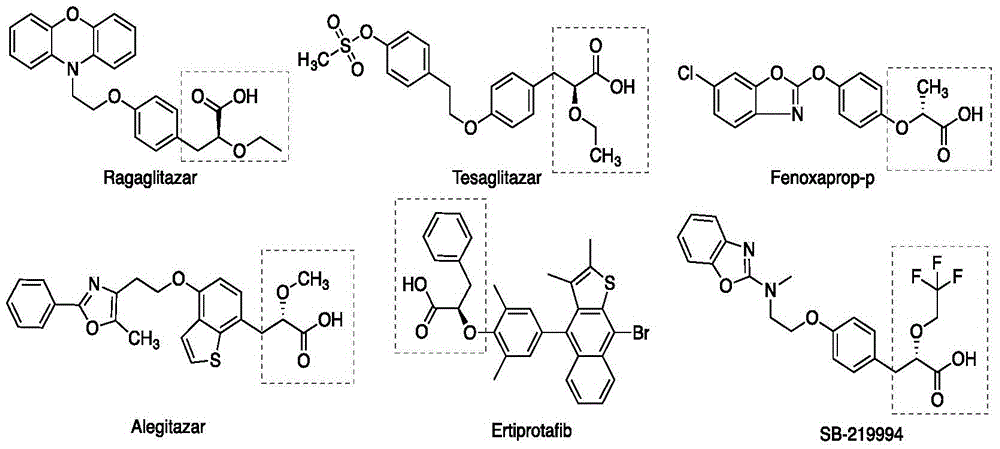
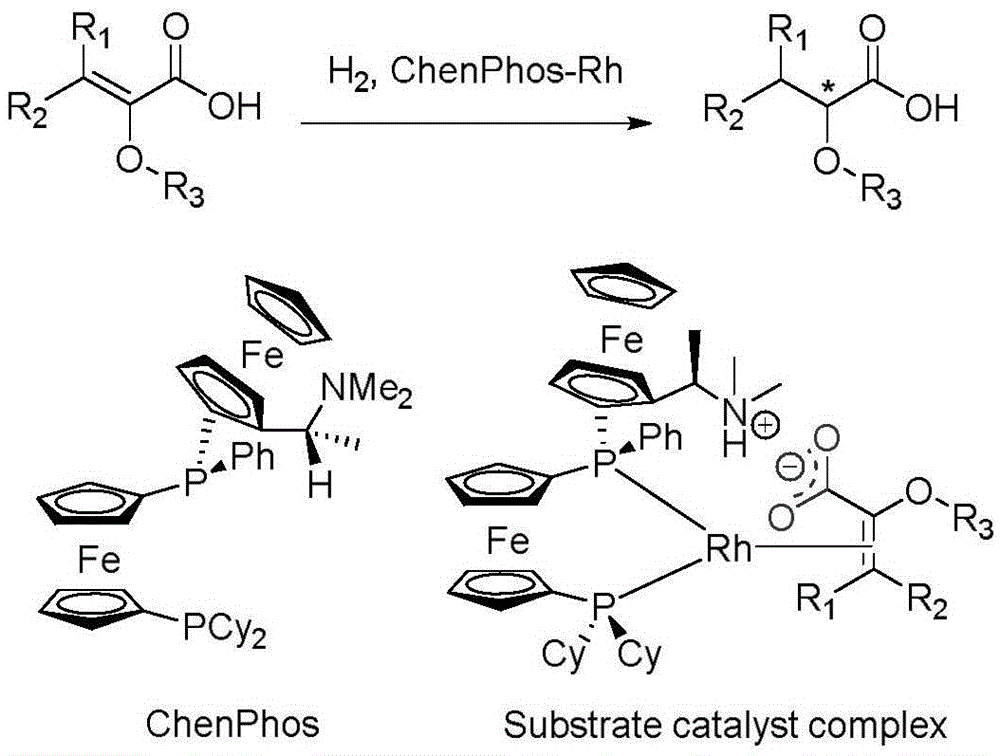
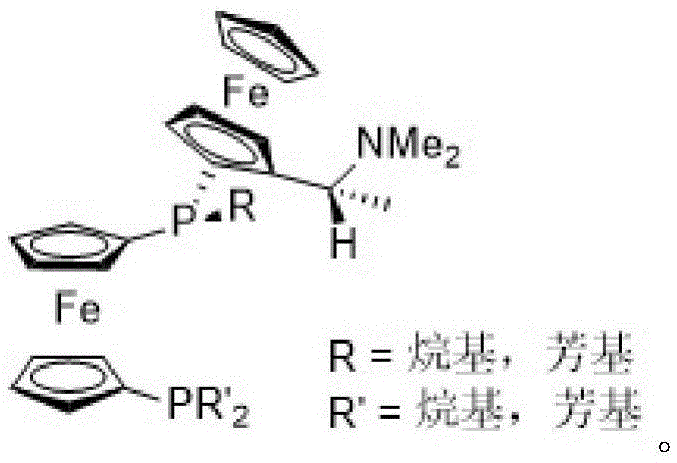
Asymmetric hydrogenation method of alpha-oxo-alpha, beta-unsaturated carboxylic acid
An asymmetric and unsaturated technology, applied in the field of asymmetric hydrogenation of α-oxo-α, β-unsaturated carboxylic acids, can solve the problem of narrow application range of catalyst substrates
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0016] Example 1, Effect of Metal Precursors
[0017] Initially selected (Z)-2-methoxyl-3-phenylacrylic acid (1a) as the template substrate to investigate the reaction, to our delight: with methanol as solvent, under 20atm hydrogen pressure, [Rh(COD ) 2 ] BF 4 (1.0mol%; NBD=2,5-norbornadiene) and ChenPhos (1.1 equivalent with respect to Rh) in situ generated ChenPhos-Rh complex can successfully catalyze the hydrogenation conversion of all substrate 1a, and obtain an ee value of 87% (Table 1 , entry1). Encouraged by this result, we next investigated metal precursors and found that different types of rhodium sources gave similar results, where [Rh(NBD)Cl] 2 gave the best results, and the ee value was only increased by 2%; in terms of iridium source, [Ir(COD)Cl] 2 gives similar ee values to rhodium, but is significantly less catalytically active.
[0018]
[0019] [a] Reaction conditions: 0.2mmol, substrate concentration 0.1mol / L, solvent 2mL, catalyst 1.0mol%.[b] 1 Th...
Embodiment 3
[0023] The suitability of embodiment 3 substrates
[0024] Determined by CF 3 CH 2 OH is used as a solvent, hydrogen gas at 20 atmospheres, 0.1 mol% ChenPhos-rhodium complex is used, and the reaction at room temperature for 20 hours is the optimal hydrogenation condition, and then the substrate applicability of the reaction is investigated.
[0025]
[0026][a-b] Reaction conditions: 0.2mmol, substrate concentration 0.1mol / L, solvent 2mL, catalyst 0.1mol%. All examples of substrates reacted completely. [b] Chiral HPLC confirmed, and the configuration was confirmed by literature comparison.
[0027]
[0028] Under optimal hydrogenation conditions, different types of α-aryloxy and α-alkyl α,β-unsaturated acid substrates can be completely converted and give very desirable enantioselectivities. The position and steric hindrance effect of the substituent on the aromatic ring of the substrate have little effect on the hydrogenation strategy, and both α-aryloxy and α-alkyl α,...
Embodiment 4
[0029] Embodiment 4 control experiment
[0030]
[0031] In order to gain a deeper understanding of the asymmetric hydrogenation conversion process of α-oxyl functionalized α,β unsaturated carboxylic acid substrates, we conducted two sets of control experiments to verify the ligands of dimethylamino and carboxylic acid Whether ionic interactions between units contribute to the high enantioselectivity of the reaction. On the one hand, with the corresponding unsaturated ester as the substrate under optimal hydrogenation conditions, the reaction does not take place, and all the raw materials are recovered (formula 1); on the other hand, when the reaction adds 50mol% Upon complete conversion, the enantioselectivity drops sharply to 46% (Eq. 2), which may be due to the interaction of the external base with the ligand and substrate, which interferes with the steric control of the reaction. These results verified our initial hypothesis that the ionic interactions in this catalyti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com