Bivalent inactivated vaccine to bacterium pyocyaneum for mink
A technology of mink Pseudomonas aeruginosa and inactivated vaccines, applied in multivalent vaccines, vaccines, antibacterial drugs, etc., can solve the problems of low immune cross-protection, weak immunogenicity, etc., and achieve prevention of epidemics, spread, and disease rate and mortality reduction, and the effect of reducing economic losses
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] 1.1 Isolation and purification method of Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacterial strain
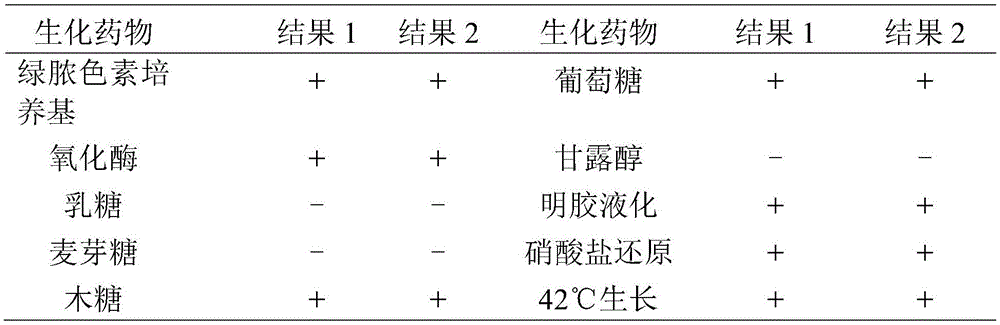
[0020] Select mink diseased from a large mink farm suspected of hemorrhagic pneumonia in mink, aseptically collect the lungs, liver and heart blood of the sick mink and inoculate them on hexadecanetrimethylammonium bromide agar medium (NAC). Cultivate in a 37°C incubator for 16h to 18h, pick round, smooth, moist, and flat colonies for Gram staining and microscopic examination, and select Gram-negative small bacilli for streaking and pure culture.
[0021] Stratify the pure culture strains on fresh blood agar plate and NAC plate respectively, culture at 37°C for 16h~18h, choose to produce green fluorescent pigment on hexadecanetrimethylammonium bromide medium, and produce β on blood agar medium Hemolyzed small colonies were purified and cultured.
[0022] According to the biochemical identification test requirements of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, the two strains will be further purified and c...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Application of mink Pseudomonas aeruginosa type B LN03 strain and G type SD17 strain in the preparation of bivalent inactivated vaccine.
[0054] Take the Pseudomonas aeruginosa type B LN03 strain with the preservation number CCTCCNO: M2016068 and the Pseudomonas aeruginosa G type SD17 strain with the preservation number CCTCCNO: M2016069 respectively, and inoculate the culture medium after activation After culturing, the bacterial liquid is collected, inactivated by formaldehyde solution, and mixed with propolis adjuvant to prepare an inactivated propolis vaccine.
[0055] The preferred operation steps are as follows:
[0056] 2.1 Strain selection
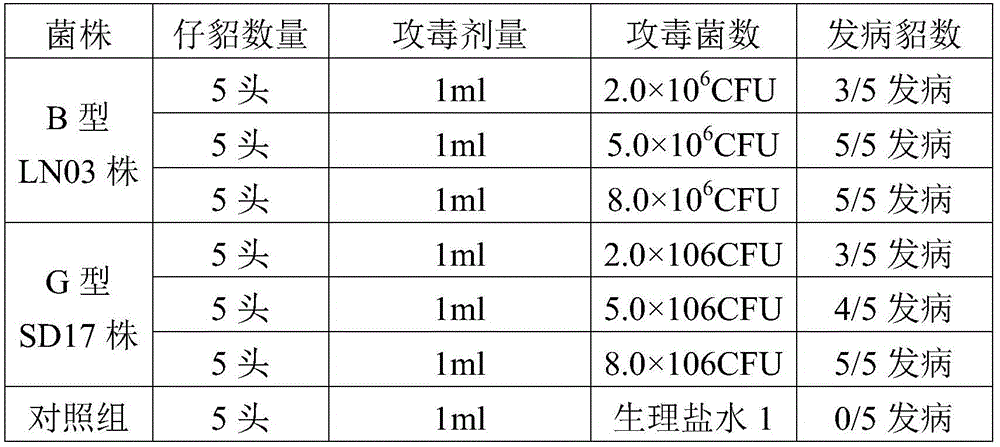
[0057] The strains used for seedling production have stable colony morphology, bacterial characteristics, biochemical characteristics, and cultural characteristics, and are highly pathogenic to minks. 1.0mL bacterial liquid (5.0×10 6 CFU / mL) injection can cause 100% of 21 to 42 days old mink disease. Good immunogenicity,...
Embodiment 3
[0098] Application of mink Pseudomonas aeruginosa type B LN03 strain and G type SD17 strain in the preparation of bivalent inactivated vaccine.
[0099] Take the Pseudomonas aeruginosa type B LN03 strain with the preservation number CCTCCNO: M2016068 and the Pseudomonas aeruginosa G type SD17 strain with the preservation number CCTCCNO: M2016069 respectively, and inoculate the culture medium after activation After culturing, the bacterial liquid is collected, inactivated by formaldehyde solution, and mixed with water adjuvant to prepare a bivalent inactivated vaccine.
[0100] The preferred operation steps are as follows:
[0101] 2.1 Strain selection
[0102] The strains used for seedling production have stable colony morphology, bacterial characteristics, biochemical characteristics, and cultural characteristics, and are highly pathogenic to minks. 1.0mL bacterial liquid (5.0×10 6 CFU / mL) injection can cause 100% of 21 to 42 days old mink disease. Good immunogenicity, min...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com