Laser-marking-machine working table board and preparation method thereof
A technology for a laser marking machine and a work surface, which is applied to the work surface of a laser marking machine and the field of its preparation, can solve the problems of being susceptible to laser erosion and insufficient heat resistance, and achieves good anti-laser erosion performance and improved performance. , strong effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
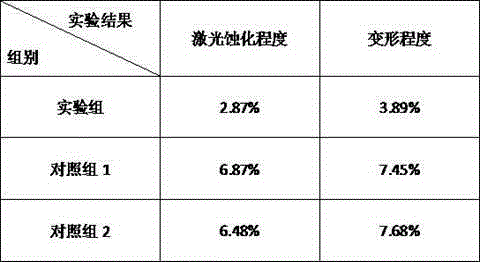
[0019] A working table of a laser marking machine, the raw materials are composed of the following parts by weight: 12 parts of nano-zinc oxide, 12 parts of sodium stearate, 18 parts of borax, 20 parts of polyvinylidene fluoride, 14 parts of sodium metasilicate , 16 parts of polyamide fiber, 14 parts of silicone rubber, 16 parts of p-phenylenedimethanol, 18 parts of vinyl acetate, 18 parts of superphosphate, 12 parts of ethylenediamine, 12 parts of EPDM rubber, dimethylaniline 16 parts, 28 parts iron and 22 parts carbon fiber.
[0020] A method for preparing a laser marking machine worktop, comprising the following steps:
[0021] 1) Take 12 parts of nano-zinc oxide, 12 parts of sodium stearate, 18 parts of borax and 20 parts of polyvinylidene fluoride, put them into the heater, raise the temperature to 80-90℃, last for 20-30min, and set aside;
[0022] 2) Take 20 parts of polyvinylidene fluoride, 14 parts of sodium metasilicate, 16 parts of polyamide fiber and 14 parts of si...
Embodiment 2
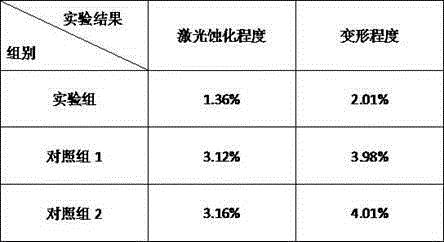
[0029] A working table of a laser marking machine, the raw materials are composed of the following proportions by weight: 14 parts of nano-zinc oxide, 11 parts of sodium stearate, 17 parts of borax, 18 parts of polyvinylidene fluoride, and 13 parts of sodium metasilicate 13 parts of polyamide fiber, 13 parts of silicone rubber, 13 parts of p-phenylenedimethanol, 15 parts of vinyl acetate, 15 parts of superphosphate, 11 parts of ethylenediamine, 10 parts of EPDM rubber, dimethylaniline 14 parts, iron 27 parts and carbon fiber 20 parts.
[0030] A method for preparing a laser marking machine worktop, comprising the following steps:
[0031] 1) Take 14 parts of nano-zinc oxide, 11 parts of sodium stearate, 17 parts of borax and 18 parts of polyvinylidene fluoride, put them into the heater, raise the temperature to 80-90℃, last for 20-30min, and set aside;
[0032] 2) Take 18 parts of polyvinylidene fluoride, 13 parts of sodium metasilicate, 13 parts of polyamide fiber and 13 par...
Embodiment 3
[0039] A laser marking machine working table, the raw materials are composed of the following proportions by weight: 16 parts of nano-zinc oxide, 10 parts of sodium stearate, 16 parts of borax, 16 parts of polyvinylidene fluoride, 12 parts of sodium metasilicate 10 parts of polyamide fiber, 12 parts of silicone rubber, 10 parts of p-phenylenedimethanol, 12 parts of vinyl acetate, 12 parts of superphosphate, 10 parts of ethylenediamine, 8 parts of EPDM rubber, dimethylaniline 12 parts, 26 parts iron and 18 parts carbon fiber.
[0040] A method for preparing a laser marking machine worktop, comprising the following steps:
[0041] 1) Take 16 parts of nano-zinc oxide, 10 parts of sodium stearate, 16 parts of borax and 16 parts of polyvinylidene fluoride, put them into the heater, raise the temperature to 80-90℃, last for 20-30min, and set aside;
[0042] 2) Take 16 parts of polyvinylidene fluoride, 12 parts of sodium metasilicate, 10 parts of polyamide fiber and 12 parts of sili...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com