Anti-CD47 antibodies and methods of use thereof
A technology of antibodies and monoclonal antibodies, applied in the fields of antibodies, antibody medical components, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve problems such as reduced efficacy and poor pharmacokinetics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0603] Example 1: Cloning, expression and purification of human CD47
[0604] clone. The sequence corresponding to the extracellular domain of human CD47 (hCD47) was amplified from human cDNA by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using specific oligonucleotides. Amplification products were gel purified and cloned into the pEAK8 mammalian expression vector (EdgeBiosystems, Gaithersburg, MD). The vector was further modified to introduce Avitag™ (Avidity, Denver CO) and a hexa-histidine tag at the C-terminus, which allows single-site biotinylation of the protein and purification by IMAC (Immobilized Metal Ion Affinity Chromatography). Constructs were verified by DNA sequencing.
[0605] Express. The plasmid is then transfected into mammalian cells using a liposome-based transfection reagent such as TransIT-LT1 (Mirus, Madison, WI). The transfection step requires only a small amount of DNA and cells, typically 2x10 5 cells and 2 μg plasmid DNA / well, and transfections were perfo...
Embodiment 2
[0608] Example 2: Cloning, expression and purification of human CD19
[0609] clone. The sequence corresponding to the extracellular domain of human CD19 (hCD19) was amplified from human cDNA by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using specific oligonucleotides. Amplification products were gel purified and cloned into the pEAK8 mammalian expression vector (EdgeBiosystems, Gaithersburg, MD). The vector was further modified to introduce Avitag™ (Avidity, Denver CO) and a hexa-histidine tag at the C-terminus, which allows single-site biotinylation of the protein and purification by IMAC (Immobilized Metal Ion Affinity Chromatography). Constructs were verified by DNA sequencing.
[0610] expression and purification. Expression, purification and biotinylation of soluble hCD19 were performed as described in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
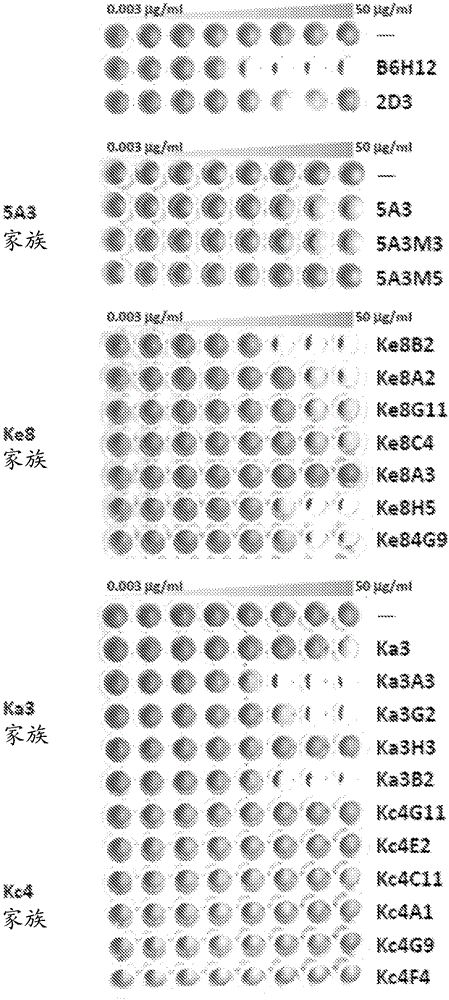
[0611] Example 3: Phage display selection using a human scFv library containing immobilized variable heavy chains
[0612] General procedures for the construction and manipulation of human scFv libraries displayed on M13 phage are described in Vaughan et al., (Nat. Biotech. 1996, 14:309-314), which is hereby incorporated by reference in its entirety. Libraries used for selection and screening encoded scFvs all sharing the same VH domain and differing only in the VL domain. Methods for producing immobilized VH libraries and their use for identifying and assembling bispecific antibodies are described in US2012 / 0184716 and WO2012 / 023053, each of which is incorporated herein by reference in its entirety. Procedures for identifying scFvs that bind hCD19 or hCD47 are described below.
[0613] Liquid phase selection. An aliquot of the scFv phage library (10 12 Pfu) were blocked with PBS containing 3% (w / v) skim milk for one hour at room temperature in a rotary mixer. Blocked pha...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com