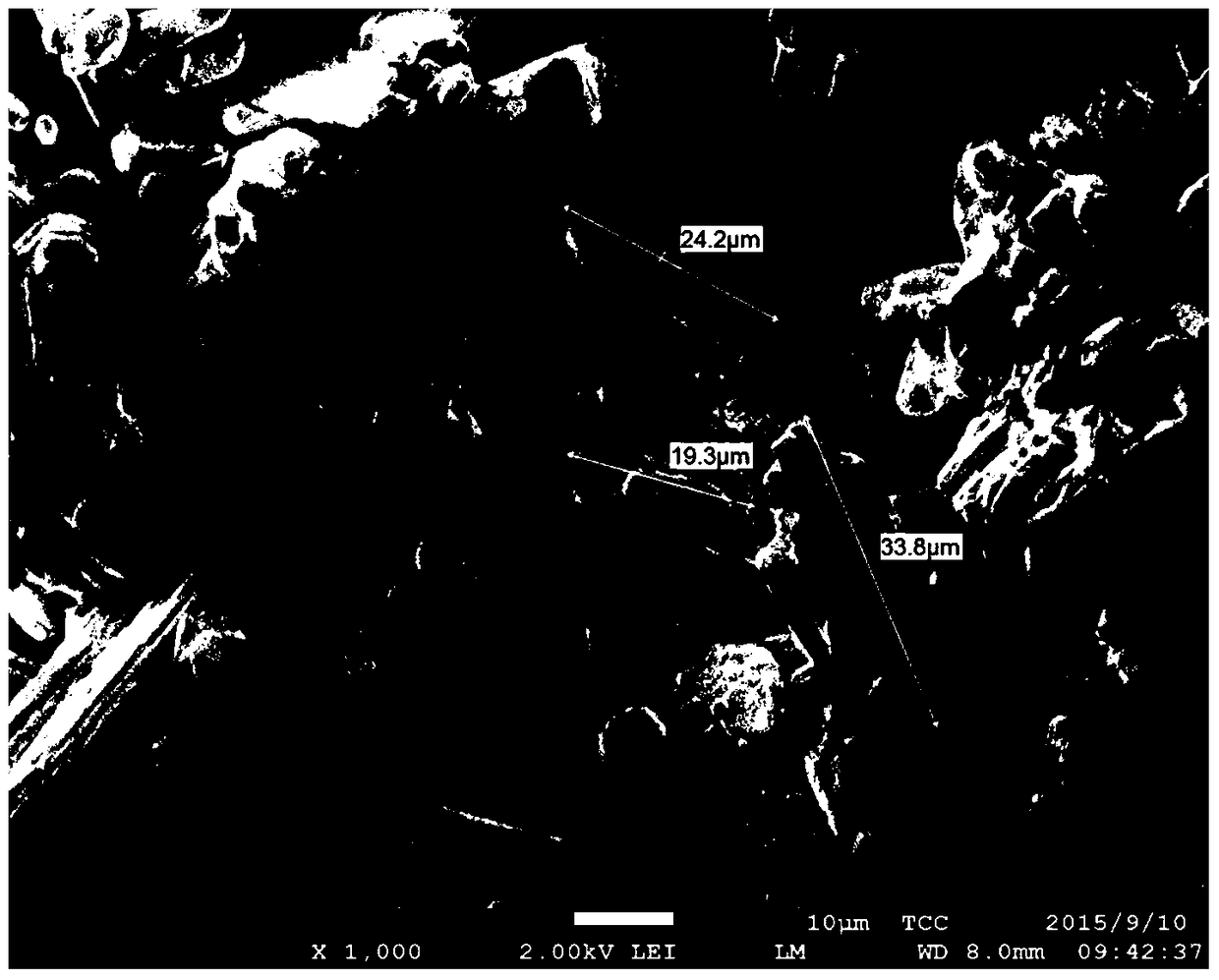
A method for crystallization and separation of ammonia nitrogen in ammonia exchange wastewater
A technology of crystallization separation and ammonia exchange, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, multi-stage water treatment, etc., can solve the complex and uneven structure of MAP double salt crystallization products, and the difficulty in the removal rate of ammonia nitrogen reaching a high efficient level. Comprehensive waste utilization efficiency and other issues to achieve the effect of improving comprehensive utilization efficiency, low utilization efficiency, and avoiding waste
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Dissolve phosphate in SAPO molecular sieve ammonia exchange wastewater, the wastewater is ammonium chloride wastewater, the initial concentration of ammonia nitrogen is 14000mg / L, the phosphate is dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, and the dissolution temperature is 26.4°C, first add phosphoric acid to the wastewater The dosage of salt and phosphate is NH in wastewater 4 + ionizable PO in phosphate 4 3- The molar ratio is n(NH 4 + ): n(PO 43- )=1:1.2, after the phosphate is completely dissolved, the magnesium salt is added to the solution, the magnesium salt is magnesium chloride, and the dosage of the magnesium salt is NH 4 + ionizable Mg in magnesium salt 2+ The molar ratio is n(NH 4 + ): n (Mg 2+ )=1:1.2; add saturated NaOH solution dropwise to control the pH value of the reaction solution to 7.5, and react for 30 minutes; add magnesium chloride twice, and the dosage of the second magnesium salt is equal to the NH 4 + ionizable Mg in the secondary magnesium ...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Dissolve phosphate in SAPO molecular sieve ammonia exchange wastewater, the wastewater is ammonium nitrate wastewater, the initial concentration of ammonia nitrogen is 1000mg / L, the phosphate is disodium hydrogen phosphate, and the dissolution temperature is 25.4°C, first add phosphate to the wastewater , the dosage of phosphate is NH in wastewater 4 + ionizable PO in phosphate 4 3- The molar ratio is n(NH 4 + ): n(PO 4 3- )=1:1.0, after the phosphate is completely dissolved, the magnesium salt is added to the solution, the magnesium salt is magnesium oxide, and the dosage of the magnesium salt is NH 4 + ionizable Mg in magnesium salt 2+ The molar ratio is n(NH 4 + ): n (Mg 2+ )=1:1.0; add saturated NaOH solution dropwise to control the pH value of the reaction solution to 8.0, and react for 20 minutes; 4 + ionizable Mg in the secondary magnesium salt 2+ The molar ratio is n(NH 4 + ): n (Mg 2+ )=1:0.1, add saturated NaOH solution dropwise to control the...
Embodiment 3
[0031] Dissolve phosphate in SAPO molecular sieve ammonia exchange wastewater, the wastewater is ammonium nitrate wastewater, the initial concentration of ammonia nitrogen is 6000mg / L, the phosphate is sodium dihydrogen phosphate, and the dissolution temperature is 28.7°C, first add phosphate to the wastewater , the dosage of phosphate is NH in wastewater 4 + ionizable PO in phosphate 4 3- The molar ratio is n(NH 4 + ): n(PO 4 3- )=1:1.0, after the phosphate is completely dissolved, the magnesium salt is added to the solution, the magnesium salt is magnesium sulfate, and the dosage of the magnesium salt is the amount of NH in the wastewater 4 + ionizable Mg in magnesium salt 2+ The molar ratio is n(NH 4 + ): n (Mg 2+ )=1:1.1; add saturated NaOH solution dropwise to control the pH of the reaction solution to 8.5, react for 30 minutes; 4 + ionizable Mg in the secondary magnesium salt 2+ The molar ratio is n(NH 4 + ): n (Mg 2+ )=1:0.1, add saturated NaOH solution...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com