Drug-resistant microbe and variant microbe disinfectant containing chlorous acid aqueous solution
A chlorous acid aqueous solution, the technology of resistant bacteria, applied in the direction of chlorous acid, disinfectant, chlorite, etc., to achieve high-efficiency disinfection ability, the effect of reliable human body
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0137] (Example 1: Preparation of chlorous acid aqueous solution)
[0138] The aqueous chlorous acid formulations used in the following examples are prepared as follows. In this article, the abbreviation "CAAS" is used in the case of aqueous chlorous acid. However, they have the same meaning.
[0139] Composition analysis table of chlorous acid aqueous solution
[0140] [Table 2]
[0141]
[0142]
[0143] An aqueous chlorous acid solution based on the following blend was used to prepare an aqueous chlorous acid solution formulation.
[0144] [table 3]
[0145]
[0146] [Table 4]
[0147] CAAS specification
Chlorous acid aqueous solution preparation prepared with chlorous acid aqueous solution
Content
3.0%
Attributes
Yellow
Match
Matching (the curve of absorbance and wavelength is shown in Figure 8 In)
Match
Purity test (1)
Below detection limit
Purity test (2)
Below detection limit
[0148] (M...
Embodiment 2
[0155] (Example 2: Effect on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus COL)
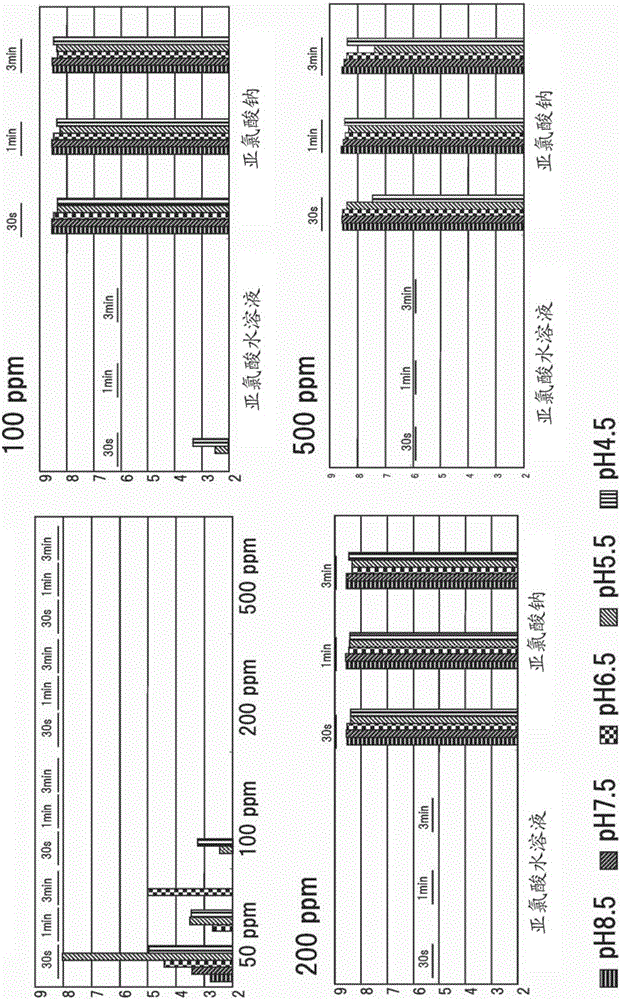
[0156] In this example, the effect on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus was tested. The method is as described above ((Method of measuring sterilization (bacterial sterilization))). The results are shown in Figure 2.
[0157] As shown in the figure, it is proved that MRSA is mostly sterilized at 100 ppm or higher. We found that MRSA is completely sterilized at 100 ppm in a neutral to alkaline zone with a high pH of 6.5 or higher. As can be seen from the above, the neutral to alkaline region is understood to be preferable for Gram-positive bacteria such as MRSA compared to the existing knowledge. More specifically, we found that MRSA is completely sterilized at 100 ppm in a neutral zone with a high pH of 6.5 to 8.5, and considering the difference from sodium chlorite, the pH is 6.5 or higher and less than 7.0. As can be seen from the above, the pH in the neutral zone is understood to be pre...
Embodiment 3
[0158] (Example 3: Effect on Multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa TUH)
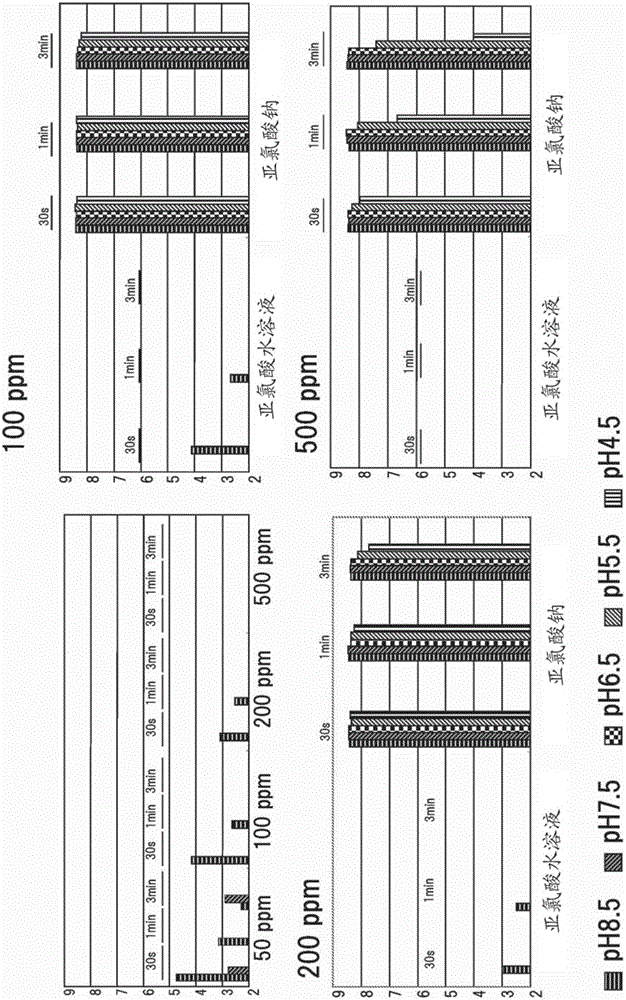
[0159] In this example, the effect on multi-drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa was tested. The method is as described above ((Method of measuring sterilization (bacterial sterilization))). The results are shown in Figure 3.
[0160] As shown in the figure, it is proved that MDRP is mostly sterilized at 100 ppm or higher, and is completely sterilized at 500 ppm. In particular, we found that MDRP was completely sterilized even at 50 ppm in an acidic zone with a low pH of 6.5 or higher. It can be seen from the above that compared with the prior knowledge, it has been found that the antibacterial effect has a preferred pH that differs depending on the bacteria.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com