Nanoemulsion vaccine adjuvant
A vaccine adjuvant and nanoemulsion technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve problems such as high cost, long process operation time, and large energy demand
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Preparation of nanoemulsion vaccine adjuvant
[0035]1) Coarse milk preparation: use squalene as oil phase, mix with Tween 80 and Span 80. In addition, PBS, a buffer agent with a neutral pH, was added as the aqueous phase. The HLB is 9.5, the total amount of surfactant is 11%, the ratio of water to oil is 0.4, stirred for 15-20 minutes and heated to 55-70°C. (2) Phase transition and formation of nanoemulsion: keep the temperature at 55-70°C, continue stirring for 5-10 minutes, then quickly transfer the hot emulsion to a large amount (5 times the initial total amount) of PBS buffer at 4-8°C Dilute in solvent while stirring constantly. Continue stirring for 10-30 minutes to prepare the nanoemulsion vaccine adjuvant product. Store the product in aliquots at 2-8°C in a refrigerator.
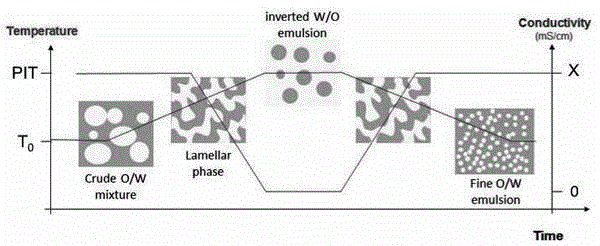
[0036] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of temperature, particle size and conductivity in the preparation of nanoemulsion vaccine adjuvant PIT method in this embodiment, as figure 1 As...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Product Stability Test
[0042] Stability is an important indicator of vaccine adjuvants. Table 2 shows the stability data of six batches of nanoemulsion vaccine adjuvants in Example 1 placed at 25°C for 12 months. As can be seen from Table 2, the nanoemulsion vaccine adjuvant has no significant change in particle size (the most important stability index) within 12 months, and the product quality is stable.
[0043] Table 2 The particle size of nanoemulsion vaccine adjuvant for 12 months
[0044]
[0045]
Embodiment 3
[0047] Sensitization of vaccine adjuvants
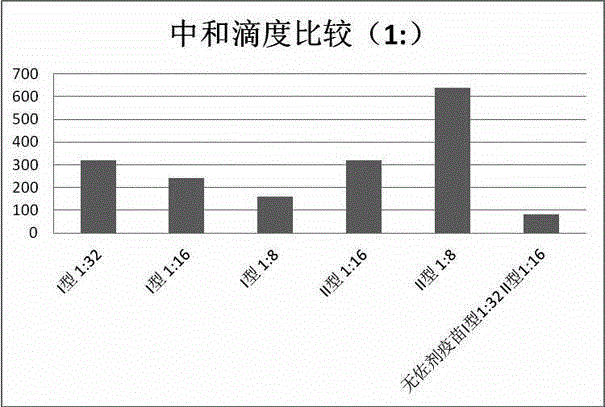
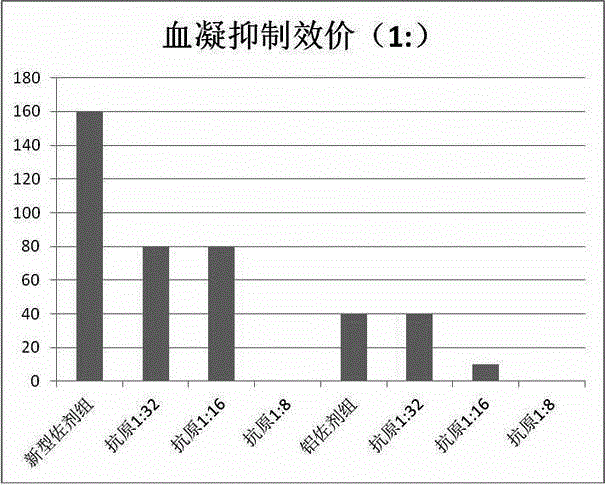
[0048] Rabbit experiments are used to verify the sensitization of the vaccine adjuvant of the present invention. Wherein the control group is a conventional hemorrhagic fever vaccine without adjuvant (1:32 for type I antigen, 1:16 for type II), and the same hemorrhagic fever antigen is selected for the experimental group, and finally the vaccine adjuvant vaccine prepared in Example 1 is added. agent, the configuration process is the same as that of conventional non-adjuvanted vaccines. Type I antigen titers were 1:32, 1:16, 1:8, and type II antigen titers were 1:16, 1:8. A booster injection was given on the 7th day after the primary immunization, and blood was collected 21 days after the primary immunization for the determination of the neutralizing fluorescence titer. The result is as figure 2 As shown, it can be seen from it that the fluorescent antibody level after its immunization of the vaccine (type I and type II HA titer i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com