Zero-discharge on-line treatment process for preparing deionized water from copper sulphate electroplating waste water
A technology for electroplating wastewater and treatment process, which is applied in the fields of metallurgical wastewater treatment, water/sewage multi-stage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc. requirements, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0061] Embodiment 1: the comparison of adsorption organic matter
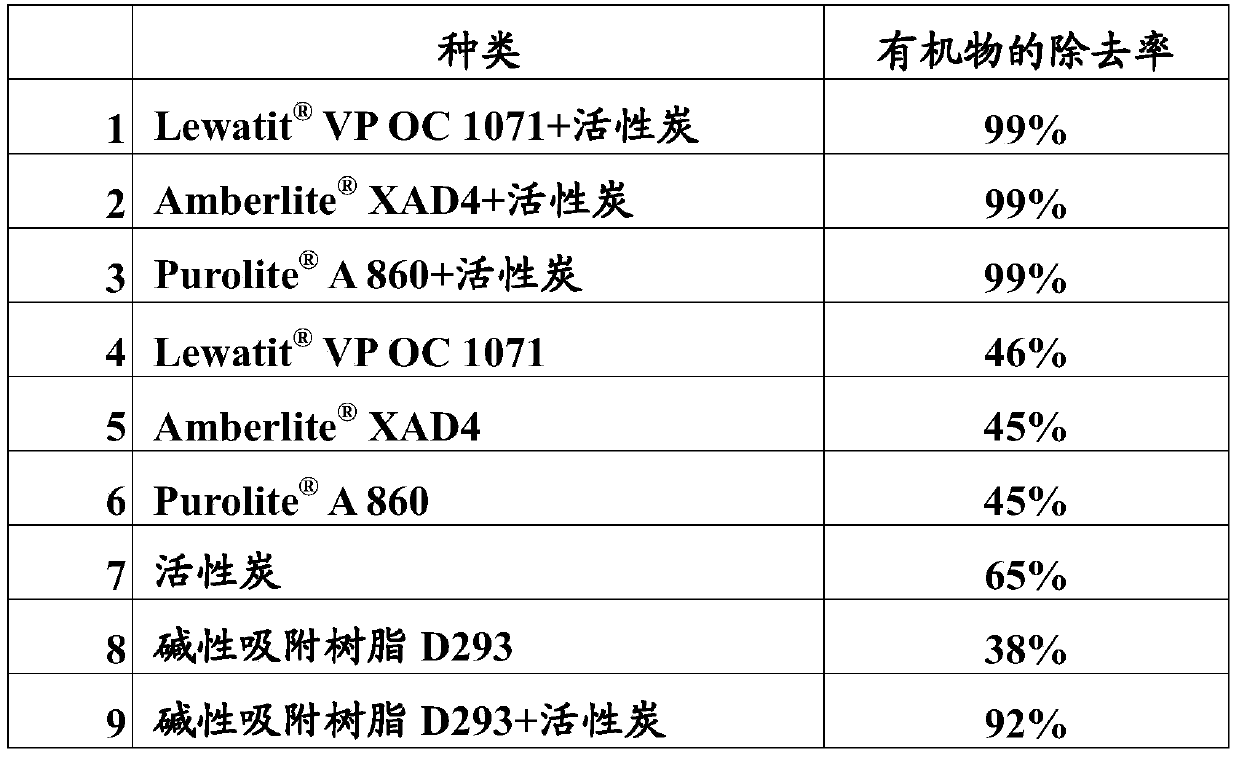
[0062] In the first step of copper sulfate electroplating wastewater treatment process, the combination of ion exchange resin and activated carbon is used to adsorb the organic matter, especially the combination of macroporous basic ion exchange resin and activated carbon has excellent adsorption performance and maximizes the removal rate of organic matter. For this adsorption performance, the present invention has carried out comparative test, detected respectively the removal rate of different adsorbents for the acid copper brightener organic matter remaining in copper sulfate electroplating wastewater, the results are shown in Table 1.
[0063] Table 1 The removal rate of different adsorbents for acid copper brightener organic matter
[0064]
[0065] By comparison, it can be seen that VPOC1071+activated carbon, A860+activated carbon, The combination of XAD4+ activated carbon has a better effect ...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Example 2: Zero-discharge online treatment process for copper sulfate electroplating wastewater
[0068] The process flow is as follows:
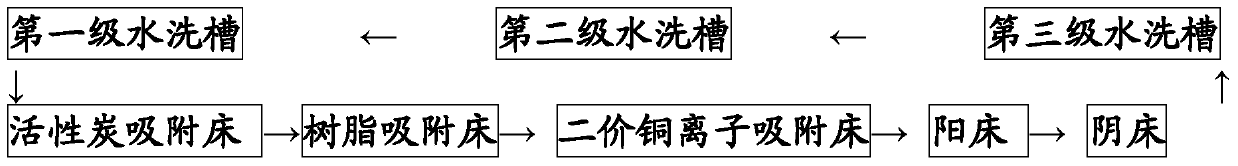
[0069] 1. The process flow of the copper sulfate electroplating unit is: acid copper electroplating→first-stage water washing→second-stage water washing→third-stage water washing→subsequent treatment. The water flow direction of the electroplating unit is: pure water storage tank→third-level washing tank→second-level washing tank→first-level washing tank→comprehensive wastewater treatment tank. The color of the copper sulfate electroplating wastewater flowing out from the first-stage washing tank is light blue-black. On-site sampling and analysis showed that the composition of the electroplating wastewater discharged from the first-stage washing tank was as follows: copper sulfate 10.60 g / L, sulfuric acid 3.43 g / L, chloride ion 3.5 ppm, acid copper brightener residue concentration 58 ppm.
[0070] 2. The treatment process of acid c...
Embodiment 3
[0080] Example 3: Zero-discharge online treatment process for copper sulfate electroplating wastewater
[0081] The process flow is as follows:
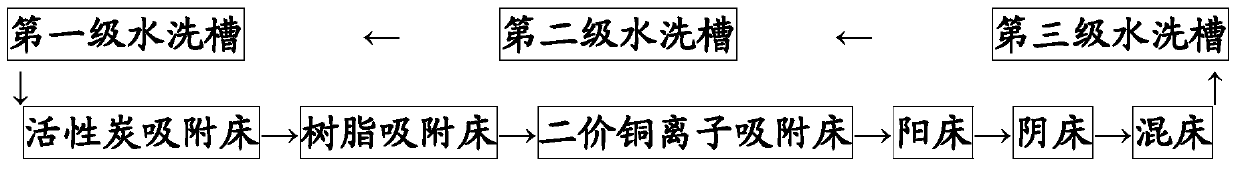
[0082] 1. The process flow of the copper sulfate electroplating unit is: acid copper electroplating→first-stage water washing→second-stage water washing→third-stage water washing→subsequent treatment. The water flow direction of the electroplating unit is: pure water storage tank→third-level washing tank→second-level washing tank→first-level washing tank→comprehensive wastewater treatment tank. On-site sampling and analysis showed that the composition of the electroplating wastewater discharged from the first-stage washing tank was as follows: copper sulfate 10.60 g / L, sulfuric acid 3.43 g / L, chloride ion 3.5 ppm, acid copper brightener residue concentration 58 ppm.
[0083] 2. The treatment process of acid copper electroplating wastewater is:
[0084] Acid copper electroplating wastewater → activated carbon + macroporous alkaline ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Critical value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com