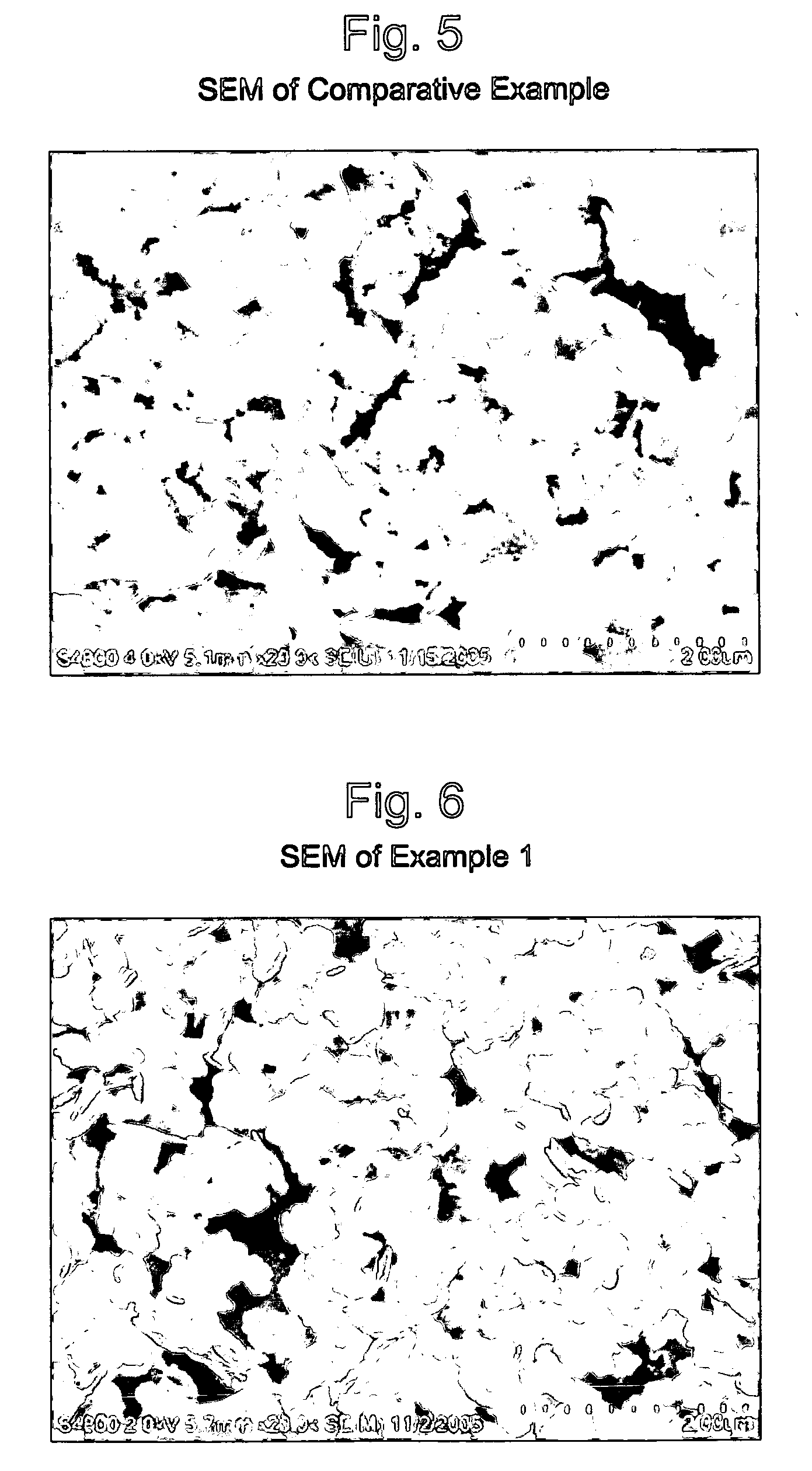
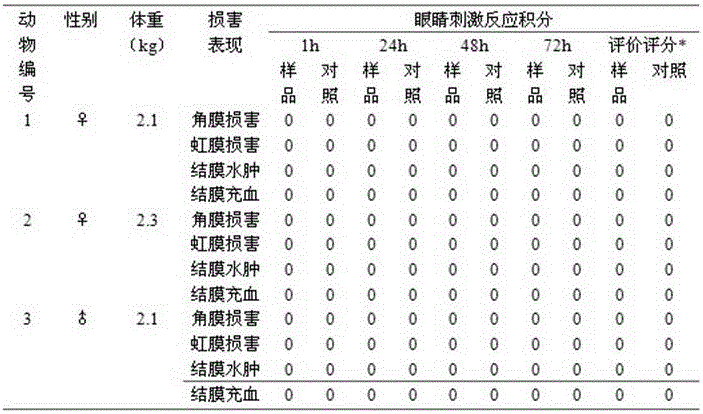
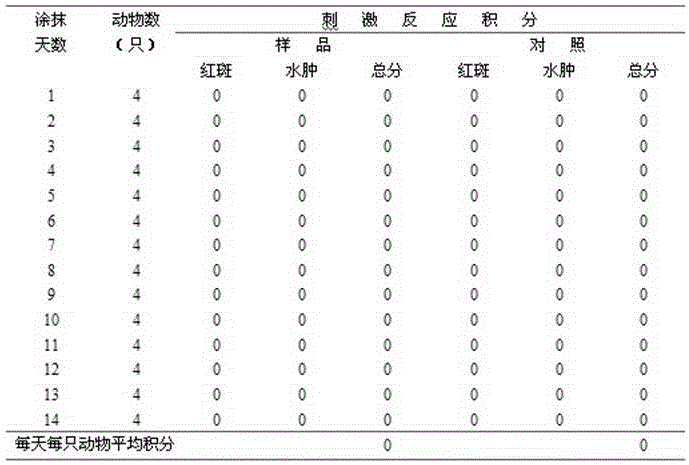
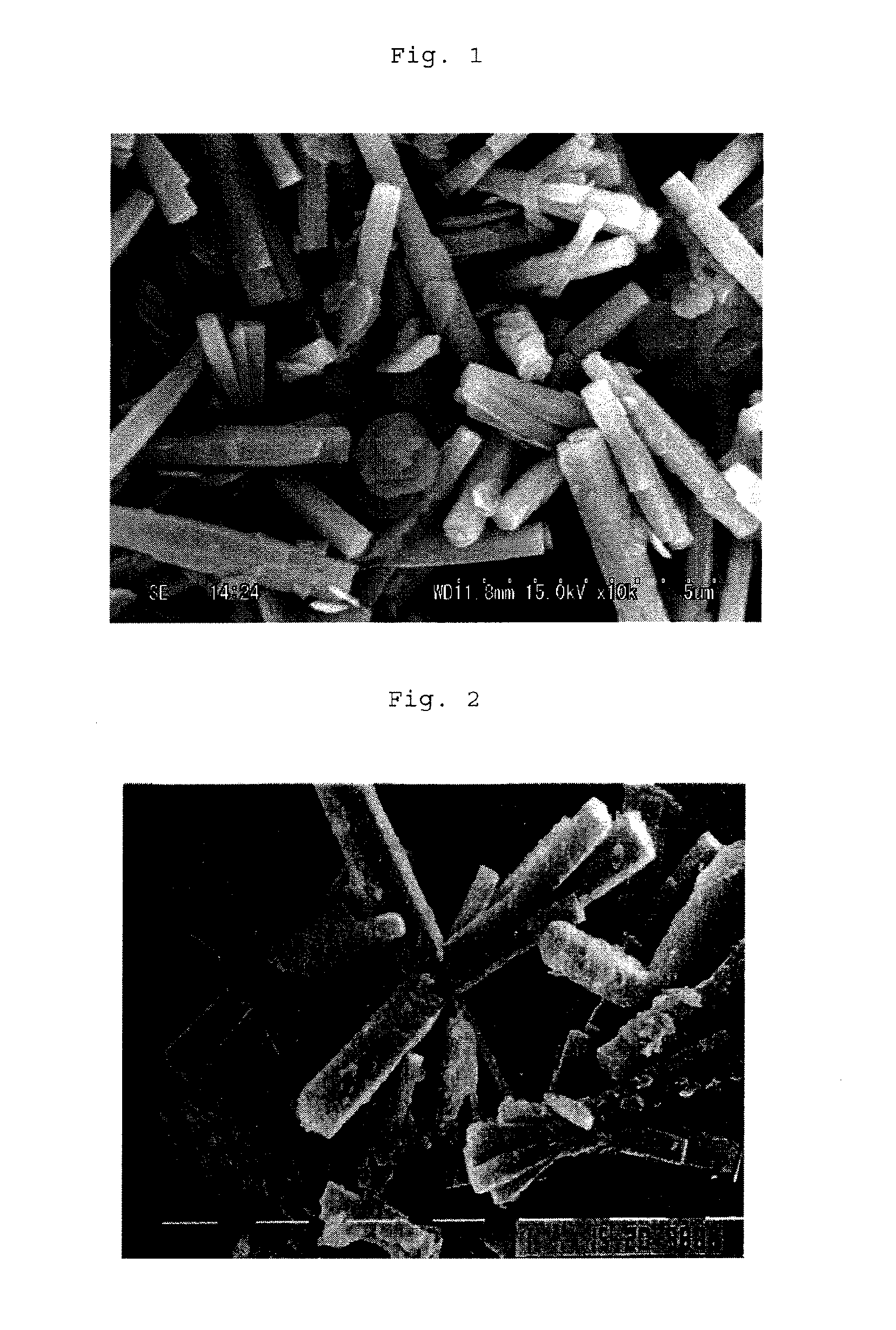
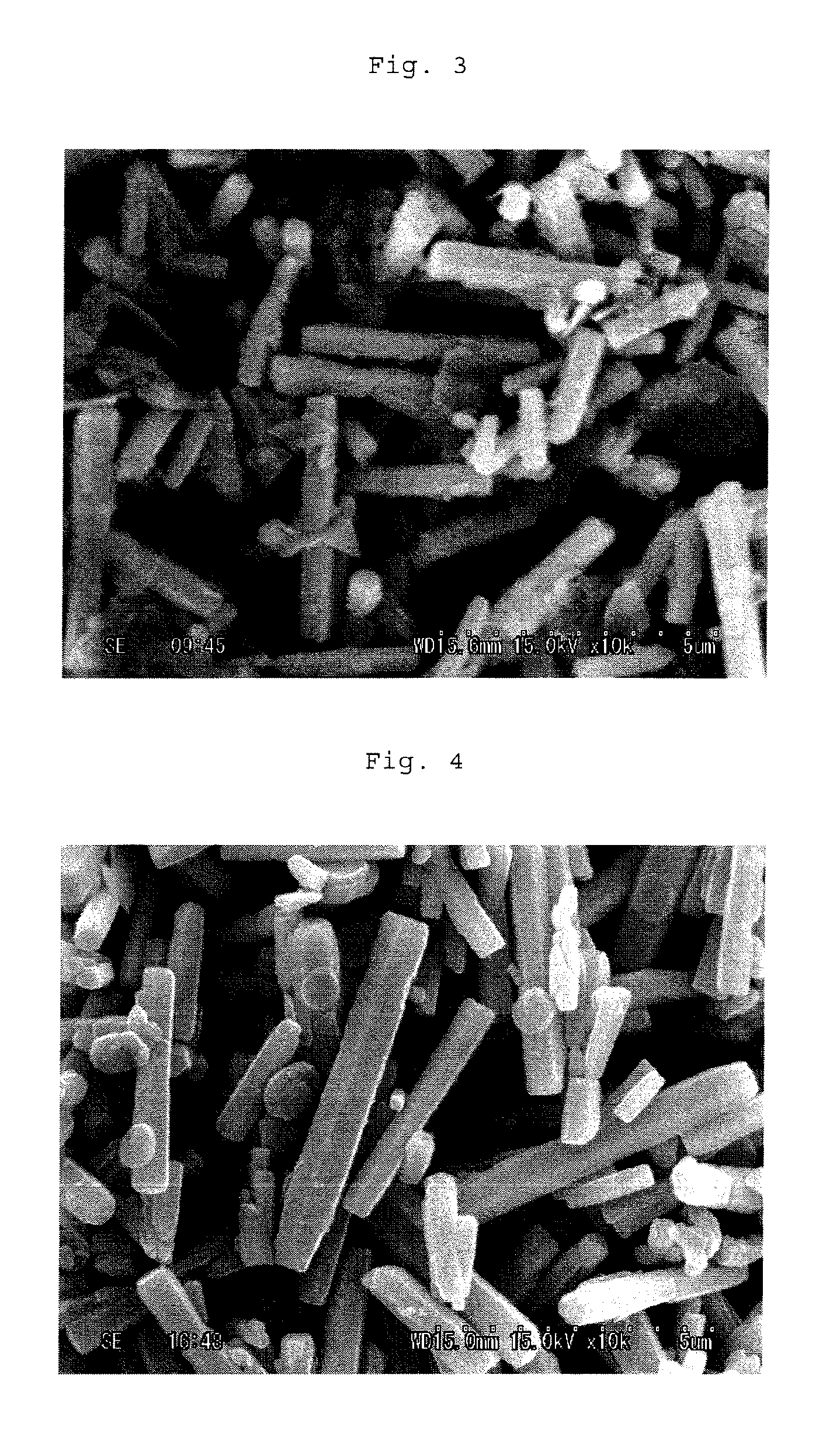
Patents
Literature
130 results about "Tetravalence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In chemistry, a tetravalence is the state of an atom with four electrons available for covalent chemical bonding in its valence. An example is methane: the tetravalent carbon atom forms a covalent bond with four hydrogen atoms. The carbon atom is called tetravalent because it forms 4 covalent bonds. A carbon atom has a total of six electrons occupying the first two shells, i.e., the K-shell has two electrons and the L-shell has four electrons. This distribution indicates that in the outermost shell there are one completely filled 's' orbital and two half-filled 'p' orbitals, showing carbon to be a divalent atom. But in actuality, carbon displays tetravalency in the combined state. Therefore, a carbon atom has four valence electrons. It could gain four electrons to form the C⁴⁻ anion or lose four electrons to form the C⁴⁺ cation. Both these conditions would take carbon far away from achieving stability by the octet rule. To overcome this problem carbon undergoes bonding by sharing its valence electrons. This allows it to be covalently bonded to one, two, three or four carbon atoms or atoms of other elements or groups of atoms.
Preparation of complex fluoride and complex fluoride phosphor
ActiveUS20120256125A1Uniform sizeSatisfactory emissive propertyTin compoundsSilicon halogen compoundsPhysical chemistryFluoride
A complex fluoride A2MF6 wherein M is a tetravalent element Si, Ti, Zr, Hf, Ge or Sn, A is an alkali metal Li, Na, K, Rb or Cs is prepared by providing a first solution containing a fluoride of M, providing a second solution containing a compound of A and / or the compound of A in solid form, mixing the first solution with the second solution and / or the solid for reacting the fluoride of M with the compound of A, and recovering the resulting solid product via solid-liquid separation.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
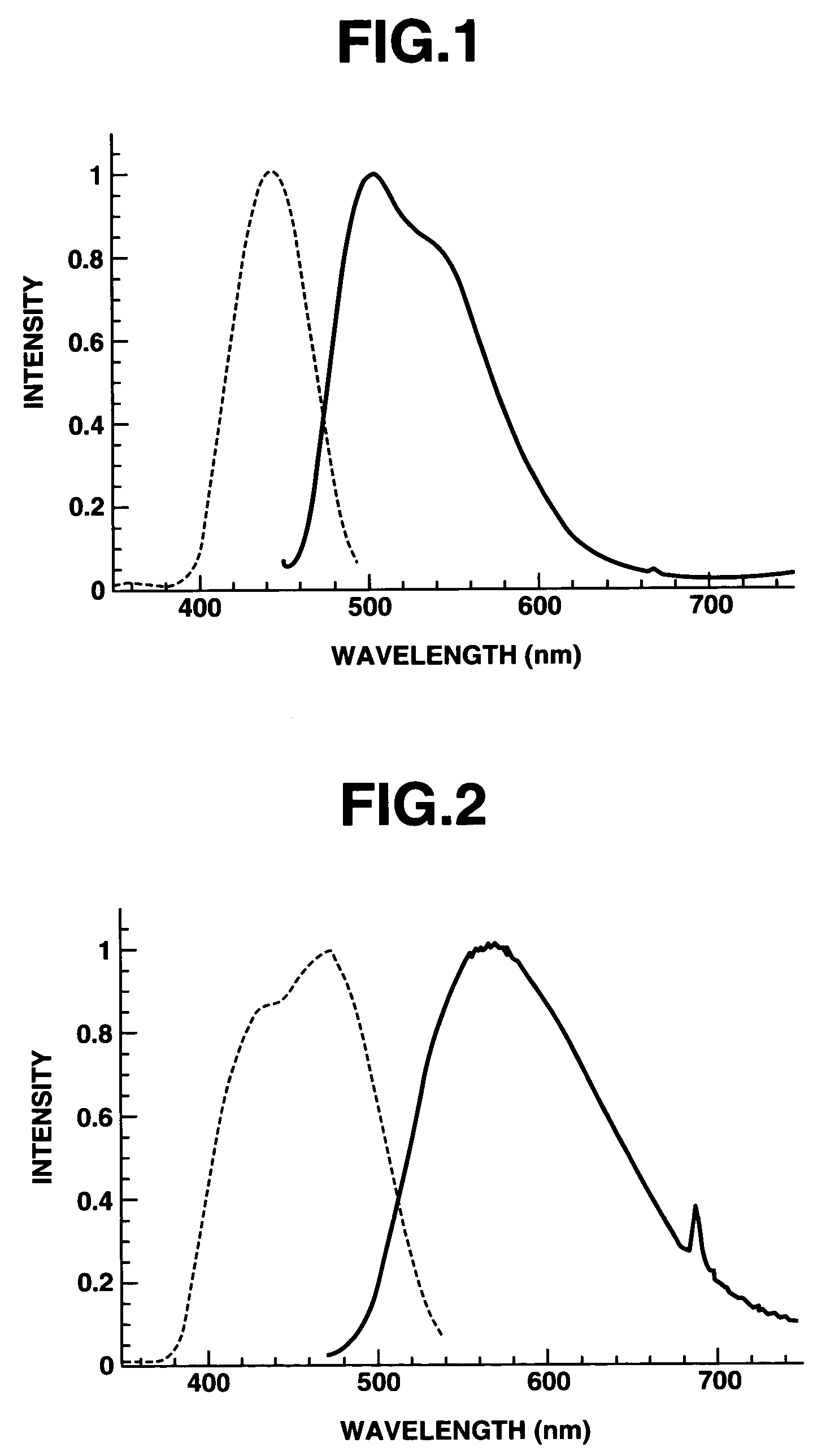
Phosphor and manufacturing method for the same, and light source
ActiveUS20060065878A1Improve emission efficiencyImprove efficiencySynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsRare-earth elementUltraviolet
To provide a phosphor having an emission spectrum with a broad peak in a range from yellow color to red color (580 nm to 680 nm) and an excellent excitation band on the longer wavelength side from near ultraviolet / ultraviolet of excitation light to visible light (250 nm to 550 nm), and having an improved emission intensity. The phosphor is provided, which is given by a general composition formula expressed by MmAaBbOoNn:Z, (wherein element M is more than one kind of element having bivalent valency, element A is more than one kind of element having tervalent valency selected from the group consisting of Al, Ga, In, Tl, Y, Sc, P, As, Sb, and Bi, element B is more than one kind of element having tetravalent valency, O is oxygen, N is nitrogen, and element Z is more than one kind of element selected from rare earth elements or transitional metal elements, satisfying m>0, a>0, b>0 o≧0, and n=2 / 3m+a+4 / 3b−2 / 3o), and further containing boron and / or fluorine.
Owner:CITIZEN ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Phosphor, light emitting device using phosphor, and display and lighting system using light emitting device
A phosphor (A) comprising a host material composed of a compound having a garnet crystal structure represented by the general formula (I):M1aM2bM3cOd (I)(wherein M1 is a divalent metal element, M2 is a trivalent metal element, M3 is a tetravalent metal element containing at least Si, a is the number of 2.7 to 3.3, b is the number of 1.8 to 2.2, c is the number of 2.7 to 3.3, and d is the number of 11.0 to 13.0), and a luminescent center ion incorporated in the host material; a light emitting device (B) comprising the phosphor as a wavelength conversion material and a semiconductor light emitting element capable of emitting a light in the range of from ultraviolet light to visible light; and a display (C) and a lighting system (D) using the light emitting device (B) as a light source. The above phosphor can be readily produced, and can provide a light emitting device having a high color rendering property.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
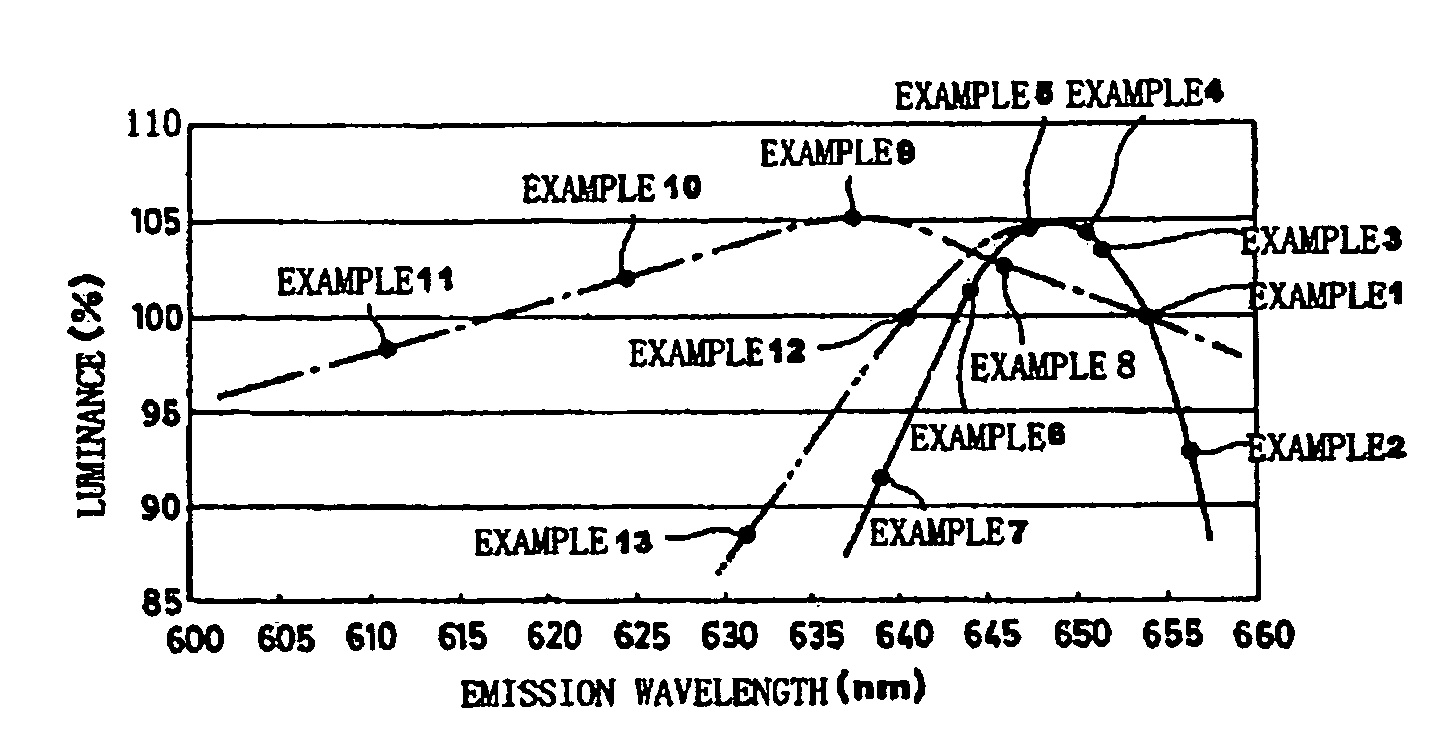
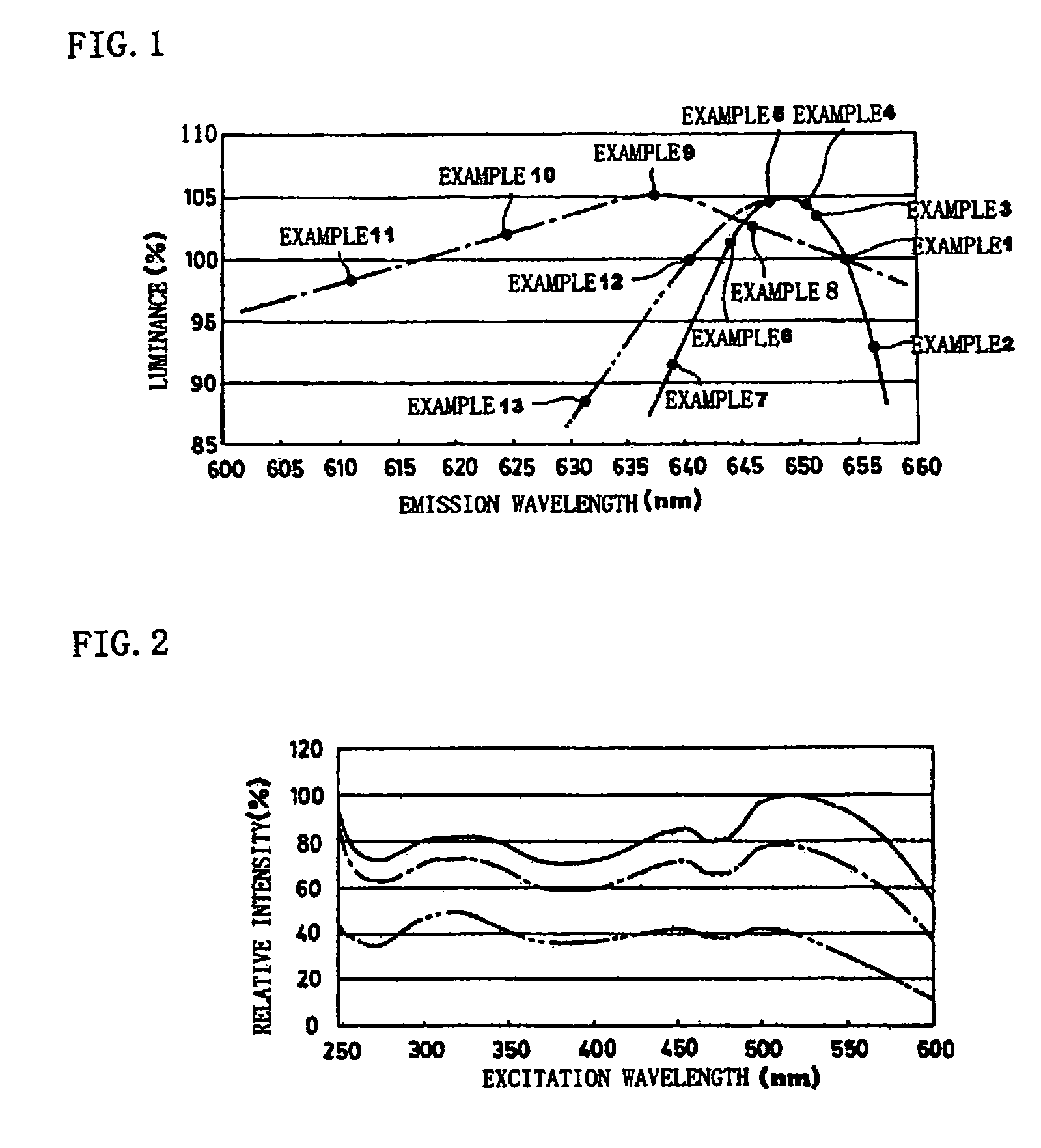
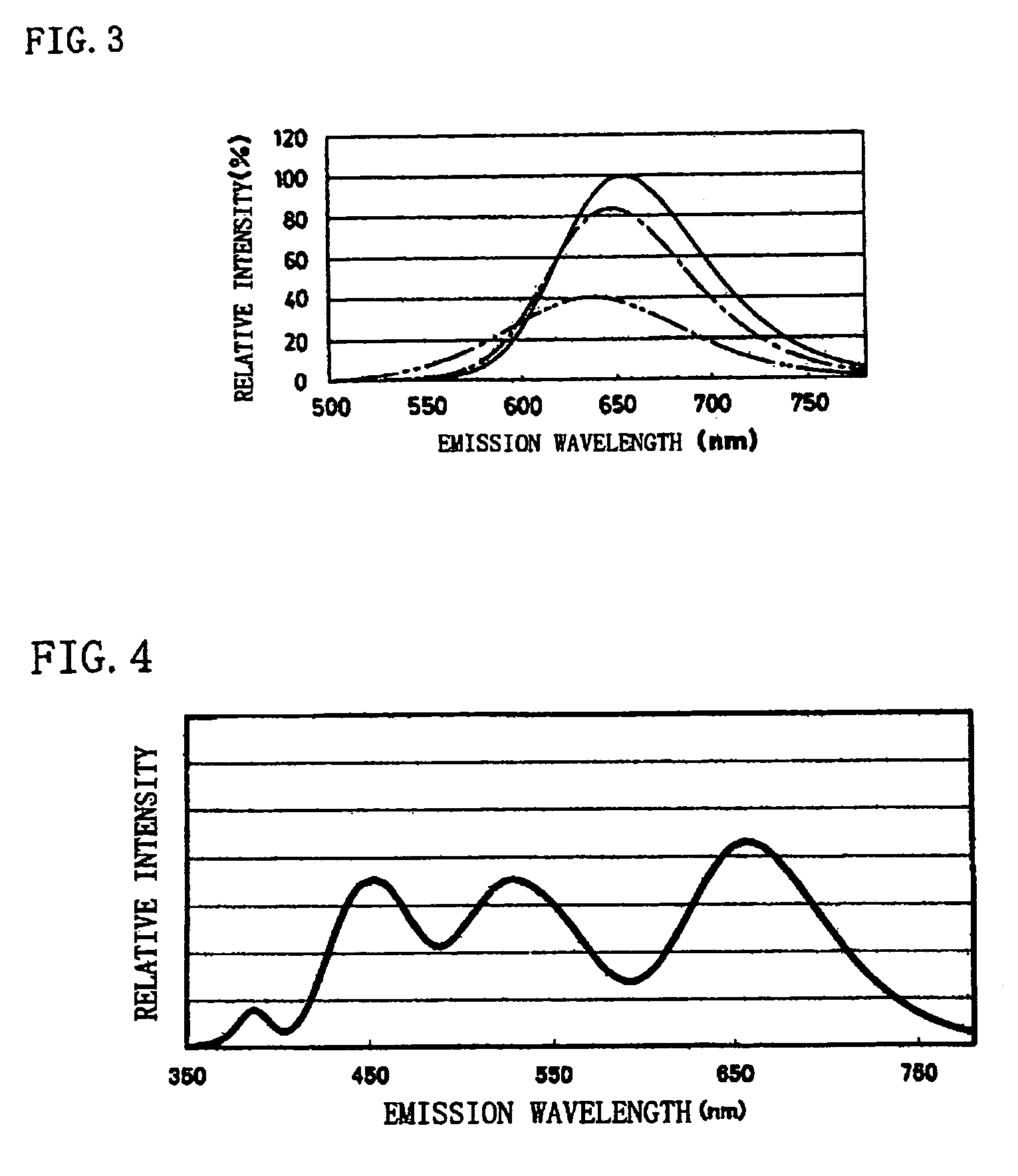
Phosphor and production method of the same, method of shifting emission wavelength of phosphor, and light source and LED
ActiveUS7273568B2High sensitivityImprove luminous performanceDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsOxygenEuropium
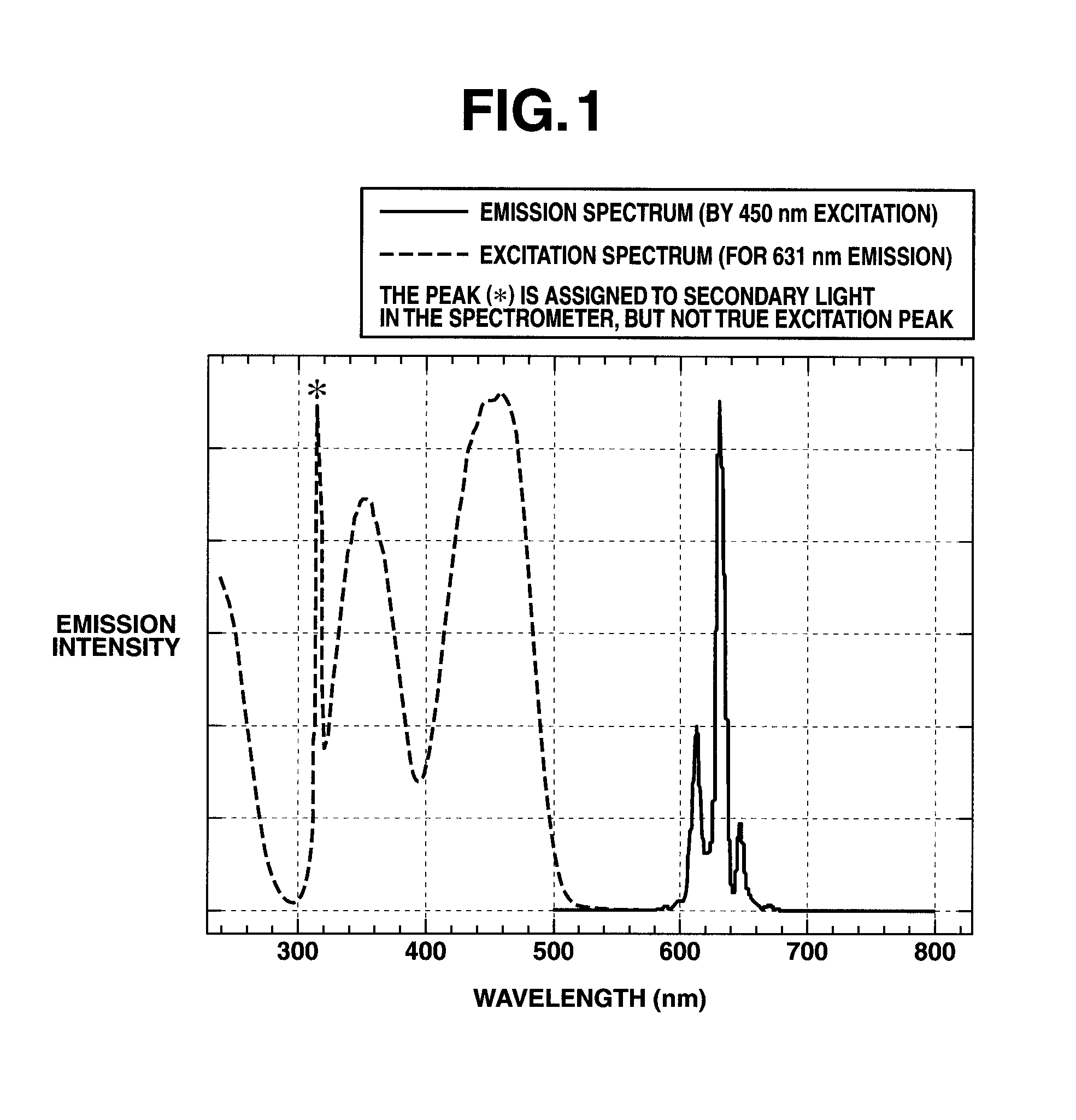
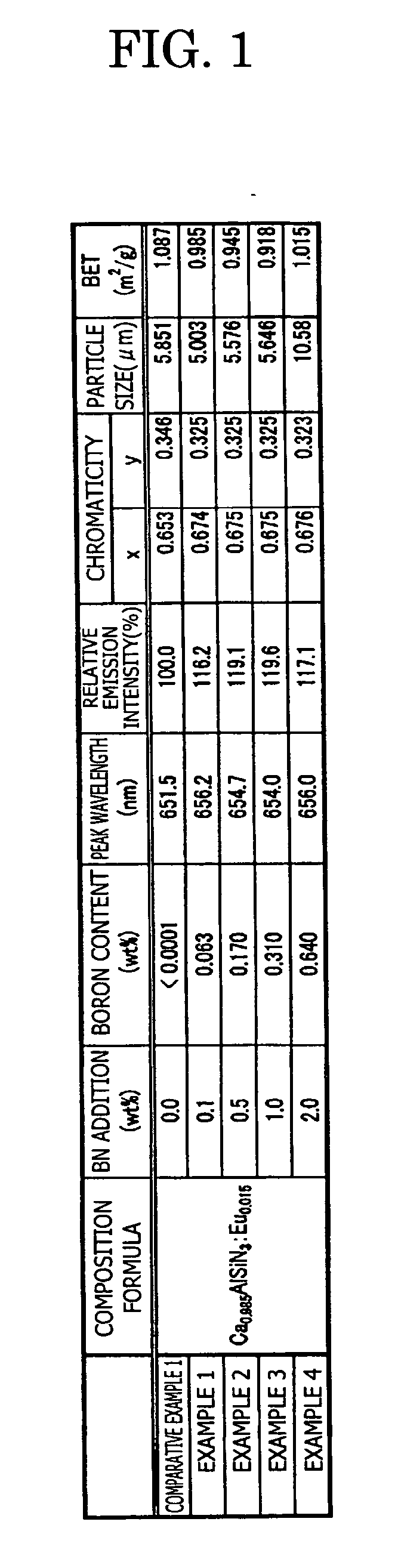
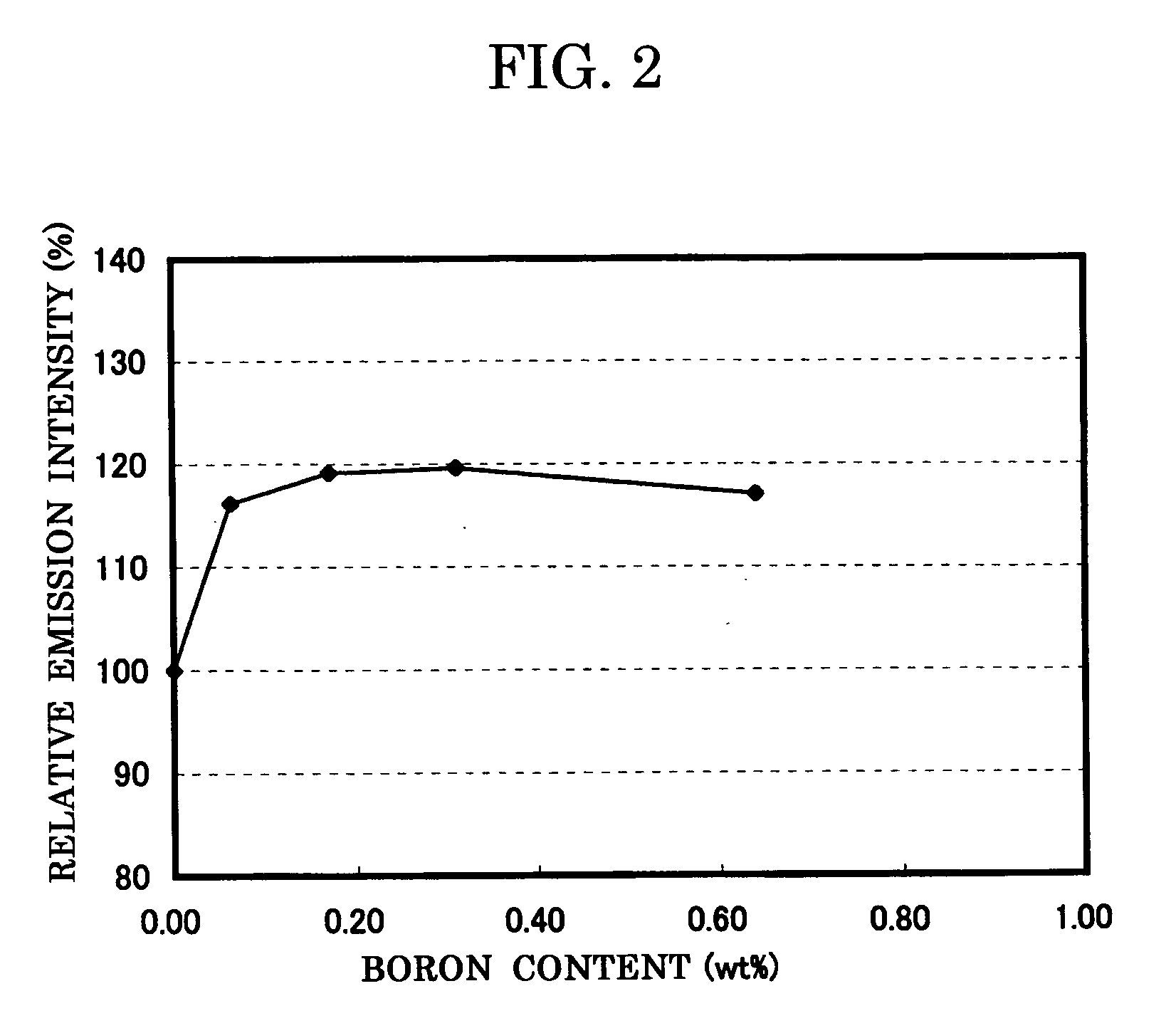
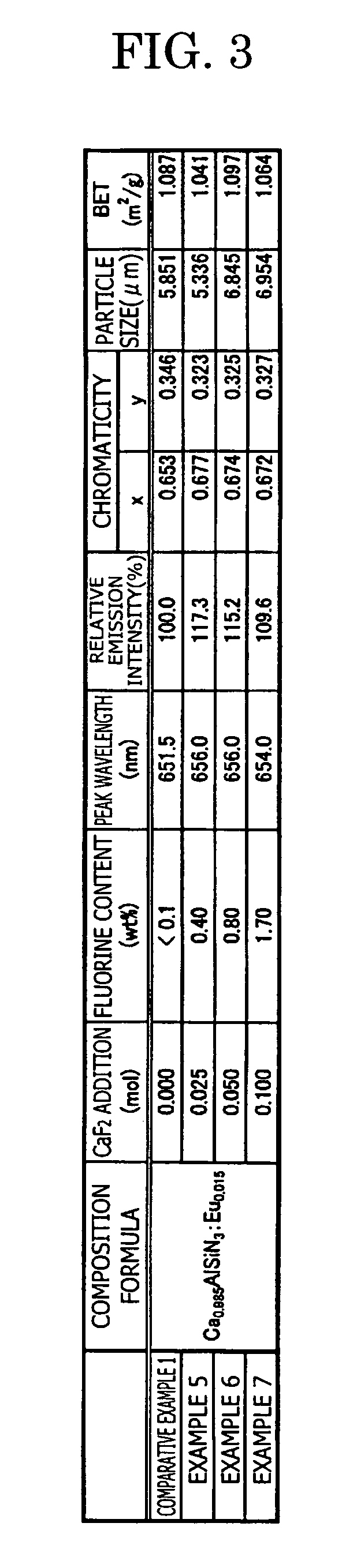
A phosphor including a main production phase of a phosphor expressed by a composition formula of MmAaBbOoNn:Zz (where an element M is one or more bivalent elements, an element A is one or more trivalent elements, an element B is one or more tetravalent elements, O is oxygen, N is nitrogen, an element Z is an activator, n=2 / 3m+a+4 / 3b−2 / 3o, m / (a+b)≧1 / 2, (o+n) / (a+b)>4 / 3, wherein m=a=b=1 and o and n is not 0). A phosphor including 24 wt % to 30 wt % of Ca (calcium), 17 wt % to 21 wt % of Al (aluminum), 18 wt % to 22 wt % of Si (silicon), 1 wt % to 15 wt % of oxygen, 15 wt % to 33 wt % of nitrogen and 0.01 wt % to 10 wt % of Eu (europium), wherein an emission maximum in an emission spectrum is in a range of 600 nm to 660 nm; and wherein color chromaticity x of light emission is in a range of 0.5 to 0.7, and color chromaticity y of the light emission is in a range of 0.3 to 0.5.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
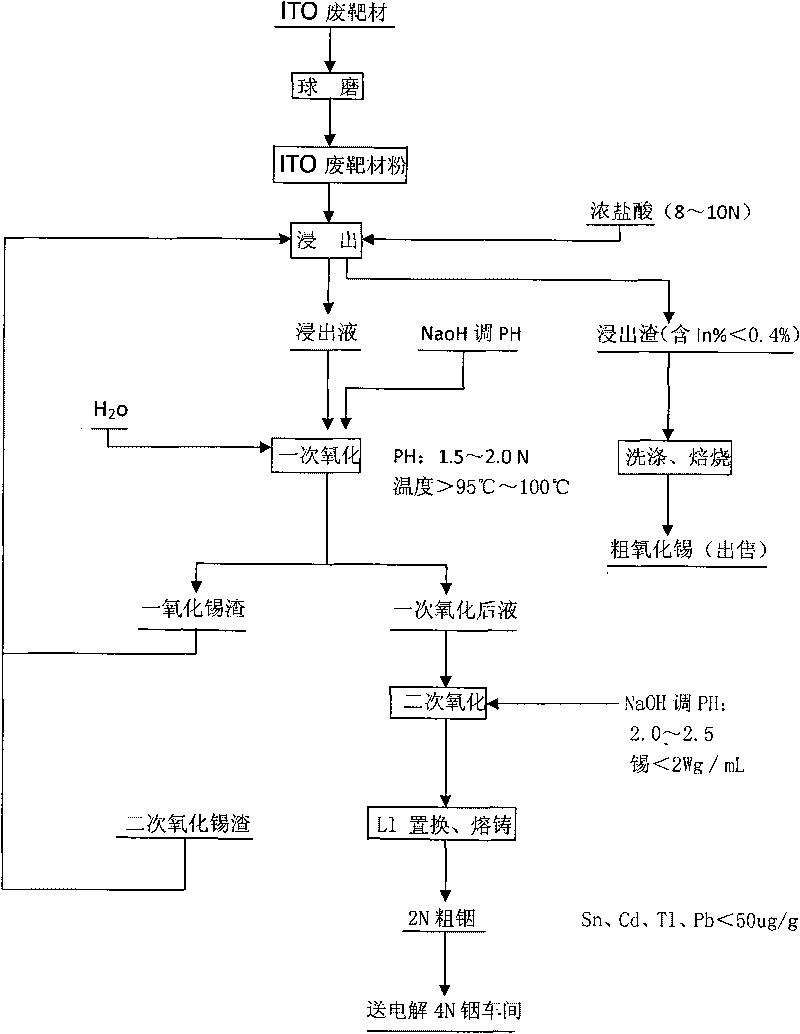
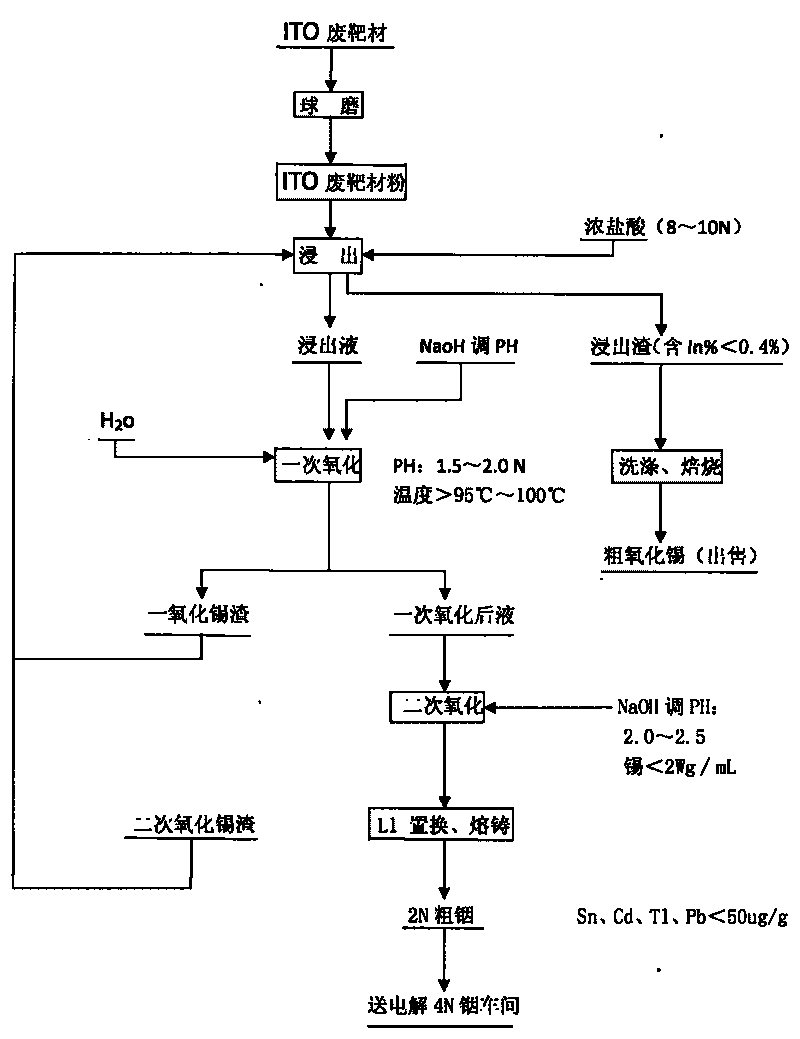
Method for recovering indium and tin from ITO waste targets by utilizing oxidation method
InactiveCN101701292AStable recoveryPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementVulcanizationIndium
The invention utilizes the characteristics that tin has two states of bivalence and tetravalence in the solution, and the difference of the pH values is great when the tetravalent tin and trivalent indium ions precipitate in the solution, so the tetravalent tin and trivalent indium ions can be controlled under a certain pH value; oxidant is utilized to oxidize tin ions into tetravalence to generate hydrolysis precipitation, while indium still remains in the water solution, thus achieving the complete separation of indium from tin. At the moment, the tin contained in the indium solution is lowered to 2ppm, aluminium cutter replacement can be directly carried out after vulcanization to ensure that the content of tin, cadmium, thallium and lead is less than 100 PPM, and the content of indium is greater than 99%; while the oxidized tin dregs return and leach, and finally coarse tin oxide can be obtained for sale after washing and roasting the leached dregs, and the grade of indium content is lower than 0.2%.
Owner:南京中锗科技有限责任公司
Process for producing middle distillates by hydrocracking of feedstocks obtained by the fischer-tropsch process in the presence of a catalyst comprising an IZM-2 solid
ActiveUS20110180455A1Shorten the timePromote formationTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyMolecular sieve catalystsAlkaneChemical composition
The invention relates to a process for producing middle distillates from a paraffinic feedstock produced by Fischer-Tropsch synthesis, implementing a hydrocracking / hydroisomerisation catalyst comprising at least one hydro-dehydrogenating metal selected from the group formed by the metals from group VIB and from group VIII of the periodic table and a substrate comprising at least one crystallised IZM-2 solid having a chemical composition, expressed on an anhydrous base, in terms of oxide moles, by the following general formula: XO2:aY2O3:bM2 / nO, wherein X represents at least one tetravalent element, Y represents at least one trivalent element and M is at least one alkali metal and / or an alkaline earth metal of valency n, a and b representing respectively the number of moles of Y2O3 and M2 / nO and a is between 0 and 0.5 and b is between 0 and 1.
Owner:ENI SPA +1
Method of preparing a molecular sieve composition
This disclosure provides a method of preparing a crystalline molecular sieve comprising: (a) providing a reaction mixture comprising at least one source of ions of tetravalent element Y, at least one source of alkali metal hydroxide, water, optionally at least one seed crystal, and optionally at least one source of ions of trivalent element X, the reaction mixture having the following molar composition:Y:X2=2 to infinity, preferably from about 2 to about 1000,OH−:Y=0.001 to 2, preferably from 0.1 to 1,M+:Y=0.001 to 2, preferably from 0.01 to 2wherein M is an alkali metal and the amount of water is at least sufficient to permit extrusion of the reaction mixture, wherein the reaction mixture is substantially free of crystalline molecular sieve; (b) extruding the reaction mixture to form a pre-formed extrudate; and (c) crystallizing the pre-formed extrudate in a liquid medium comprising water under liquid phase crystallization conditions to form a crystallized extrudate having the crystalline molecular sieve.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Catalyst for synthesizing methanol through CO2 hydrogenation as well as preparation method and application
ActiveCN103721719ALarge specific surface areaGood dispersionOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationPtru catalystHalogen
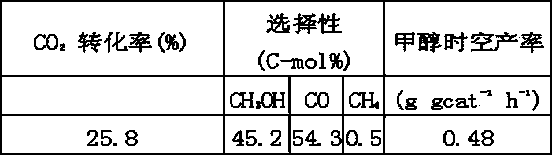
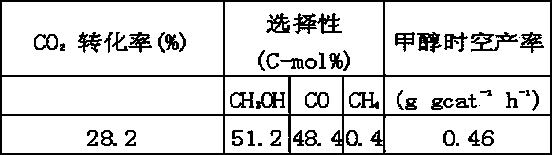
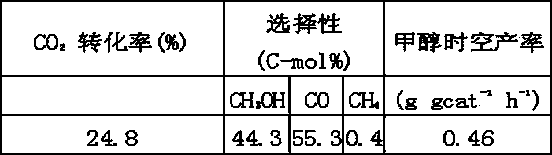
The invention discloses a catalyst for synthesizing methanol through CO2 hydrogenation, comprising Cu, Zn, Al, X, halogen and oxygen elements, oxides and halides, wherein the molar ratio of [Cu+Zn+MA] to [Al+Mb] is 2-18; the molar ratio of Cu to Zn is 0.5-5; the molar ratio of MA to [Cu+Zn] is 0-5; the molar ratio of MB to Al is 0-9; the molar ratio of halogen to Al is 0.05-5; MA and MB cannot be 0 at the same time; MA represents a mono-valent or divalent metal ion in X; MB represents a trivalent and / or tetravalent metal ion in X; X is one or a combination of more elements of Li, K, Mg, B, Ga, In, transition metal elements and rare-earth metal elements. The catalyst has the advantages of high carbon dioxide conversion rate, good methanol selectivity and high methanol yield.
Owner:SHANXI INST OF COAL CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Polyimide precursor, polyimide, and materials to be used in producing same
InactiveUS20130178597A1High transparencyHigh glass transition temperatureOrganic chemistryCoatingsHydrogenHydrogen atom
Disclosed is a novel co-polyimide precursor for producing a polyimide having high transparency. The co-polyimide precursor comprises a unit structure represented by general Formula (A1) and a unit structure represented by general Formula (A2):wherein, in general Formula (A1), R1 represents a hydrogen atom or an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms; and R2 and R3 each independently represent a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms, or an alkylsilyl group having 3 to 9 carbon atoms,wherein, in general Formula (A2), R4 represents a hydrogen atom or an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms; R5 and R6 each independently represent a hydrogen, an alkyl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms, or an alkylsilyl group having 3 to 9 carbon atoms; and X represents a tetravalent group other than those represented by Formulae (A3):
Owner:UBE IND LTD
Multiphase formulations of organosilicon compounds
A process for the preparation of multiphase formulations of organosilicon compounds by (A) formation of a mixture containing organic compound(s) (1) containing at least two aliphatic double bonds and of the general formulain whichR1 are a hydrogen atom or an alkyl radical having 1 to 6 carbon atoms per radical,R2 is a divalent, trivalent or tetravalent hydrocarbon radical having 1 to 25 carbon atoms per radical; andx denotes 2, 3 or 4 corresponding to the valence of R2; andan organopolysiloxane (2) having on average more than one Si-bonded hydrogen atom per molecule;a catalyst (3) promoting the addition of Si-bonded hydrogen at an aliphatic double bond;an emulsifier (4); andan agent (5) immiscible with (1) and (2); and(B) emulsification of the mixture,with the proviso that the ratio of aliphatic double bond in organic compound (1) to Si-bonded hydrogen in the organopolysiloxane (2) in (A) is such that toluene-soluble siloxane copolymers are obtained.
Owner:WACKER CHEM GMBH
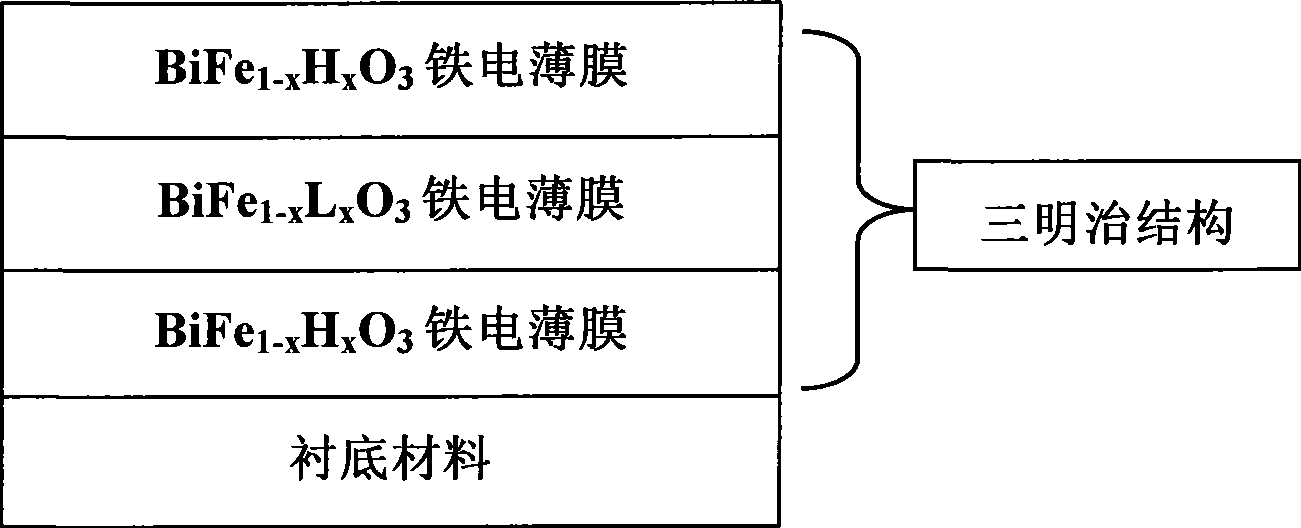
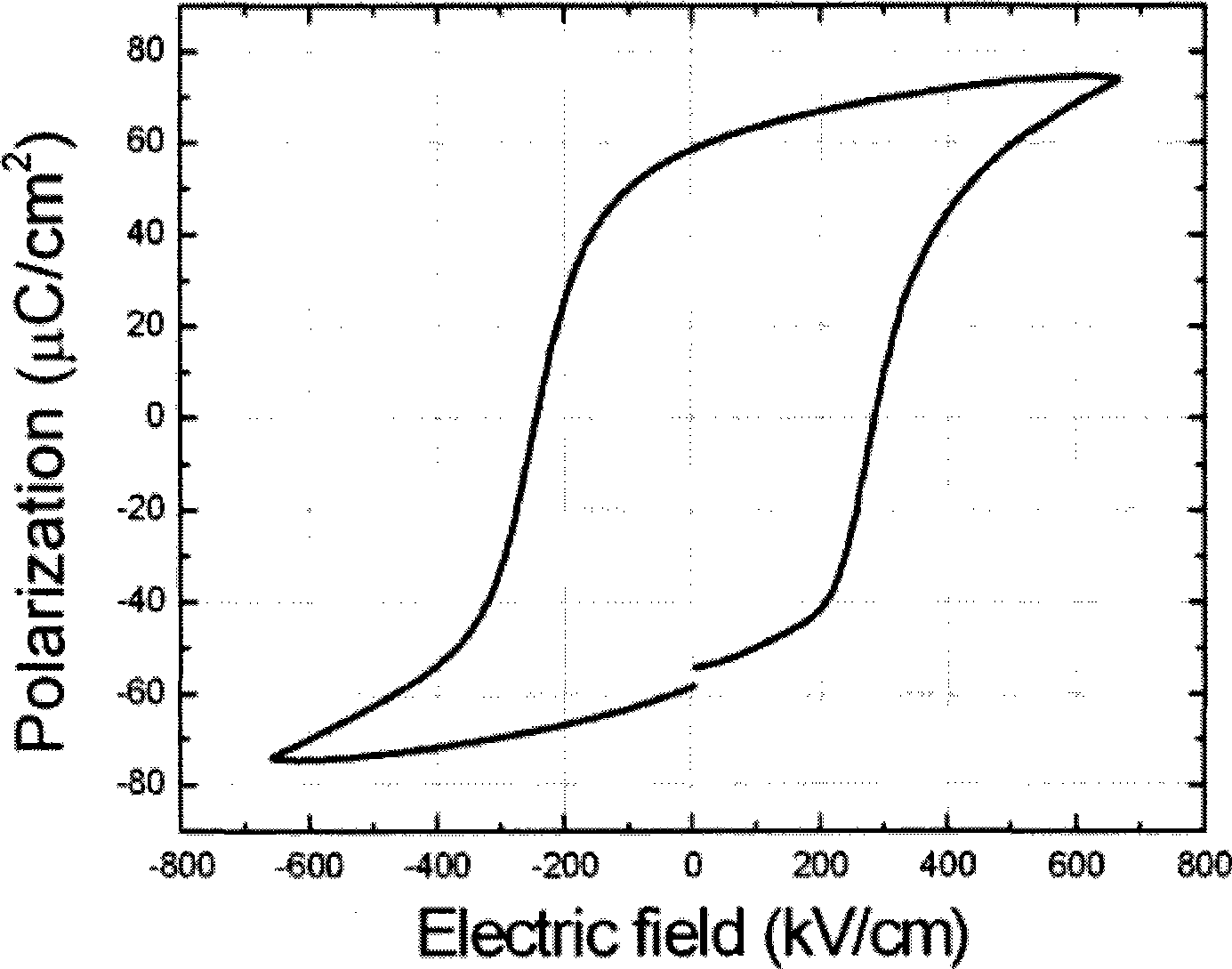
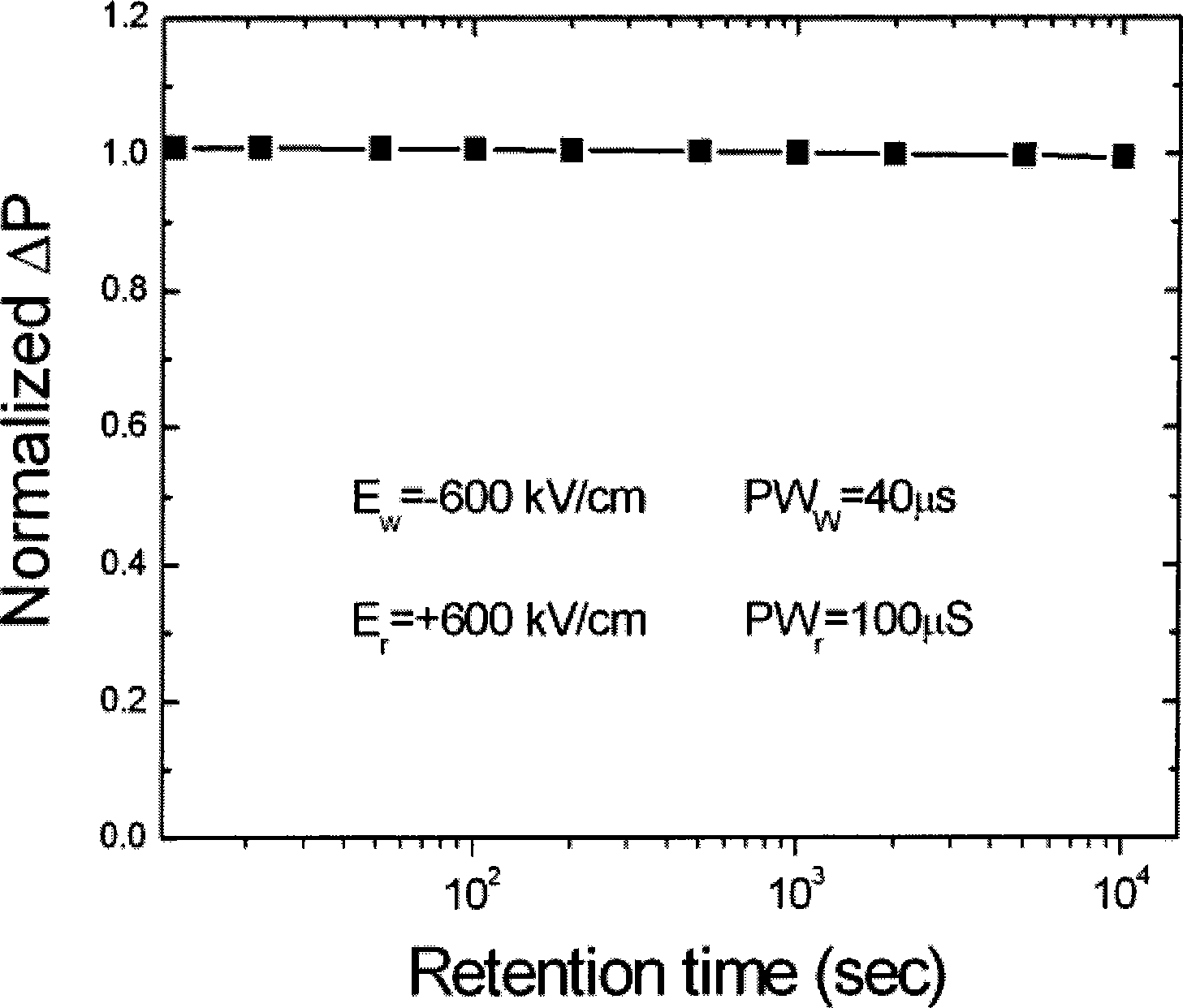
BiFeO3 based sandwich construction thin-film for ferro-electric memory and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101388395AReduce leakage currentLower coercive fieldSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical solutionSurface layer
The invention relates to a BiFeO3-base sandwich structure film used for a ferroelectric memory and a process for preparation, belonging to the technical field of microelectronic new materials, wherein the upper surface component and the lower surface component of the BiFeO3-base sandwich structure film both are BiFe1-xHxO3, H is doped high valence ion with quadravalence or over quadravalence, the component of the intermediate layer is BiFe1-xLxO3, L is doped high valence ion with trivalence or below trivalence. The process for preparation comprises adopting the chemical solution method combined with the annealing technology in layer by layer, and preparing through depositing precursor solution in the surface layers of different materials in the spin-coating method. The invention greatly reduces the drain current of the film through adopting a special sandwich structure, effectively reduces coercive field, significantly increases the charge retention, obtains the ferroelectric film with low drain current, large residual polarization, low coercive field and excellent charge retention under the annealing temperature of 500 DEG C-600 DEG C, and has great practicable prospects in further ferroelectric memories.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Process for manufacturing MCM-22 family molecular sieves
ActiveUS20070191657A1Aluminium compoundsTreatment with hydrotreatment processesMolecular sieveAlkali metal
A method of manufacturing a molecular sieve of the MCM-22 family, said method comprising the steps of (a) providing a mixture comprising at least one source of ions of tetravalent element, at least one source of alkali metal hydroxide, at least one directing-agent (R), water, and optionally at least one source of ions of trivalent element, said mixture having the following mole composition:Y:X2=10 to infinityH2O:Y=1 to 20OH−:Y=0.001 to 2M+:Y=0.001 to 2R:Y=0.001 to 0.34wherein Y is a tetravalent element, X is a trivalent element, M is an alkali metal; (b) treating said mixture at crystallization conditions for less than 72 hr to form a treated mixture having said molecular sieve, wherein said crystallization conditions comprise a temperature in the range of from about 160° C. to about 250° C.; and (c) recovering said molecular sieve.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Oxynitride piezoelectric material and method of producing the same
ActiveUS7931821B2Excellent piezoelectric propertiesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyNitrogen compoundsNitrogen oxideNitride
An oxynitride piezoelectric material, which exhibits ferroelectricity and has good piezoelectric properties, and a method of producing the oxynitride piezoelectric material. The oxynitride piezoelectric material includes a tetragonal perovskite-type oxynitride represented by the following general formula (1):A1−xBix+δ1B1−yB′y+δ2O3−zNz (1),where A represents a divalent element, B and B′ each represent a tetravalent element, x represents a numerical value of 0.35 or more to 0.6 or less, y represents a numerical value of 0.35 or more to 0.6 or less, z represents a numerical value of 0.35 or more to 0.6 or less, and δ1 and δ2 each represent a numerical value of −0.2 or more to 0.2 or less, in which the A includes at least one kind selected from Ba, Sr, and Ca and the B and the B′ each include at least one kind selected from Ti, Zr, Hf, Si, Ge, and Sn.
Owner:CANON KK +5
MTW zeolite and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103922362ARegular shapeUniform grainCrystalline aluminosilicate zeolitesChemical industryAlkaline earth metal
The invention belongs to the technical field of inorganic materials, and in particular discloses MTW zeolite with a novel structure and a preparation method thereof. The method adopts a hydro-thermal synthesis method and comprises the following steps: mixing a silicon source, an aluminum source, an alkali source, an organic template and a water phase, and stirring to be a gel mixture as a raw material for synthesizing the MTW zeolite. The MTW zeolite with the novel structure has the chemical composition of TO2:aY2O3:bM2 / nO, wherein T represents at least one quadrivalent element, Y represents at least one trivalent element, M represents at least one alkali metal (or) alkaline-earth metal element and has the valence state of n, a and b respectively represent the mole numbers of T2O3 and M2 / nO, a ranges from 0 to 1, and b ranges from 0 to 0.8. The MTE zeolite prepared by using the method is tidy in morphology and uniform in crystal granule; compared with the conventional disordered MTW zeolite, the MTE zeolite has the advantages of fixed mass transfer orientation, high activity, high mechanical strength and the like, and can be widely applied to the chemical industry.
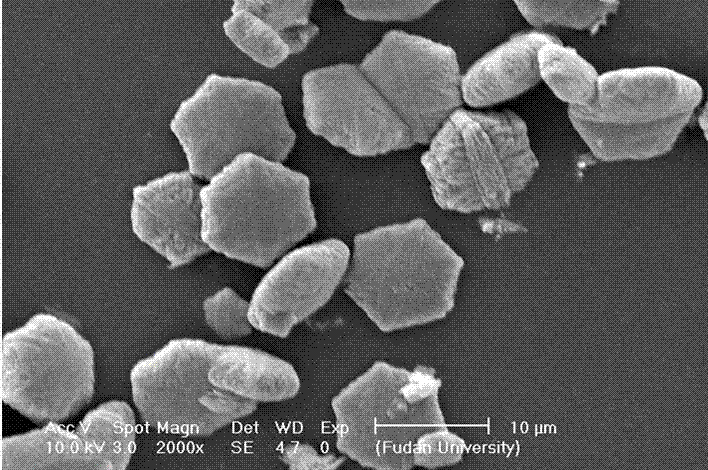
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
High activity MTT framework type molecular sieves
ActiveUS20100147741A1Aluminium compoundsMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieveAlkaline earth metal
A process is described of producing an MTT framework type molecular sieve by crystallizing a mixture capable of forming said molecular sieve, wherein the mixture comprises sources of alkali or alkaline earth metal (M), an oxide of trivalent element (X), an oxide of tetravalent element (Y), water and a directing agent (R) of the formula (CH3)3N+CH2CH2CH2N+(CH3)2CH2CH2CH2N+(CH3)3, and has a composition, in terms of mole ratios, within the following ranges.YO2 / X2O3 less than 45H2O / YO2 5 to 100OH− / YO2 0.05 to 0.5M / YO2 0.05 to 0.5 andR / YO2>0 to <0.5.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
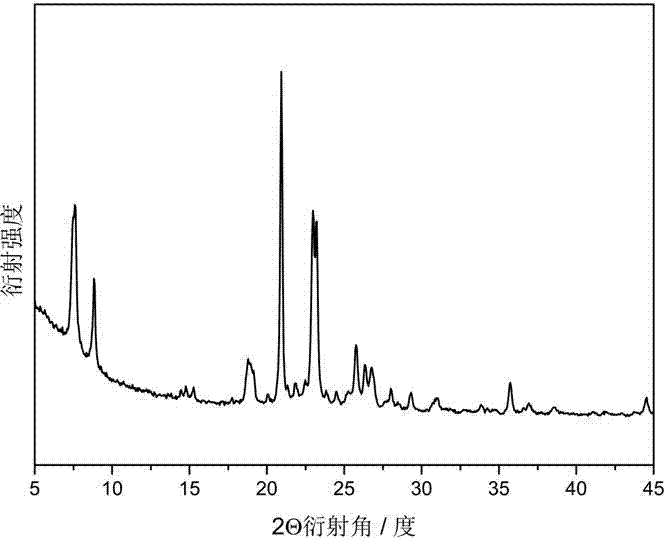
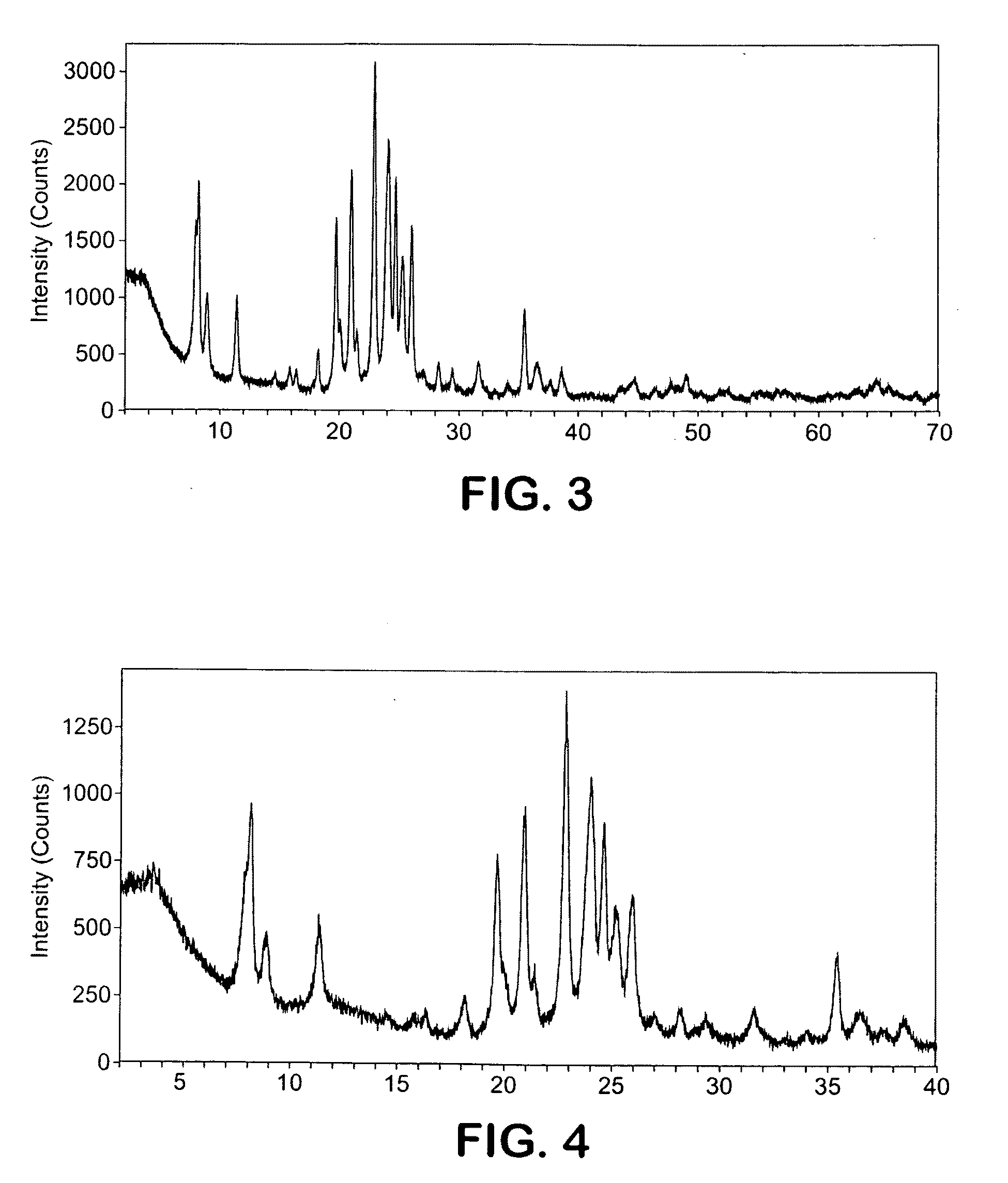
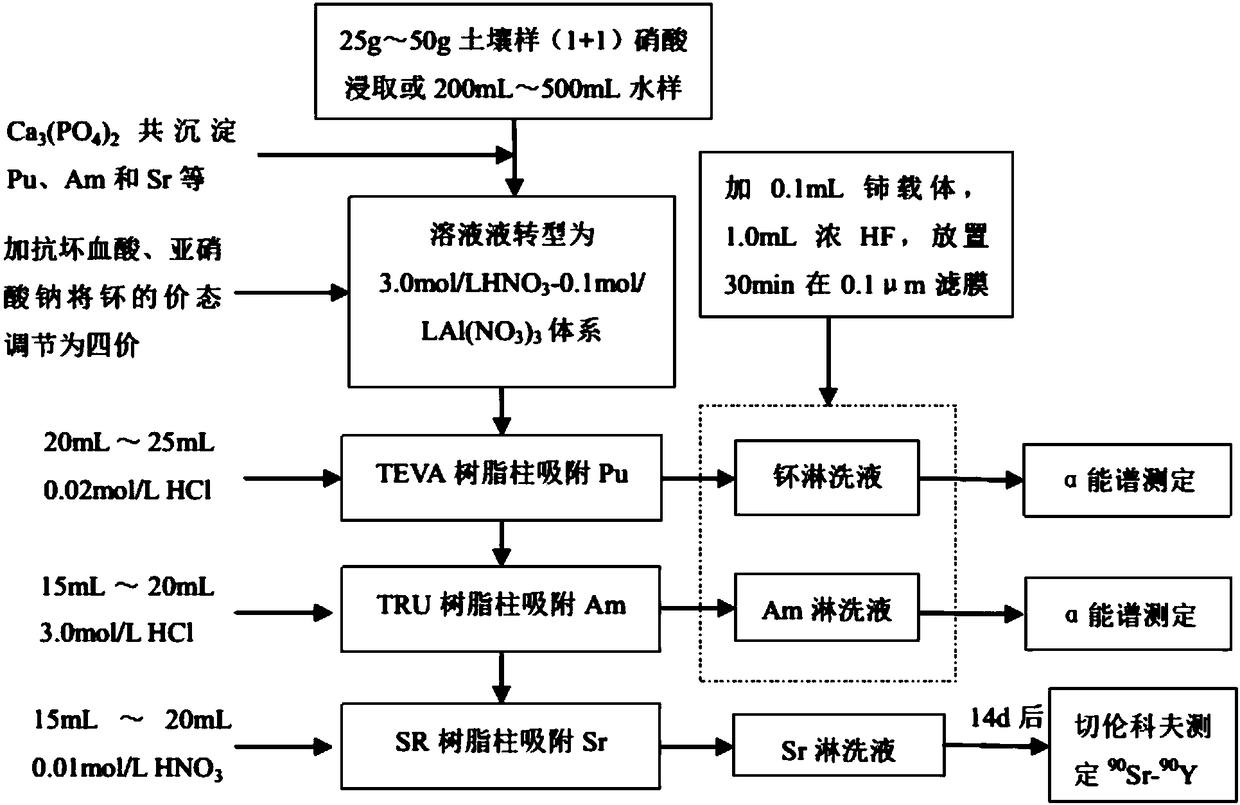
Method for separating and determining Pu, <241>Am and <90>Sr in low-radioactivity sample
InactiveCN108152112AShorten the analysis cycleLess staffX-ray spectral distribution measurementPreparing sample for investigationPu elementSodium nitrite
The invention relates to a method for separating and determining <238-240>Pu, <241>Am and <90>Sr in a low-radioactivity sample, which comprises the following steps: (1) sample pretreatment; (2) separation and enrichment of <238-240>Pu, <241>Am and <90>Sr: after ascorbic acid and sodium nitrite are added into a solution obtained in step (1) to regulate the valence state of plutonium into tetravalence, the solution passes through a TEVA, TRU and SR tandem extraction chromatography resin column, and the flow velocity is kept at 1mL / min to 1.2mL / min; at the moment, <238-240>Pu is adsorbed on the TEVA column, <241>Am is adsorbed on the TRU column, and <90>Sr is adsorbed on the SR column; 20mL to 25mL of hydrochloric acid solution which is 0.02mol / L is used for eluting <238-240>Pu on the TEVA column, 15mL to 20mL of hydrochloric acid solution which is 3.0mol / L is used for eluting <241>Am on the TRU column, and 15mL to 20mL of nitric acid solution which is 0.01mol / L is used for eluting <90>Sron the SR column; (3) determination of <238-240>Pu, <241>Am and <90>Sr: a cerium fluoride micro-deposition method is adopted to prepare an Alpha source, and the <238-240>Pu eluent and the <241>Am eluent are measured on the Alpha energy spectrum; the <90>Sr eluent is placed for 14 days, and after <90>Sr<-><90>Y is balanced, determination is carried out by the Cerenkov counting method. The analysismethod can be adopted to separate and enrich Pu, <241>Am and <90>Sr in a sample, and the period of analyzing Pu, <241>Am and <90>Sr is shortened.
Owner:THE 404 COMPANY LIMITED CHINA NAT NUCLEAR
Application of inorganic acids as additives for improving concentration and stability of vanadium electrolyte solution
InactiveCN106299432AImprove stabilitySimple processing methodRegenerative fuel cellsAcid electrolytesElectrolytic agentInorganic acids
The invention relates to the field of battery manufacturing and energy storage, in particular, relates to an application of inorganic acids as additives for improving the concentration and stability of a vanadium electrolyte solution, and is used for solving the problem of poor stability of a vanadium battery electrolyte solution in the prior art. With the electrolyte solution having a certain vanadium concentration and sulfuric acid concentration as a raw material, inorganic acid with a certain concentration is added in the electrolyte solution; by reducing the concentration of sulfuric acid in an original electrolyte solution, other species of inorganic acids are added; therefore, the H<+> concentration is increased, the concentration of SO4<2-> is decreased, the stability of tetravalence vanadium ions is comprehensively increased, and the electrolyte solution can work in a temperature range of -10 to 50 DEG C. The method has the advantages of simpliness, easy operation, and easily obtained raw materials, and the good-stability vanadium battery electrolyte solution can be obtained.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Chicken egg-yolk antibody capable of resisting influenza virus and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105968195AEfficient killingLarge range of protectionEgg immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against virusesInfluenza A virus subtype H3N2Virology
The invention discloses a chicken egg-yolk antibody capable of resisting influenza virus. The chicken egg-yolk antibody is used for specifically resisting tetravalence influenza virus. The influenza virus includes influenza A virus subtype H1N1, influenza A virus subtype H3N2, influenza B virus subtype Victoria series and influenza A virus subtype Yamagata series. The preparation method of the chicken egg-yolk antibody comprises the following steps of 1, preparing a tetravalence influenza virus antigen; 2, performing immunity on hens; 3, collecting immunized eggs laid by the immunized hens; 4, preparing a mixed antibody stock solution from the immunized eggs; 5, detecting titer of the antibody stock solution, and a stabilizer is added cooperatively, so that the chicken egg-yolk antibody capable of resisting tetravalence influenza virus is obtained. The chicken egg-yolk antibody can be combined with the tetravalence influenza virus specificity pathogen for a short period of time, the tetravalence influenza virus can be effectively killed for a long period of time, the safety performance is good, no toxic or side effect is generated, and the chicken egg-yolk antibody can be effectively used for preventing pathogen corresponding to human pharyngeal and nasopharynx mucosas.
Owner:CHENGDU ANTIK BIOTECH CO LTD
Columnar zinc oxide particles and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20120097888A1Sufficient thermal conductivity conductivitySufficient conductivity electrical conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyConductive materialZincMetal
Owner:KYOWA CHEM IND
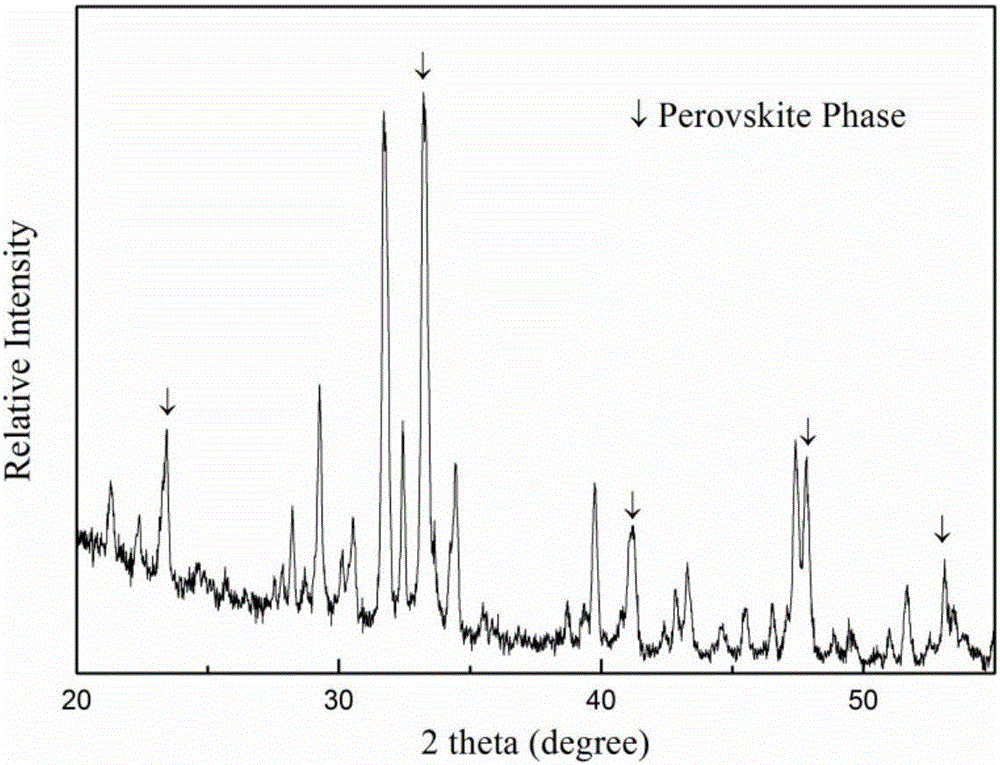
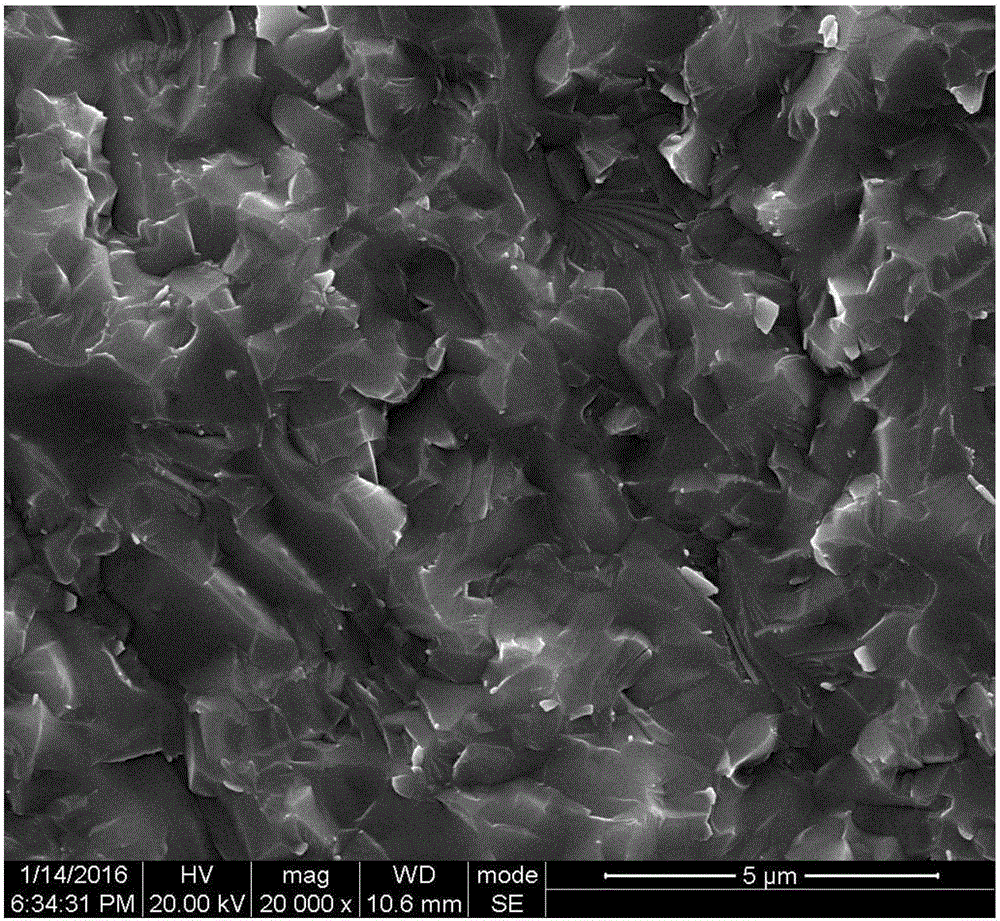
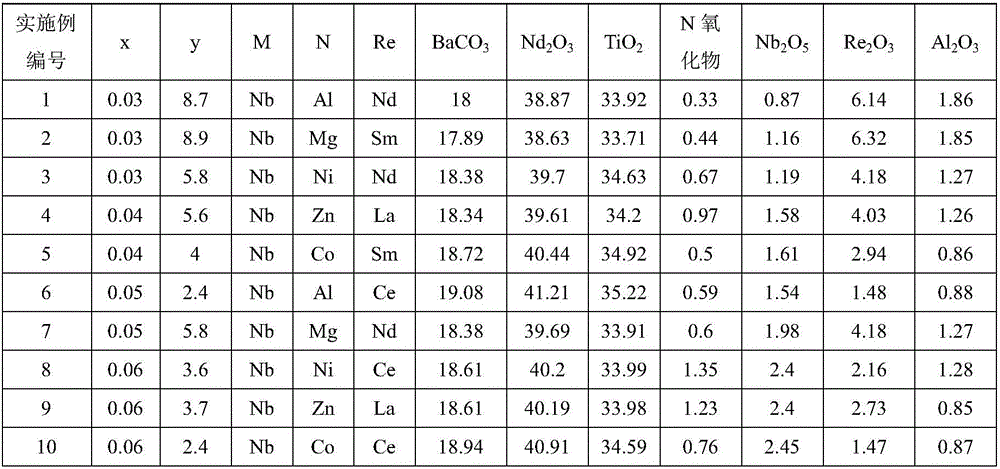
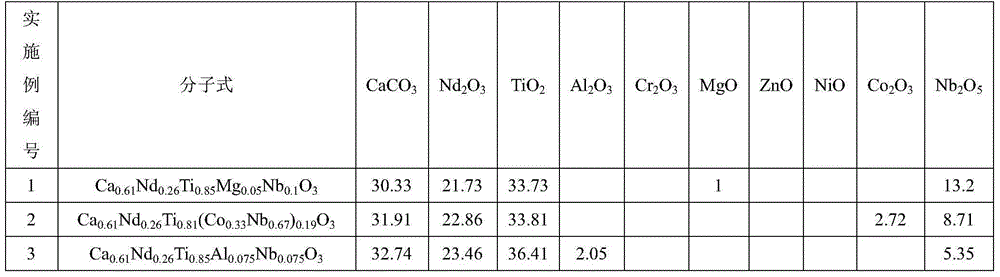
Microwave dielectric ceramic material doped with ReAlO3 and preparation method thereof.
The present invention provides a microwave dielectric ceramic material doped with ReAlO3 and a preparation method thereof. The material has a chemical formula of Ba3.75Nd9.5 (Ti1-xCx) 18O54+y wt%ReAlO3. C equals to MN; x represents molar concentration ratio; x satisfies the relation of 0.03<=x<=0.06; y satisfies the relation of 2<=y<= 9, and y is the mass percent content of ReAlO3 added to the Ba3.75Nd9.5 (Ti1-xCx) 18O54; M represents Nb with valence higher than tetravalence; N represents one element, selected from Zn, Co, Ni, Mg and Al, with valence lower than tetravalence and ionic radius similar to Ti; M and N substitute at the same time; and Re represents one of Nd, replace Sm, La, and Ce. A preparation method comprises: preparing ingredients; conducting ball milling and mixing; pre-sintering the two phases at 1100-1150 DEG C and 1450-1500 DEG C, and then sintering at 1400-1450 DEG C. The prepared material has high dielectric constant and adjustable frequency temperature coefficient and maintains high Q*F value; the formula does not contain Pb, Cd and other volatile or heavy metal, so as to significantly improve the performance; and the raw materials have sufficient domestic supply and low price, so as to make possible the low cost of the high performance microwave ceramics.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
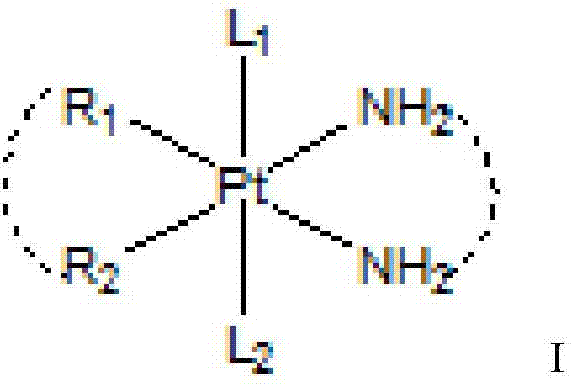
Platinum compound with anti-tumor activity as well as preparation method and application
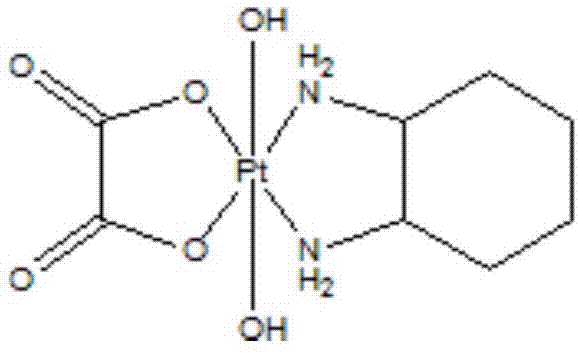
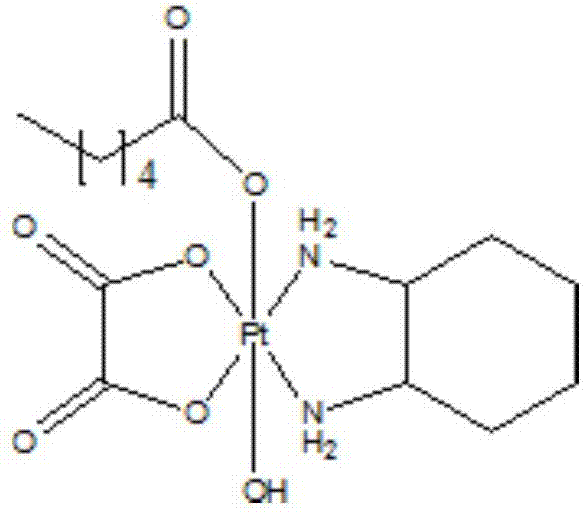
ActiveCN107955042AHas anticancer activityImprove anti-tumor activityPlatinum organic compoundsAntineoplastic agentsGallic acid esterCarboxylic acid
The invention provides a tetravalence platinum anti-tumor compound based on gallic acid. A carboxylic acid ligand part is adjusted to find out that the platinum compound not only has relatively high anti-tumor activity, but also has certain tumor cell selectivity; the platinum compound also has an inhibition effect on drug-resisting cells.
Owner:THE AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF QINGDAO UNIV
Method for preparing potassium ion battery electrode potassium type birnessite
The invention discloses a method for preparing a potassium type birnessite manganese ore layered crystal potassium ion battery electrode material from a potassium salt and tetravalence manganite witha high-temperature solid-phase method together with an ion exchange method process. Due to adoption of the ion exchange process, the content of potassium ions in potassium type birnessite manganese ore can be increased, and properties of a potassium ion battery electrode are improved. The high-potassium type birnessite electrode material of water solution exchange is high in electric property, thecurrent density of the material is 16mA*g<-1>, the mass specific capacity of the material is up to 125mAh*g<-1>, and when the current density of the material is increased to 400mA*g<-1>, the mass specific capacity of the material is still maintained at 68mAh*g<-1>. After 50 times of circulation at a current density of 80mA*g<-1>, the mass specific capacity of the material is still maintained at 68mAh*g<-1>, and the capacity retention rate of the material is 79%. When being used as a potassium ion battery electrode material, a sample prepared with the method is excellent in rate capability andcirculation stability.
Owner:HANGZHOU INST OF ADVANCED MATERIAL BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
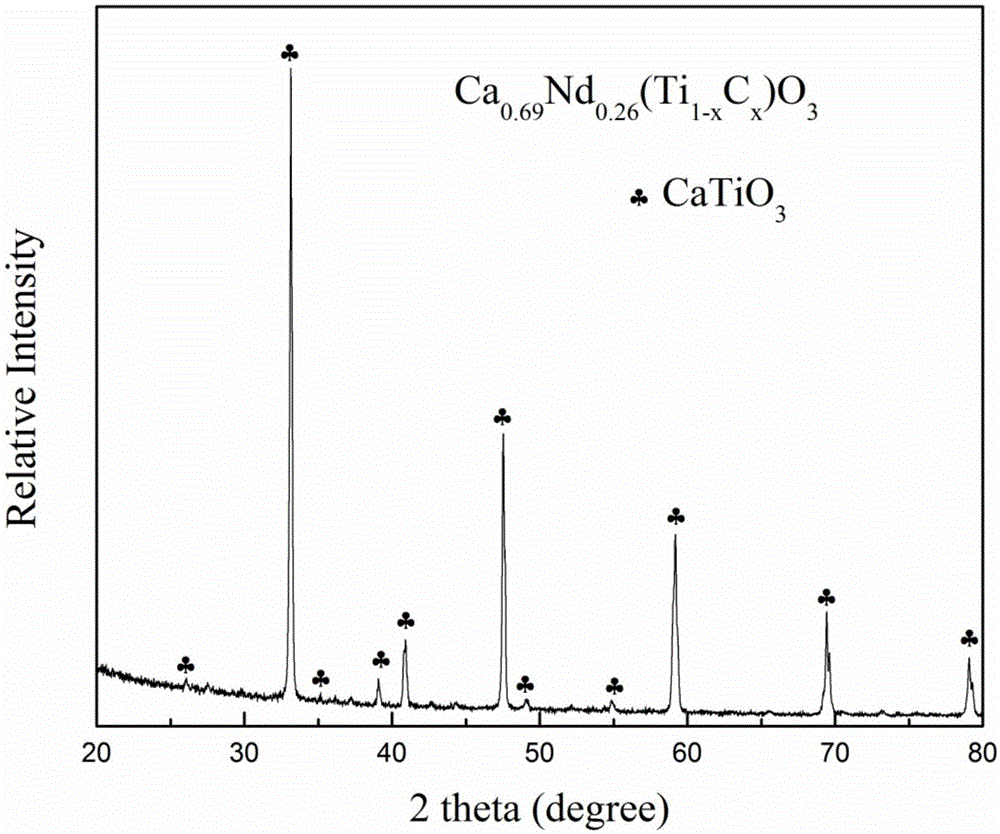
Ca-Nd-Ti microwave dielectric ceramic material and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a Ca-Nd-Ti microwave dielectric ceramic material and a preparation method thereof. The general chemical formula of the material is Ca0.61Nd0.26(Ti1-xCx)O3 and C=MN, wherein x is larger than or equal to 0.15 and smaller than or equal to 0.2, and the aim of controlling the microwave performance of a system is achieved through B-site substitution; M represents Nb with valence state higher than tetravalence, N represents one or more of elements with valence state lower than tetravalence and ionic radius similar to that of Ti, and simultaneous substitution or independent substitution is achieved for M and N. The preparation method includes the steps of determining weight percentage contents of all components according to the general chemical formula, conducting ball-milling and mixing, conducting presintering at a temperature of 1050 DEG C to 1150 DEG C, and conducting sintering at a temperature of 1350 DEG C to 1450 DEG C to obtain the material. The dielectric constant, ranging from 70 to 100, of the obtained material and the frequency temperature coefficient of the material can be adjusted, and meanwhile the excellent Q*f value is kept between 9000 GHz and 16000 GHz; Pb, Cd and other volatile or heavy metal are not contained in the formula, performance is greatly improved compared with other systems, raw materials are sufficiently supplied in domestic, price is lower than that of other systems, and it is made possible that high-performance microwave ceramic is low in cost.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
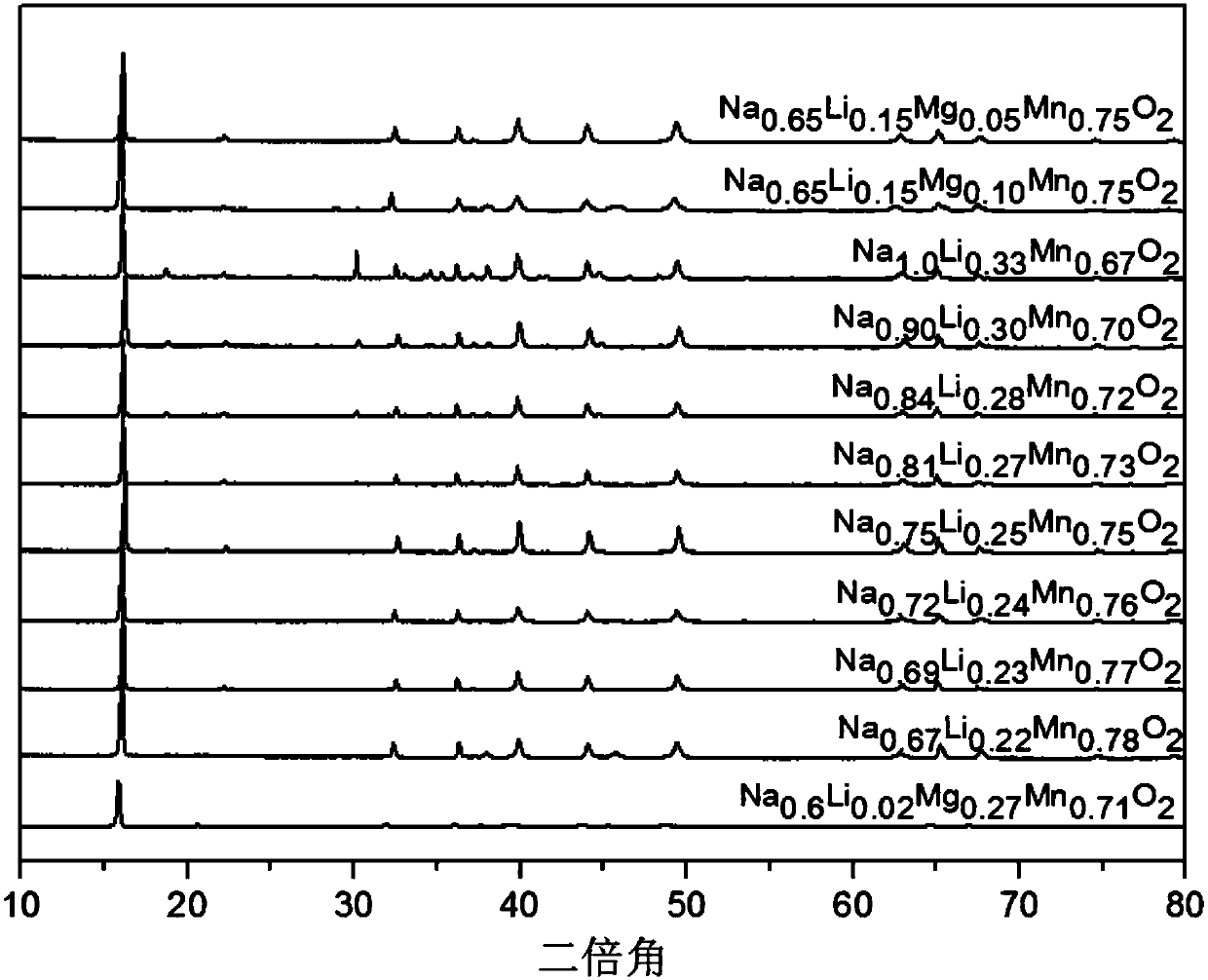
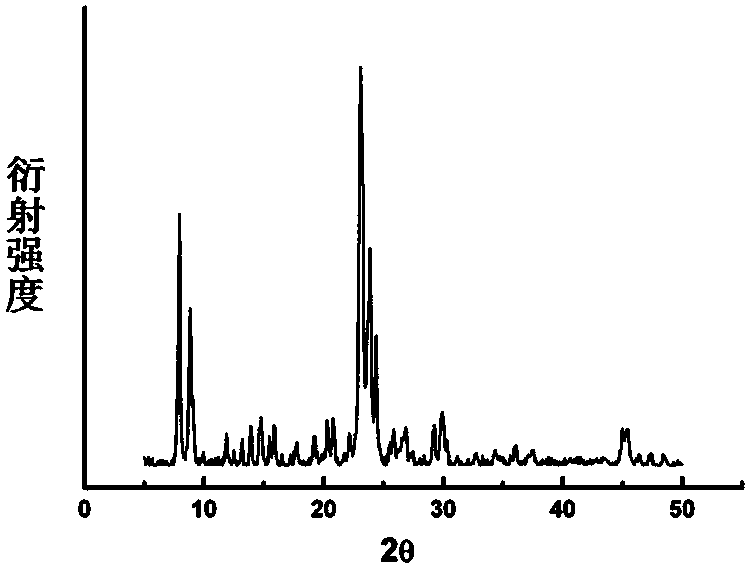
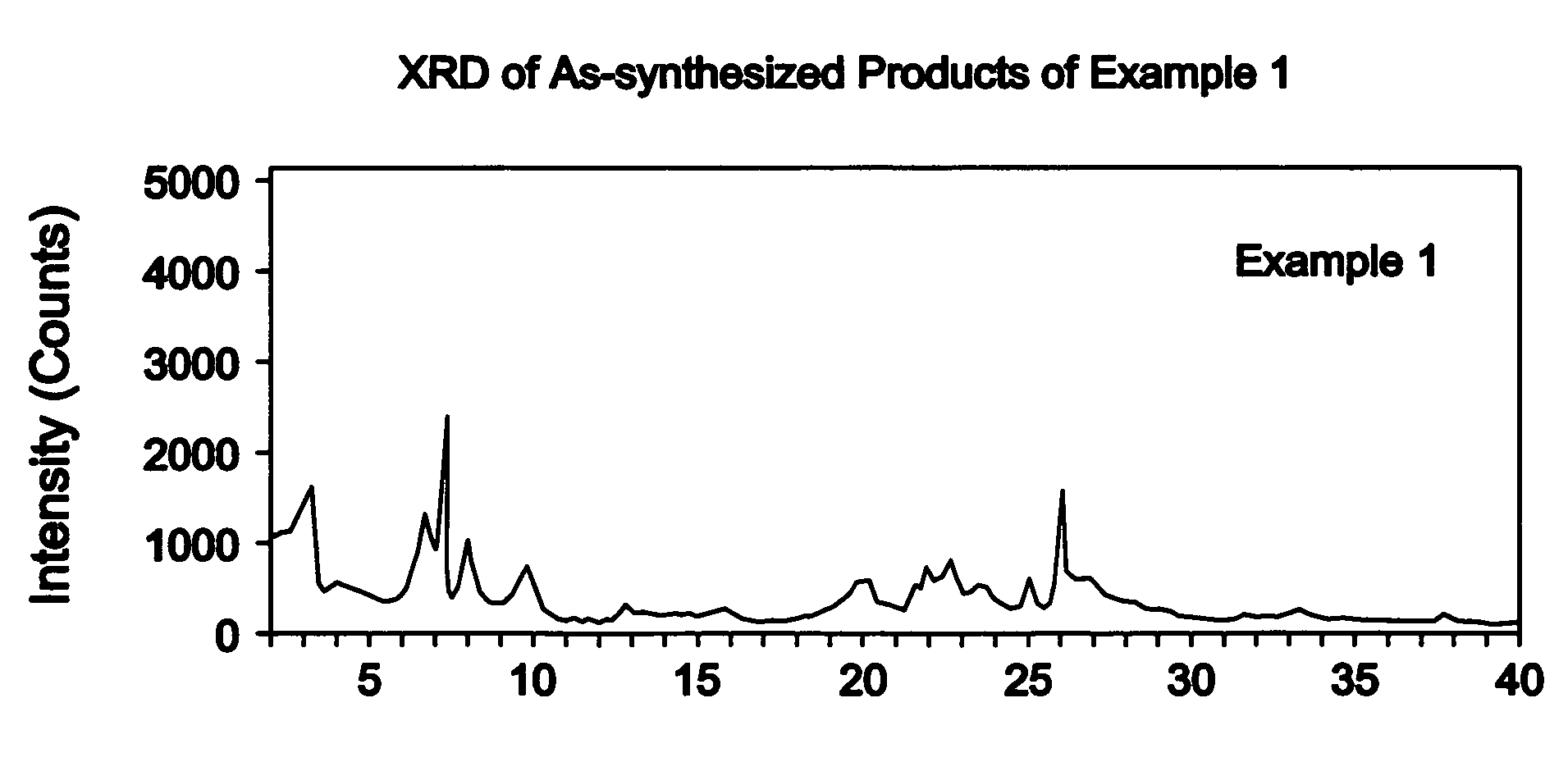
Anion valence-varying layer oxide material, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109560258AEasy to makeAchieve activationCell electrodesSecondary cellsSpace groupLattice oxygen
The invention discloses an anion valence-varying layer oxide material, and a preparation method and application thereof. The chemical formula of the material is: Naa[LibMncMd]O2+[beta]; M is an element which is doped and substituted for a transition metal site; a, b, c , d and [beta] are the mole percentages of the corresponding elements respectively; the relationship between a, b, c, d and [beta]satisfies the formula: b+c+d=1, and a+b+4c+md=2(2+[beta]); 0.6<=a<=1, 0<=b<=0.4, 0.5<=c<=0.8, 0<=d<=0.3, and -0.02<=[beta]<=0.02; m is the valence state of M; and the space group of materials is P63 / mmc or R-3m, the corresponding structure is P2 phase or P3 phase, and the anion valence-varying layer oxide material is used for the positive electrode active material of sodium ion secondary battery.When charging is performed in the first week, the lattice oxygen ion is converted from a negative bivalence to a higher valence state, electrons are completely provided by the oxygen ions to achieveactivation of the material; when discharge is performed in the first week, the oxygen ions losing electrons regain electrons from the high valence state to the negative bivalence, and the manganese metal is converted from a tetravalence to a tervalence, and the charging and discharging process after two weeks has the valence varying of the oxygen ions and the valence varying of the manganese.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of nanorod particle ordered-assembly ZSM-5 zeolite molecular sieve
InactiveCN103708495ANo pollution in the processLow costPentasil aluminosilicate zeoliteMolecular sieveInorganic salts
The invention belongs to the technical field of inorganic materials, and particularly relates to a preparation method of a nanorod particle ordered-assembly ZSM-5 zeolite molecular sieve. By adopting a hydrothermal synthesis method, a silicon source, an aluminum source, an alkali source, a MFI zeolite crystal seed, an inorganic salt and a water phase are mixed and stirred into a gel mixture which is used as a raw material for synthesizing the ZSM-5 zeolite molecular sieve. The chemical composition of the MOR zeolite in such special structure is TO2:aY2O3:bM2 / nO, wherein T represents at least one quadrivalent element; Y represents at least one trivalent element, such as Al, B, Ga, Fe and the like; M represents at least one alkali metal or alkali earth metal element, and the valence state is n; a and b are respectively mole numbers of Y2O3 and M2 / nO; and a is 0-0.5, and b is 0-0.5. The method has the advantages of lower cost and no environmental pollution, and is suitable for popularization.
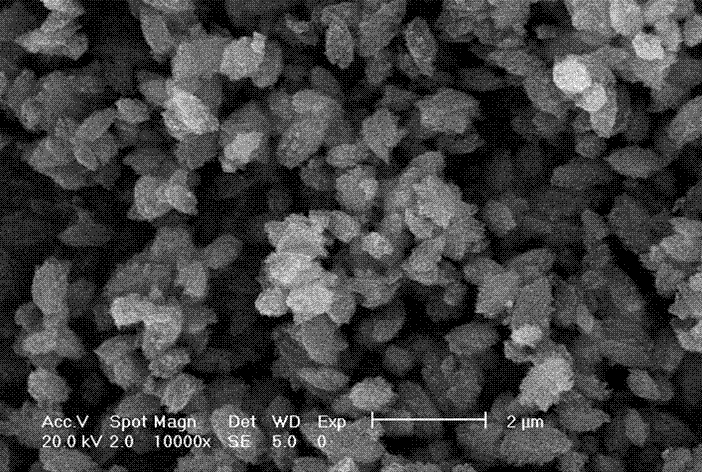
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Process for manufacturing MCM-22 family molecular sieves
ActiveUS7799316B2Aluminium compoundsTreatment with hydrotreatment processesMolecular sieveMetallurgy
A method of manufacturing a molecular sieve of the MCM-22 family, said method comprising the steps of (a) providing a mixture comprising at least one source of ions of tetravalent element, at least one source of alkali metal hydroxide, at least one directing-agent (R), water, and optionally at least one source of ions of trivalent element, said mixture having the following mole composition:Y:X2 =10 to infinityH2O:Y =1 to 20OH−:Y =0.001 to 2M+:Y =0.001 to 2R:Y =0.001 to 0.34wherein Y is a tetravalent element, X is a trivalent element, M is an alkali metal; (b) treating said mixture at crystallization conditions for less than 72 hr to form a treated mixture having said molecular sieve, wherein said crystallization conditions comprise a temperature in the range of from about 160° C. to about 250° C.; and (c) recovering said molecular sieve.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
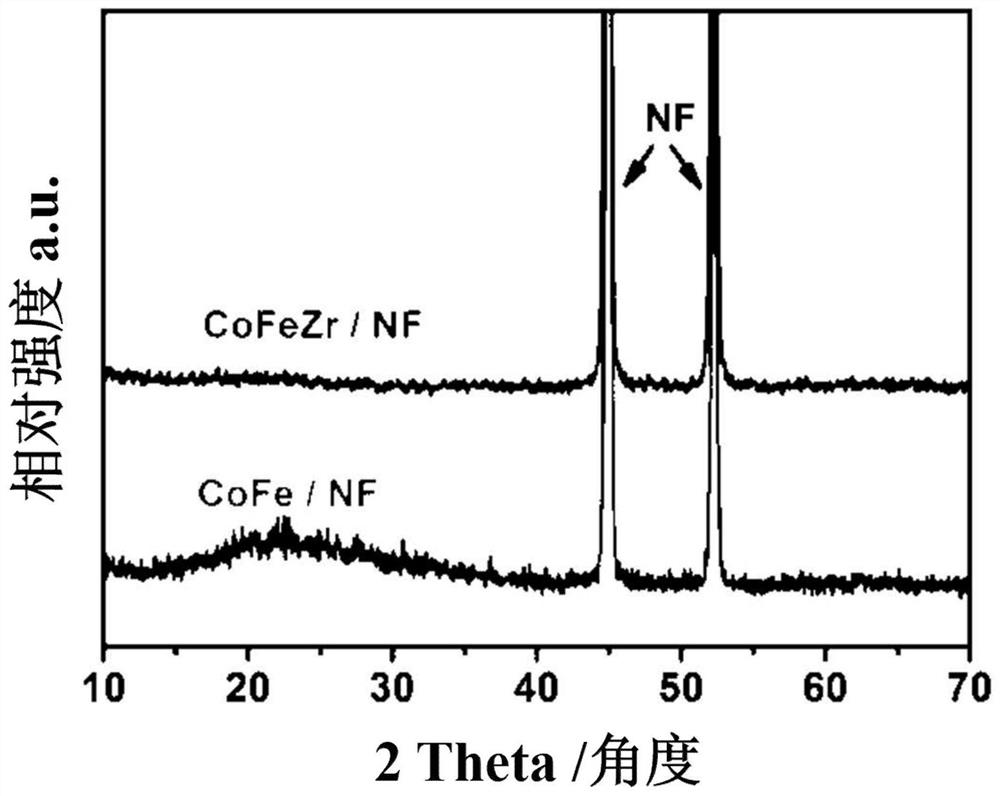
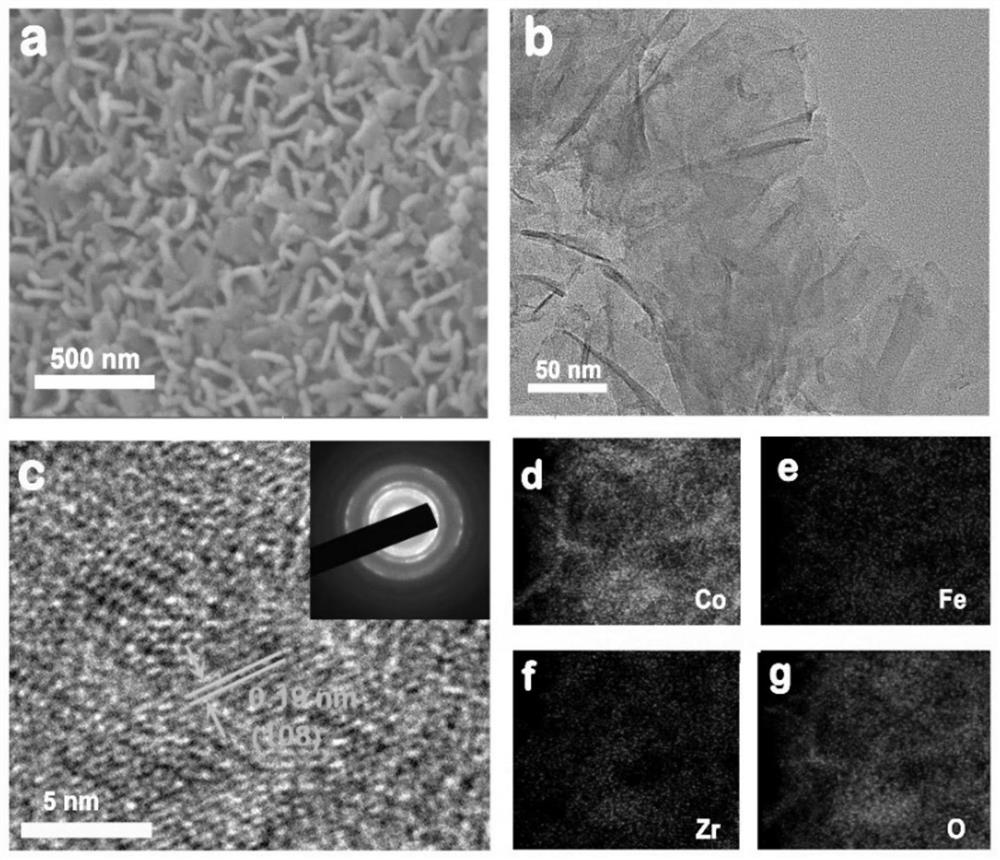
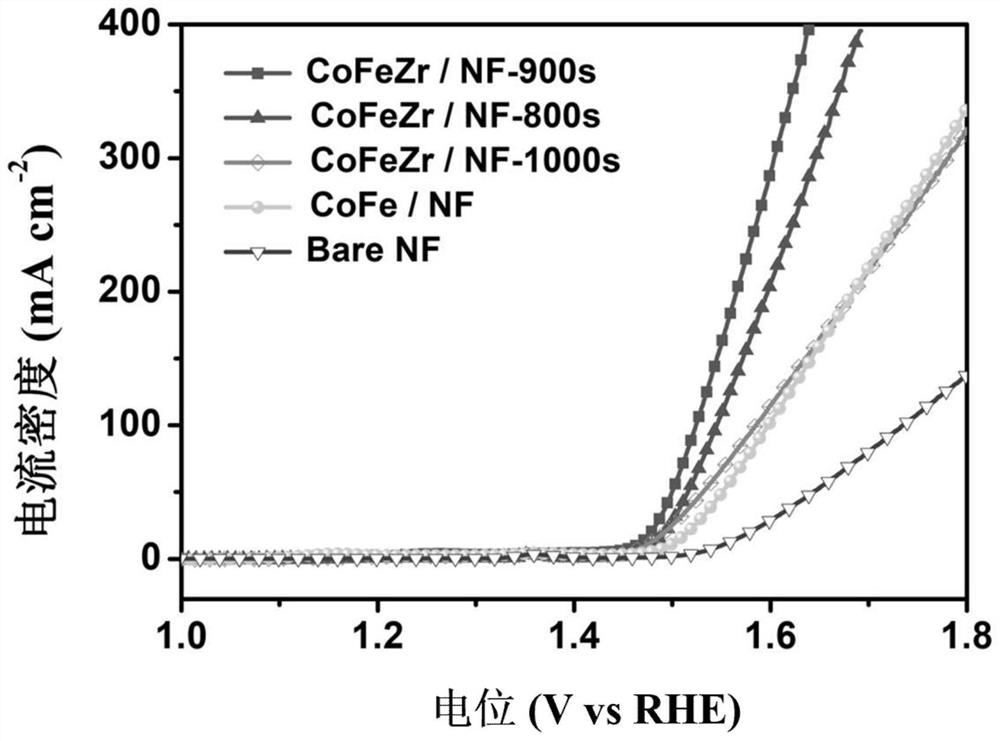
Preparation method of low-crystallinity zirconium-doped ferrocobalt layered double hydroxide and application of low-crystallinity zirconium-doped ferrocobalt layered double hydroxide in water electrolysis for hydrogen production
ActiveCN113481534AWide variety of sourcesLow priceElectrolytic inorganic material coatingElectrodesPtru catalystFerrocobalt
The invention belongs to the technical field of functionalized nanometer electrode materials, and relates to a preparation method of low-crystallinity zirconium-doped ferrocobalt layered double hydroxide. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving a divalent cobalt source, a trivalent iron source and a tetravalent zirconium source in a deionized water solution of potassium nitrate, and carrying out stirring at a constant speed to fully and uniformly mix the above sources; placing a pretreated substrate NF in a solution obtained in the previous step, and carrying out constant-voltage electro-deposition of deposition negative potential for 600-1200 s by using a three-electrode system; and washing a prepared material, and carrying out vacuum drying at 60-80 DEG C for 2-4 hours to obtain the product. The prepared low-crystallinity zirconium-doped ferrocobalt layered double hydroxide is applied as an anode and a cathode of water electrolysis to hydrogen production through water electrolysis. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple and easy to operate, wide in raw material source, low in price, mild in reaction and friendly to environment. The prepared catalyst has high bifunctional electrocatalytic activity, can be applied to a full-electrolysis water electrocatalyst of seawater, and can also be used for desalting seawater.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
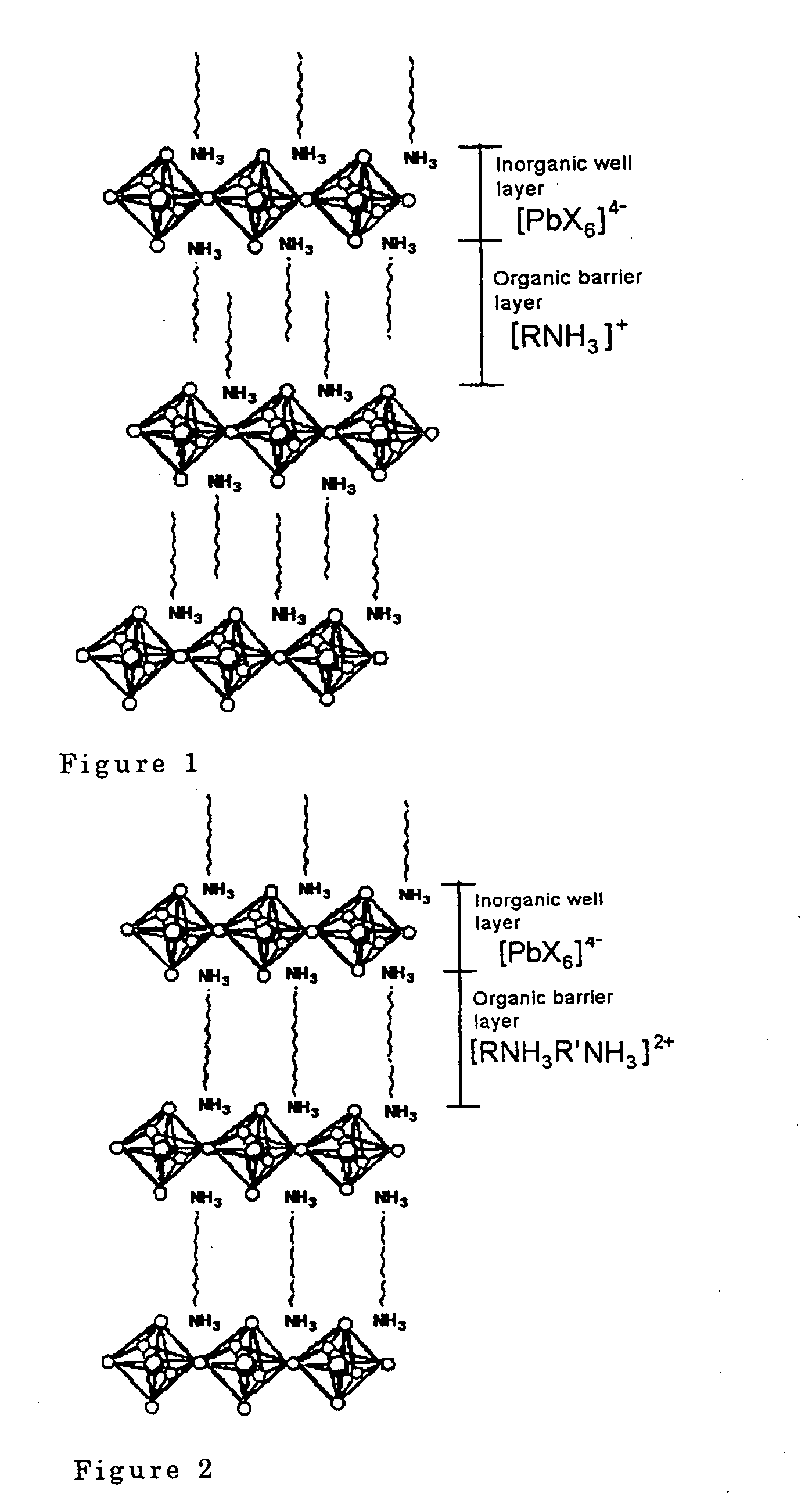
Radiation detection
InactiveUS20040084654A1Luminescent compositionsRadiation intensity measurementExtinctionHybrid compound
This invention relates to a radiation detection device for detecting ionizing beam discharges such as gamma rays, x-rays, electron beams, charged particle beams and neutral particle beams. Specifically, it relates to a radiation detection device which can measure radiations which exist for a very short time (of the order of subnanoseconds or less) from the appearance of photoemission to extinction. It is an object of this invention to provide a radiation detection device using a perovskite organic-inorganic hybrid compound as a scintillator, the formula of this compound being (R<1>-NR<11>3)2MX4 or (R<2>=NR<12>2)2MX4, or alternatively, (NR<13>3-R<3>-NR<13>3)MX4 or (NR<14>2=R<4>=NR<14>2)MX4 (in the formula, R<1 >is a monovalent hydrocarbon group which may contain a heterocyclic ring and may be substituted by halogen atoms, R<2 >is a divalent hydrocarbon group which may contain a heterocyclic ring and may be substituted by halogen atoms, and may be cyclic, R<3 >is a divalent hydrocarbon group which may contain a heterocyclic ring and may be substituted by halogen atoms, R<4 >is a tetravalent hydrocarbon group which may contain a heterocyclic ring and may be substituted by halogen atoms, R<11>-R<14 >may be identical or different, and may be hydrogen atoms or alkyl groups having two or more atoms, M is a Group IVa metal, Eu, Cd, Cu, Fe, Mn or Pd, and X is a halogen atom). This radiation detection device can quantify the radiation amount of the detected radiation.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Desulfurization application method of super-deep oxidative desulfurization catalyst
InactiveCN102430428AEfficient oxidation capacityReduce desulfurization costOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsRefining with oxygen compoundsPhosphoniumTransition metal atoms
The invention relates to a super-deep oxidative desulfurization catalyst and desulfurization application thereof. The super-deep oxidative desulfurization catalyst is an amphiphilic catalyst and has an expression of Qp[HqSexMyOz], wherein in the expression, p is an integer greater than or equal to 1, q is an integer greater than or equal to 0 and less than 2x and x is an integer greater than or equal to 1; y is greater than or equal to 2x and is less than or equal to 16x; z is greater than or equal to 3(x+y) and is less than or equal to 4x+5y; p is equal to 2x-q; Q represents surfactant cation which can be quaternary ammonium salt cation, alkyl pyridine salt cation, phosphonium cation, sulfonium cation and the like, generally quaternary ammonium salt cation with at least one alkyl chain of which the number of carbon atoms is not less than 4 is chosen; Se represents selenium atom which can be in the valence state of tetravalence or sexavalence; Se in a contrast catalyst can also be P, AS, S or Si of the highest valence, be blank, and the like, M represents transition mental atom which can be W, Mo, Ti, V, Mn, Ru, Cr, Fe, Co and the like, and generally can be W or Mo; and O represent oxygen atom. The catalyst in the invention can also be used for preparing an ultra-low-sulfur oil product with sulfur content of less than 5 ppm; implement conditions are mild; and the utilization rate of an oxidant is high.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Intermediate transfer member, image forming apparatus and image forming method
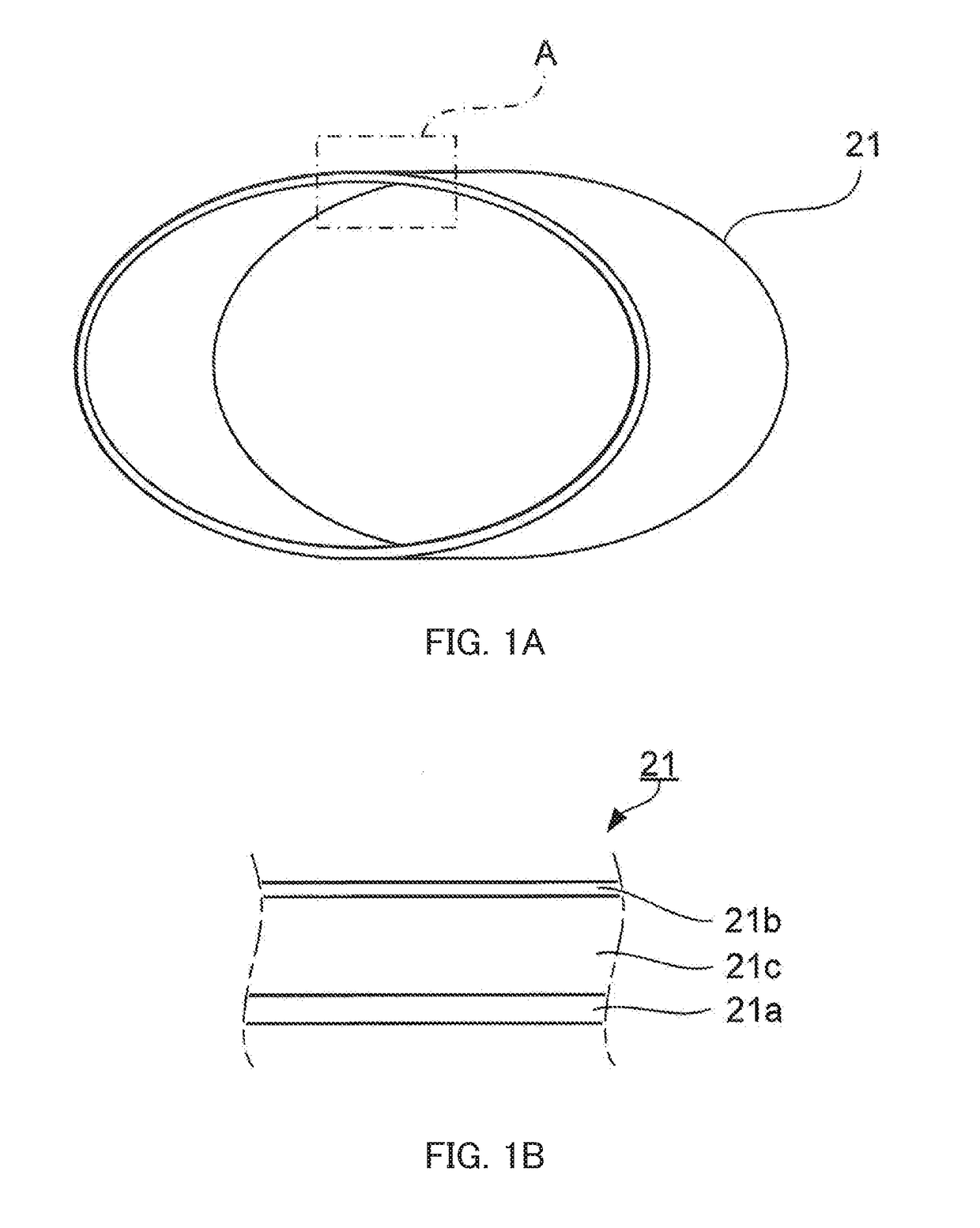
ActiveUS20170357191A1Suppressing increase in dynamic friction forceEasy to cleanElectrographic process apparatusSurface layerImage formation
According to the present invention, increase in a dynamic friction force can be suppressed and cleaning performance of a cleaning member can be improved under any operating environment without additionally providing a special mechanism. An intermediate transfer member includes a substrate layer and a surface layer, the surface layer contains a cured product of a polymerizable monomer, and the monomer contains a compound represented by the following formula (1):A-[(L-B)k-D]m(D)l (1)wherein A represents a tetra- or higher-valent organic group, B independently represents an alkylene oxide group having 4 to 15 carbon atoms, D independently represents a (meth)acryloyl group, L independently represents —(CO)— or a single bond, k independently represents an integer of 1 or more, l represents an integer of 0 to 3, m represents an integer of 2 or more, and a sum of l and m represents an integer of 3 or more.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com