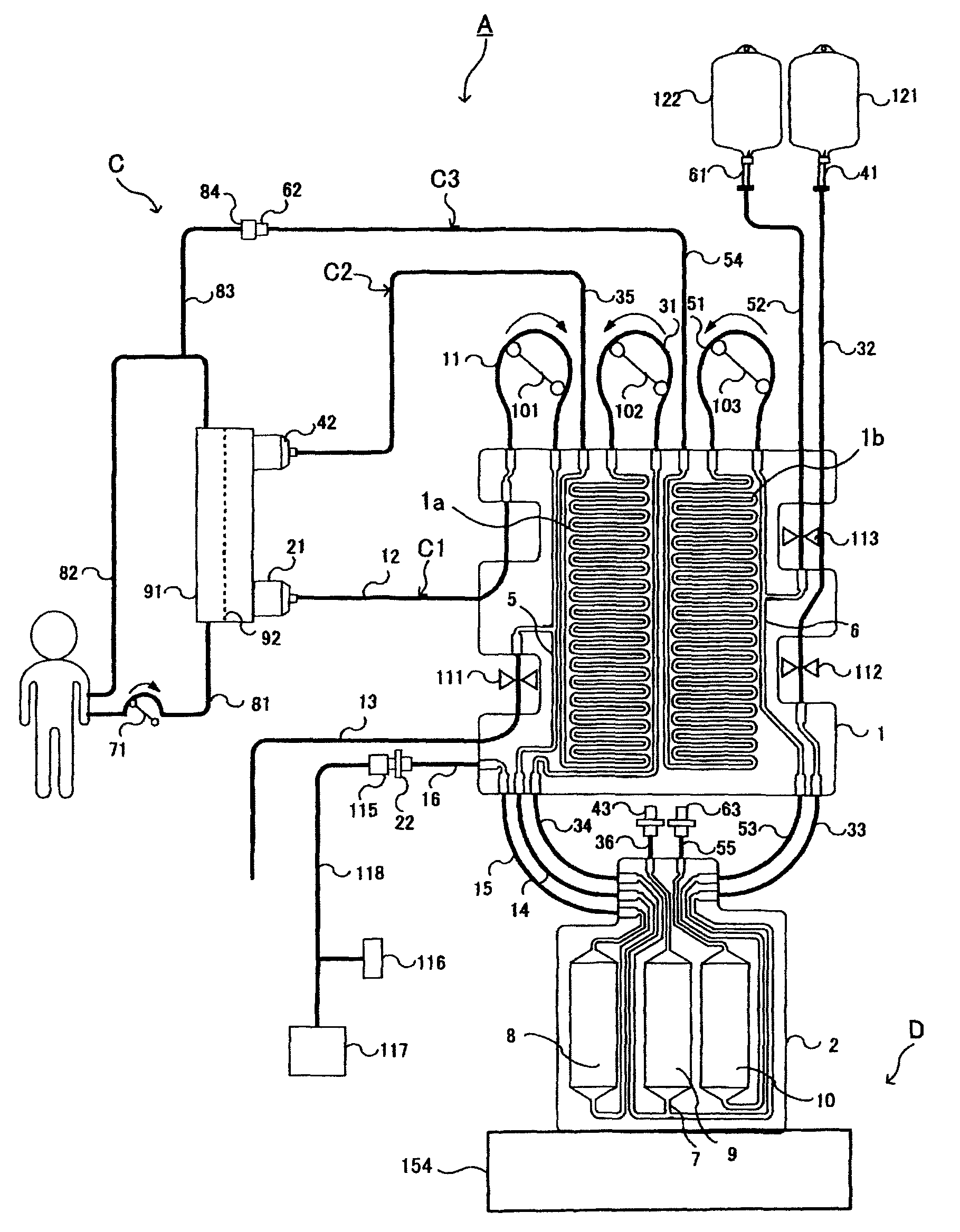
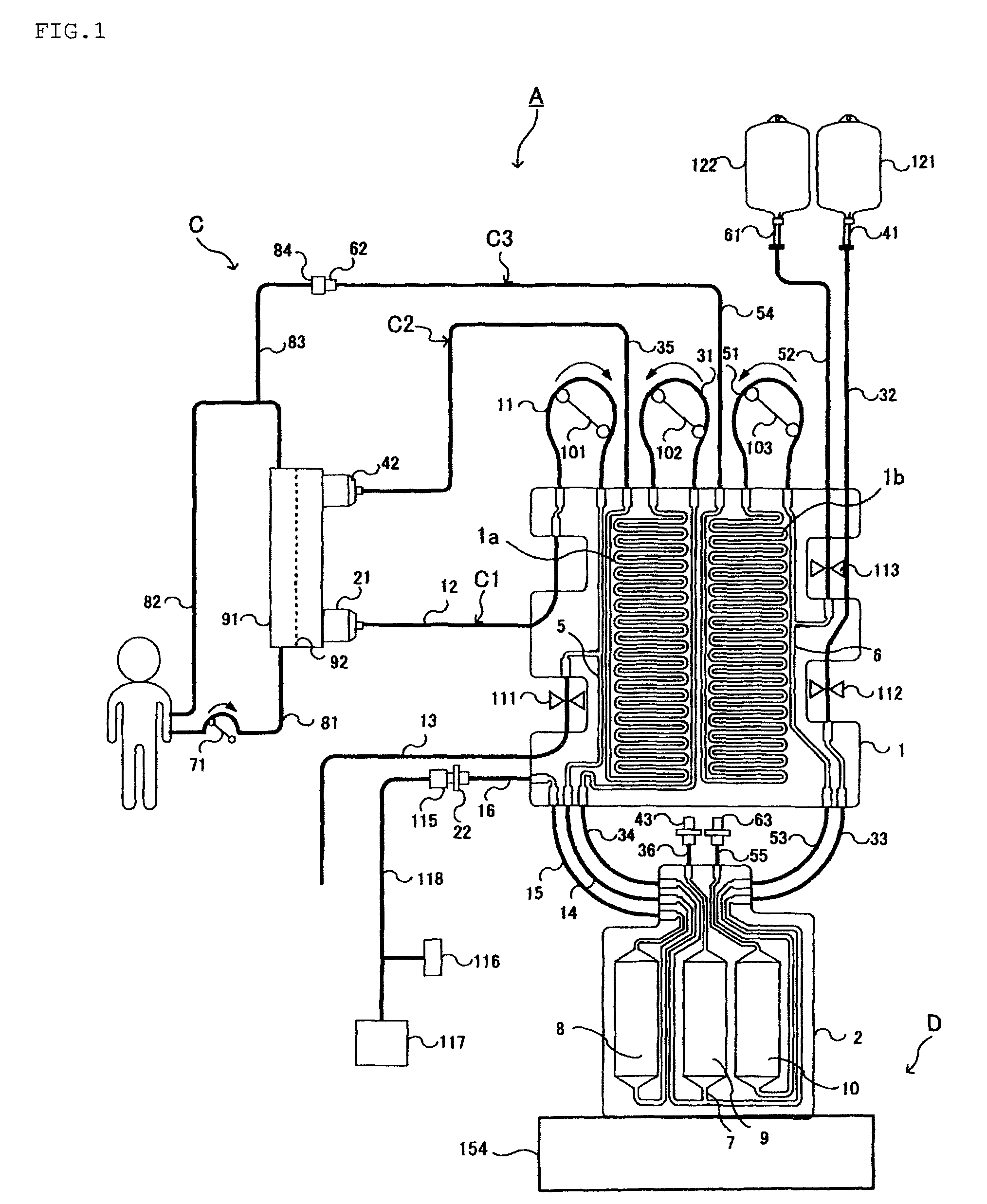
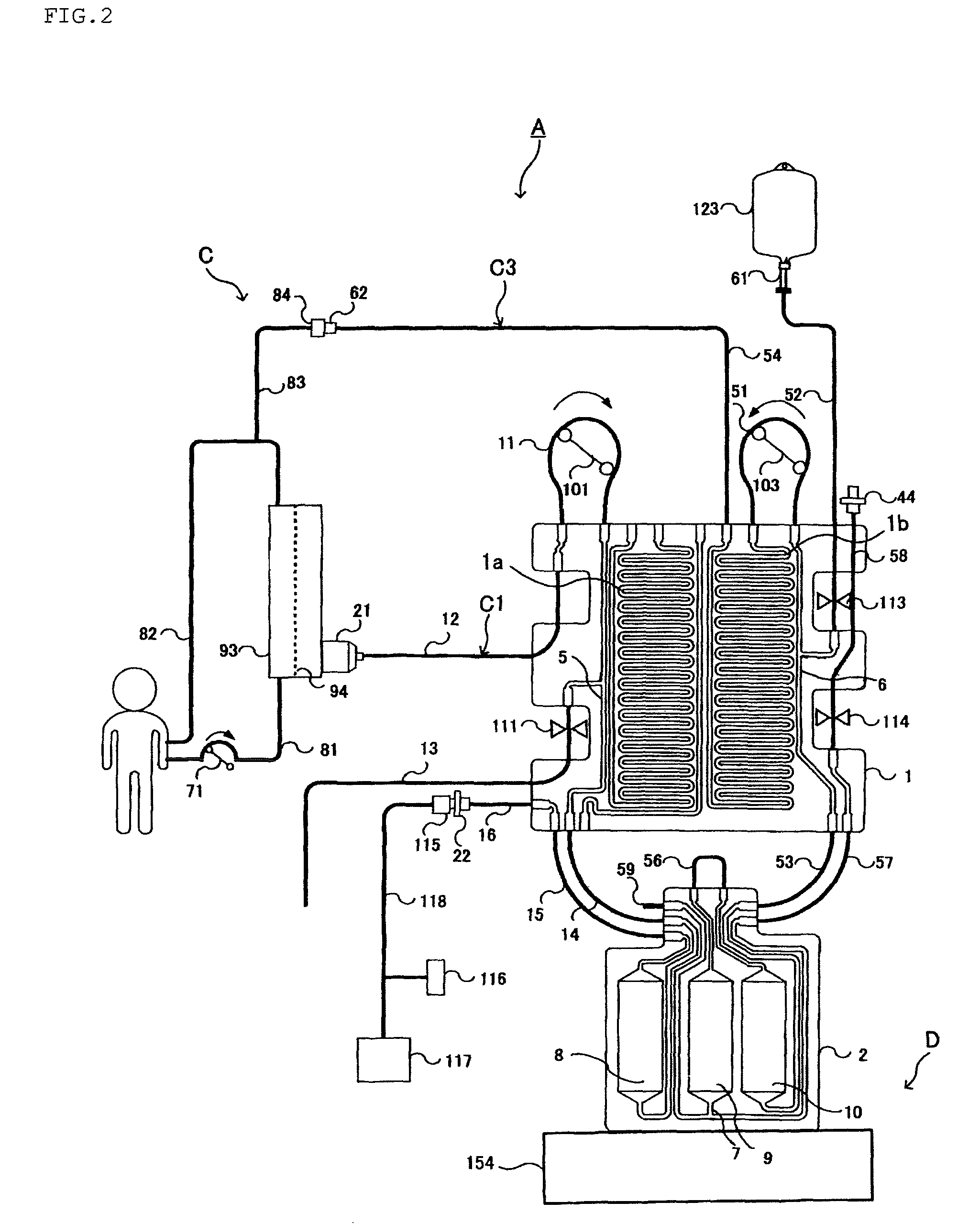
Blood purification system
InactiveUS8202241B2Easy to measureImprove reliabilityElectrotherapyHaemofiltrationHematological testSurgery
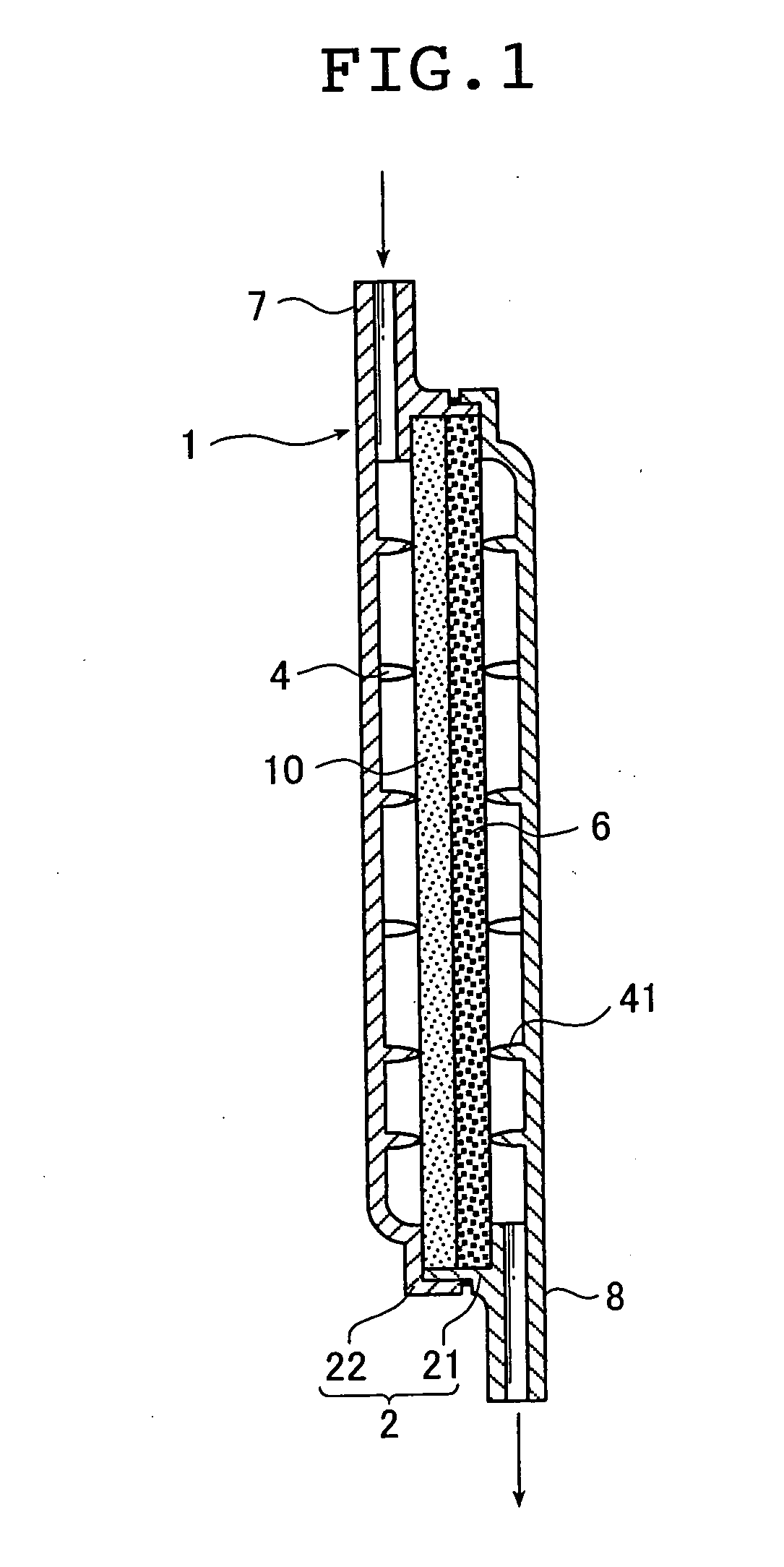
Provision of a blood purification system comprising a blood purification tubing and a blood purification apparatus particularly suitable for use in continuous hemofiltration in which in the treatment of a patient with renal disease, multiple organ failure, and the like, the amount of water removed from the patient and the amount of supply to the patient can be more accurately controlled, and in which preparation operation is easy. A blood purification system comprising a blood purification tubing and a blood purification apparatus wherein the soft tubes of flow paths connecting a first planar panel and a second planar panel, and the location of the soft tubes are selected to satisfy a formula of a predetermined condition.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI MEDICAL CO LTD
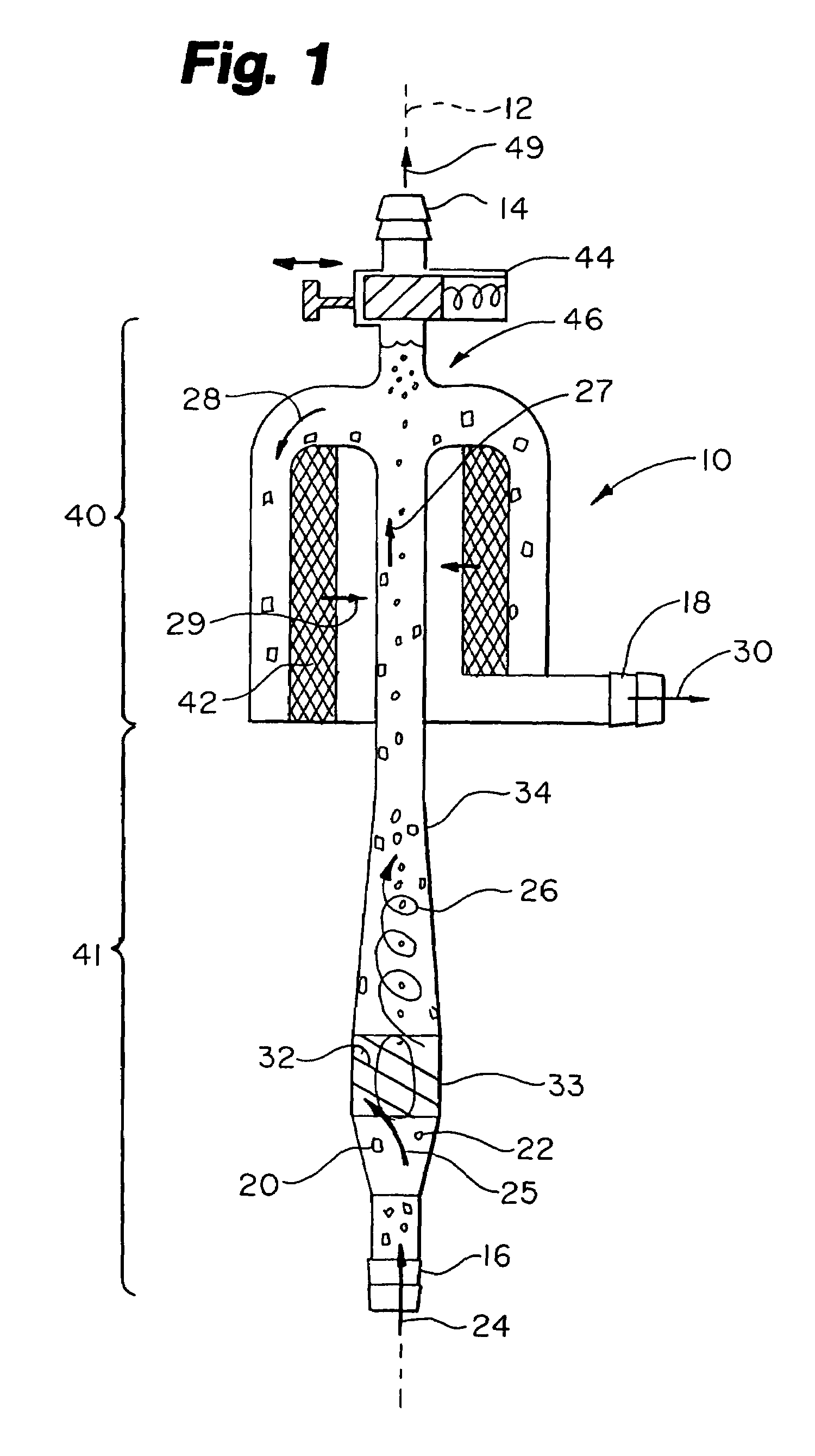
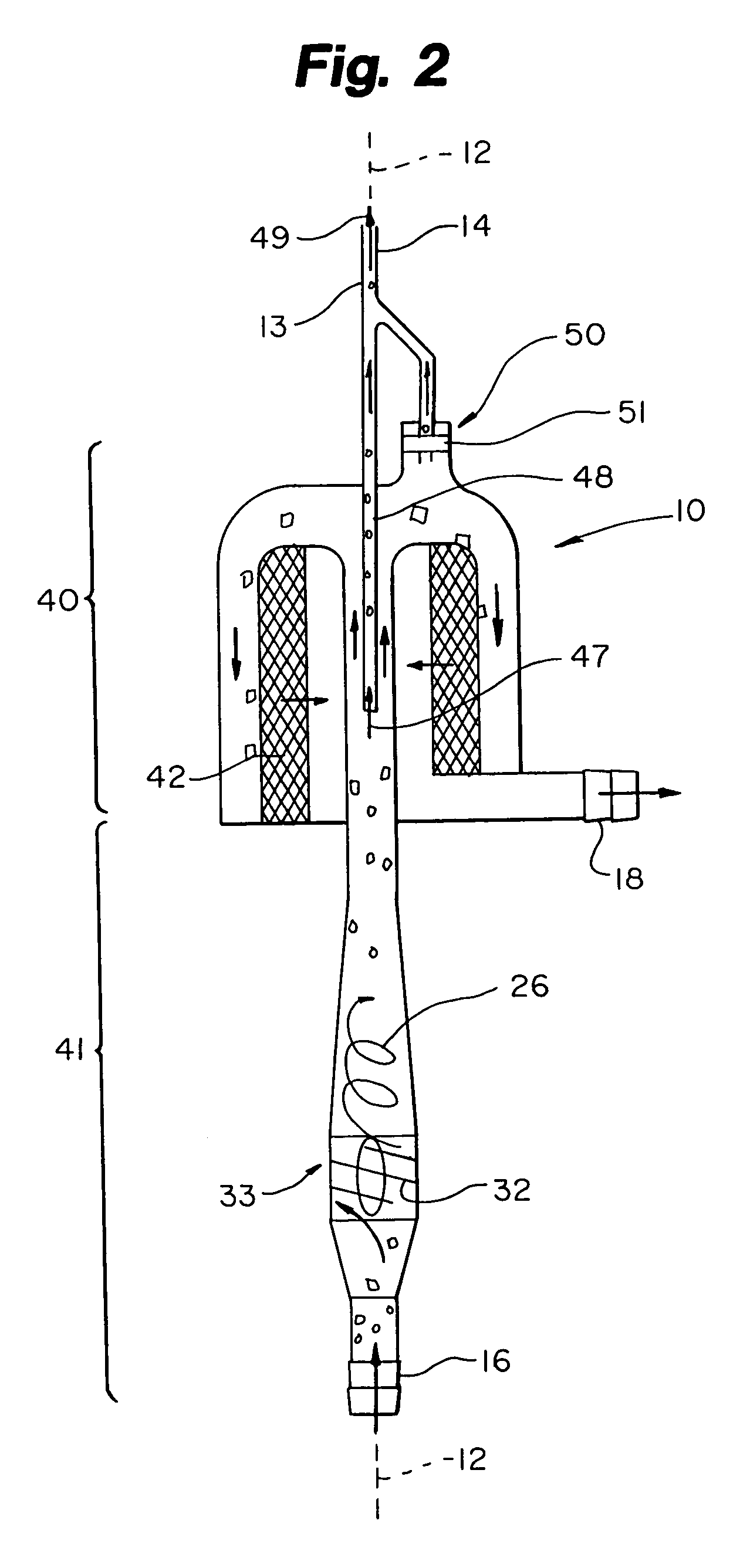
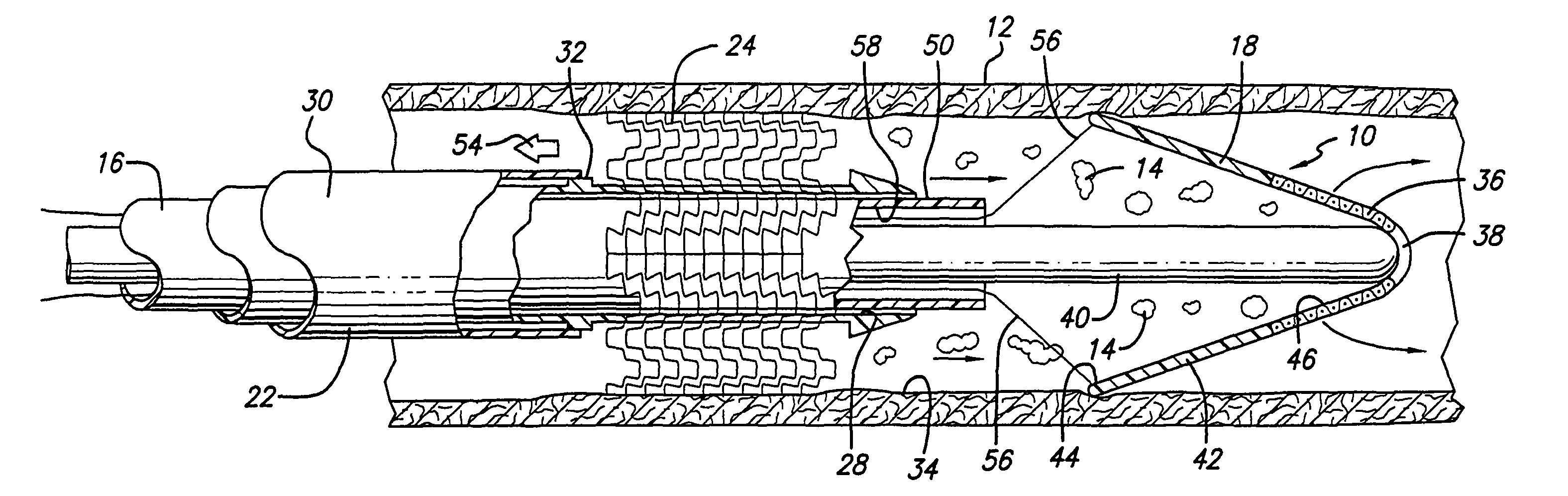
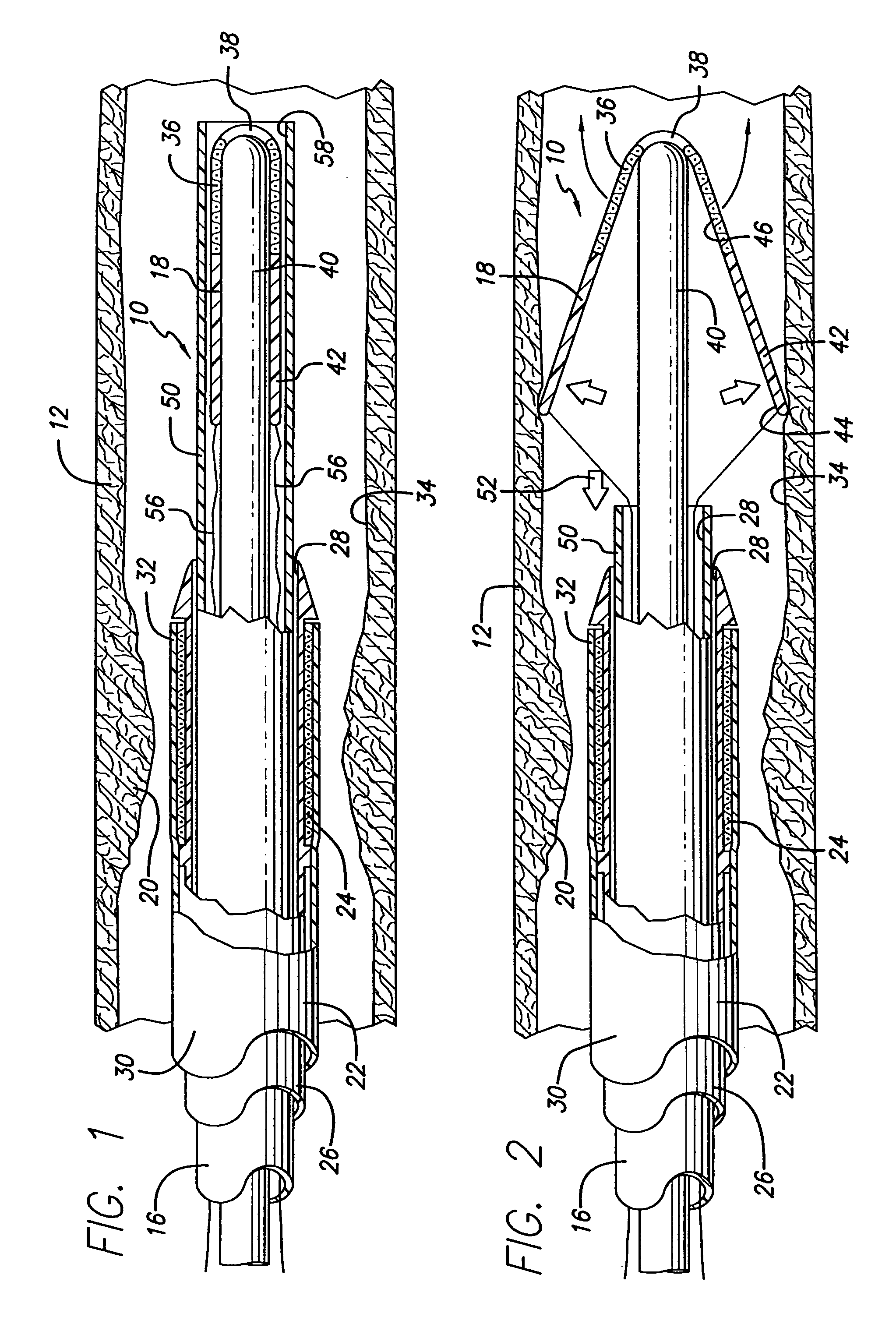
Extracorporeal Blood Filter System
InactiveUS20080230473A1Effective guidanceEasy and efficient to manufactureLiquid degasificationSettling tanks feed/dischargeFilter systemEngineering
A blood filter system used for the sequential filtering of blood while actively removing air bubbles and debris comprising a filter housing with unique conical, or cylindrical shape, a flared inlet port, a unique up and down blood flow path, a multi-stage sequential filter assembly, an active air purge assembly and a unique downspout assembly with outlet port. The filter housing is adapted so that blood passes from the inlet port through the multi-stage sequential filter assembly to the outlet port following an up and down flow path, while its unique shape and angled filters effectively direct any air bubbles and debris up and out of the blood stream toward the active air purge assembly where they are removed.
Owner:HERBST DANIEL PATRICK
Two stage hemofiltration that generates replacement fluid
The present invention relates to a system for two-stage blood dialysis of a patient. In one embodiment, the system comprises a first filtration device for receiving the blood from the patient and for producing a first filtrate and processed blood. The system further comprises a second filtration device for receiving the first filtrate and producing replacement fluid and waste product. At least one of the first and second filtration devices preferably comprises a Taylor vortex-enhanced blood filtration device.
Owner:MCLAUGHLIN TRUSTEE OF THE JENNIFER MCLAUGHLIN TRUST JENNIFER K
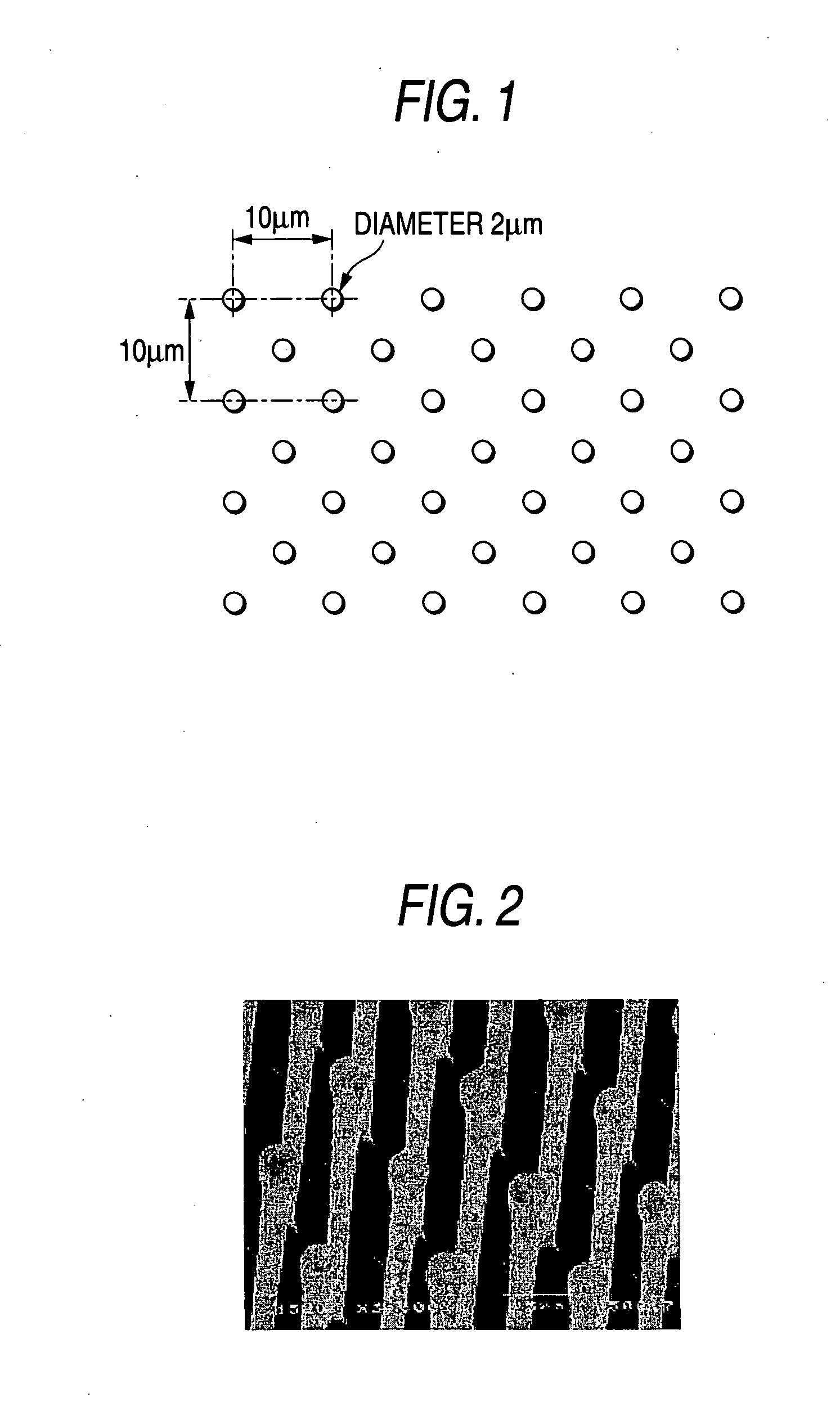
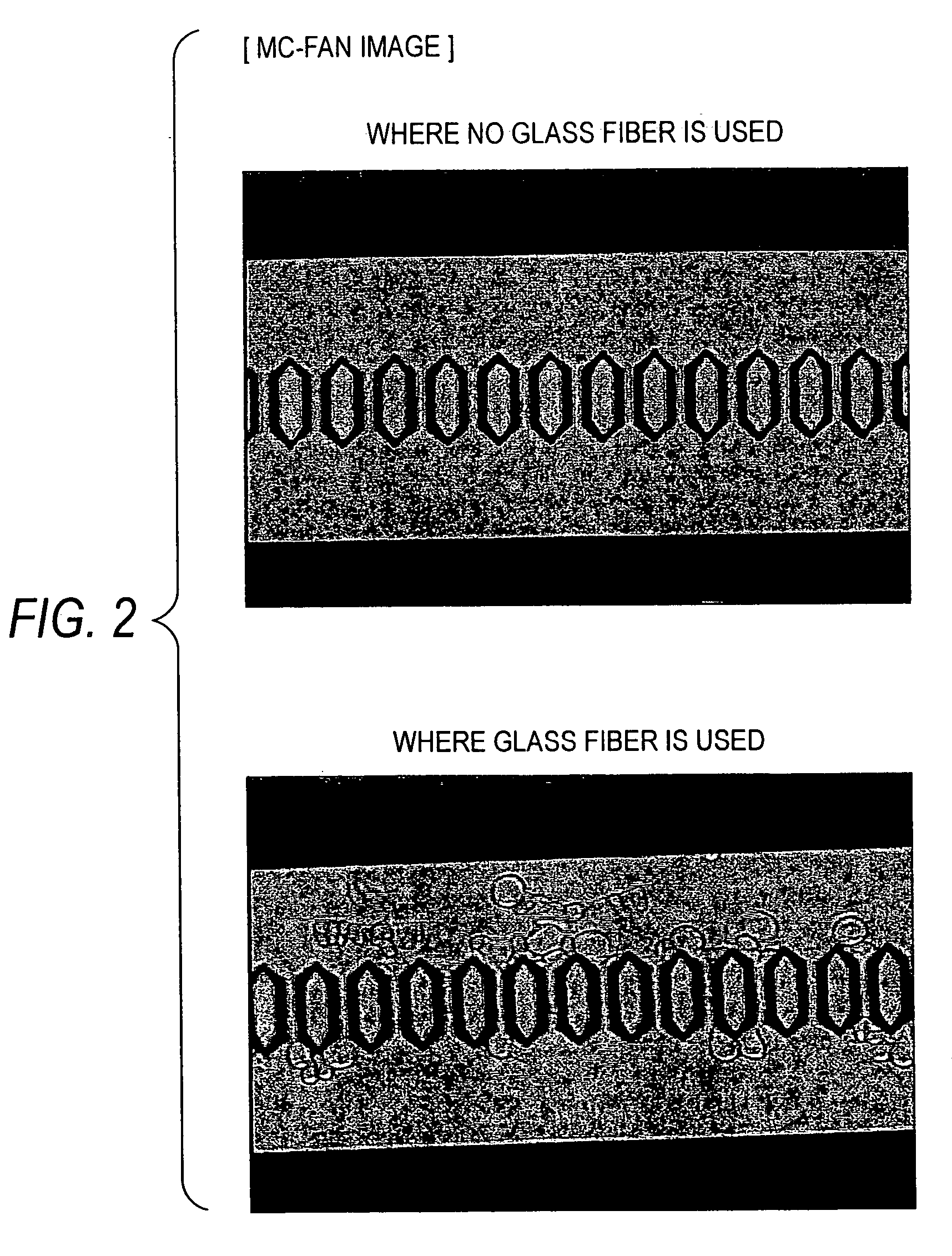
Filter for separating blood cells
InactiveUS20070227967A1Maintains voids of glass fibers constantSemi-permeable membranesAnalysis using chemical indicatorsWater insolubleRed blood cell
A filter for separating blood cells, which comprises: a substrate; and at least one water-insoluble substance fixed to the substrate, wherein the at least one water-insoluble substance has an equivalent circle diameter of 4 μm or less and a height equal to or larger than the equivalent circle diameter, wherein blood cells are separated by substantially being captured with the at least one water-insoluble substance; and a blood filtration instrument and a blood analytical device, using the filter for filtration of blood and body fluid.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Antithrombogenic hollow fiber membranes and filters
ActiveCN102316965AReduce adhesionReduce needSemi-permeable membranesHaemofiltrationMedicineHemofiltration
The invention relates to extracorporeal blood circuits, and components thereof (e. g. , hollow fiber membranes, potted bundles, and blood tubing), including 0. 005% to 10% (w / w) surface modifying macromolecule. The extracorporeal blood circuits have an antithrombogenic surface and can be used in hemofiltration, hemodialysis, hemodiafiltration, hemoconcentration, blood oxygenation, and related uses.
Owner:INTERFACE BIOLOGICS INC
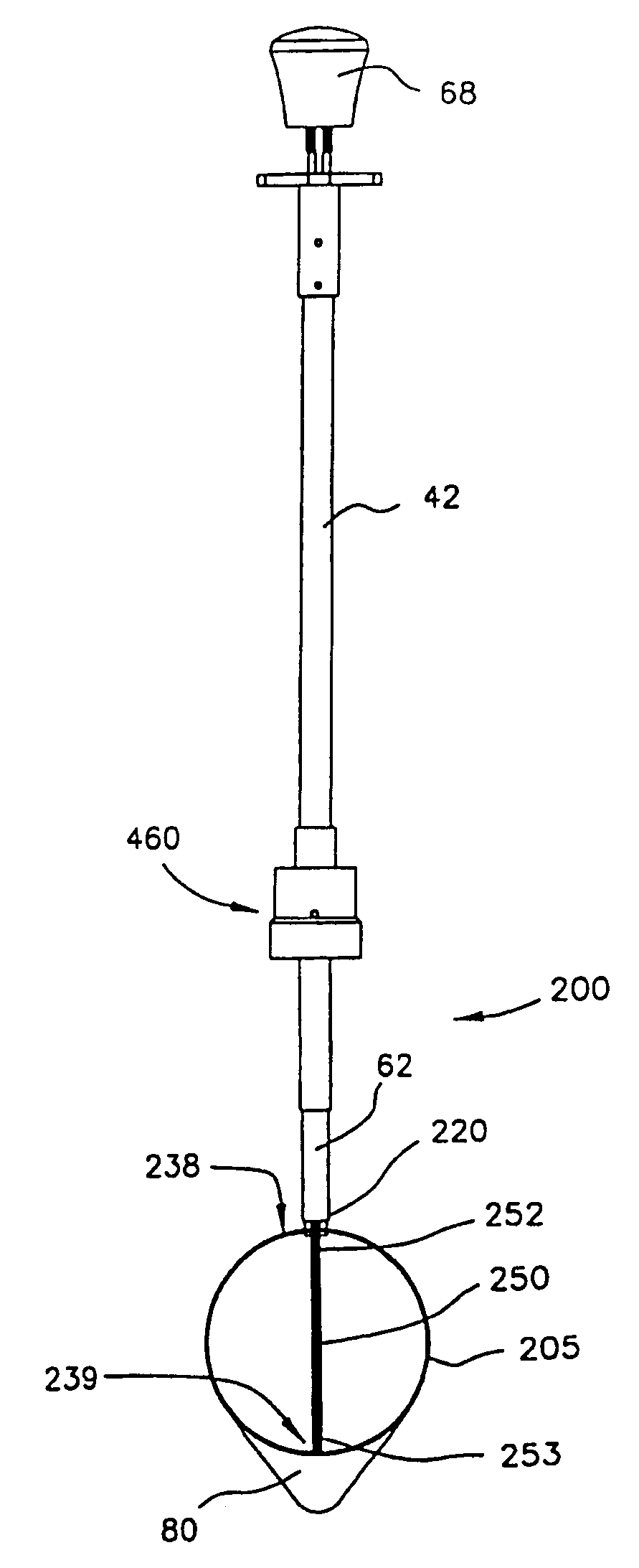
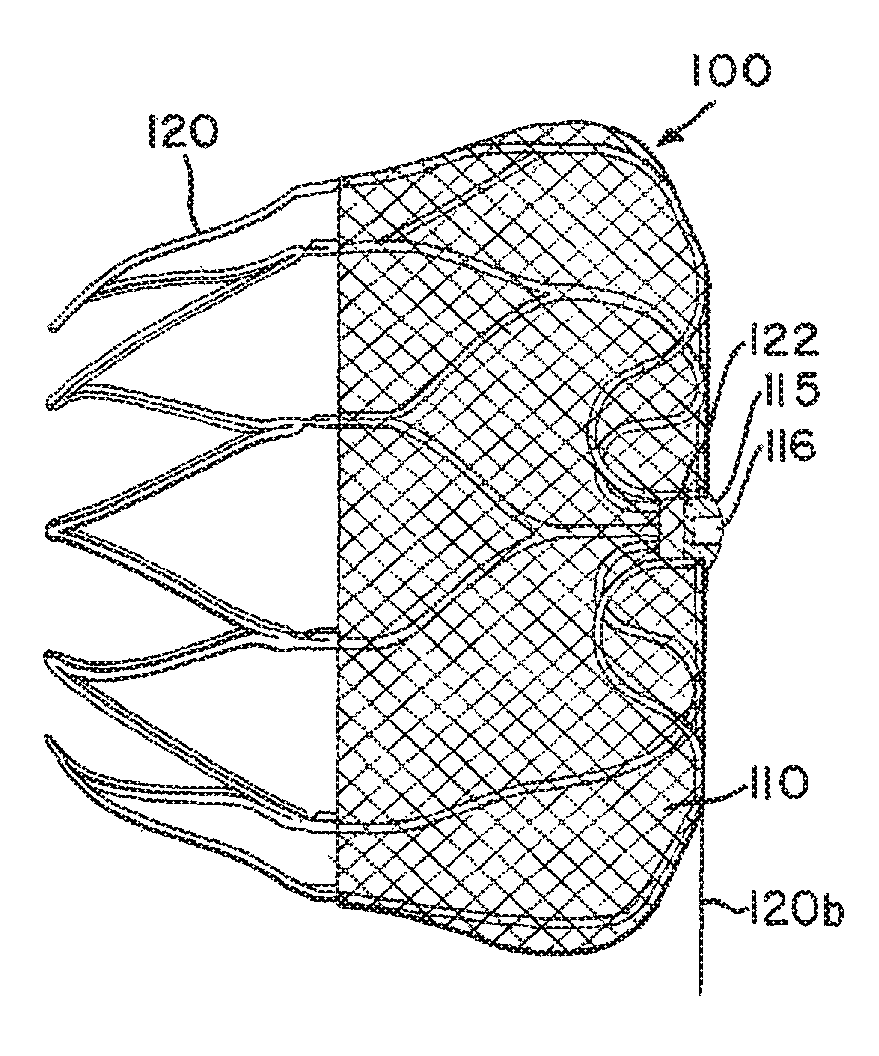
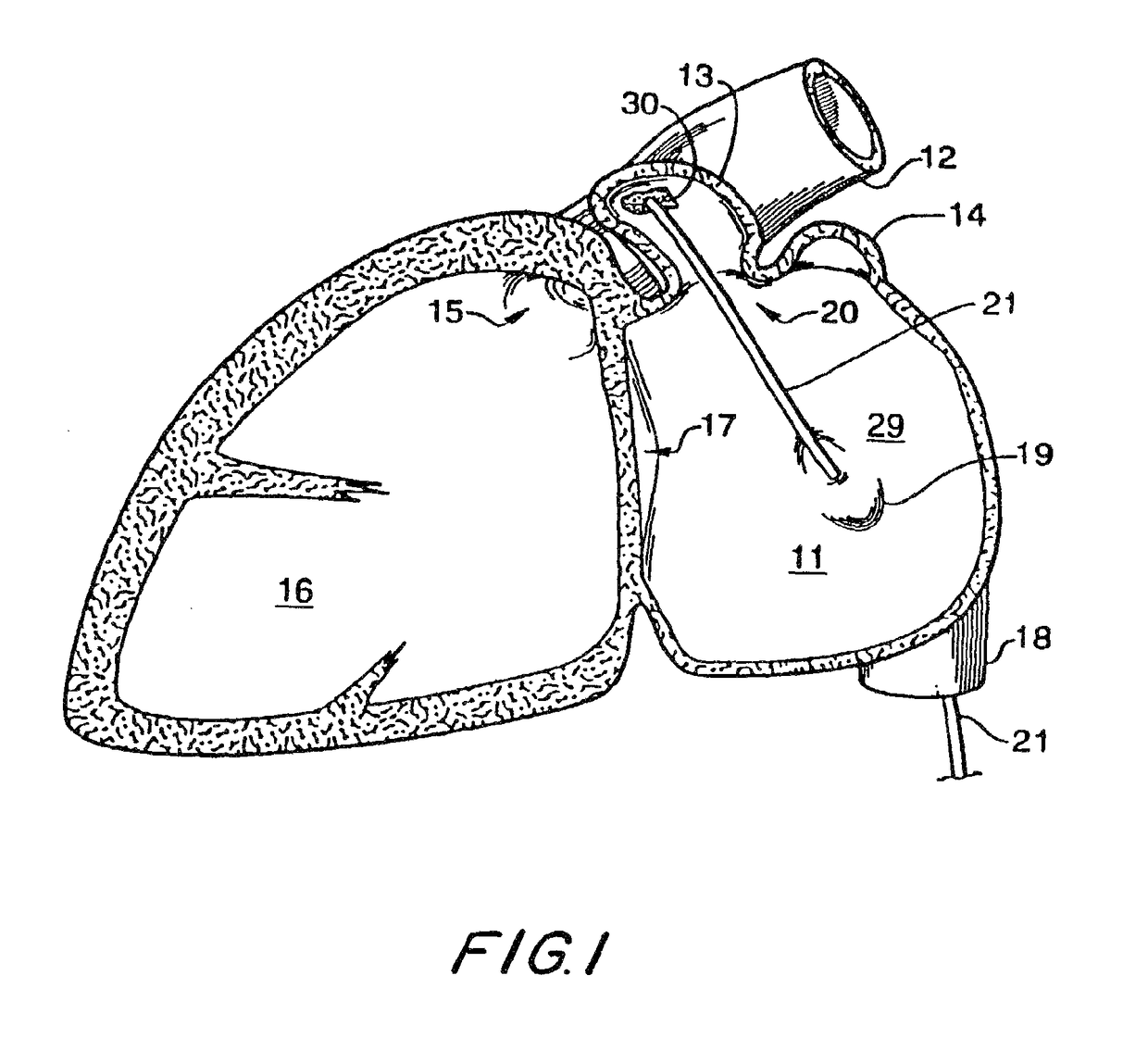
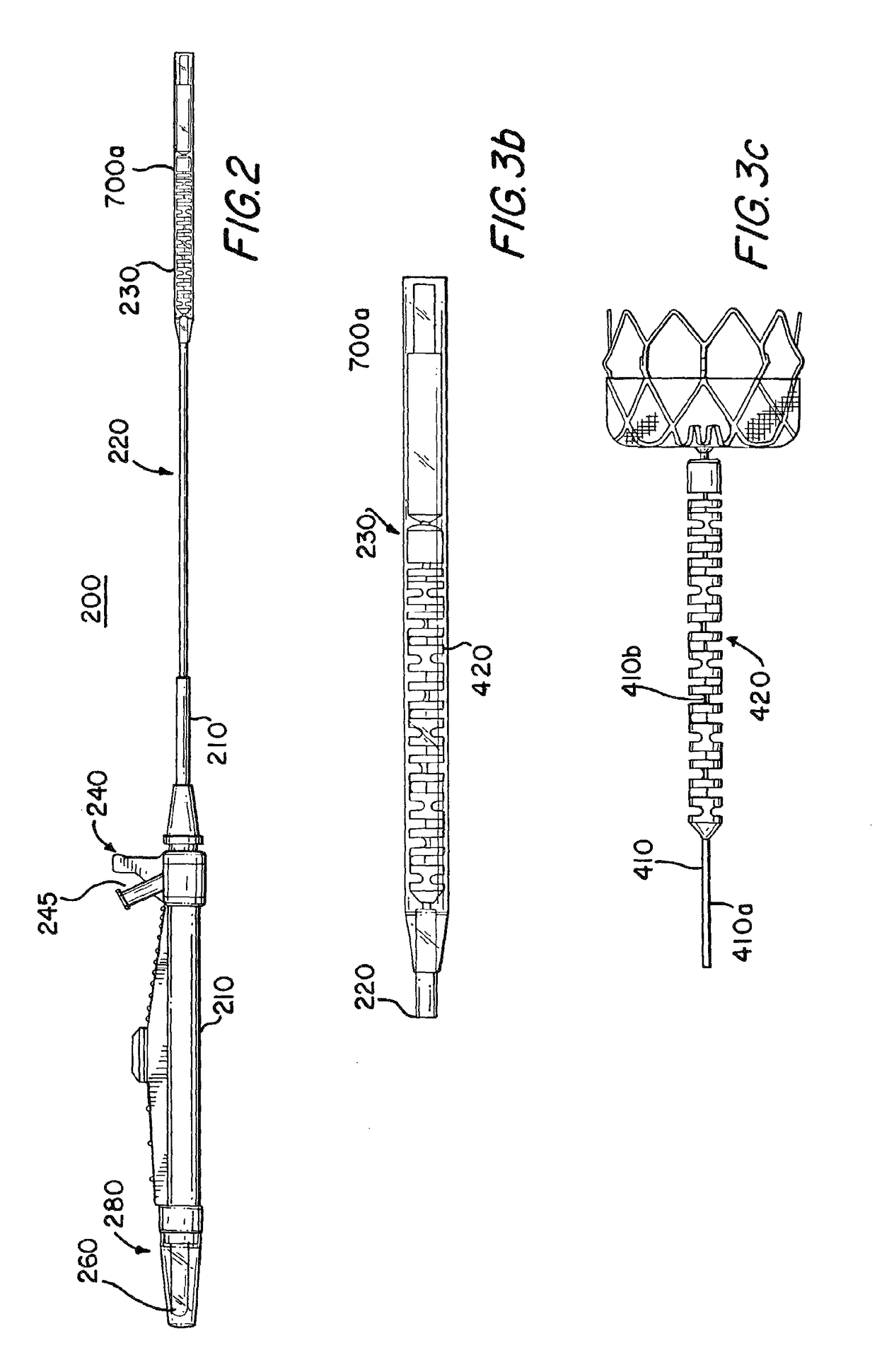
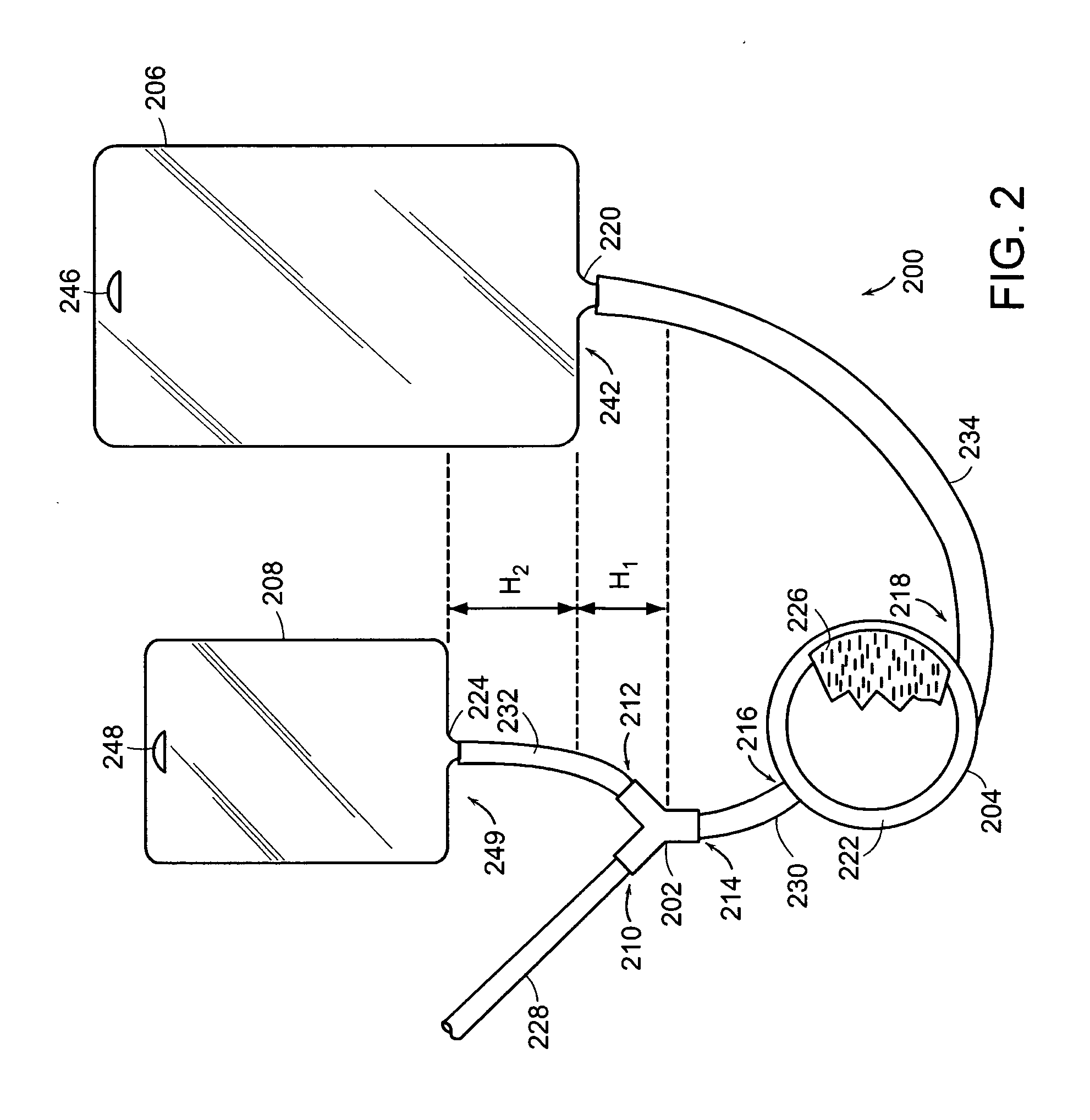
Atrial appendage blood filtration systems
InactiveUS9883936B2Prevent proliferationRigid enoughDilatorsOcculdersAppendageBiomedical engineering
Instrumentation for percutaneous delivery of blood filtration devices to atrial appendages includes a curved access sheath and a delivery tube. A compressed filter device attached to a tether wire is loaded in the delivery tube. The access sheath and the delivery tube can be mechanically locked and moved together to place the device in a suitable deployment position. The device is deployed by expelling it from the delivery tube either by retracting the delivery tube over the tether wire, or by moving the tether wire forward through the delivery tube. A filter membrane in the deployed device extends across the appendage ostium to filter blood flow through the ostium. The filter membrane is configured to present a flat surface to atrial blood flow past the ostium.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
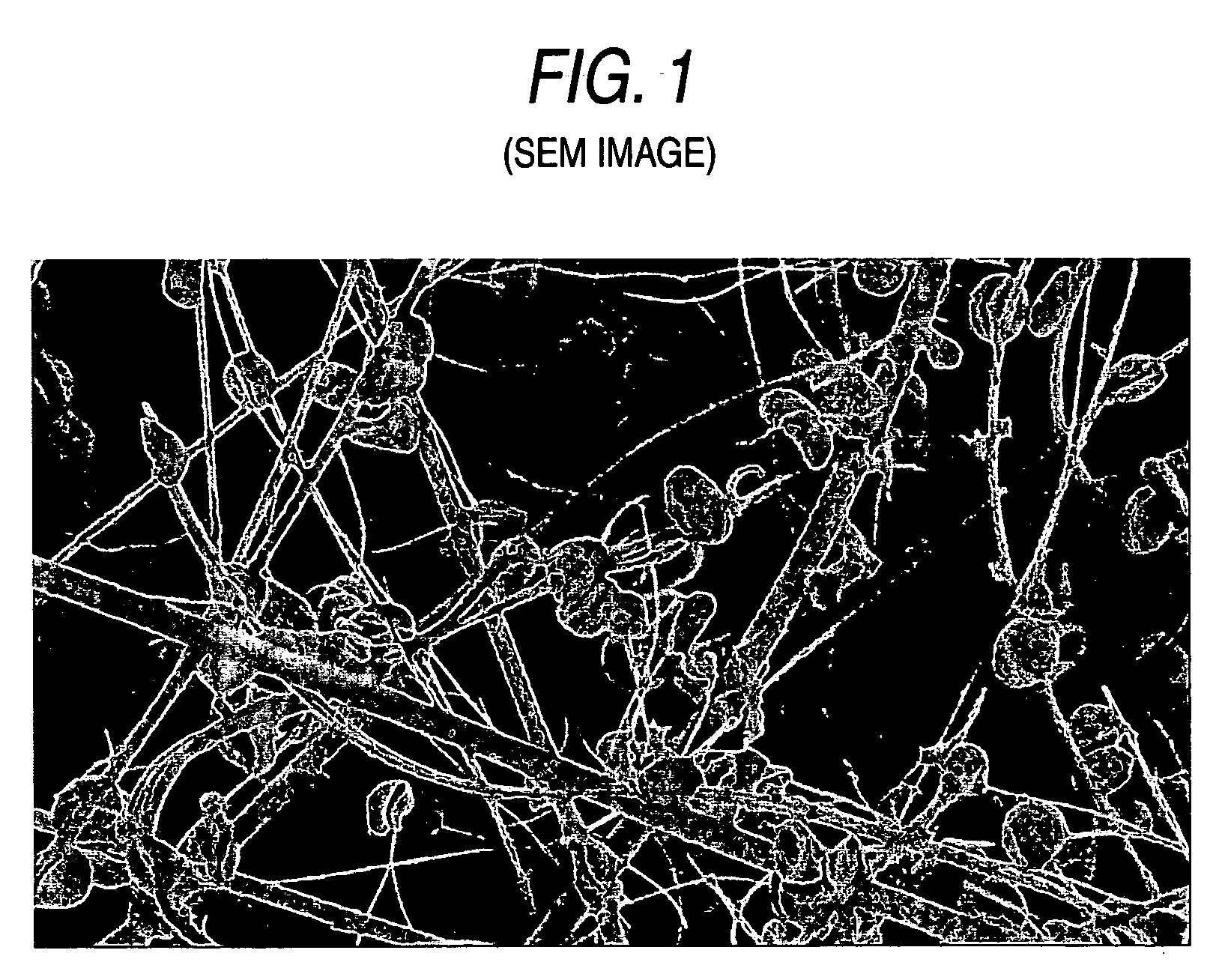
Glass-fiber filter for blood filtration, blood filtration device and blood analysis element
A glass fiber filter for blood filtration, in which a glass fiber is cleaned with an organic acid and then the surface of a glass fiber is coated with a biocompatible polymer such as poly (alkoxy acrylate), a blood filtration device and a dry-type blood analysis element in which the glass fiber filter for blood filtration is used.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Systems for utilizing the water content in fluid from a renal replacement therapy process
ActiveUS20170065762A1High Salt RejectionReduce energy consumptionHaemofiltrationUltrafiltrationHaemodialysis machineNephropathy
The present invention relates to systems, methods and uses for recycling at least a part of water lost during various renal replacement therapy processes, e.g. in the preparation of a fresh dialysate solution or fresh reconstitution fluid for kidney disease dialysis and hemofiltration by utilizing water from the spent fluids. The system of the invention is useful in hemodialysis and in peritoneal dialysis as well as in hemofiltration for reuse of water from filtrates and spent fluids. In addition, the system of the invention is useful in the development of a renal assist device or artificial kidney.
Owner:AQUAPORIN AS
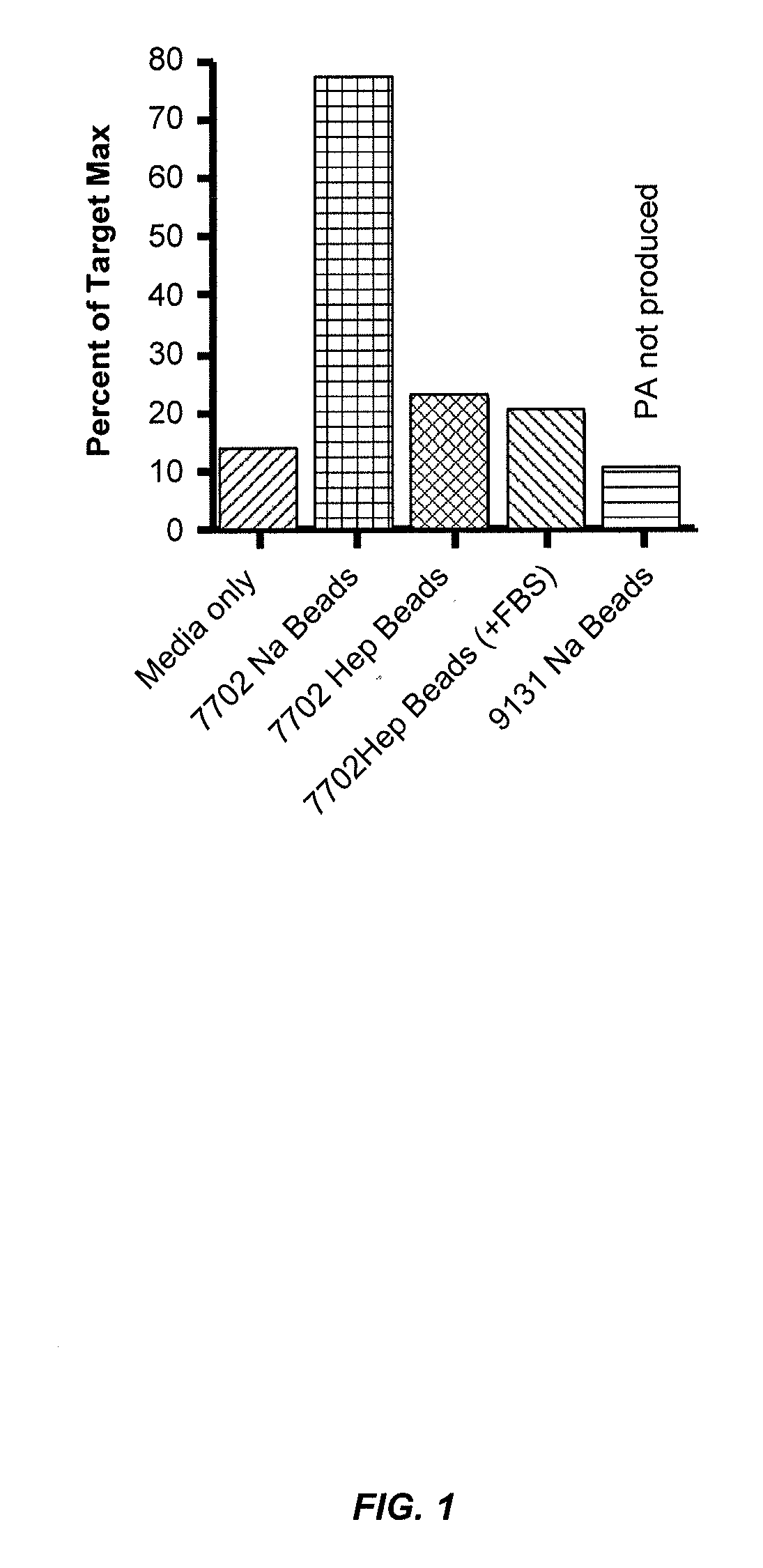
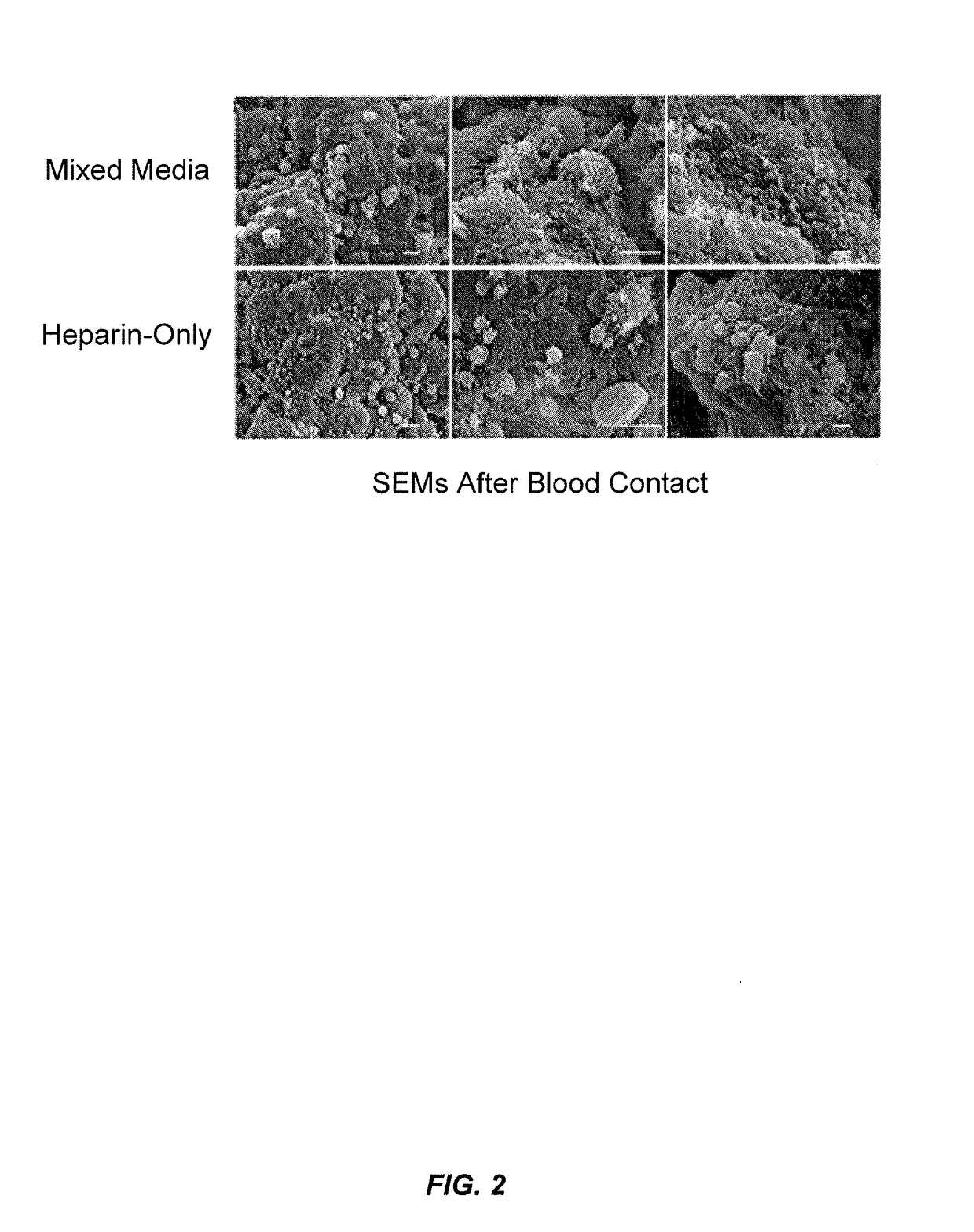
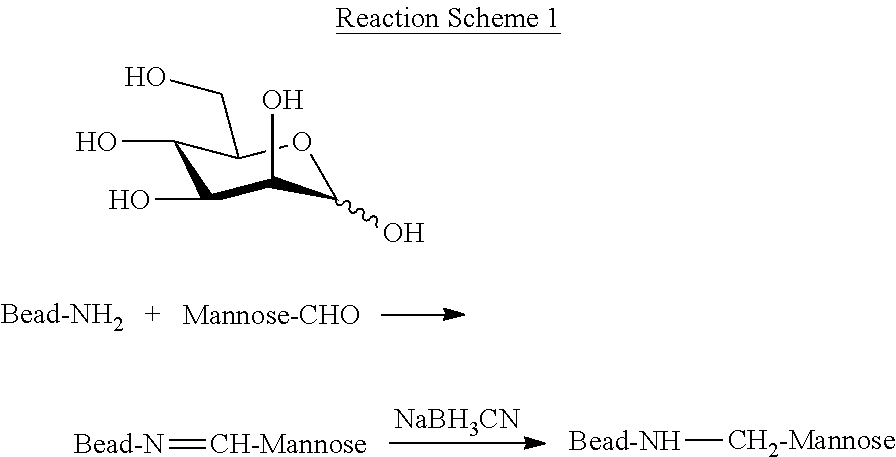
Blood filtration system containing mannose coated substrate
InactiveUS20160101229A1Improve securityWidely targetedOther blood circulation devicesHaemofiltrationPhotochemistryMannose
Owner:EXTHERA MEDICAL
Continuous blood filtration and method of use
InactiveUS7601268B2Avoid enteringMaintain continuityLiquid separation auxillary apparatusSemi-permeable membranesReservoir bagWhole blood product
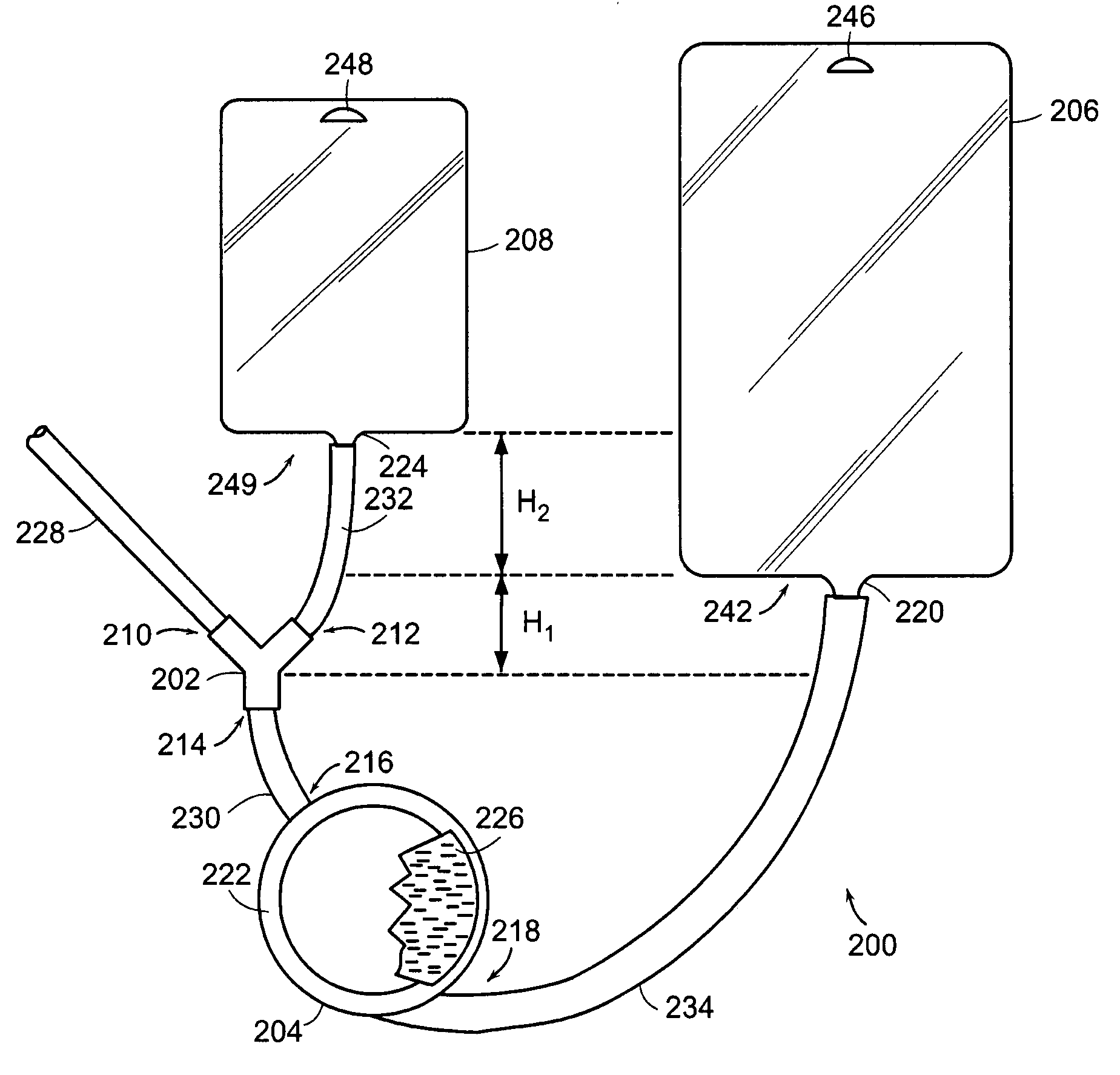
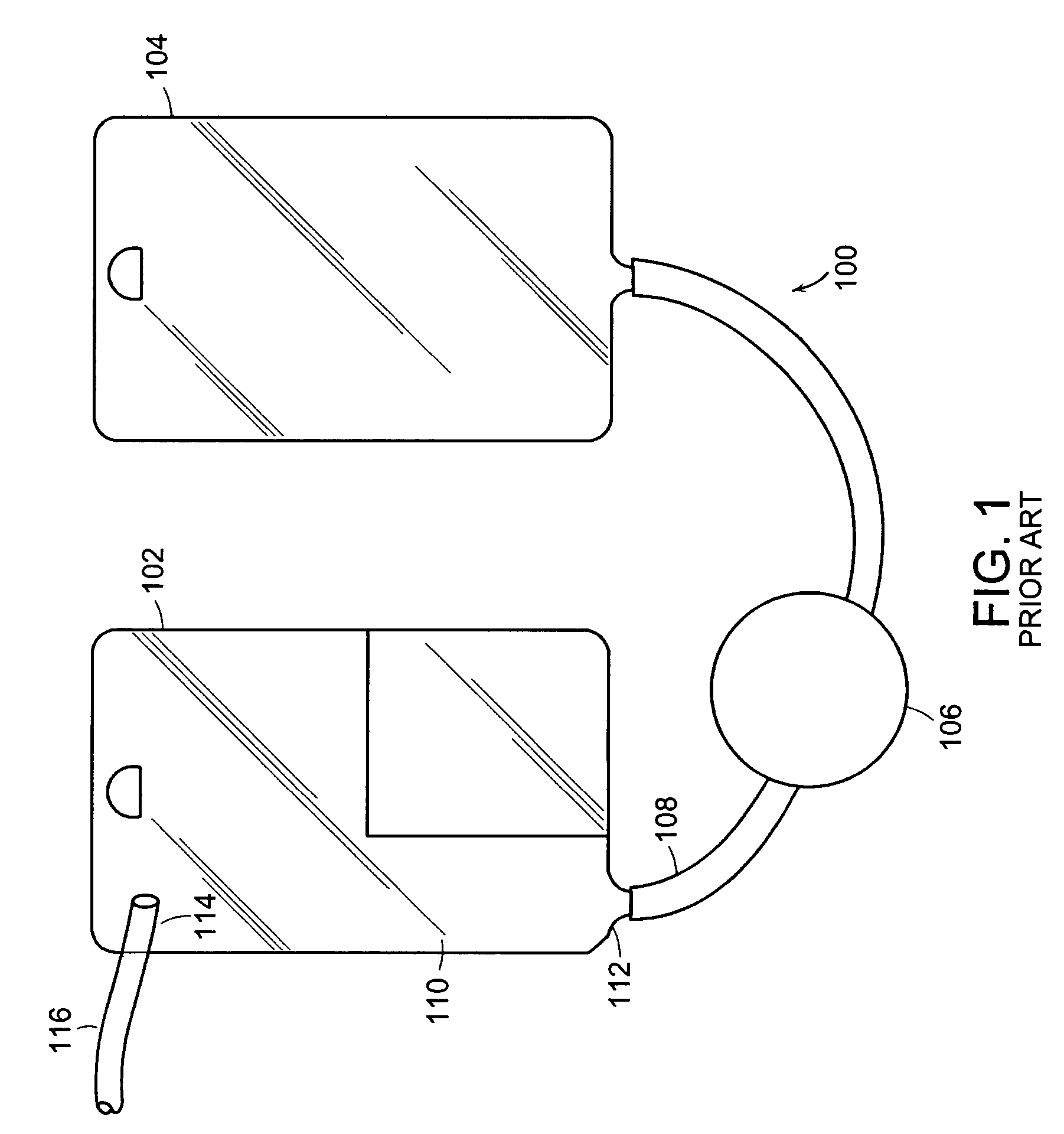
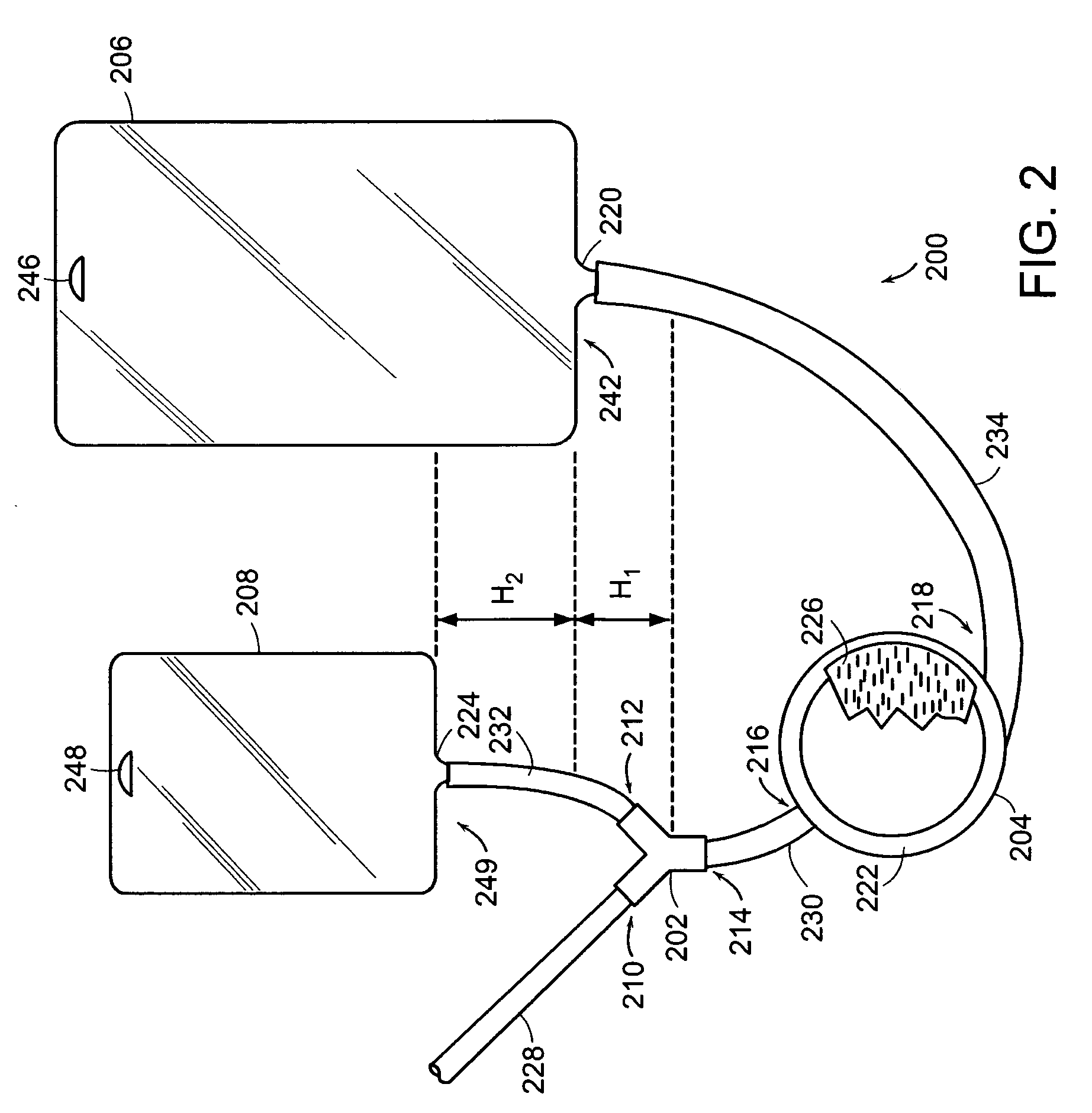
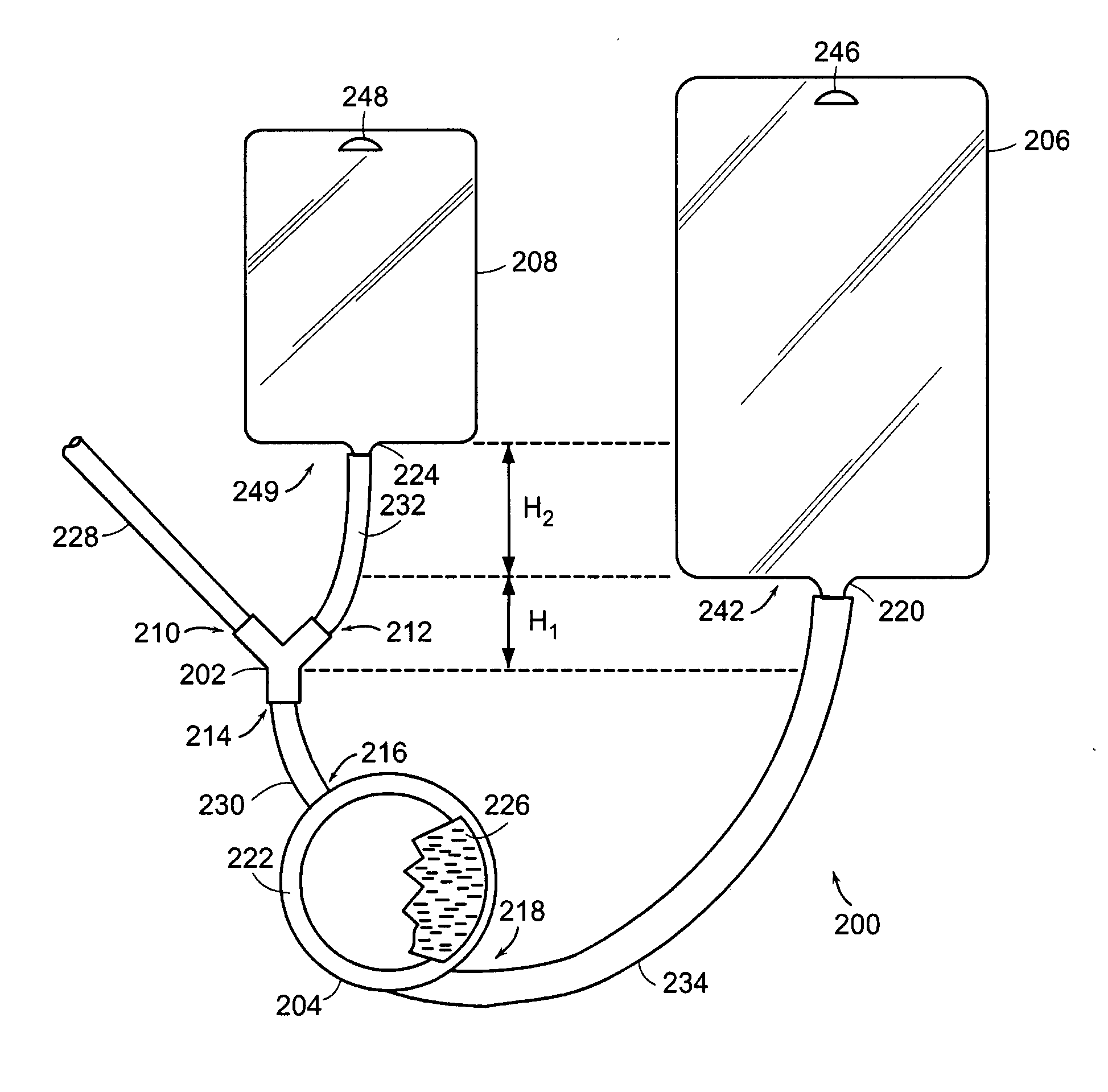
The invention is directed to a system for continuously filtering a blood product including whole blood or any of its component(s), erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets and plasma either alone or in combination. The system includes a connector for receiving the blood product, a filter coupled to the connector for filtering the received blood product, a collection bag coupled to the filter for collecting the filtered blood product, and a reservoir bag connected to the connector for temporarily storing received blood product, and providing received blood product through the connector to the filter to maintain continuity in filtration. The reservoir bag and the collection bag are suspended, the connector near or below the bottom of the collection bag, and the bottom of the reservoir bag is above the bottom of the collection bag. Also provided is a method of filtering a blood product using the continuous blood filtration system.
Owner:HAEMONETICS
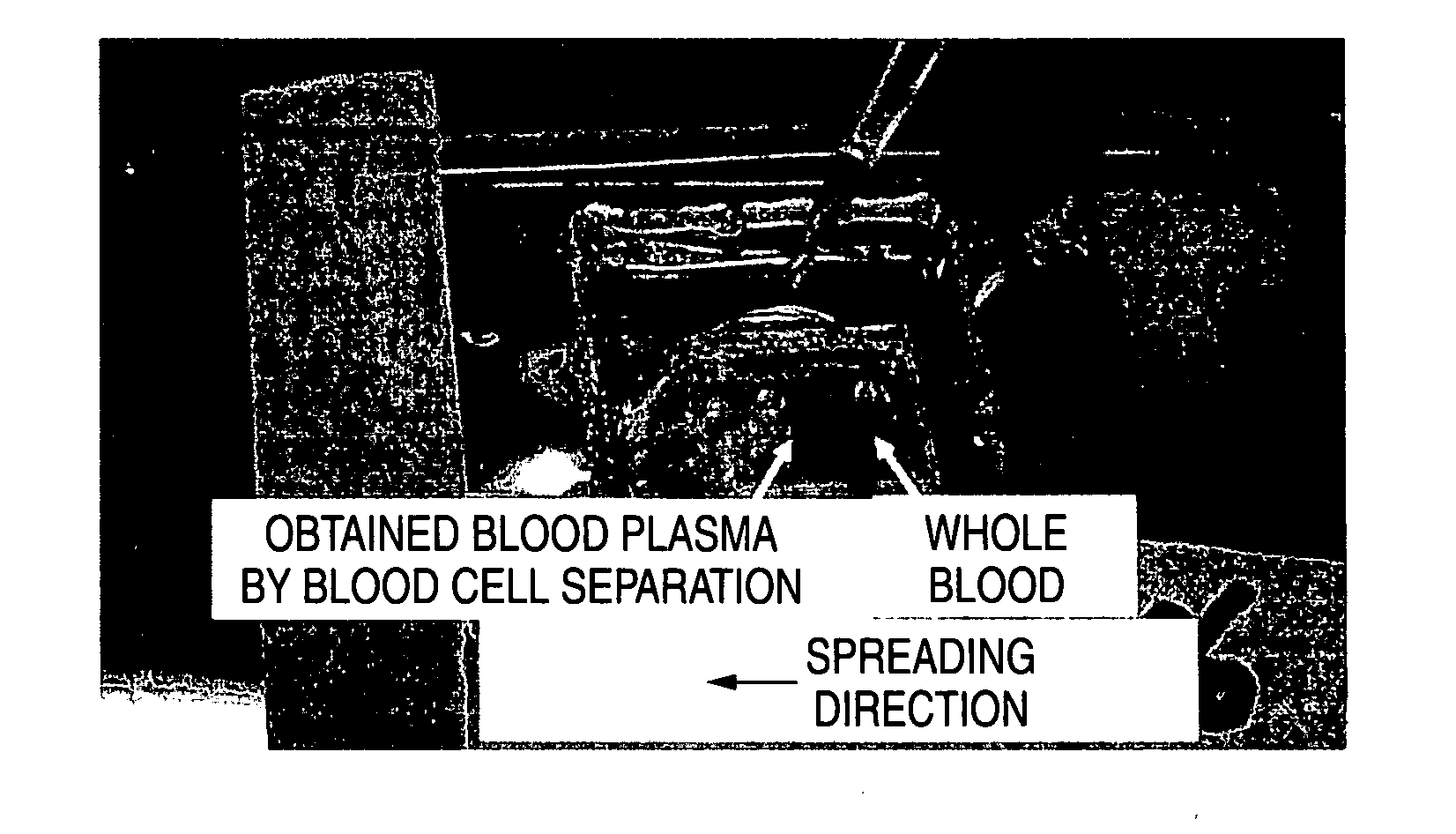
Continuous blood filtration apparatus
InactiveUS7059480B2Material analysis by optical meansLoose filtering material filtersBlood plasmaVALVE PORT
This invention provides a continuous blood filtration apparatus capable of filtering a plurality of blood samples continuous by using blood filter units to prepare plasma or serum samples in a short period, which comprises, a conveyor conveying a plurality of blood reservoirs each of which contains a blood sample and in which a suction nozzle of a blood filter unit has been put, a manifold connected to a suction line, couples of a valve and a connector for connecting the manifold to the blood filter unit provided on the end of each branch of the manifold, and a mechanism of moving the blood reservoirs in vertical direction.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP
Device for oxygenating blood in an extracorporeal circuit
InactiveUS7238320B2Maximum safetyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsOther blood circulation devicesBlood collectionExtracorporeal circulation
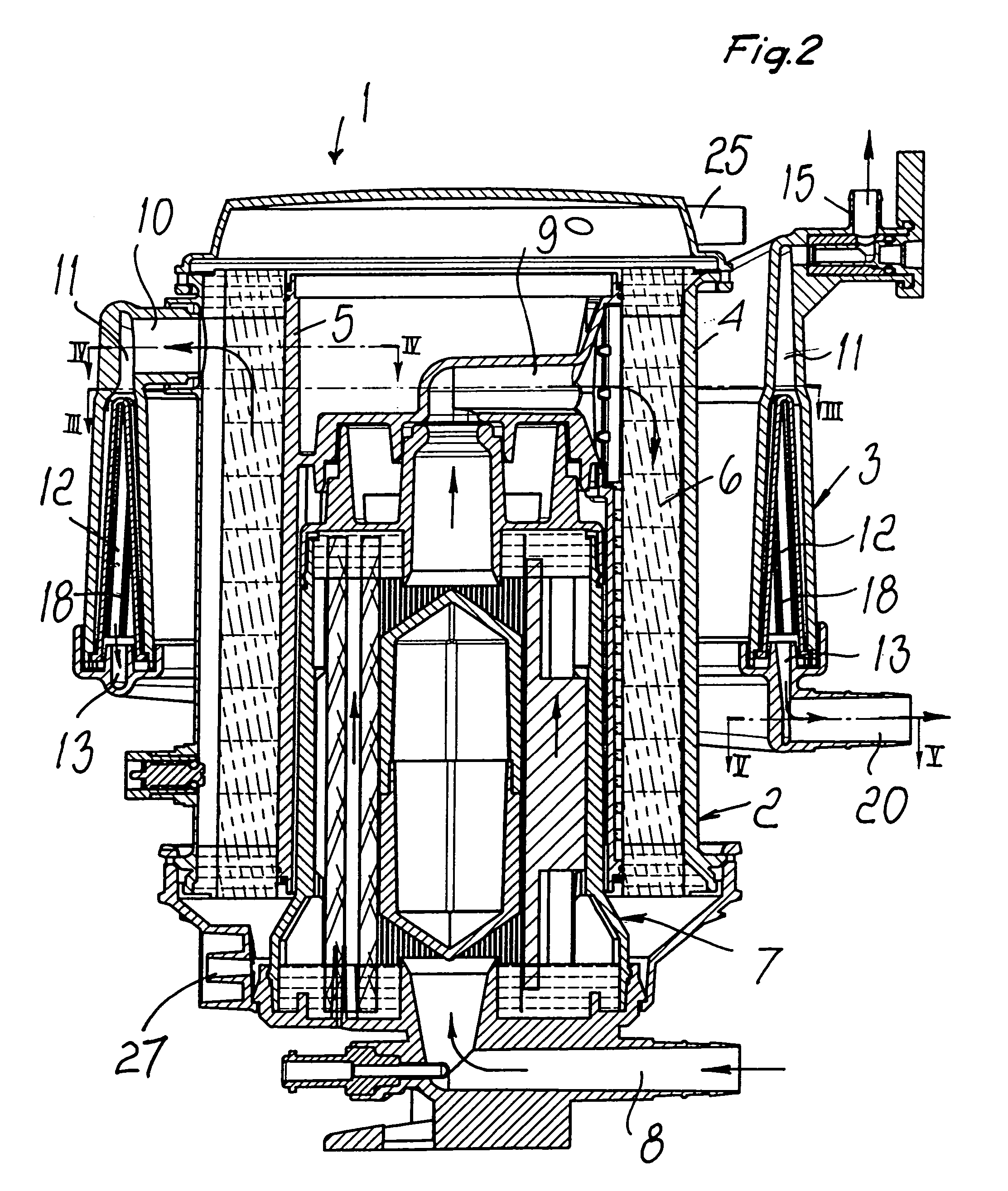
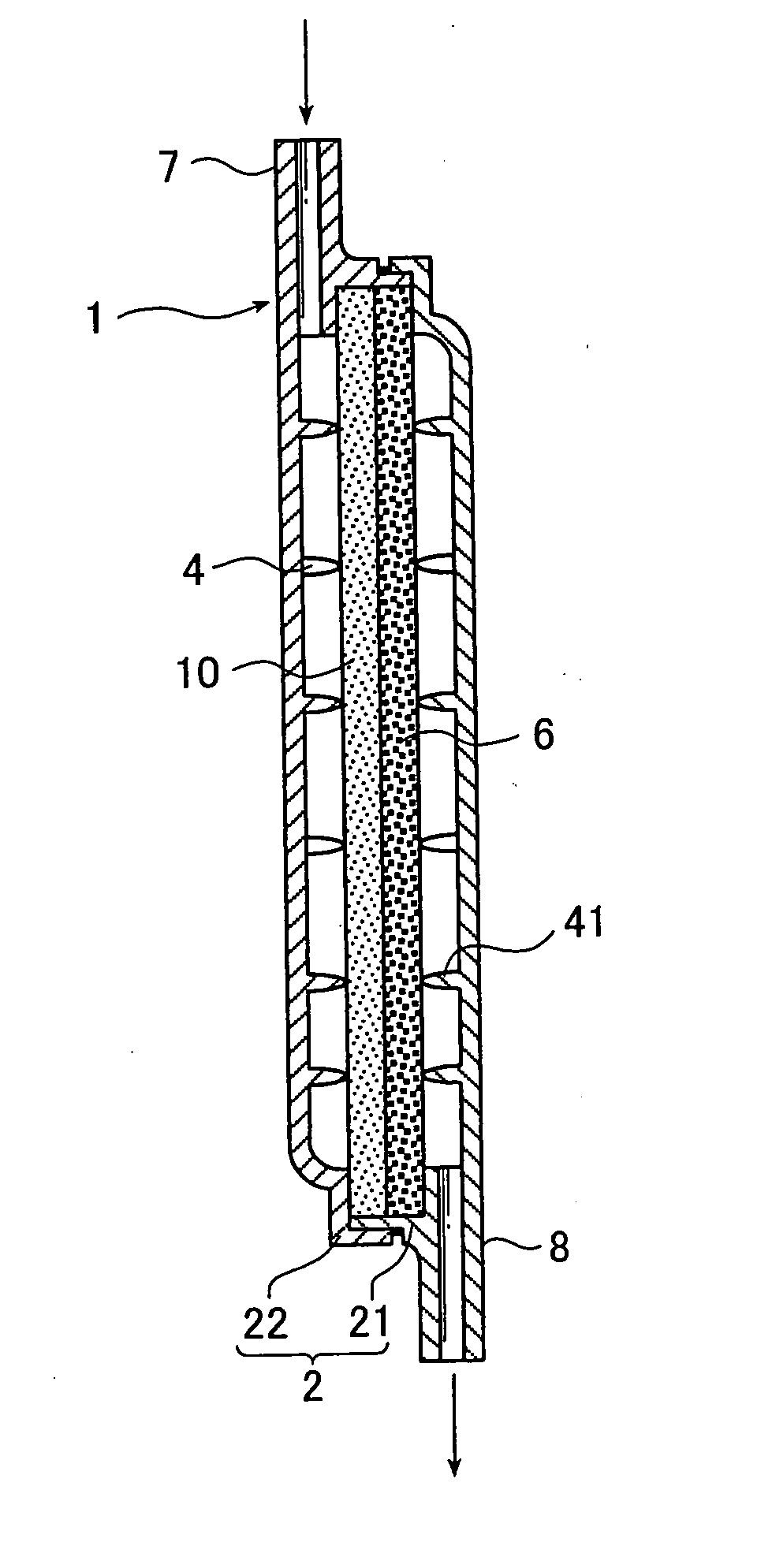
A device for oxygenating blood in an extracorporeal circuit includes a first structure suitable to delimit a portion of space-containing capillaries made of microporous membrane. The capillaries convey oxygen and are wet externally by blood flowing through a portion of space between an intake connector, which is connected to a venous line of the extracorporeal circuit, and a delivery connector. The device includes a second structure monolithically connected and contiguous to the first structure. The second structure is suitable to contain blood filtration means that divide the portion of space delimited thereby into a blood distribution chamber, provided with an air vent and connected to the delivery connector of the first structure, and a blood collection chamber provided with a delivery connector connected to the arterial line of the extracorporeal circuit.
Owner:SORIN GRP ITAL SRL
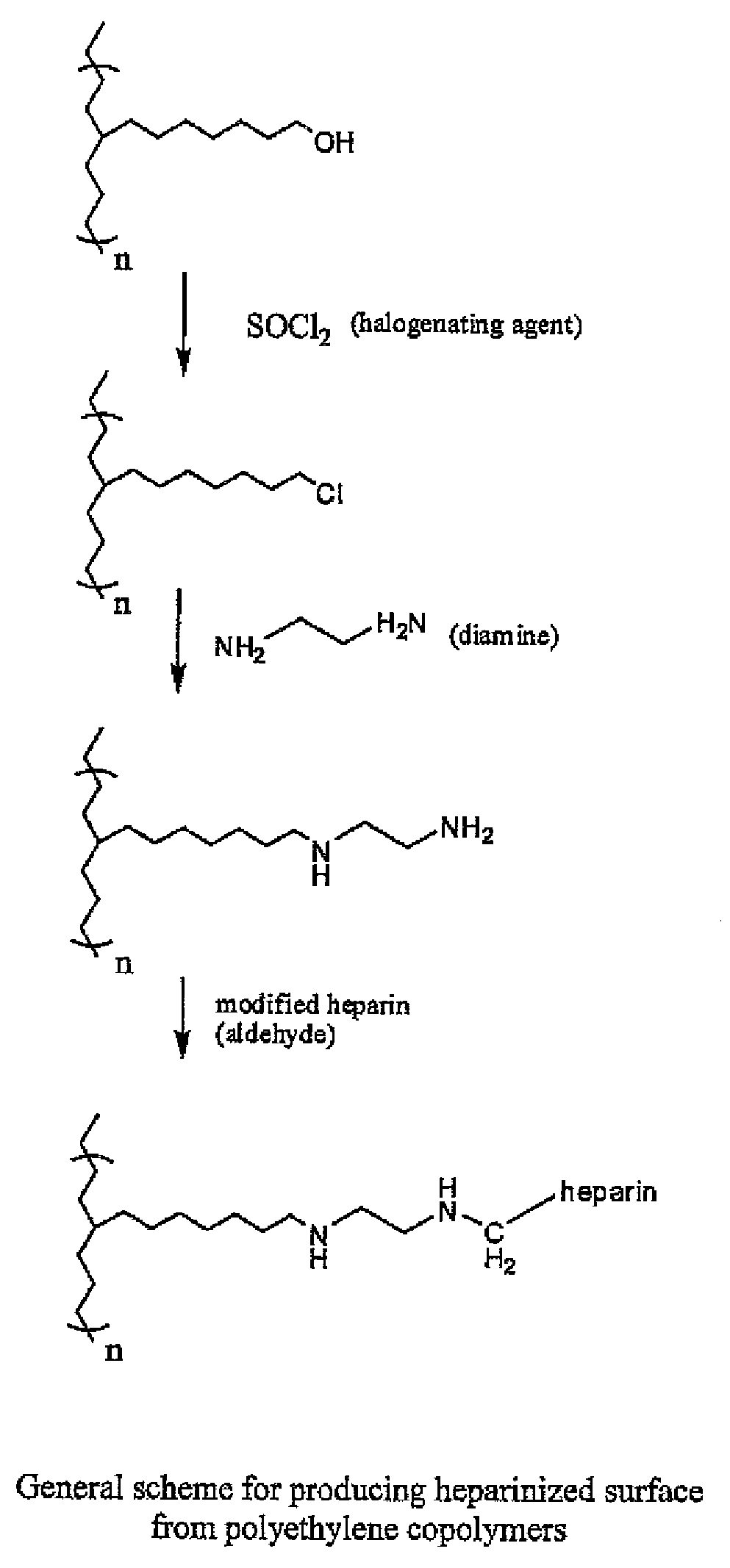
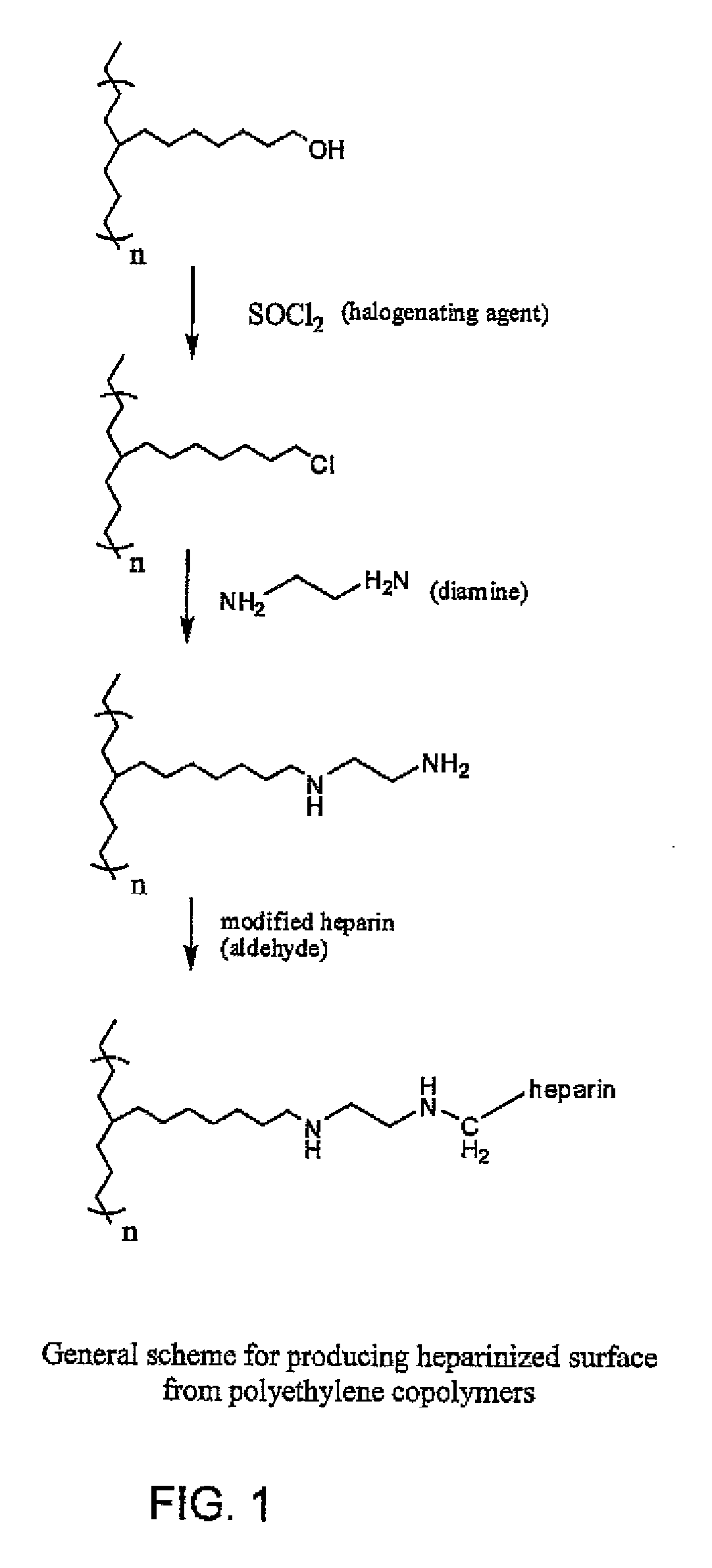
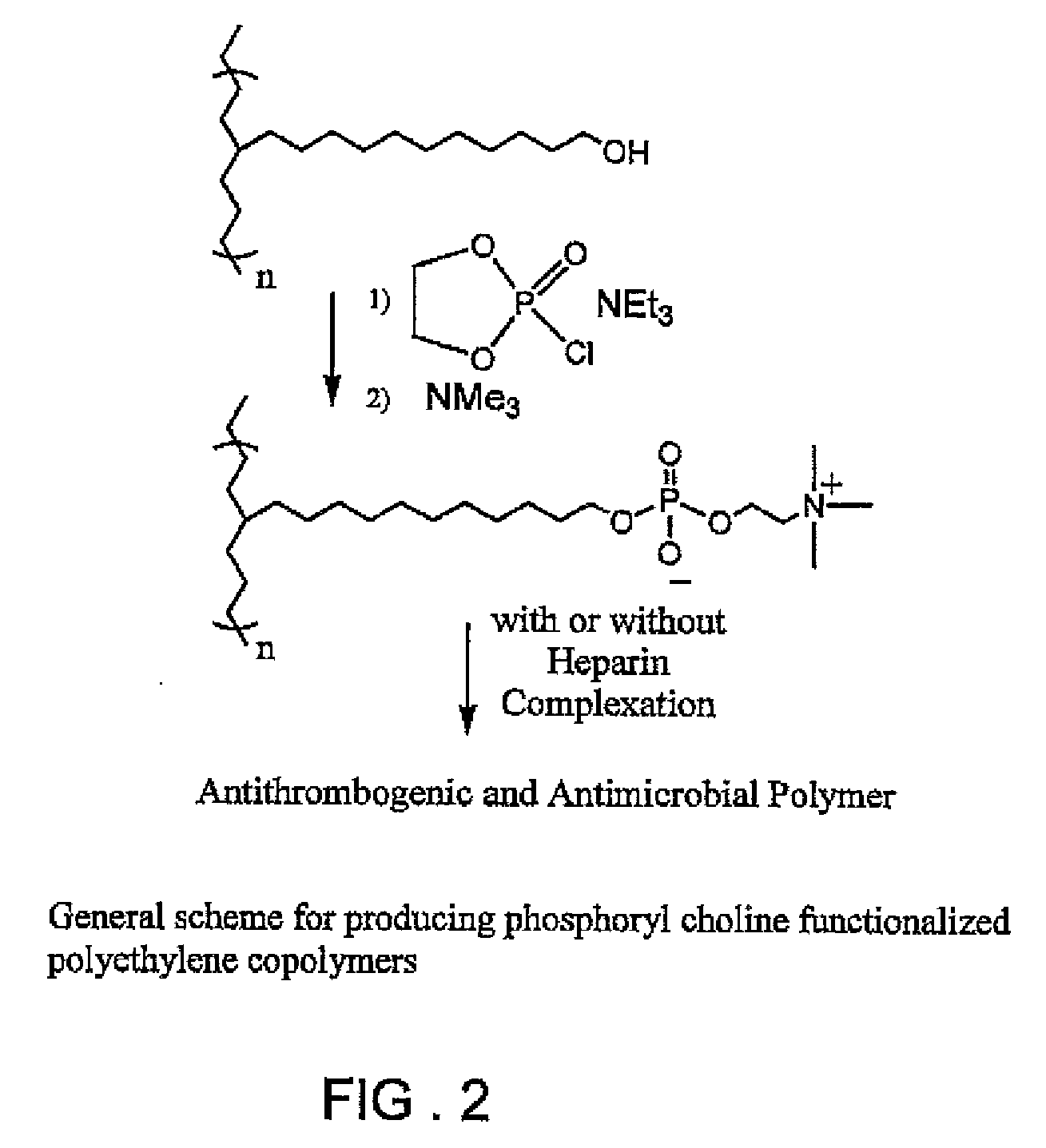
Polymers with bio-functional self assembling monolayer endgroups for therapeutic applications and blood filtration
InactiveUS20100179284A1Improve equipment efficiencyPromote healingOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSelf-assembled monolayerEnd-group
Medical device, prosthesis, or packaging assembly made up of polymer body comprising at least one polymer having the formula R(LE)x wherein R is a polymeric core having a number average molecular weight of from 5000 to 7,000,000 daltons, and having x endgroups, x is an integer≧1, E is an endgroup which is covalently linked to polymeric core R by linkage L, L is a divalent oligomeric chain which has at least 5 repeat units and which can self-assembly with L chains on adjacent molecules of the polymer, and moieties L and / or E in the polymer(s) may be the same as or different from one another in composition and / or molecular weight. The polymer body includes plural polymer molecules located internally within the body, at least some of which internal polymer molecules have endgroups that form a surface of the body. The surface endgroups include at least one self-assembling moiety.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Integrated apparatus and methods for treating liquids
InactiveUS7743928B2Finely controlled geometricalFinely controlled flow conditionSolvent extractionDecorative surface effectsSuspended particlesLab-on-a-chip
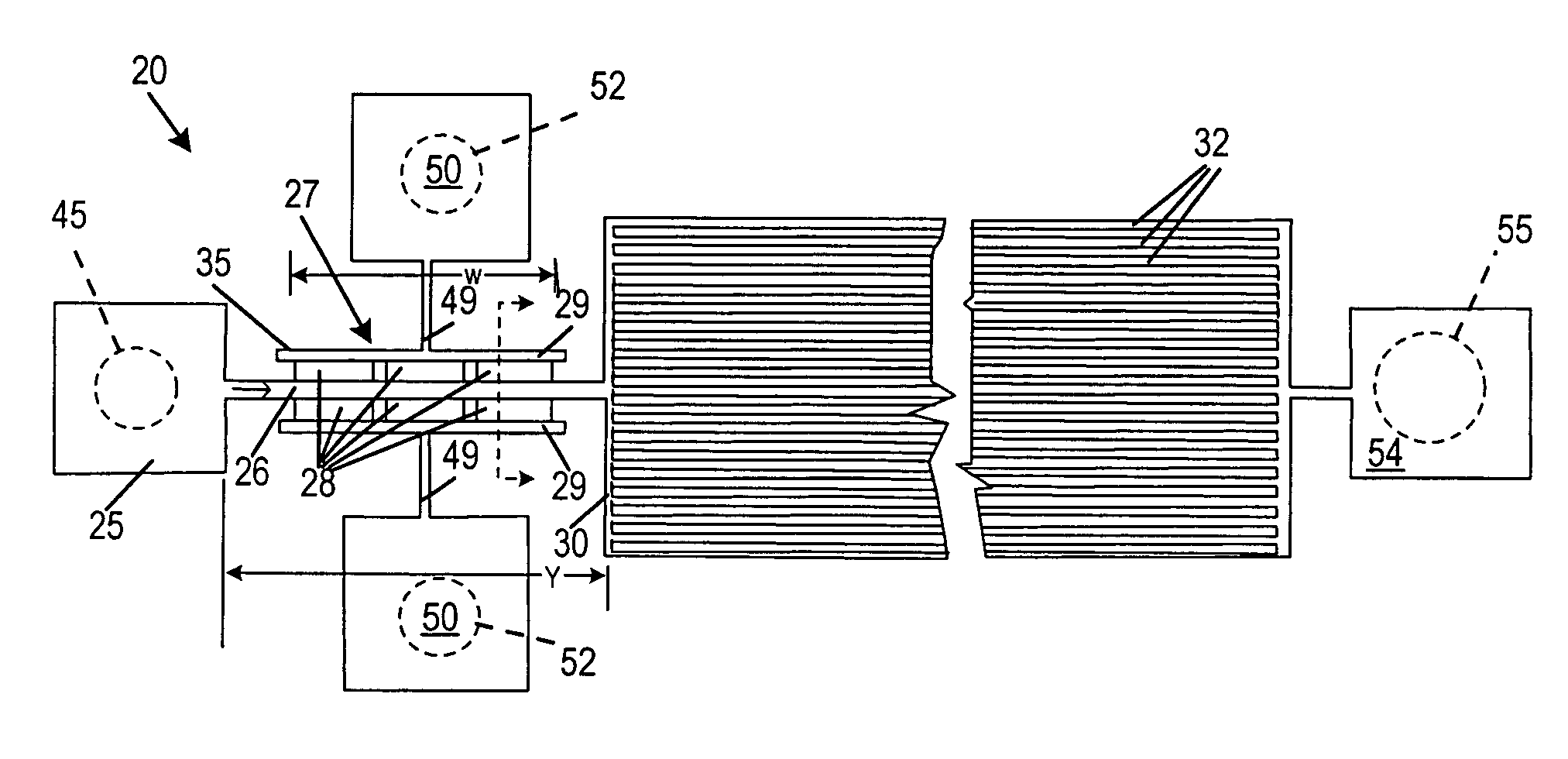
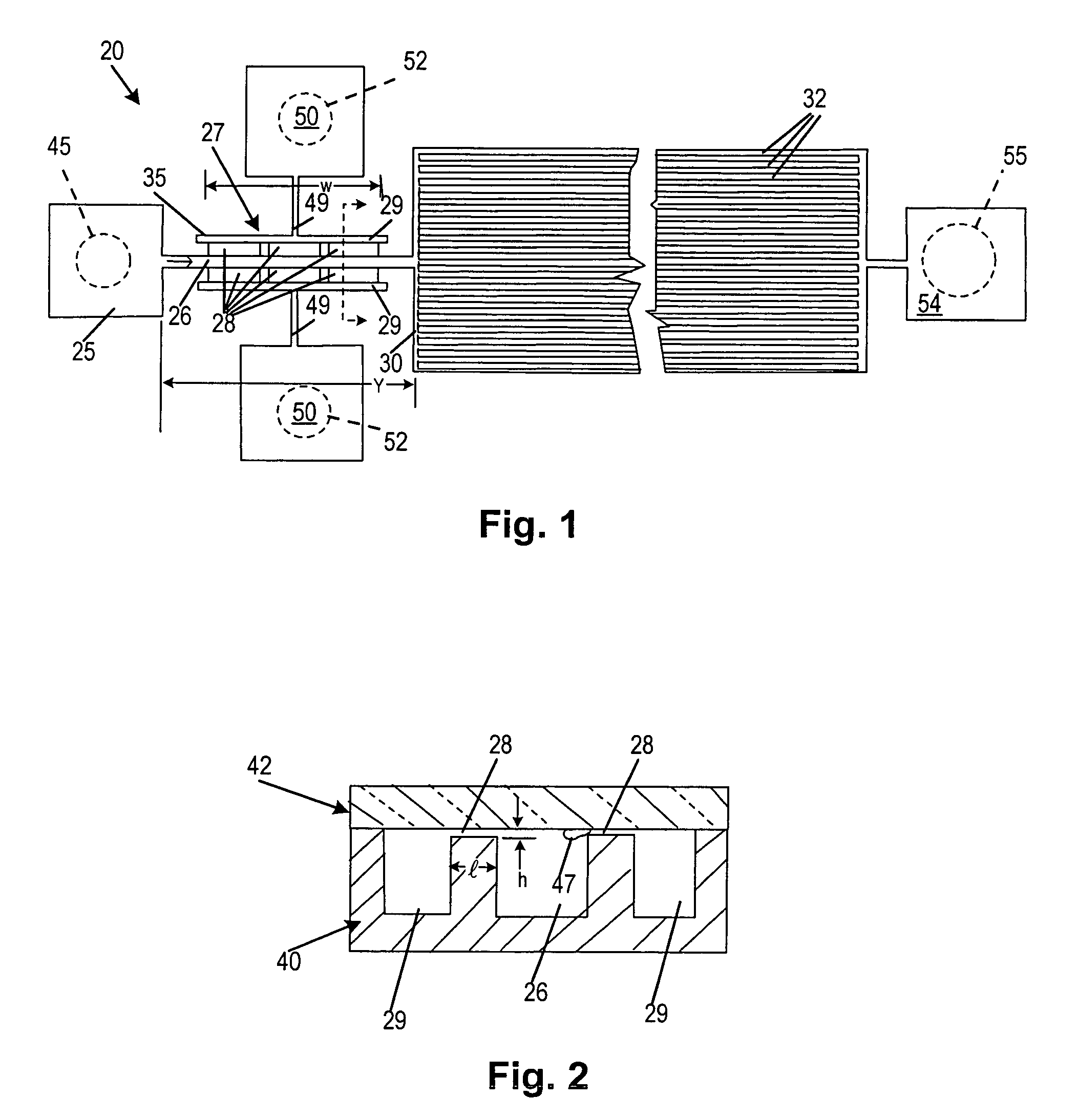
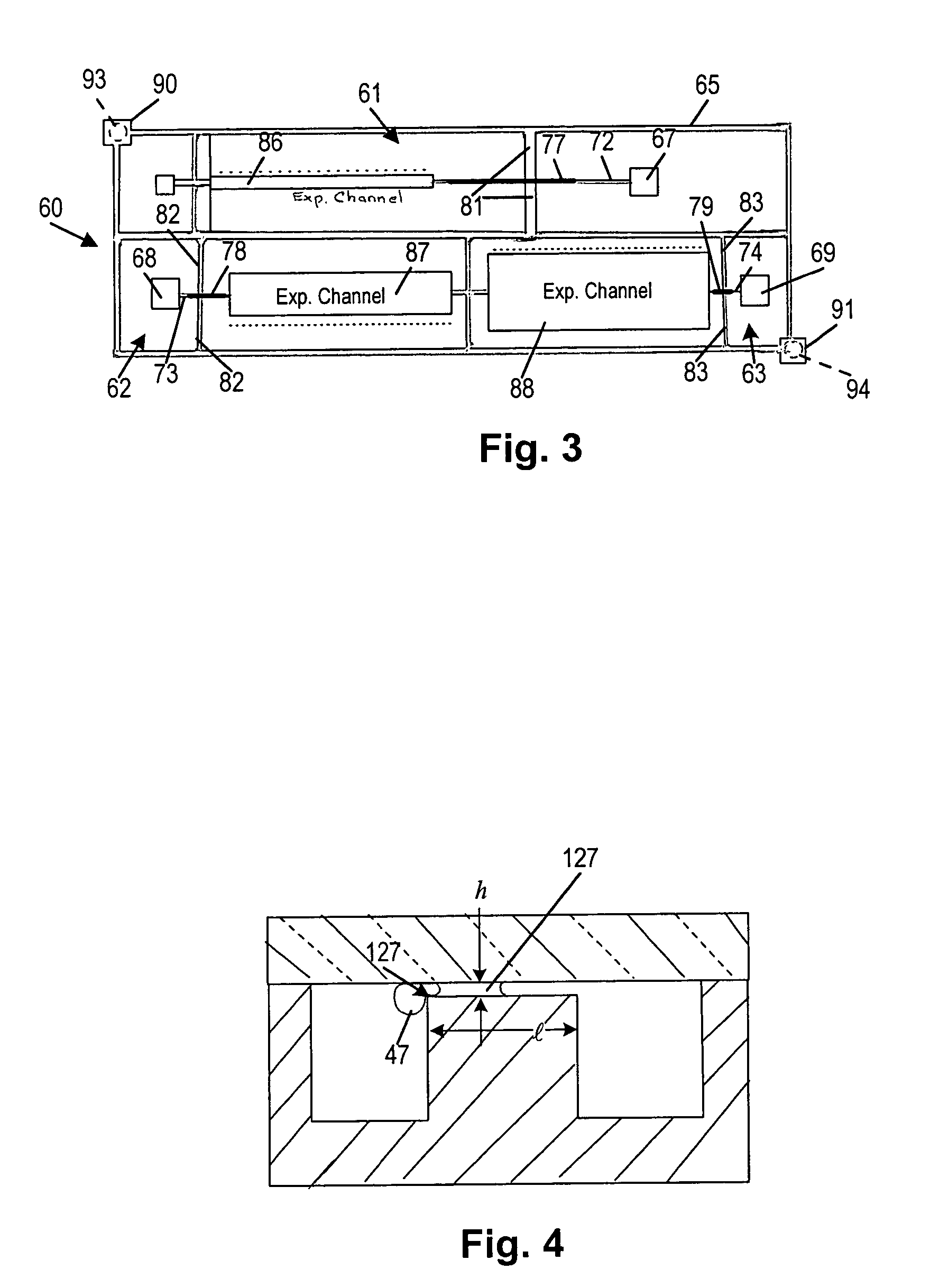
A passive self energized, liquid device operates entirely on capillary action. A microfilter fractionates nanoliter volumes of suspension such as whole blood into suspended particles or cells and liquid fractions. Blood, for example, is fractionated with minimal cell lysis, and the filtrate (plasma) flux is dependent upon design parameters similar to factors controlling blood filtration in microporous membranes, i.e. active filter area, fluid velocity and microfilter geometry. Weir-style filters communicate with a blood flow channel to separate plasma from blood moving by capillary action. An expanded downstream channel with multiple parallel capillary blood flow path provides continuing movement of blood past the filters. Lysing is controlled by the size of the filter pores and the duration of adherence of the red blood cells to the pores. The controlled lysis or prevention of lysis of red blood cells is accomplished by manipulating the significant capillary forces generated in the filters. Filtration, cell lysis and microchannel blood flow models are integrated into an overall microfilter design useful for fabricating microfilter devices for lab-on-a-chip clinical applications where they can be coupled with on-chip electrical and electro-optical devices.
Owner:CROWLEY TIMOTHY PHD +1
Copolymers and blood filter using the same
InactiveUS20050148748A1High leucocyteHigh platelet removing abilitySemi-permeable membranesOther blood circulation devicesMeth-Blood component
A copolymer having excellent blood compatibility comprising an alkoxyalkyl (meth)acrylate and a comonomer having a basic functional group, a surface treating agent for blood filter using the same, and blood filter coated with the same on the surface thereof. The copolymer is useful as blood filter material for efficiently removing leucocytes and platelets while preventing damages of blood components at the time of blood filtration to a low level.
Owner:TERUMO KK
Continuous blood filtration and method of use
InactiveUS20040238444A1Other blood circulation devicesSolvent extractionWhole blood productReservoir bag
The invention is directed to a system for continuously filtering a blood product including whole blood or any of its component(s), erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets and plasma either alone or in combination. The system includes a connector for receiving the blood product, a filter coupled to the connector for filtering the received blood product, a collection bag coupled to the filter for collecting the filtered blood product, and a reservoir bag connected to the connector for temporarily storing received blood product, and providing received blood product through the connector to the filter to maintain continuity in filtration. The reservoir bag and the collection bag are suspended, the connector near or below the bottom of the collection bag, and the bottom of the reservoir bag is above the bottom of the collection bag. Also provided is a method of filtering a blood product using the continuous blood filtration system.
Owner:HAEMONETICS
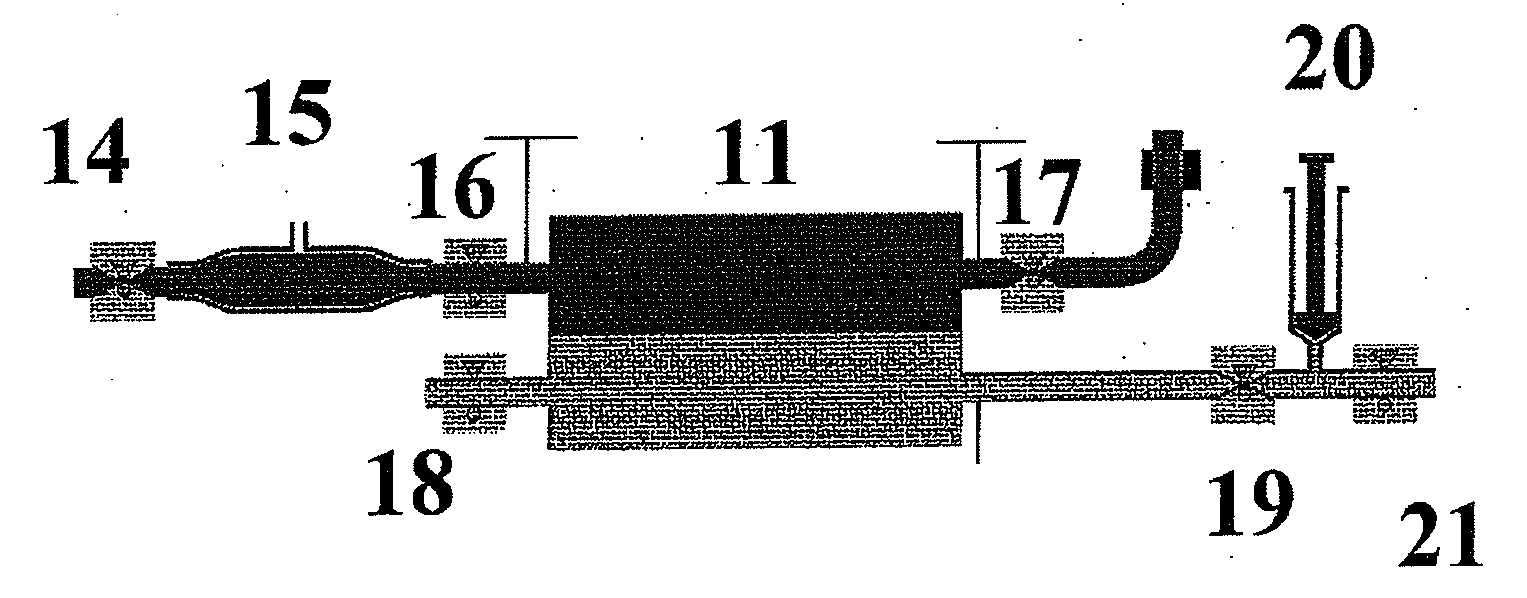
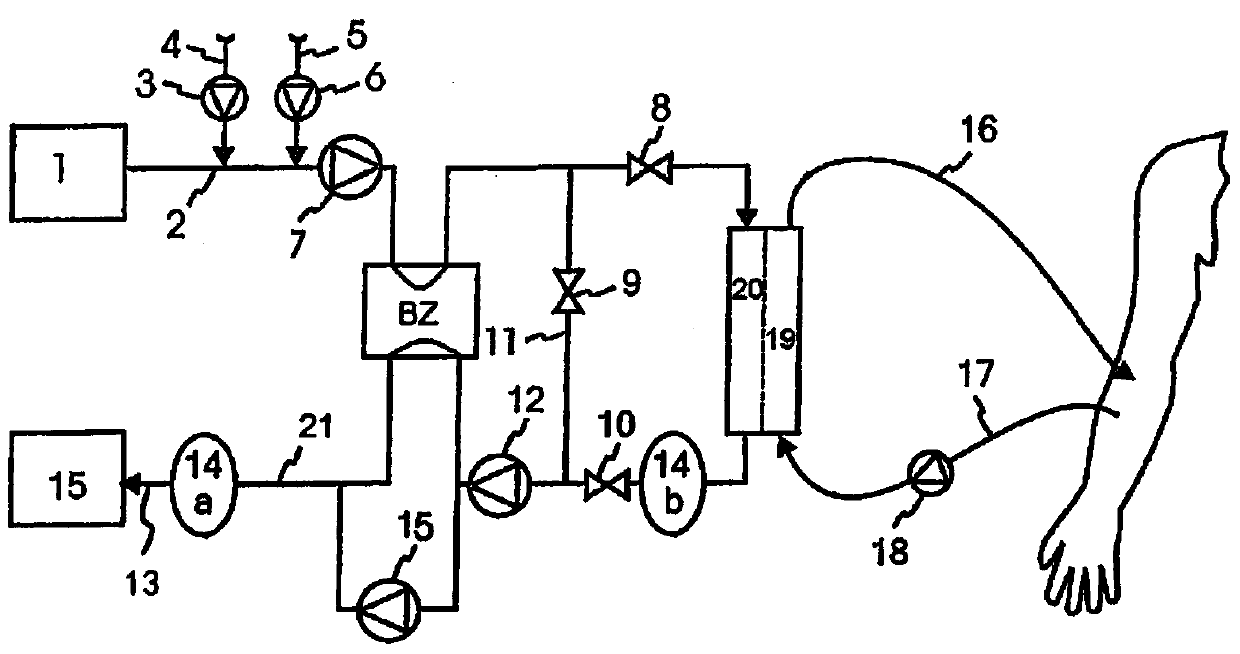
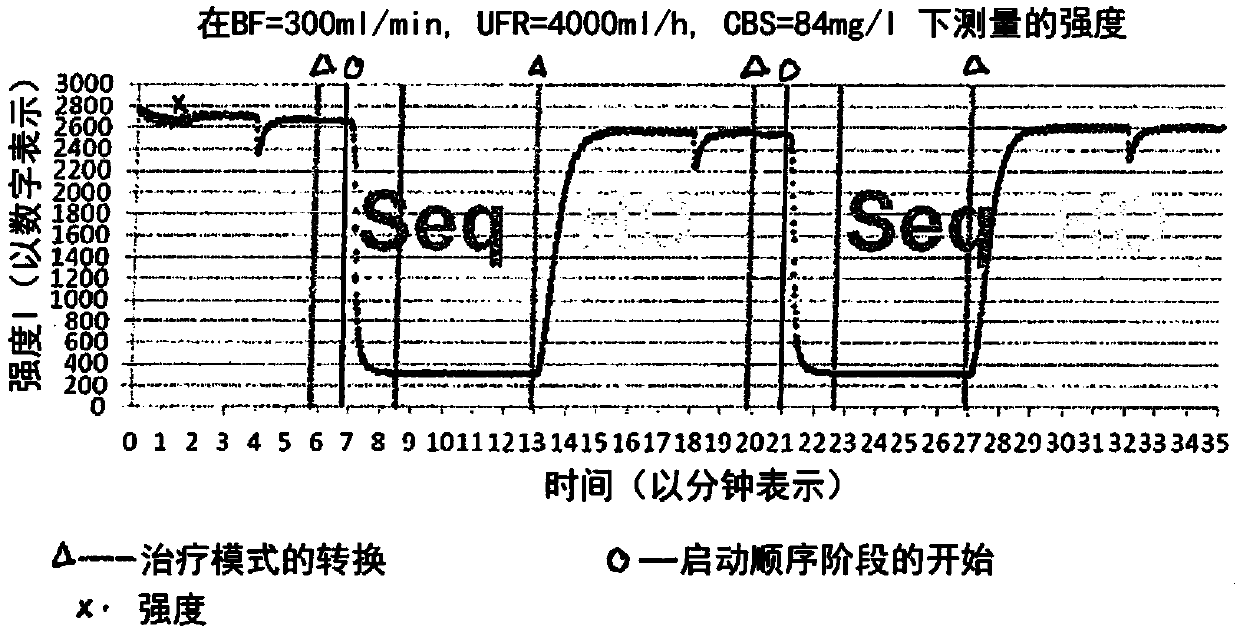
Dialysis optimisation method
A method as well as an apparatus is disclosed for determining the efficiency of a currently performed kidney replacement therapy on the dialysis side making use of a dialysis machine which in a first step is operated in a hemodialysis or hemodiafiltration process and in a second step is sequentially changed over to a hemofiltration process or is changed over to a sequential mode in which merely a flow from the blood compartment via the semipermeable membrane to the dialysis fluid compartment of the dialyser is generated in which, according to a third step, a sensor for determining or measuring the concentration at least of uremic toxins in the saturated dialysate or ultra-filtrate which is connected downstream of a dialyser on the dialysis side outputs corresponding measuring signals that are representative of the current concentration at least of uremic toxins in the blood to a calculation or determination unit.
Owner:B BRAUN AVITUM
Blood filtration methods
InactiveUS7217365B2Easy to operateEfficient removalLoose filtering material filtersGravity filtersWhite blood cellMedicine
Methods wherein a blood cell concentration gradient is formed in a pooling unit in which blood is pooled before or after introducing the blood into a filter for eliminating leukocytes followed by the filtration are disclosed. By the first method comprising forming a blood cell concentration gradient in the pooling unit before introducing blood into the filter for eliminating leukocytes followed by the filtration, leukocytes can be efficiently eliminated from a whole blood preparation or a high platelet collection ratio can be established while maintaining a high leukocyte elimination ratio. By the second method comprising forming a blood cell concentration gradient in the pooling unit after introducing blood into the filter for eliminating leukocytes followed by the filtration, leukocytes can be efficiently eliminated from a whole blood preparation or a platelet preparation and platelets can be collected at a high ratio.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI MEDICAL CO LTD
Blood conditioning device
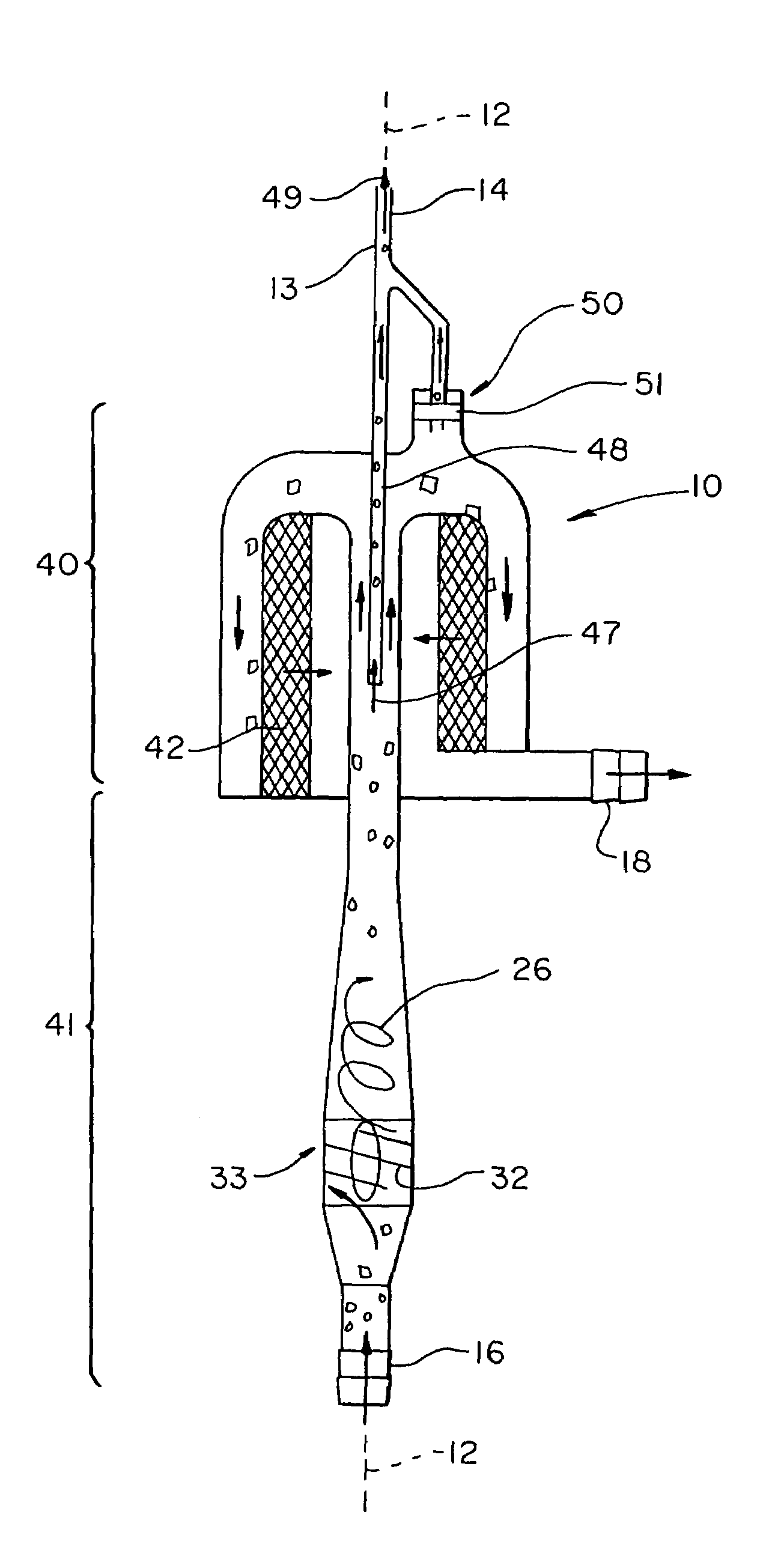
InactiveUS7108785B1Dispersed particle filtrationLiquid degasification by filtrationCardiotomy reservoirCardiotomy
A blood conditioning device having a housing with a helical blood acceleration section which includes a helical flow path for impressing centrifugal forces on the entrained bubbles in the blood to concentrate them towards the center of the flow path, a bubble pick off tube aligned with the centerline of the acceleration section which collects and recirculates the bubbles to the cardiotomy reservoir upstream of the device during operation, and a blood filtration section to intercept the flow of particles in the blood.
Owner:CONVERGENZA
Device for, and method of, blocking emboli in vessels such as blood arteries
A filtering device has a directional member and filtering member disposable in a vessel (e.g. blood artery) at a position past a lesion in the direction of fluid flow. The filtering member is made from a resilient material having properties of passing the fluid while blocking the passage of emboli in the fluid. This material may be selected from a group consisting of blood filter material and a braided / woven biocompatible material with the properties specified above. The inner end of the filtering member is attached to a shaft which provides for the disposition of the members in the vessel at the position past the lesion and the withdrawal of the members from the vessel. The directional member has a length extending at least to the vessel wall. The directional member is made from a pliable and elongatable material with properties of blocking fluid and emboli passage. The directional member is deployable within the vessel by the fluid flow in the vessel and directs the fluid in the vessel and any emboli in the fluid into the filtering member. The filtering and directional members are disposed at an acute angle relative to the shaft to create a trapping pocket. Restraining wires attached to the directional member are used to collapse the directional member and draw at least a part of the directional member into an outer sheath to prevent emboli from backflowing into the vessel.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Embolus blood clot filter with floating filter basket
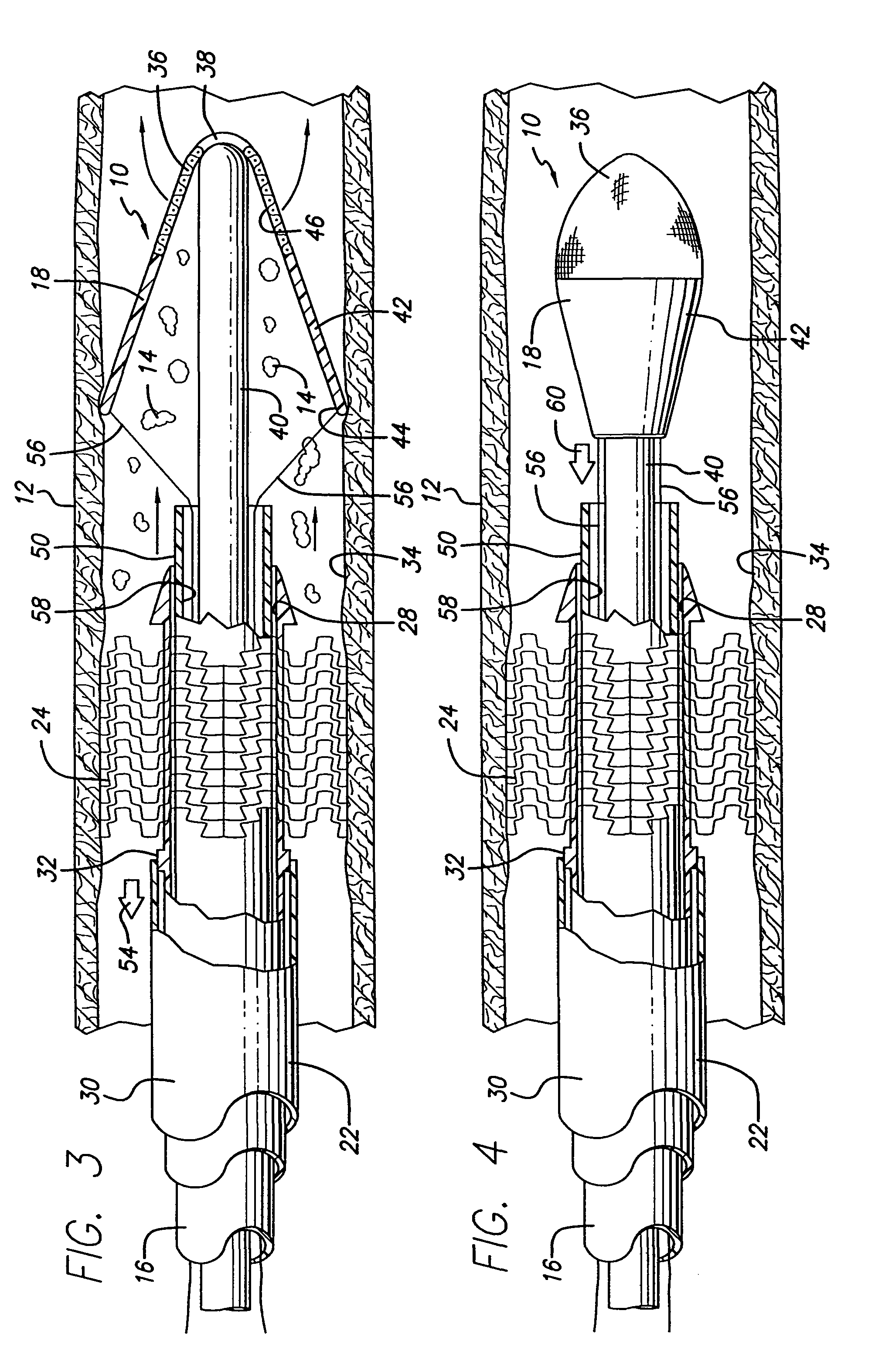
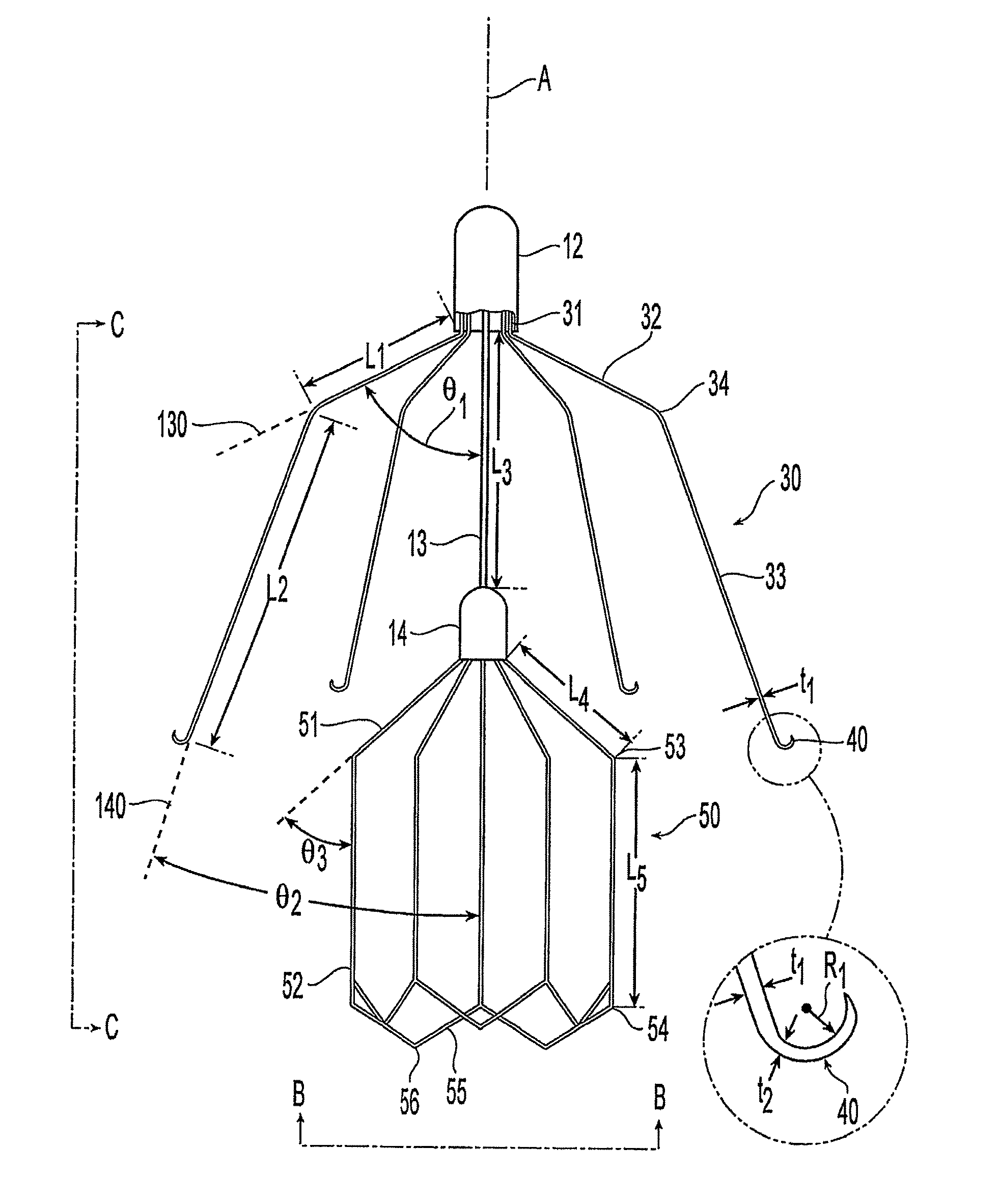
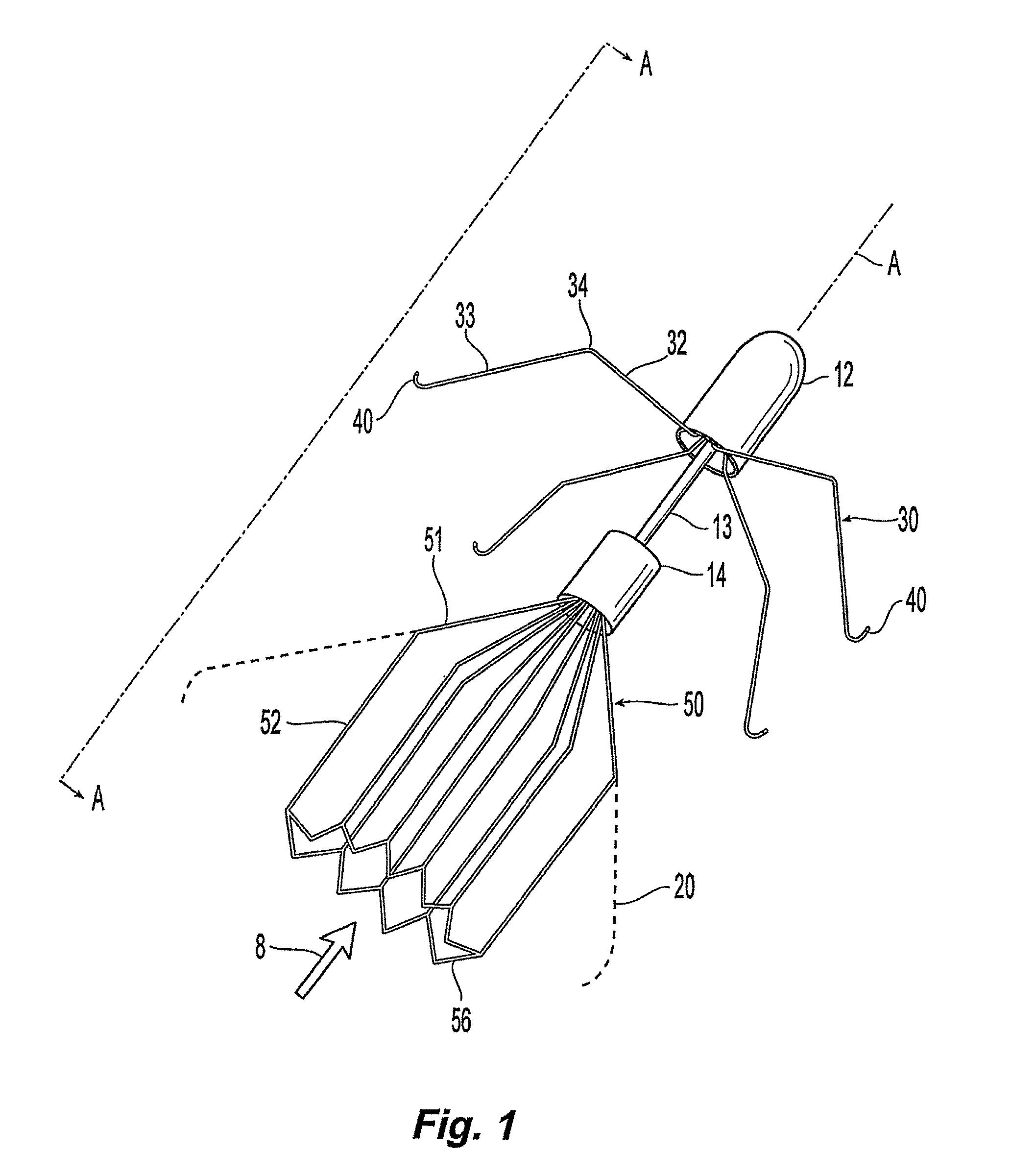
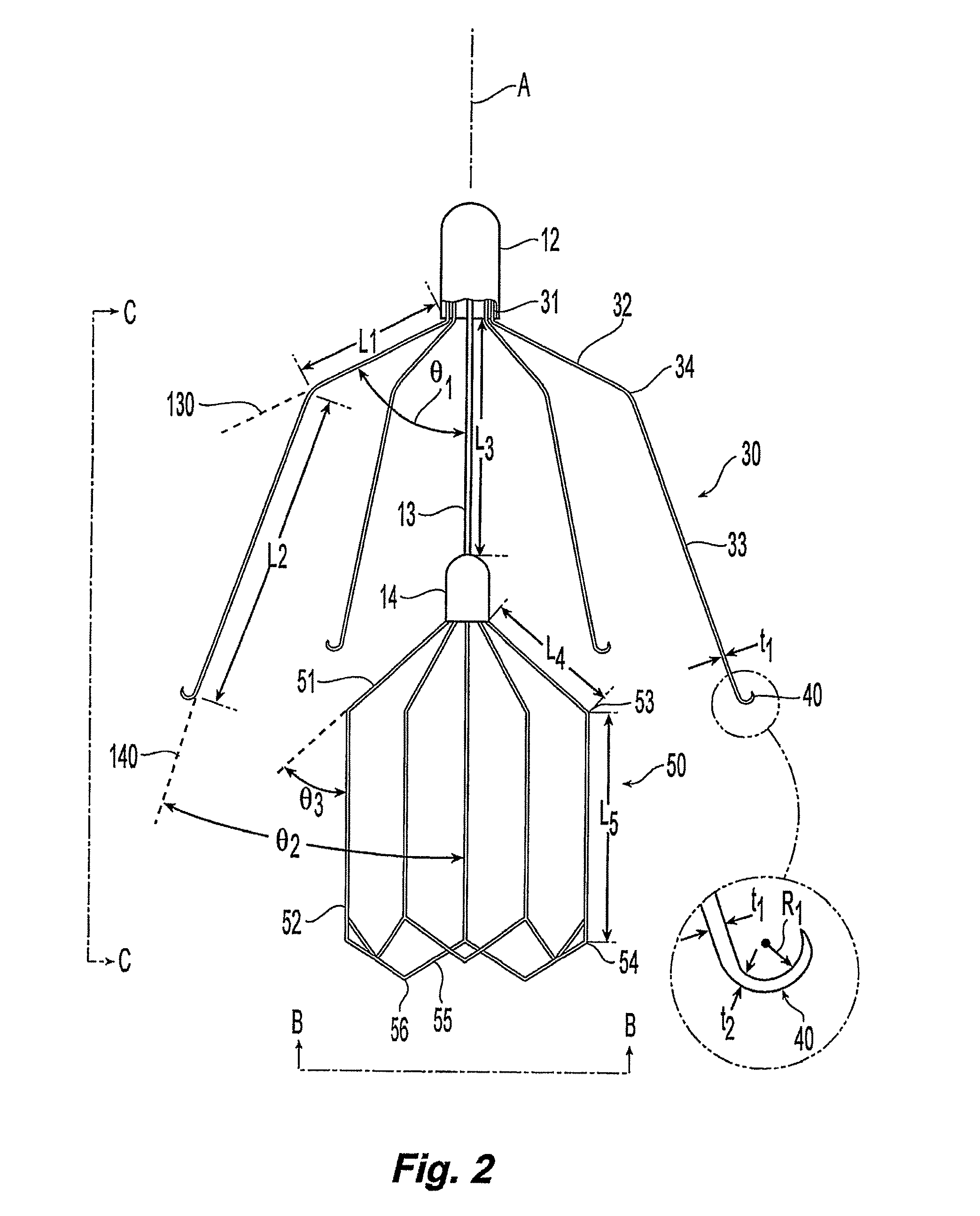
ActiveUS8562638B2Avoid vertical movementControl expansionSurgeryDilatorsBlood vesselPlasma viscosity
A blood filter device for placement in a blood vessel including a plurality of anchor members disposed radially and extending angularly about a first hub. A filter basket is preferably positioned upstream from the anchor members. The anchor members each include a hook configured to penetrate the vessel wall to prevent longitudinal movement due to blood flow. The filter basket is made up of a number of filter members configured to retain blood clots within the basket without completely blocking blood flow or applying additional force to vessel walls. Portions of the filter members may project radially outward to position the basket near the vessel centerline, but the filter basket preferably does not include hooks or anchors for anchoring the filter basket to the blood vessel.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Blood filtration system containing mannose coated substrate
ActiveUS20190038826A1Improve securityWidely targetedSemi-permeable membranesSugar derivativesPhotochemistryMannose
Owner:EXTHERA MEDICAL
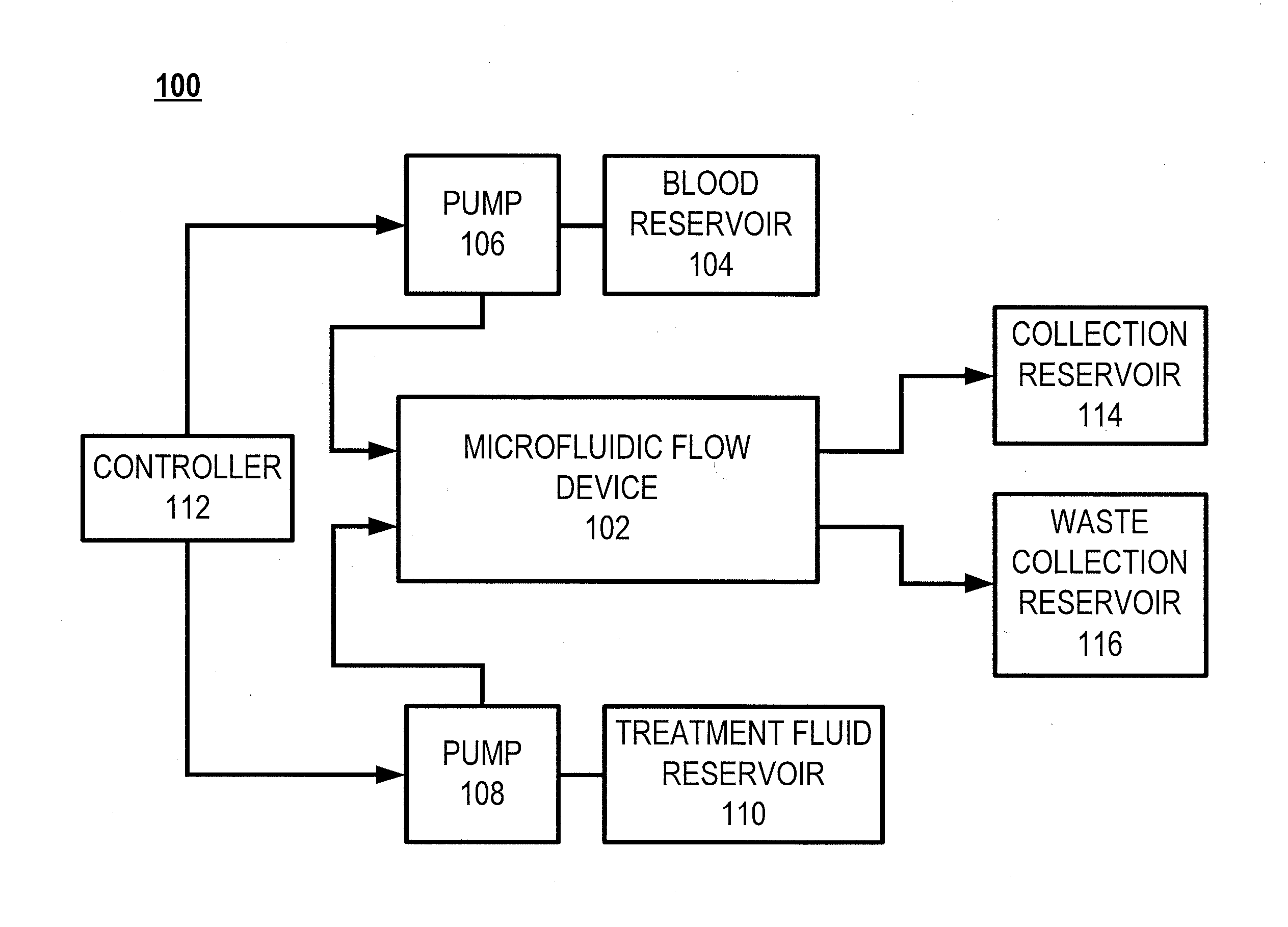
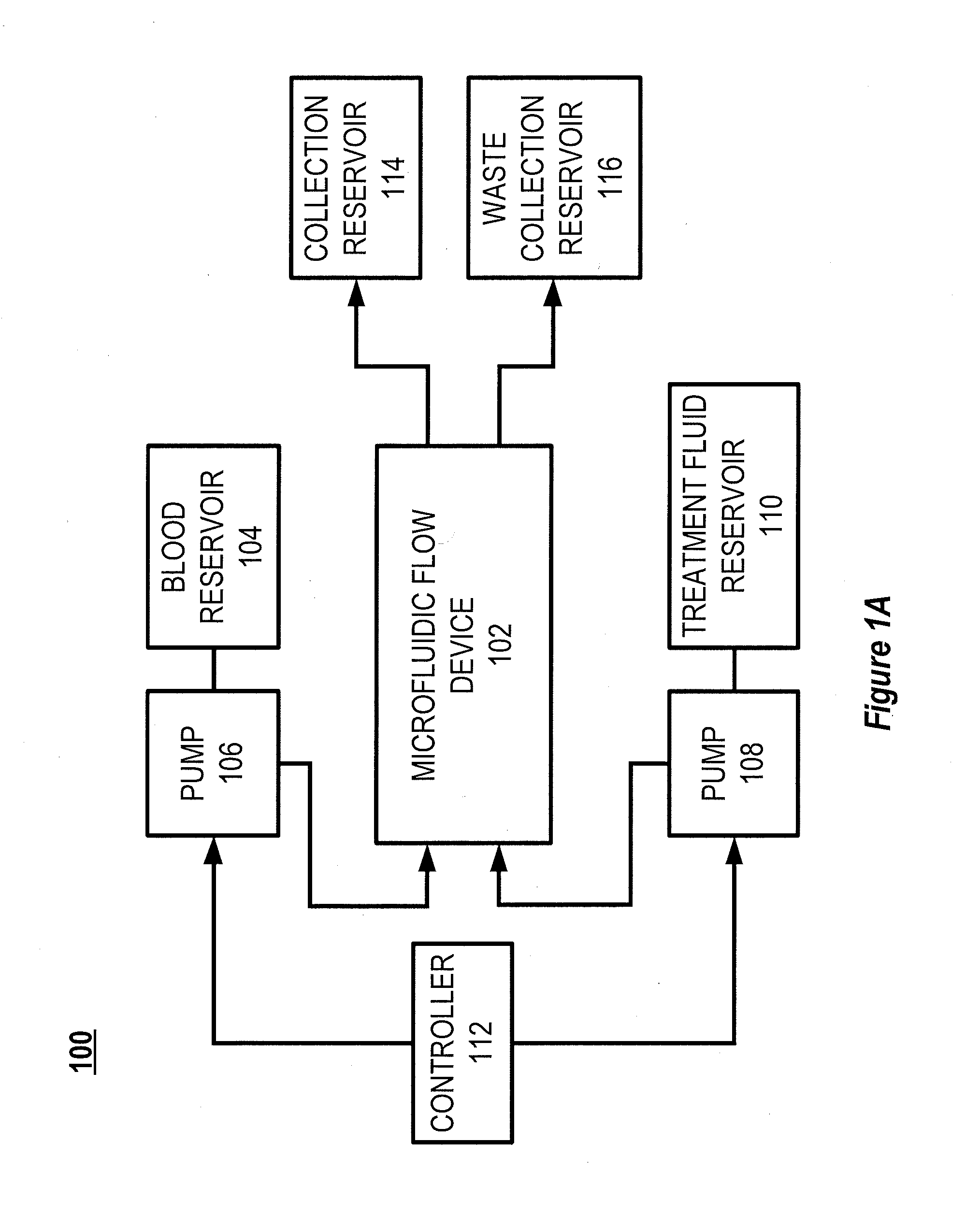
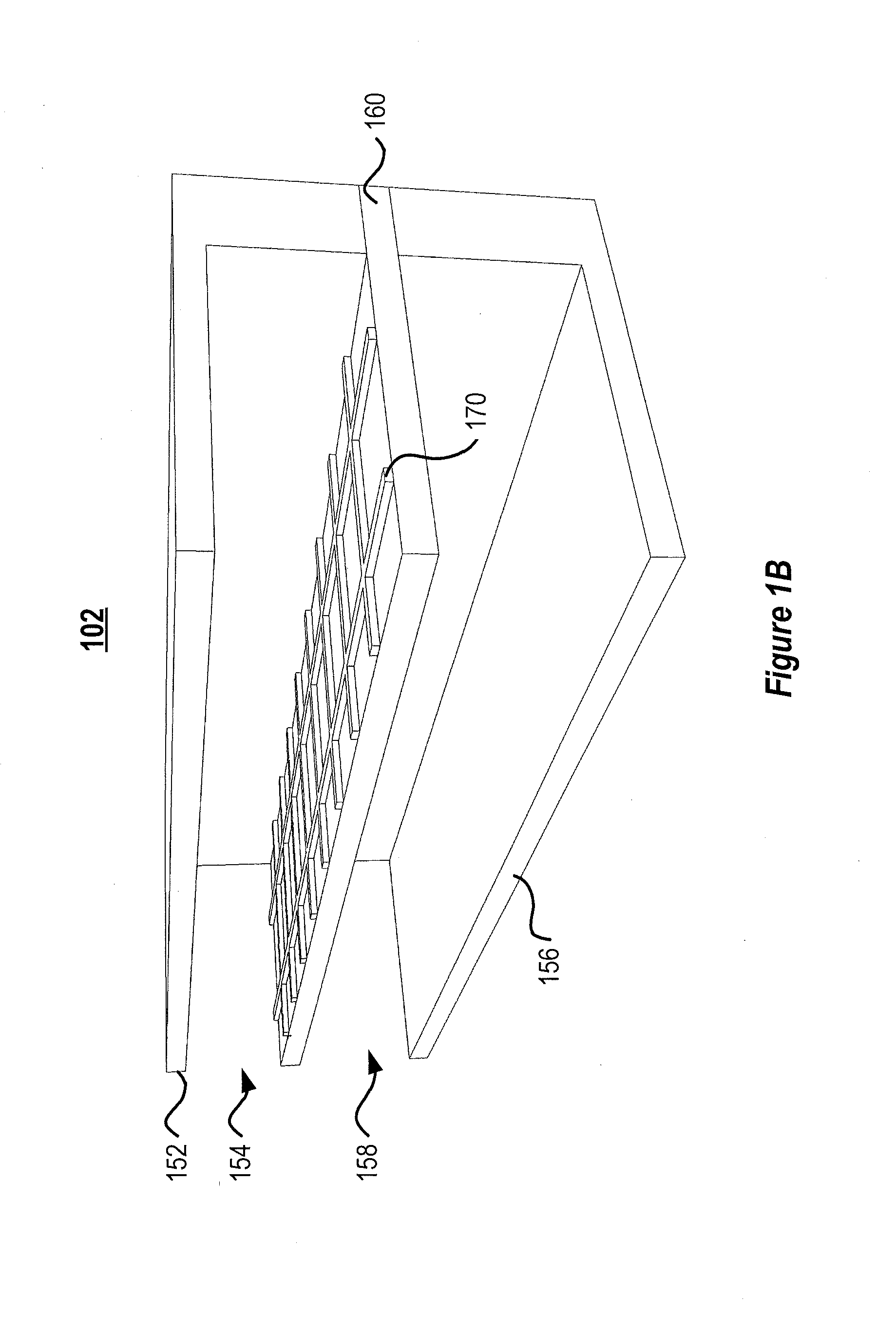
Microfluidic organ assist device incorporating boundary layer disrupters
The general disclosure discusses a system and method for improving the efficacy of blood filtration treatments such as hemodialysis, hemofiltration, and hemodiafiltration. More particularly, the disclosure discusses a microfluidic device that includes first and second channels separated by a permeable membrane. One of the channels is configured for blood flow and includes a protein gel disruption layer. The protein gel disruption layer includes a plurality of elements at least partially extending across the blood flow channel that reduce the formation of a boundary layer or gel layer at the blood-membrane interface.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON INNOVATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com