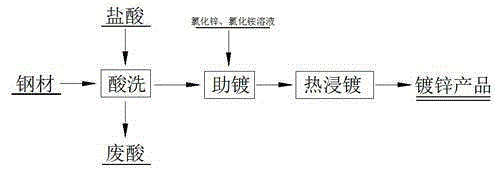
Preparation method of iron oxide red and ammonium chloride
A technology of iron oxide red and ammonium chloride, applied in iron oxide/iron hydroxide, iron oxide, ammonium halide and other directions, can solve the problem of high equipment investment and energy consumption, iron oxide tinting strength and color uniformity are not described, The problem of huge waste acid output, etc., achieves the effect of small investment in equipment, uniform and bright colors, and environmental friendliness.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
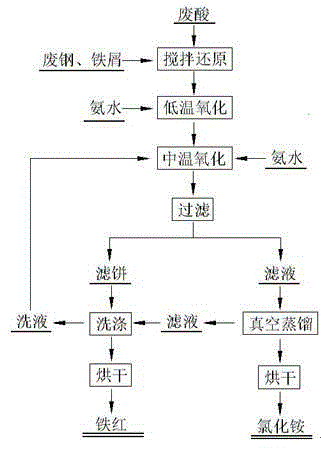
[0029] Such as figure 2 Shown, this preparation iron oxide red and the method for ammonium chloride, its concrete steps comprise as follows:
[0030] (1) Reduction: First, mix and stir the waste acid and scrap steel chips or scrap steel scraps according to the liquid-solid ratio of 20:1ml / g to get all the iron into Fe 2+ solution (the Fe in the spent acid 3+ All reduced to Fe 2+ ); where the waste acid is the waste acid produced in the hot-dip galvanizing process, including the following mass percentage components: FeCl 2 40%, FeCl 3 5%, HCl4%, impurity content 0.3%, the balance is water;
[0031] (2) Low-temperature oxidation: adjust the pH value of the solution obtained in step (1) to 9.2 with ammonia water at a temperature of 3°C, and pass air into it for low-temperature oxidation for 150 minutes to make the FeCl in the waste acid 2 Converted to γ-FeOOH; the amount of air introduced is 0.3m 3 · Cubic solution -1 h -1 ;
[0032] (3) Medium-temperature oxidation: ra...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Such as figure 2 Shown, this preparation iron oxide red and the method for ammonium chloride, its concrete steps comprise as follows:
[0037] (1) Reduction: First, mix and stir the waste acid and scrap steel chips or scrap steel scraps according to the liquid-solid ratio of 50:1ml / g to obtain all the iron as Fe. 2+ solution (the Fe in the spent acid 3+ All reduced to Fe2+ ); where the waste acid is the waste acid produced in the hot-dip galvanizing process, including the following mass percentage components: FeCl 2 8%, FeCl 3 0.1%, HCl0.2%, impurity content 0.05%, the balance is water;
[0038] (2) Low-temperature oxidation: adjust the pH value of the solution obtained in step (1) to 11.9 with ammonia water at a temperature of 5°C, and pass air into it for low-temperature oxidation for 360 minutes to make the FeCl in the waste acid 2 Converted to γ-FeOOH; the amount of air introduced is 3.5m 3 · Cubic solution -1 h -1 ;
[0039] (3) Medium-temperature oxidatio...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Such as figure 2 Shown, this preparation iron oxide red and the method for ammonium chloride, its concrete steps comprise as follows:
[0044] (1) Reduction: First, mix and stir the waste acid and scrap steel chips or scrap steel scraps according to the liquid-solid ratio of 500:1ml / g to get all the iron into Fe 2+ solution (the Fe in the spent acid 3+ All reduced to Fe 2+ ); where the waste acid is the waste acid produced in the hot-dip galvanizing process, including the following mass percentage components: FeCl 2 25%, FeCl 3 4%, HCl3%, impurity content 0.25%, the balance is water;
[0045] (2) Low-temperature oxidation: adjust the pH value of the solution obtained in step (1) to 11.5 with ammonia water at a temperature of 7°C, and pass air into it for low-temperature oxidation for 400 minutes to make the FeCl in the waste acid 2 Converted to γ-FeOOH; the amount of air introduced is 3.2m 3 · Cubic solution -1 h -1 ;
[0046] (3) Medium-temperature oxidation:...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com