Method for producing ethanol from microbial fermentation lignocellulose raw material
A lignocellulose and microbial fermentation technology, applied in the field of microbial fermentation, can solve the problem of low conversion rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
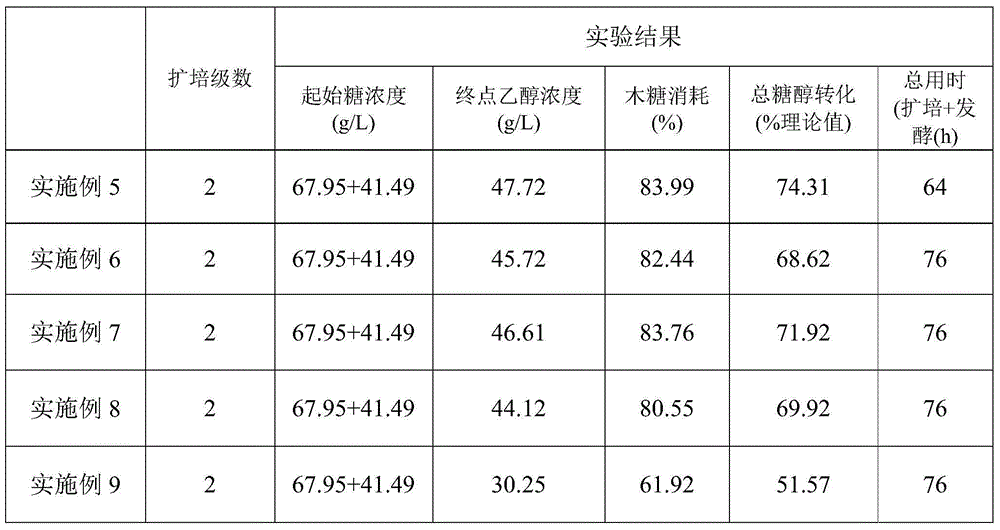
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0071] This embodiment provides an expanded culture method for co-fermenting C5 and C6 microorganisms to produce ethanol. Taking recombinant S. )(如CellulosicethanolproductionfromAFEX-treatedcornstoverusingSaccharomycescerevisiae424A(LNH-ST),M.W.Lau,B.E.Dale,ProcNatlAcadSciUSA,106(2009),pp.1368-1373;Two-stepSSCFtoconvertAFEX-treatedswitchgrasstoethanolusingcommercialenzymesandSaccharomycescerevisiae424A(LNH-ST),M.Jin,M.W.Lau,V .Balan, B.E.Dale, BioresourTechnol, 101(2010), pp.8171-8178 etc. report), is commercially available, and described expanded cultivation method adopts one-level expanded cultivation step, specifically comprises:
[0072] A. Seed liquid culture steps
[0073] Prepare YEPD medium, inoculate the preserved above bacteria into YEPD medium, control the temperature at 25°C, pH 6.0, rotating speed at 200rpm, ventilation rate at 0.2L / L.min, and cultivate for 12h until the concentration of the above bacteria is (0.1 -0.5)×10 9 / ml;
[0074] The YEPD medium specif...
Embodiment 2
[0079] This embodiment provides a method for expanding cultivation of microorganisms that co-ferment C5 and C6 to produce ethanol. Taking Candida tropicalis as an example to carry out the expansion cultivation experiment, the Candida tropicalis is commercially available, and the expansion cultivation method adopts Secondary expansion cultivation steps, specifically include:
[0080] A. Seed liquid culture steps
[0081] Prepare the YEPD medium, inoculate the preserved above bacteria into the YEPD medium, control the temperature at 25°C, pH6.0, rotating speed at 200rpm, air flow at 0.2L / L.min, and cultivate until the concentration of the above bacteria is (0.1-0.5 )×10 9 / ml;
[0082] The YEPD medium specifically contains 10 g / L of yeast powder, 20 g / L of peptone, and 20 g / L of glucose, and the pH is adjusted to 6.0.
[0083] B. Expand the cultivation steps
[0084] 1) Put the cultured seed solution into a 50L primary expansion tank containing a primary expansion medium acc...
Embodiment 3
[0088] This embodiment provides a kind of expanded culture method of co-fermenting C5 and C6 to produce ethanol microorganisms, take recombinant S. Three-level expanded cultivation steps, specifically including:
[0089] A. Seed liquid culture steps
[0090] Prepare YEPD medium, inoculate the preserved above bacteria into YEPD medium, control the temperature at 30°C, pH 6.0, ventilation rate 0.2L / L.min, rotation speed 200rpm, and cultivate for 14h until the concentration of the above bacteria is (0.2 -0.3)×10 9 / ml;
[0091] The YEPD medium specifically contains 10 g / L of yeast powder, 20 g / L of peptone, and 20 g / L of glucose, and the pH is adjusted to 6.5.
[0092] B. Expand the cultivation steps
[0093] 1) Put the cultured seed solution into a 50L primary expansion tank containing a primary expansion medium according to the inoculum amount of 10% (v / v), control the temperature at 30°C, pH 5.0, and rotate at 200rpm Ventilate the air, the ventilation rate is 0.5L / L.min, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com