A high-temperature-resistant decomposing bacteria agent for organic waste and its application
A technology of organic waste and decomposed bacteria agent, which is applied in the field of waste resource utilization and microbial fermentation, which can solve the problems of low microbial activity, long fermentation cycle, and unstable temperature, and achieve good microbial metabolic activity, convenient preparation, and accelerated production. The effect of the composting process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
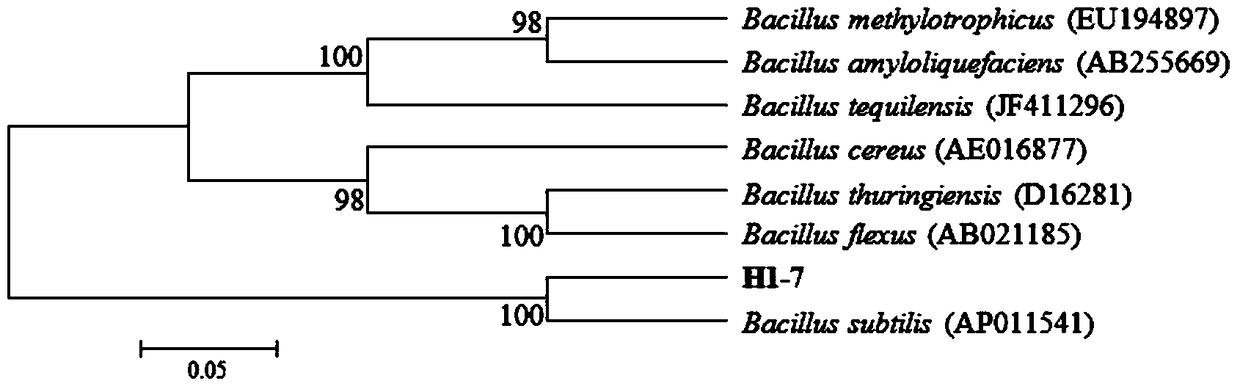
[0021] Example 1: Screening and Identification of Thermostable Bacillus H1-7 Provided in the Examples of the Present Invention
[0022] Sampling was taken from natural compost and activated sludge, and microorganisms were isolated by serial dilution coating method. Place the diluted coated plate in a 55°C incubator for constant temperature incubation for 24h. Select the faster-growing strains to isolate and purify. Spot the isolated and purified strains on starch plates, protein plates and cellulose Congo red plates with an inoculation needle. Observe the transparent circle after culturing for 24 hours. Carry out primary screening by measuring transparent circle and bacterial colony diameter ratio (seeing table 1), carry out liquid enzyme production fermentation re-screening after primary screening, obtain 8 strains degrading starch, protein, cellulose effect better bacterium (seeing table 2) from compost ), among them, the H1-7 strain has significantly better enzyme produc...
Embodiment 2
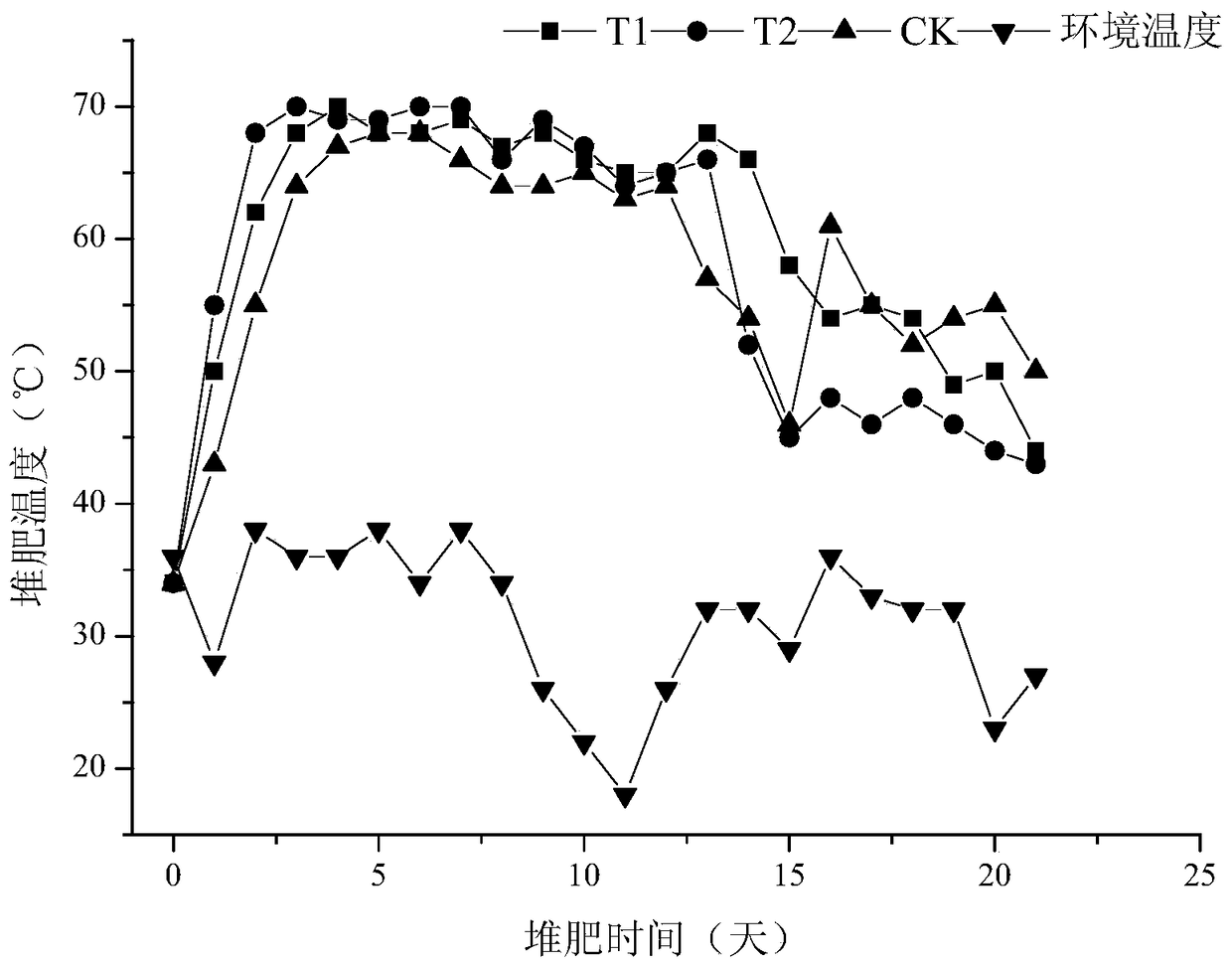
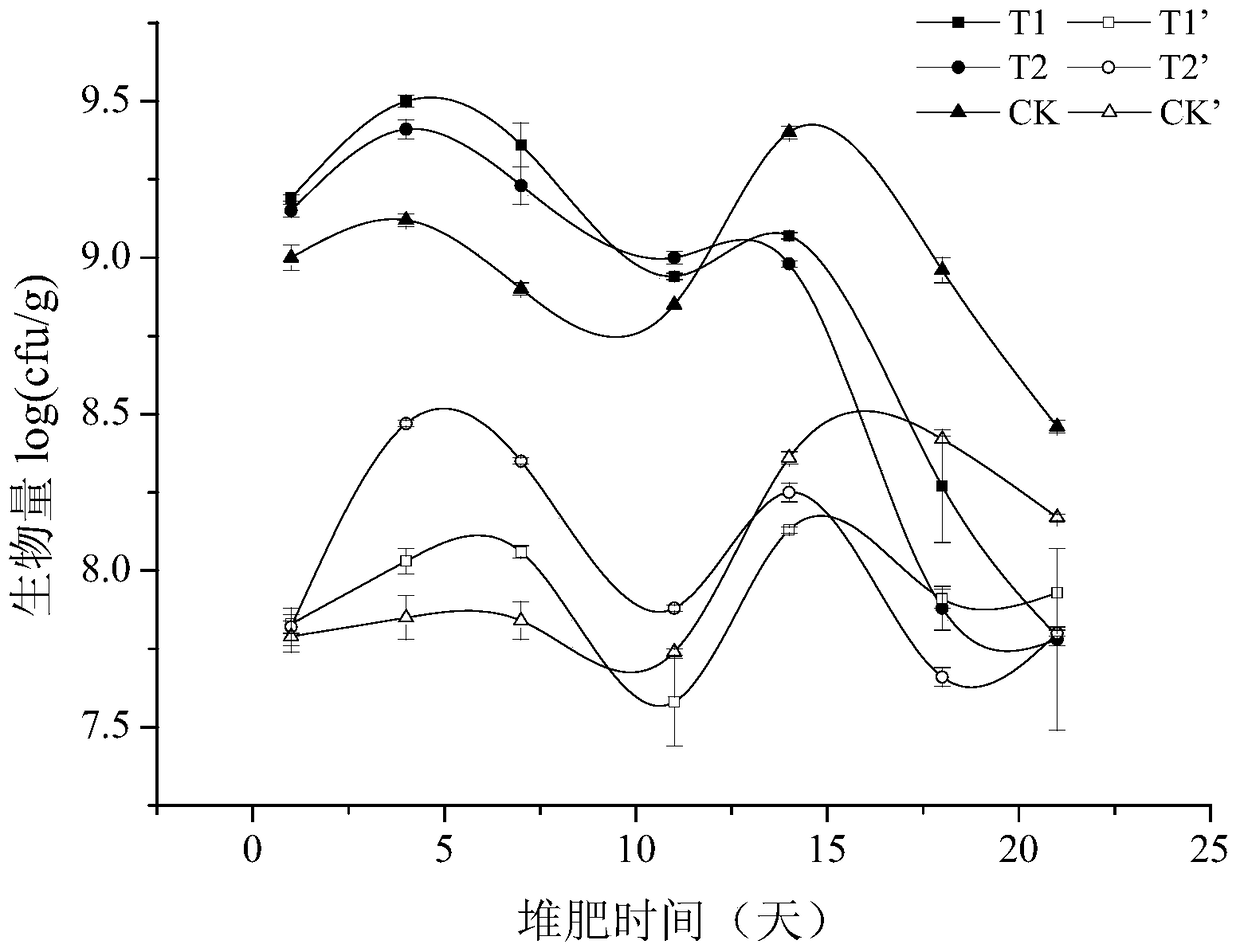
[0032] Example 2 Application of the high temperature-resistant bacteria H1-7 provided by the example of the present invention in the mixed composting of kitchen waste and straw
[0033] 1. Food waste straw mixed composting process
[0034] Mix food waste and straw (corn stalks, rice stalks) according to the wet substrate ratio of 5:1, or adjust the C / N ratio according to the physical and chemical properties, so that the C / N ratio of the mixed material is 25-35.
[0035] In the method for preparing stacking materials, the particle size of the kitchen waste may be 2-3 cm; the particle size of the filler (rice stalk, corn stalk, etc.) may be 1-3 cm.
[0036] Mix the fermentation liquid of H1-7 and the commercially available decomposing agent at a mass ratio of 1:10, and insert it into the food waste pile at the inoculation amount of 0.2%. The length, width and height of the pile are 1.5m×1.5m×1.0 m, the moisture content of the heap is maintained at 60-65%, and it can be decompos...
Embodiment 3
[0056] Example 3 Application of the high temperature resistant bacteria H1-7 provided in the examples of the present invention in the composting of fruit and vegetable waste
[0057] Apply the high-temperature-resistant bacterial agent in the present invention to fruit and vegetable waste composting, select oyster mushroom residue as an auxiliary material, mix the fruit and vegetable waste with the auxiliary material according to the range of C / N of 25-30, and maintain the moisture content at 55%- Between 65%, inoculate the commercially available decomposing agent with the stacking material, after fully mixing, compound the H1-7 fermentation liquid described in the present invention and the commercially available decomposing agent according to the mass ratio of 1:20, and inoculate according to the inoculation amount of 0.2% Put it in the pile, mix it well, turn it every 3-4 days, and it will be completely decomposed in 12-15 days. The degradation rate of organic matter increas...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com