Two-stage mbbr device for removing carbon, nitrogen and sulfur in pharmaceutical wastewater and method for using it to treat pharmaceutical wastewater
A pharmaceutical wastewater, carbon and nitrogen technology, applied in multi-stage water treatment, sulfur preparation/purification, special compound water treatment, etc. Highly resistant to toxic effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
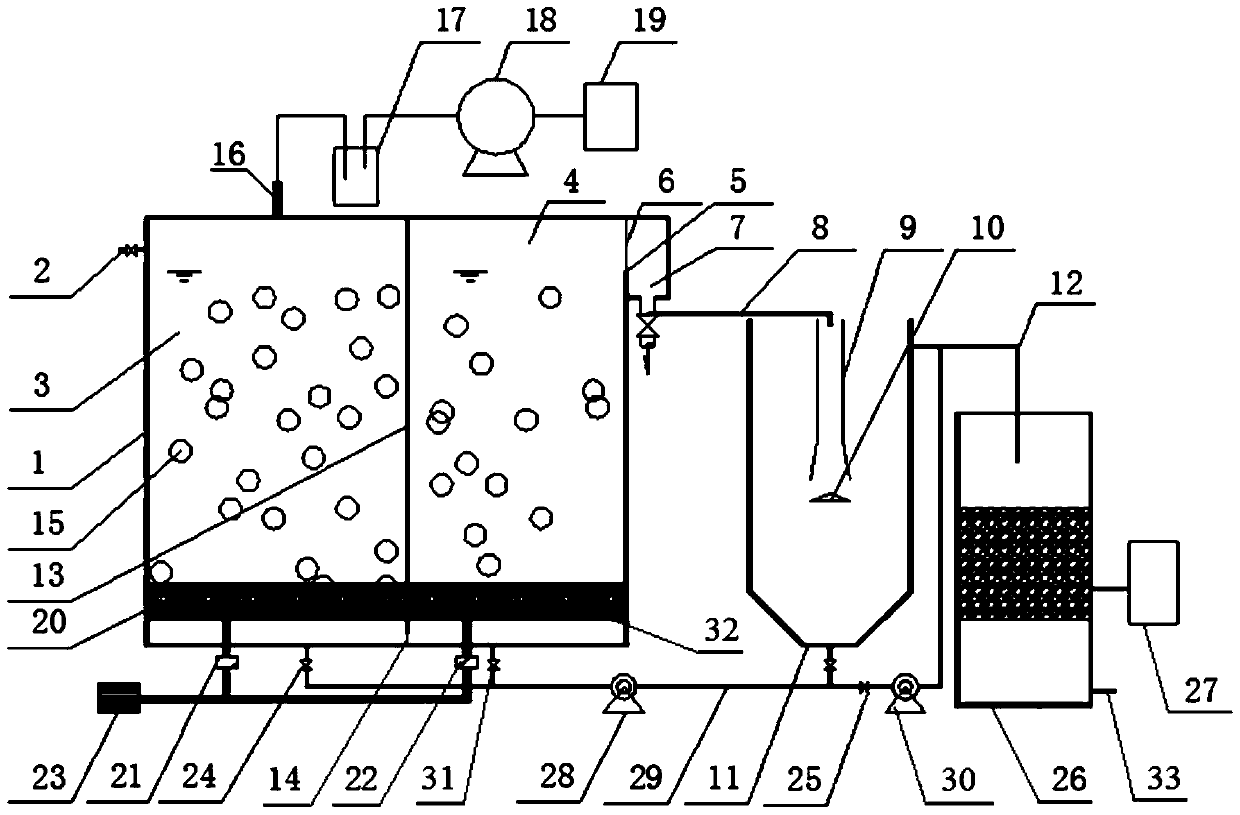
[0029] Embodiment 1: The device for removing carbon, nitrogen and sulfur in pharmaceutical wastewater by two-stage MBBR in this embodiment includes a pool body 1, a water inlet 2, an anoxic MBBR pool 3, an aerobic MBBR pool 4, an overflow weir 5, and an overflow screen Net 6, sump 7, drainage pipe 8, diversion pipe 9, reflection plate 10, sedimentation tank 11, sedimentation tank drainage pipe 12, partition wall 13, screen mesh 14, filler 15, biogas vent 16, water seal Bottle 17, biogas purification device 18, CH 4 Collection device 19, micro-oxygen aerator 20, anoxic gas flowmeter 21, aerobic gas flowmeter 22, blower 23, anoxic solenoid valve 24, quartz sand composite filter bed 26, elemental sulfur separation device 27, sludge reflux Pump 28, mud pump 30, aerobic solenoid valve 31, aerobic aerator 32 and water outlet 33;
[0030] Pool body 1 is separated into anoxic MBBR pool 3 and aerobic MBBR pool 4 by partition wall 13, water inlet 2 is set at the side wall upper end of ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0031] Specific embodiment two: the present embodiment utilizes the two-stage MBBR described in specific embodiment one to remove the method for the device processing pharmaceutical wastewater of carbon, nitrogen and sulfur in the pharmaceutical wastewater, specifically according to the following steps:
[0032] 1. Inoculation acclimatization: first inoculate the anoxic inoculation sludge in the anoxic MBBR pool 3, then fill the anoxic MBBR pool 3 with filler 15, and the dosage of the filler 15 in the anoxic MBBR pool 3 is the anoxic MBBR pool 3 Two-thirds of the effective volume, inoculate the aerobic inoculated sludge in the aerobic MBBR pool 4, and then fill the aerobic MBBR pool 4 with filler 15, and the dosage of filler 15 in the aerobic MBBR pool 4 is preferably Two-thirds of the effective volume of the oxygen MBBR pool 4, and then inject pharmaceutical wastewater into the anoxic MBBR pool 3 through the water inlet 2, and then the pharmaceutical wastewater flows into the ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
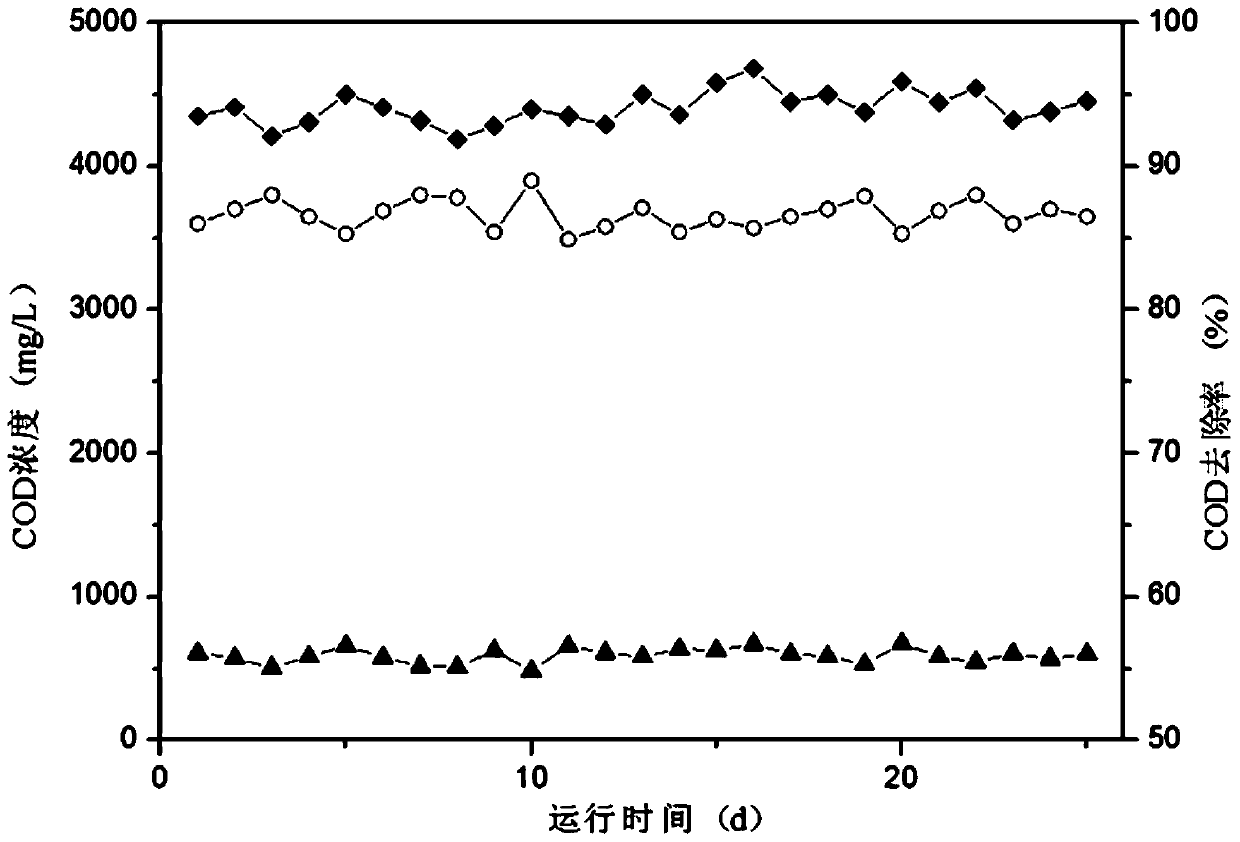
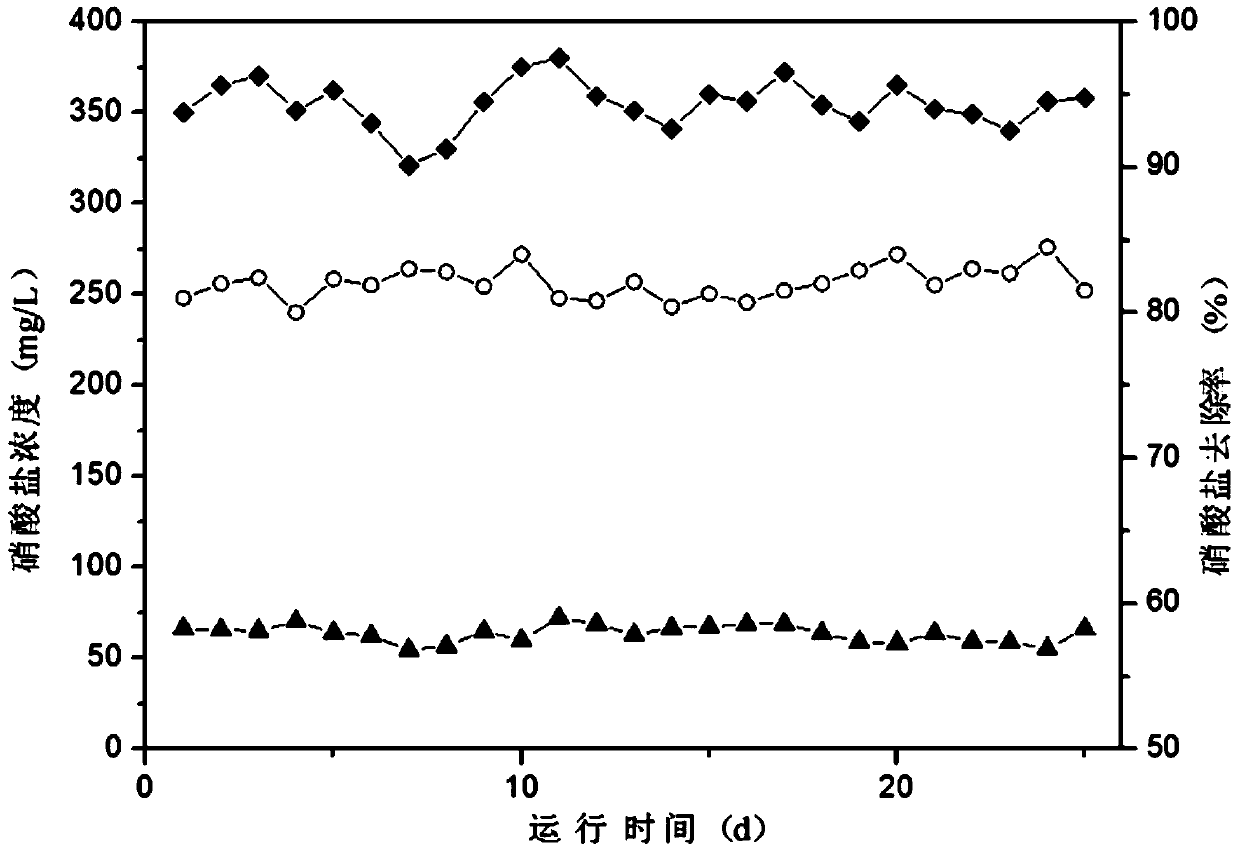
[0041] Specific embodiment three: The differences between this embodiment and specific embodiment two are: the COD concentration in the pharmaceutical wastewater described in steps 1, 2 and 3 is 3000 mg / L to 5000 mg / L, and the sulfate radical load is 1 kg / m 3 ·d~2kg / m 3 d, the nitrate volume load is 0.5kg / m 3 ·d~1kg / m 3 d. Others are the same as in the second embodiment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| quality score | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com