Low-temperature lead-free solder alloy
A lead-free solder alloy, solder alloy technology, applied in welding/cutting media/materials, welding media, welding equipment, etc., can solve the adverse effects of increasing temperature performance and assembly quality, increasing electronic assembly energy consumption, comprehensive energy It can improve the mechanical shock resistance and drop performance, improve the coarse grain size of Bi phase, and reduce welding defects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
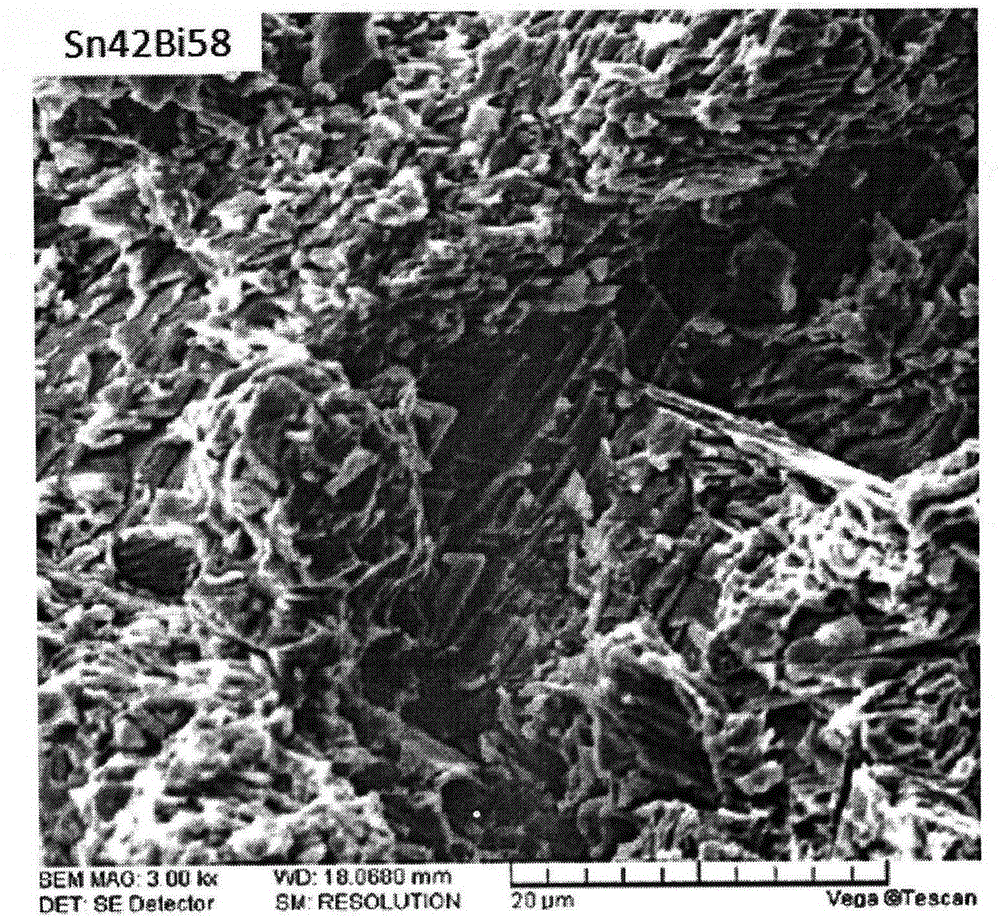
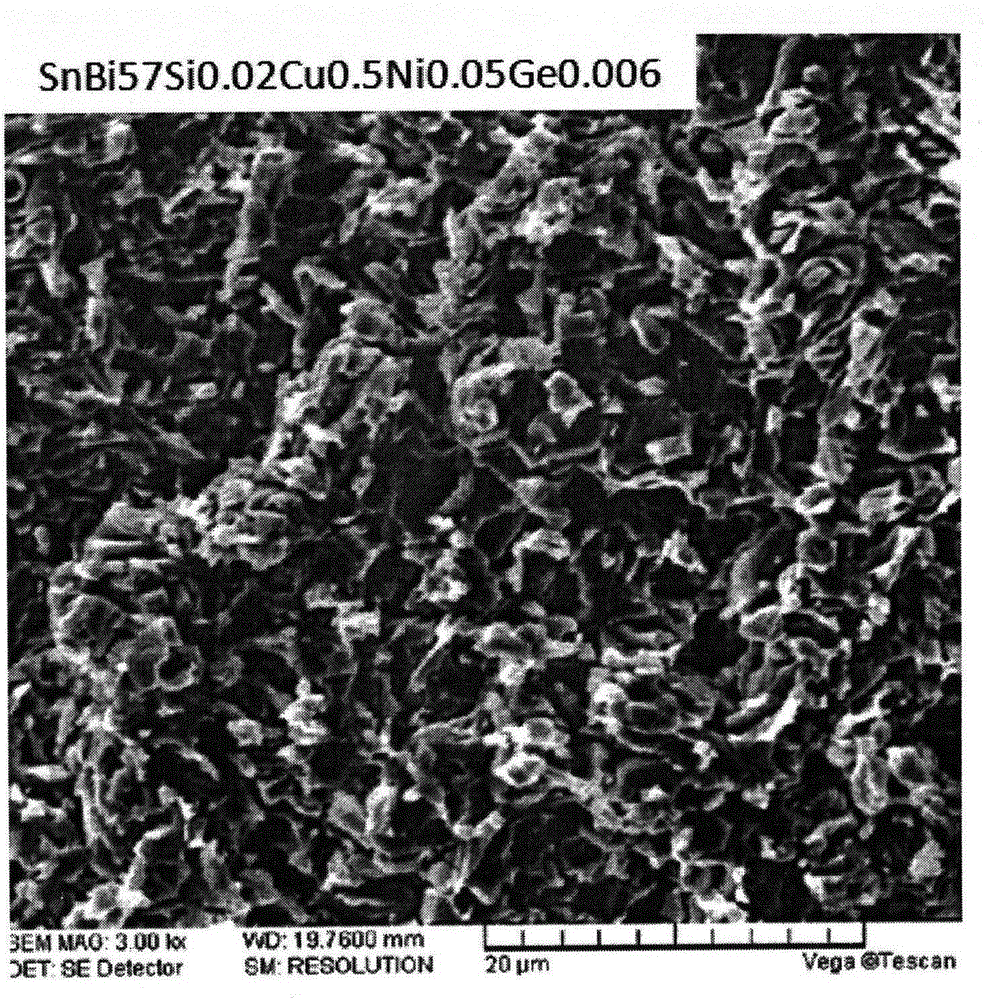
[0080] The formulations of the solders of the specific examples and comparative examples of the present invention are shown in Table 1, wherein the contents of the main components Sn and Bi of comparative examples 1 and 2 are basically the same as those of the examples so that performance comparisons can be carried out.
[0081] Table 1: Examples and Comparative Examples
[0082]
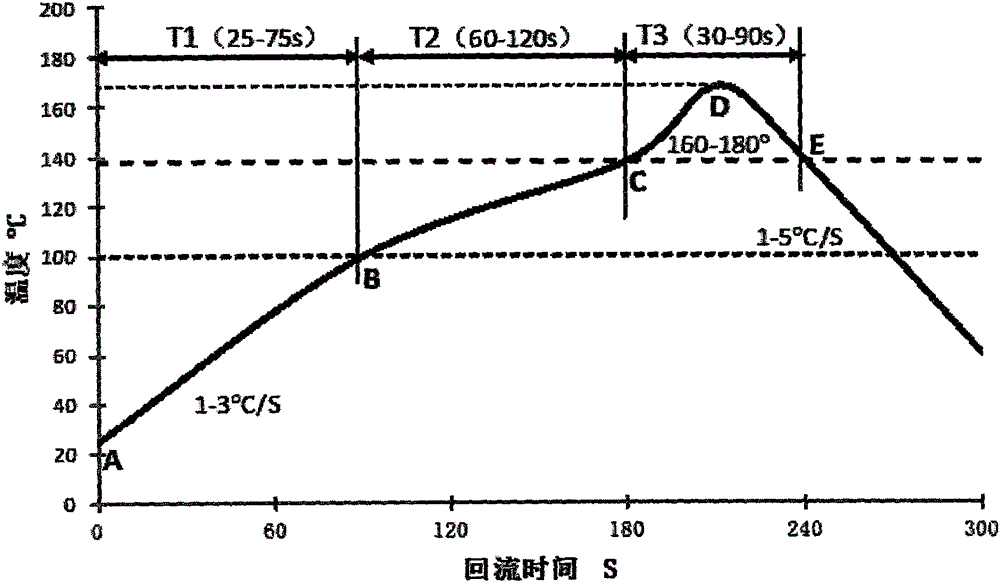
[0083] The steps of the manufacturing method of each of the above-mentioned embodiments are as follows:
[0084] (1) The Si is heated to 1450-1500° C. for 2-3 hours in a vacuum induction heating furnace according to the proportion (percentage by weight) of Sn-0.25% in powder form, and cast into a Sn-Si master alloy ingot after cooling ;
[0085] (2) Prepare the above-mentioned Sn-Si master alloy ingot by mechanical crushing method or metal atomization method to make alloy powder with particle size less than 100 microns;
[0086] (3) melting one or more of the above-mentioned microalloying eleme...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com