Method capable of facilitating bioremediation of oil-contaminated soil
A technology for bioremediation and oil pollution, applied in the field of environmental governance, can solve problems such as difficult operation, secondary pollution, and high cost, and achieve the effects of fewer procedures, lower repair costs, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
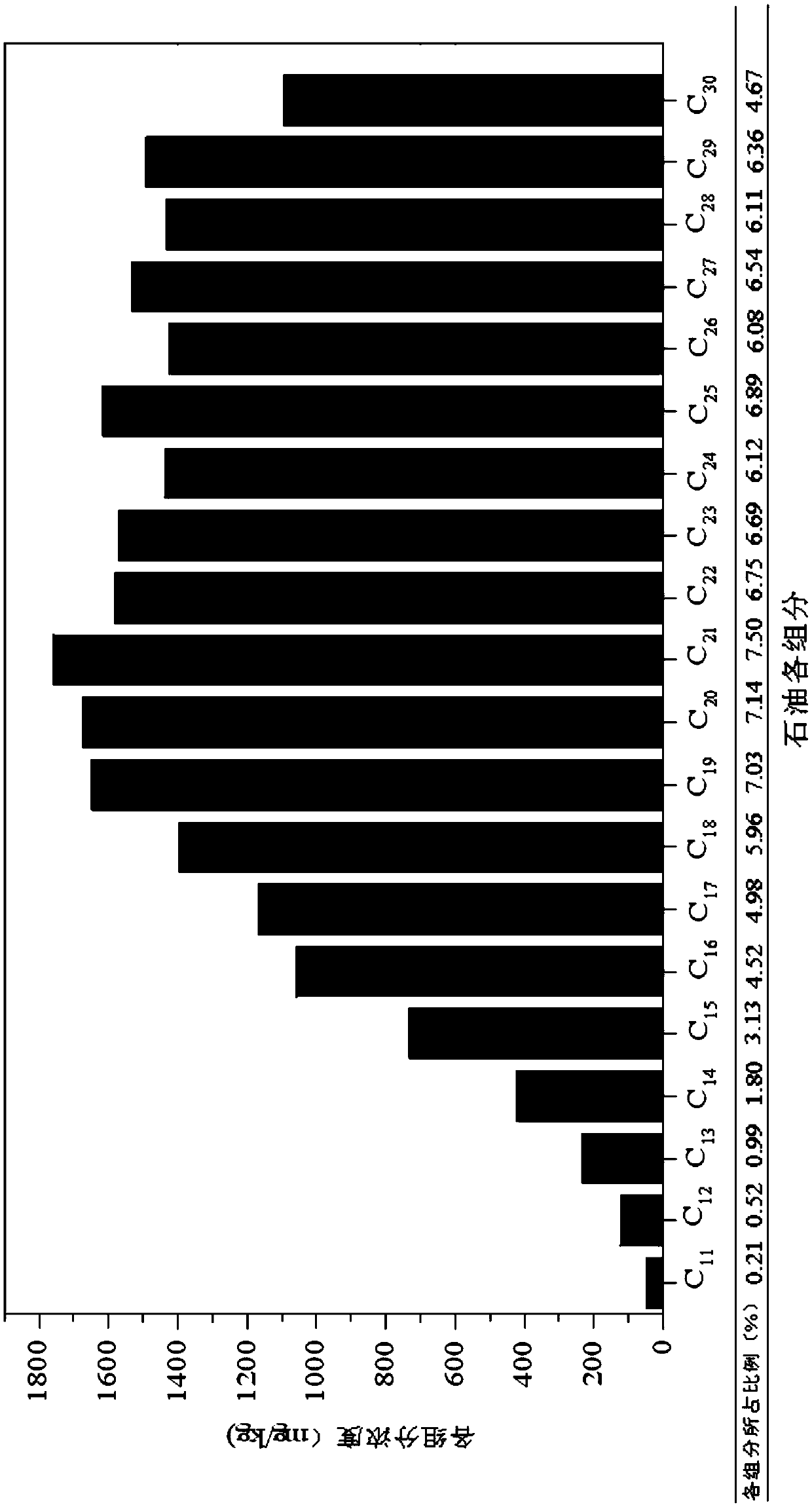
[0033] Example 1: H 2 o 2 Experiments on the effect of concentration on biomass and soluble nutrients.
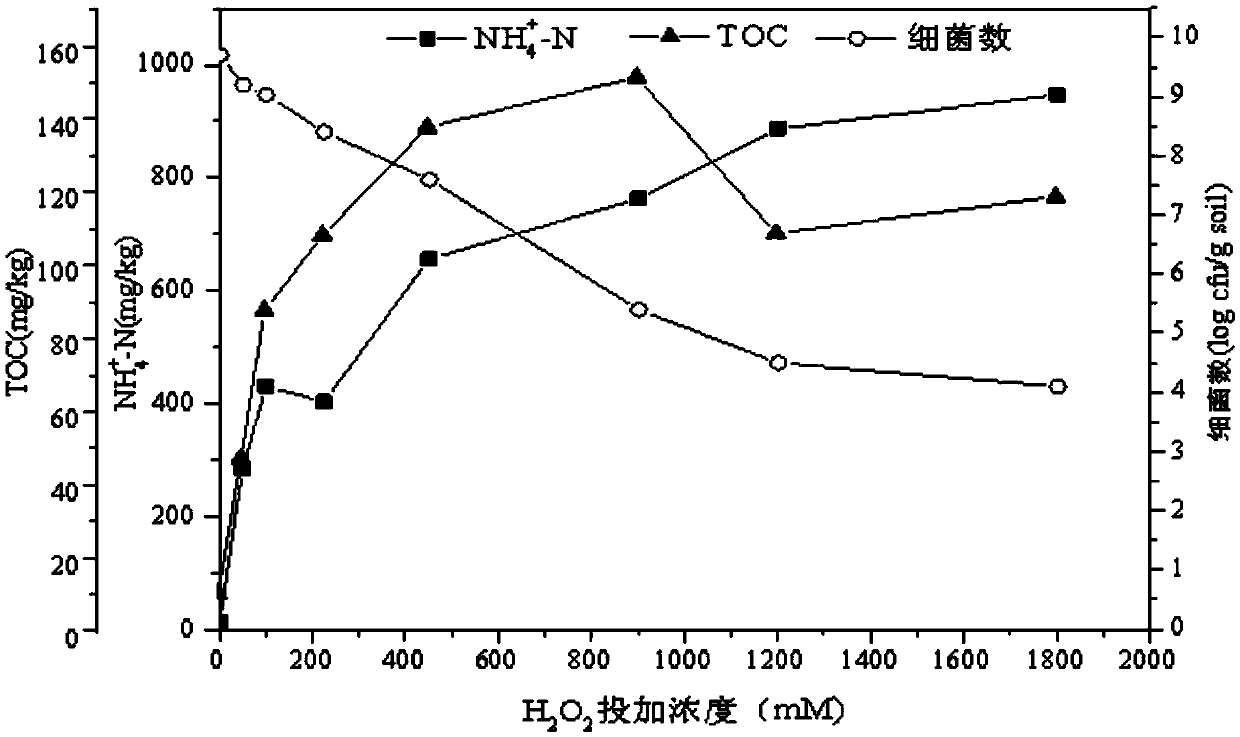
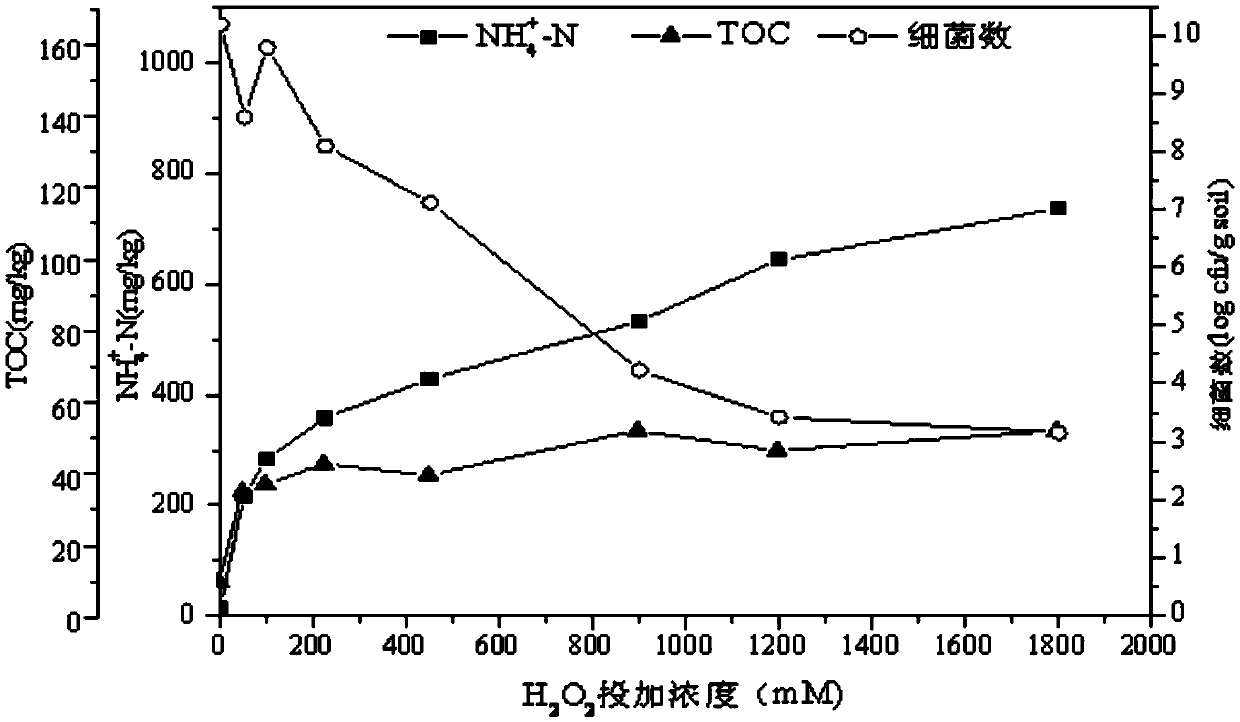
[0034] The experiments were divided into two groups, a and b, both of which were carried out in 250mL reaction bottles. First, 5g of petroleum-contaminated soil samples were added, and then 5mL of citric acid-FeSO was added to the reaction bottles of group a. 4 Solution (2.9mM), add 5mL distilled water in the reaction bottle of group b experiment. Then add 30% H in the reaction flask 2 o 2 0.3mL, 0.6mL, 1.35mL, 2.7mL, 5.4mL, 7.2mL, 10.8mL. And add distilled water simultaneously to make the solution total volume of reaction system be 60mL, at this moment, H in the reaction bottle 2 o 2 The concentrations are 50mM, 100mM, 225mM, 450mM, 900mM, 1200mM, 1800mM, respectively. At the same time do not add H 2 o 2 The reaction bottle was used for the control experiment. Determination of TOC and NH in the supernatant before and after oxidation 4 + - the concentration of N...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Example 2: Effect test of bioremediation after Fenton treatment.
[0036] The experiment was also divided into two groups a and b, and the experiment was carried out in a 250mL saline bottle. Group a added 5mL of citric acid-FeSO4 solution (2.9mM), add 5mL of distilled water to group b. On the basis of embodiment 1, choose 225Mm (F 1 ), 450mM (F 2 ), 900mM (F 3 ) after Fenton treatment with three concentrations of hydrogen peroxide, the reaction bottle was placed on a shaker for 80 days of bioremediation experiments (125rmp, 25°C) (Tim, 2014). The reaction bottle was sealed with a rubber stopper and poured to Oxygenate the reaction bottle to ensure that the oxygen concentration in the reaction bottle is not lower than 10%. On the 10th day, the 20th day, the 40th day, the 60th day and the 80th day, the oil in the reaction bottle was extracted to determine the TPH, and the TOC and NH in the supernatant were measured 4 + -N, NO 2 - -N, NO 3 - -N concentration and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com