N-acetyl-beta-D glucosidase reagent and detection method
A glucosidase and detection method technology, applied in the field of N-acetyl-β-D glucosidase detection reagents, can solve the problems of long operation time, cumbersome operation, insoluble substrate, etc., and achieve improved analysis sensitivity and stability Strong, good water solubility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
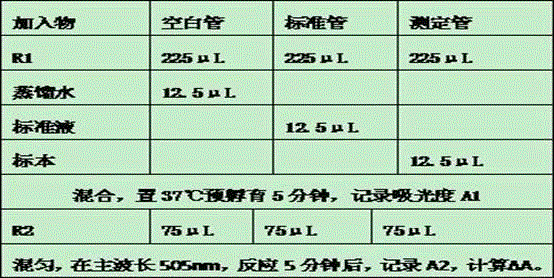
[0033] Detection reagents for N-acetyl-β-D-glucosidase, including reagent R1 and reagent R2:
[0034] 1) The components of reagent R1 are:
[0035] Citric acid-sodium hydrogen phosphate disodium buffer solution (PH=5.0)..........................100mmol / L
[0036] VRA-NAG................................................ ...................................3mmol / L
[0037] BSA................................................................ ...................................1g / L
[0038] Ethylene glycol................................................ ...................................1ml / L
[0039] TritonX-100................................................................ ...................................1ml / L
[0040] Ascorbate oxidase................................................ ...................1ml / L
[0041] Preservative NaN 3. ................................................... ..............2mmol / L
[0042] 2) The components of reagent R2 are:
[0043] ...
Embodiment 2
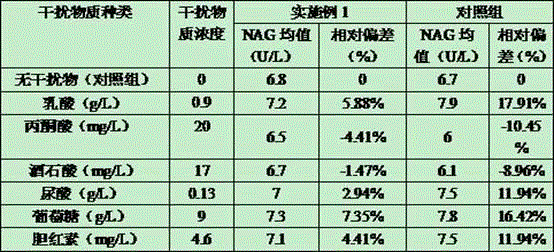
[0051] Interference test: Take fresh urine, divide it into 2 equal parts, then divide each equal part into 5 equal parts, add different interfering substances, and make the concentration in the urine meet the requirements in Table 2. Then, the reagents obtained in Example 1 were used to compare and measure the UA content in serum at the same time as the common and recognized NAG reagents in the market. Relative deviation (%) = (measuring mean value of interference samples - measuring mean value of control samples) / measured mean value of control samples × 100%.
[0052] As can be seen from Table 2, the reagents of Example 1 are lactic acid≤0.9g / L, pyruvic acid≤20mg / L, tartaric acid≤17mg / L, uric acid≤g / L, glucose≤g / L, bilirubin≤mg / L L did not significantly interfere with the determination results. However, the contrast reagent was significantly interfered when the interfering substance at the above-mentioned concentration existed, which shows that the anti-interference performa...
Embodiment 3
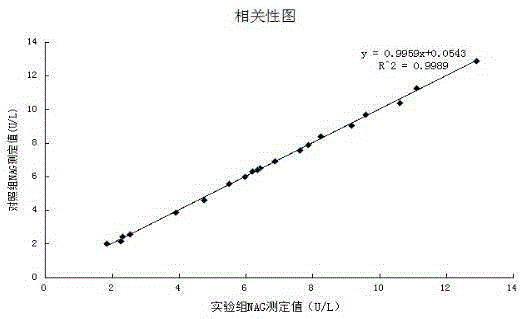
[0056] Correlation test: using the formula in Example 1 to prepare reagents, and compared with the NAG kit of a company approved by the State Food and Drug Administration, which is common in the market, and tested 20 clinical samples at the same time, the test results are shown in Table 3. And obtained the correlation curve of the two reagents (such as figure 1 Shown), the results show that the correlation coefficient of the two kits is 0.9994, indicating that there is a great correlation between the two.
[0057] Table 3 Example 1 and the market common and recognized NAG assay kit comparative detection results
[0058]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com