Method and reactor for million kilowatt nuclear power station to process radioactive wastewater
A technology for radioactive wastewater and nuclear power plants, applied in radioactive purification, nuclear engineering, etc., can solve problems such as increased water head loss and failure of fixed bed adsorption reactors to achieve the effects of reducing reaction time, shortening settlement distance, and improving separation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
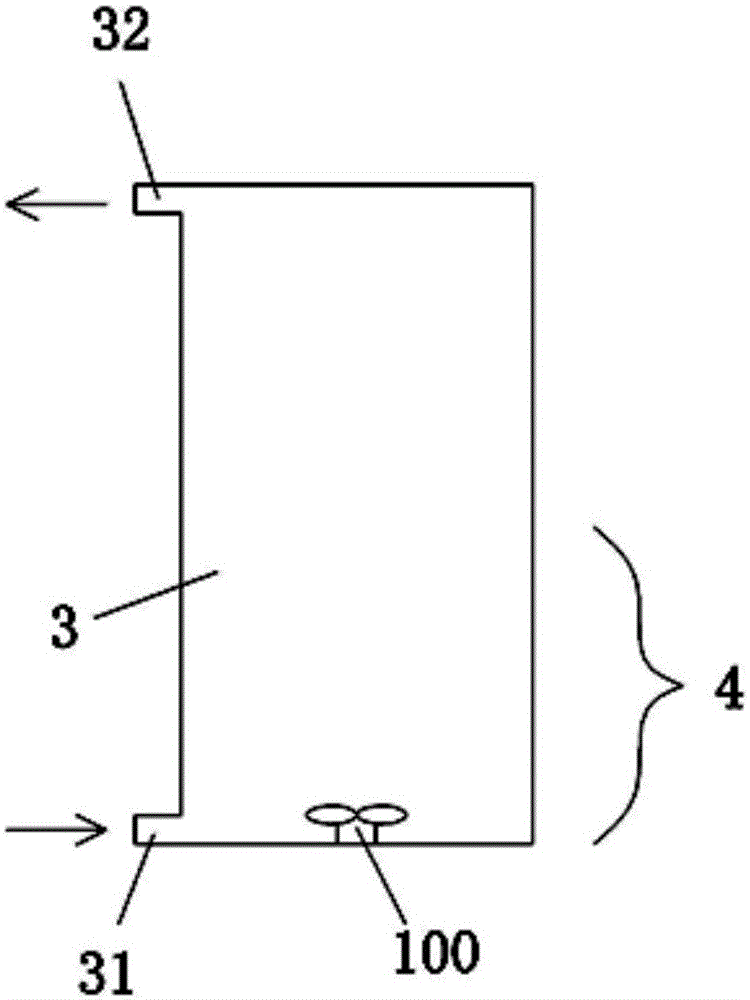
[0066] The reactor 3 used in this embodiment to treat radioactive waste water in a million-kilowatt nuclear power plant is as follows: figure 2 As shown, the lower part of the reactor 3 has a water inlet 31 for radioactive waste water (raw water), and the upper part has a water outlet 32 for treated waste water. An adsorption reaction zone 4 is arranged in the inner cavity of the reactor 3, and the adsorption reaction zone 4 is placed There are granular adsorbents, and the specific gravity of the adsorbent is greater than that of the wastewater.
[0067] The reactor 3 in this embodiment is used to treat radioactive waste water. The method is: the radioactive waste water is input into the reactor 3 from the water inlet 31 and discharged from the water outlet 32. During this period, the adsorbent is suspended and dispersed in the adsorption reaction by stirring with the mechanical stirrer 100. In the radioactive wastewater in zone 4, the mechanical agitator 100 is specificall...
Embodiment 2
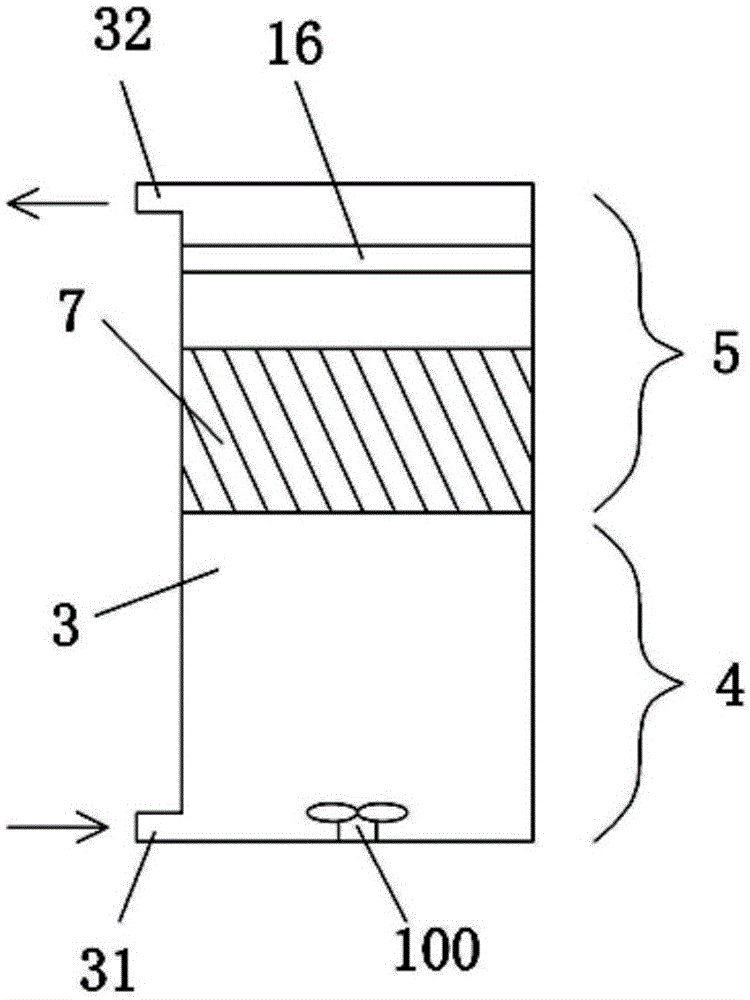
[0069] The reactor 3 used in this embodiment to treat radioactive waste water in a million-kilowatt nuclear power plant is as follows: image 3 As shown, the bottom of the reactor 3 inner cavity is an adsorption reaction zone 4, and the upper part of the reactor 3 inner cavity is a separation zone 5; the adsorption reaction zone 4 is provided with a water inlet 31 and a stirring device for radioactive waste water, and the stirring device is used in this implementation In an example, it is specifically a mechanical stirrer 100, such as a paddle stirrer. A granular adsorbent is placed in the adsorption reaction zone 4, and the specific gravity of the adsorbent is greater than that of the waste water. The mechanical agitator 100 suspends and disperses the adsorbent particles whose specific gravity is greater than that of the wastewater in the radioactive wastewater.
[0070] An intercepting device for retaining the adsorbent in the reactor 3 is provided in the separation zone 5 ...
Embodiment 3
[0073] The reactor 3 used in this embodiment to treat radioactive waste water in a million-kilowatt nuclear power plant is as follows: Figure 4 As shown, the bottom of the reactor 3 inner cavity is an adsorption reaction zone 4, and the upper part of the reactor 3 inner cavity is a separation zone 5; the adsorption reaction zone 4 is provided with a water inlet 31 and a stirring device for radioactive waste water, and the stirring device is used in this implementation In an example, it is specifically a mechanical stirrer 100, such as a paddle stirrer. A granular adsorbent is placed in the adsorption reaction zone 4, and the specific gravity of the adsorbent is greater than that of the waste water. The mechanical agitator 100 suspends and disperses the adsorbent particles whose specific gravity is greater than that of the wastewater in the radioactive wastewater.
[0074] An intercepting device for retaining the adsorbent in the reactor 3 is provided in the separation zone 5...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com