Method for preparing vanadyl sulfate by using spent vanadium battery electrolyte
A technology of vanadyl sulfate and electrolyte, applied in fuel cells, regenerative fuel cells, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of easy precipitation, high equipment requirements, complicated procedures, etc., to solve processing problems, increase economic benefits, and simple process Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
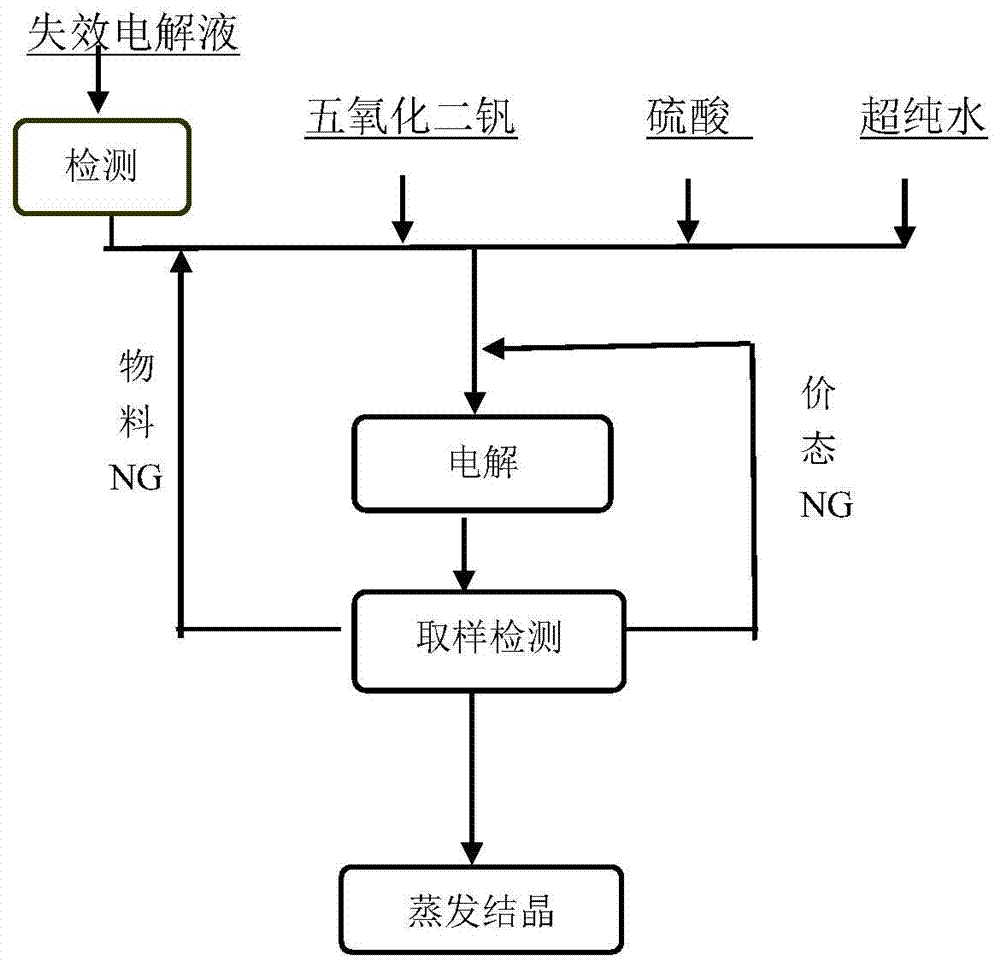
[0046] By chemical titration, the vanadium concentration of the recovered spent electrolyte was measured to be 3.6moL / L, and the average valence state was 4.7. The sulfate concentration of the spent electrolyte was measured to be 4.3moL / L by chemical precipitation. Take 1500mL of the above spent electrolyte solution in the negative electrode pool of the electrolytic cell, and calculate by formula (3) that the electrolysis time is 5.1 hours under the current of 20A. After the electrolysis is completed, the sample solution is subjected to an ultraviolet test, and there is no trivalent or pentavalent absorption peak. The electrolyzed liquid was taken out from the electrolytic cell, evaporated, crystallized and dried to obtain 1010.26 g of blue vanadyl sulfate crystals with a recovery rate of 94.01%.
Embodiment 2
[0048] By chemical titration, the vanadium concentration of the recovered spent electrolyte was measured to be 2.5moL / L, and the average valence state was 3.8. The sulfate concentration of the spent electrolyte was measured to be 4.5moL / L by chemical precipitation. Take 1500mL of the above spent electrolyte solution in the positive electrode pool of the electrolytic cell, and calculate by formula (3) that the electrolysis time is 1.0 hour under the current of 20A. After the electrolysis is completed, the sample solution is subjected to an ultraviolet test, and there is no trivalent or pentavalent absorption peak. The electrolyzed liquid was taken out from the electrolytic cell, evaporated, crystallized and dried to obtain 901.3 g of blue vanadyl sulfate crystals with a recovery rate of 95.02%.
Embodiment 3
[0050] By chemical titration, the vanadium concentration of the recovered spent electrolyte was measured to be 5.2moL / L, and the average valence state was 4.9. The sulfate concentration of the spent electrolyte was measured to be 8.7moL / L by chemical precipitation. Take 750mL of the above spent electrolyte solution in the negative electrode pool of the electrolytic cell, add deionized water to dilute to 1500ml, and calculate by formula (3) that the electrolysis time is 4.6 hours under 20A current. After the electrolysis was completed, the sample solution was subjected to ultraviolet testing, and it was found that there was still a pentavalent vanadium ion absorption peak. According to the tested pentavalent vanadium ion concentration, the electrolysis was continued for 0.1 hour. After the electrolysis was completed, there was no trivalent or pentavalent absorption peak. The electrolyzed liquid was taken out from the electrolytic cell, evaporated, crystallized and dried to obtai...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com