Method and apparatus for producing resin particles using granulation-prevention agent, and resin particles produced by the method
a technology of granulation prevention agent and resin particle, which is applied in the field of method of producing resin particle and resin particle produced by method, can solve the problems of difficult to sufficiently enhance the strength of resin particle, low strength of resin particle produced in such a manner, and high cost of production, so as to achieve the effect of increasing the amount of toner to be packed in the cartridge, superior electrification properties and durability, and increasing the bulk density of toner
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0217]First, 100 parts by weight of an epoxy resin (a modified epoxy resin, glass transition point Tg: 70° C., melting point Tm: 110° C. manufactured by Arakawa Chemical Industries, LTD.) as a binder resin. 5 parts by weight of a phthalocyanine pigment (phthalocyanine blue, manufactured by Dainichiseika Color & Chemicals Mfg. Co., Ltd.) as a coloring agent, and 300 parts by weight of tetrahydrofuran (manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd) as a solvent were prepared.
[0218]These components were mixed and dispersed using a ball mill for 10 hours to prepare a resin solution (a resin liquid).
[0219]At the same time, 10 parts by weight of sodium polyacrylate (average degree of polymerization n=2,700 to 7,500, manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd.) as a dispersant was dissolved in 590 parts by weight of ion-exchange water to prepare an aqueous solution.
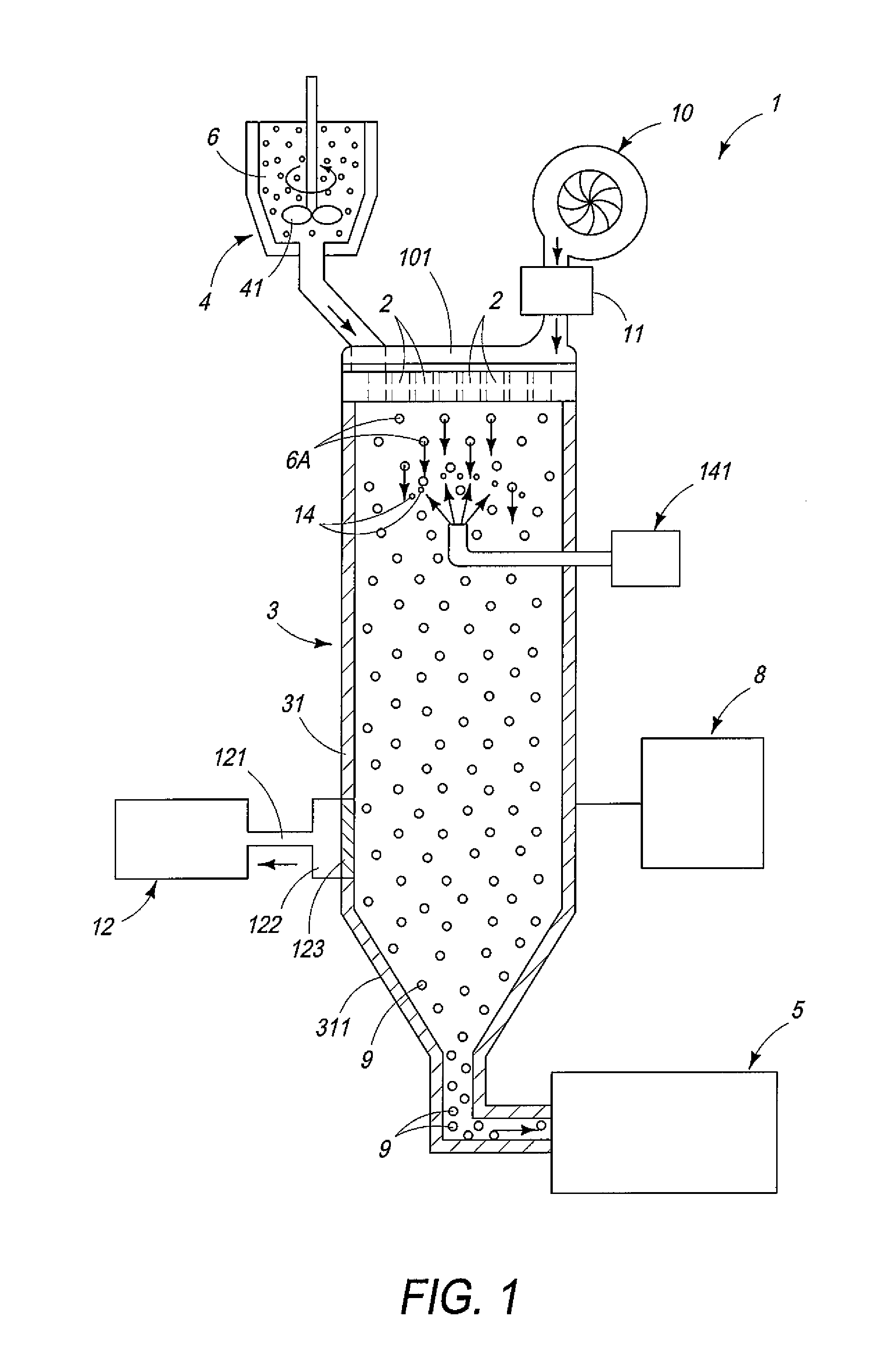
[0220]Next, 600 parts by weight of the aqueous solution was poured into a 3-liter round-bottom stainless containe...
example 2
[0231]A toner was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the resin was changed to a styrene-acrylic ester copolymer (glass transition point Tg: 52° C., melting point Tm: 105° C.).
example 3
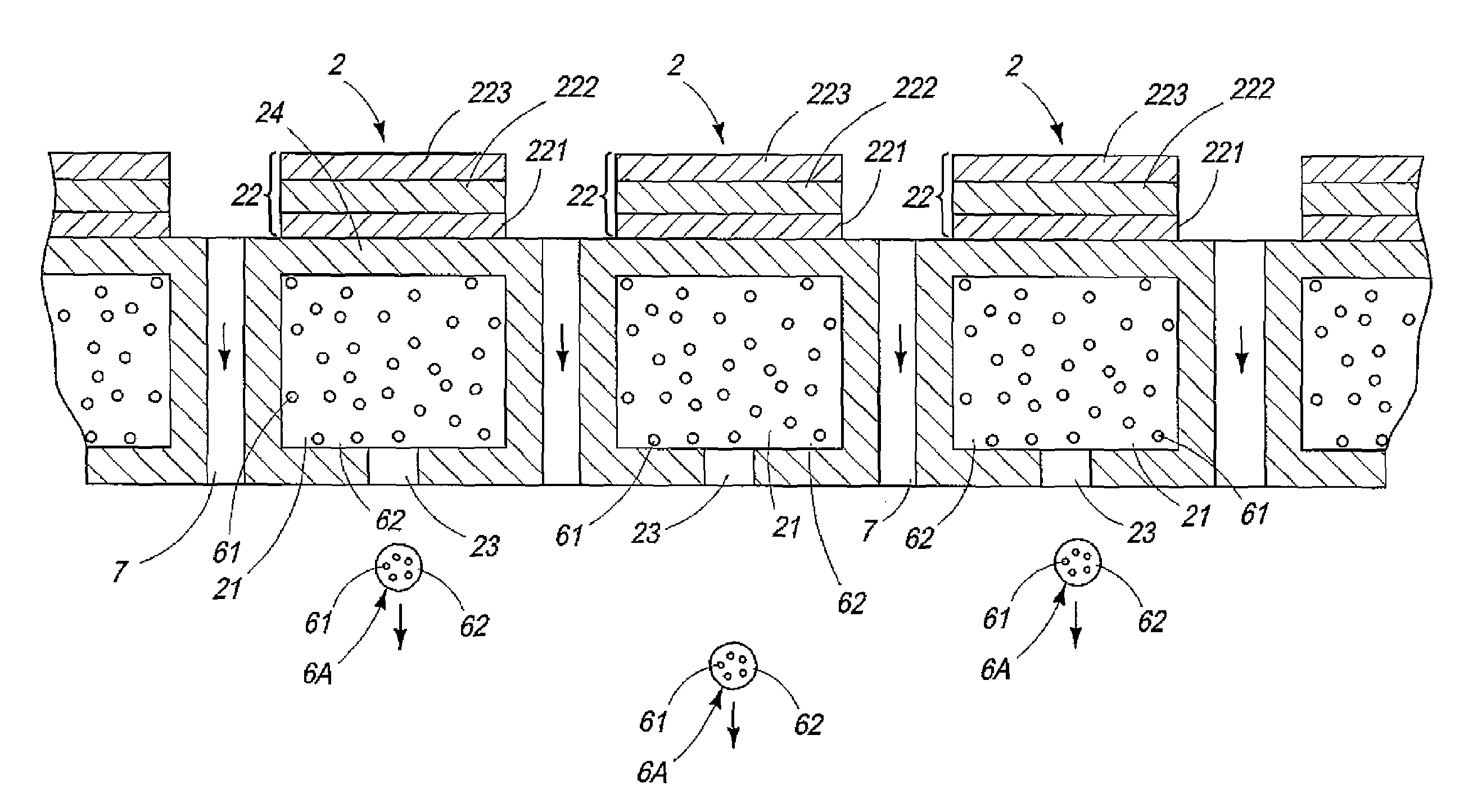
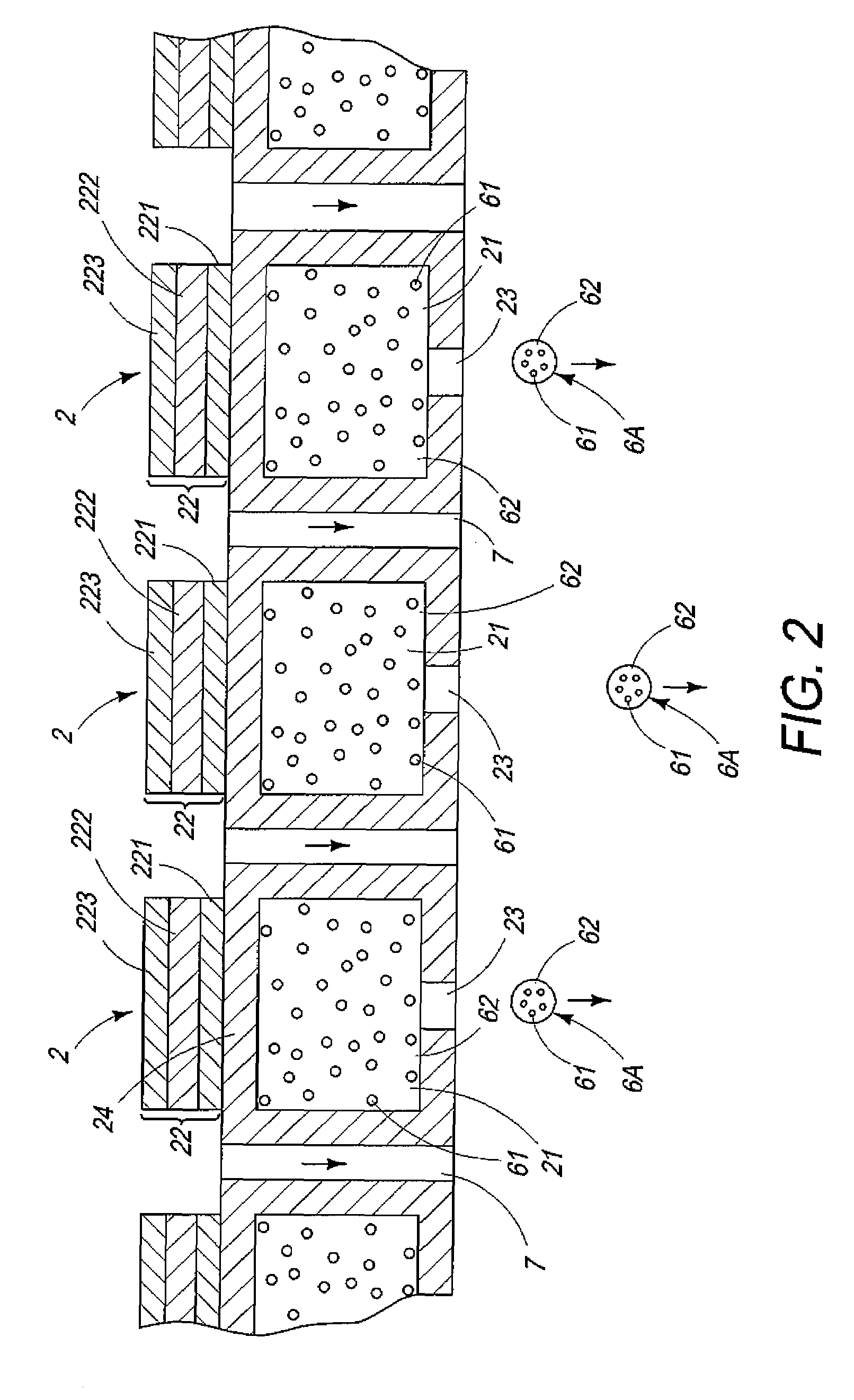
[0232]A toner was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the granulation prevention agent was changed to titanium oxide having an average particle diameter of 30 nm which had been subjected to hydrophilic treatment, and it was injected so that the amount of the granulation prevention agent contained in the finally obtained toner powder was 1.0 wt %.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com