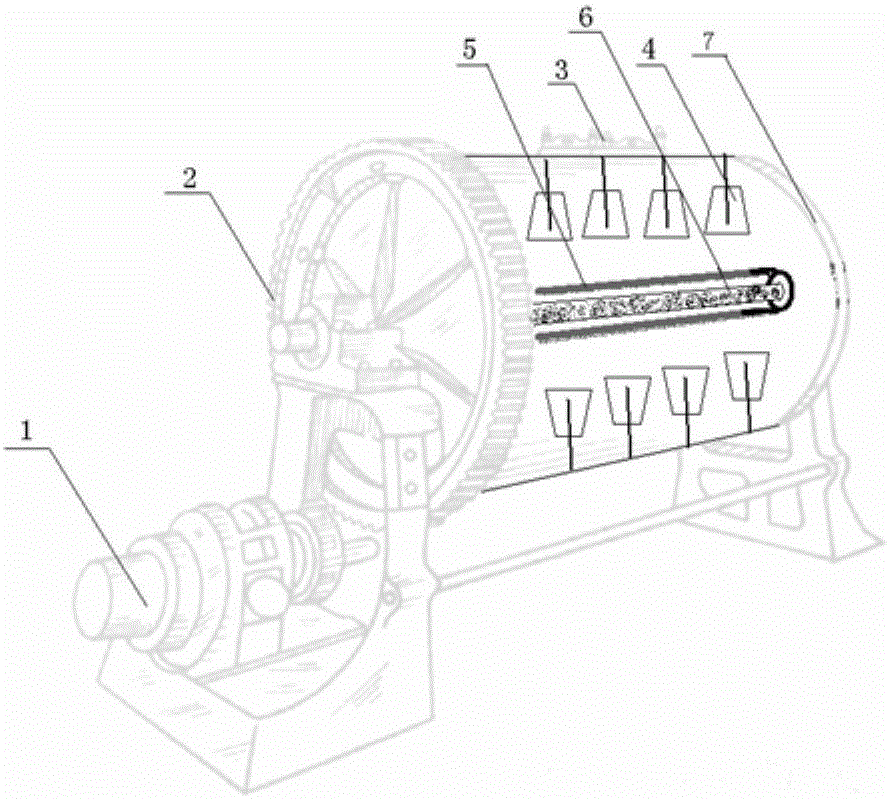
Rotating reaction generator and method for repairing organic contaminated soil based on photocatalysis of rotating reaction generator
An organic pollution, rotary technology, applied in the field of organic pollutant remediation, can solve the problem of slow photochemical reaction, achieve the effect of mechanized production, low investment cost and enhanced mass transfer efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Use metatitanic acid as raw material, first use alkaline solution (NH 4 OH aqueous solution, NaOH aqueous solution or a combination of the two) to neutralize the metatitanic acid, adjust its pH to 7-9, then add iron oxide to the metatitanic acid at a mass ratio of 1:100, and use hot air to dissolve the metatitanic acid Acid spray drying yielded spherical particles, which were then sintered at 500°C for 2 hours to yield TiO 2 Powder (iron-doped mesoporous nano-titanium dioxide nanoparticles). The TiO 2 The powder has hierarchical porous secondary particles and a large specific surface area, which is an economical and efficient TiO 2 powder.
Embodiment 2
[0034] P-nitrophenol (PNP) and pentachlorophenol (PCP) were selected as target pollutants to study the photochemical process of phenolic pollutants in soil. First pass the contaminated soil sample through a 100-mesh sieve to remove gravel and large particle debris, adjust the pH of the soil to 6.5, and the moisture content to 50%, and add 2% of homemade TiO 2 powder. After the treatment is completed, add a rotary reaction generator, set the rotation speed to 50r / min, and the reaction time to 12h. After the reaction, the initial concentration of PNP dropped from 100mg / kg to 21.2mg / kg, and the photoconversion rate was 71.8%. After continuing the reaction for 12 hours, the concentration dropped to 13.7mg / kg, and the photoconversion rate was 86.3%. From 100mg / kg to 23.7mg / kg, the photoconversion rate was 76.3%. After continuing the reaction for 12 hours, the concentration dropped to 3.5%, and the photoconversion rate was 96.5%.
Embodiment 3
[0036] Benzo[a]pyrene (BaP) was selected as the target pollutant to study the photochemical process of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in soil. Benzo[a]pyrene (BaP) is a typical macromolecular PAH with a 5-ring structure. It is one of the most potentially carcinogenic PAHs and one of the most studied pollutants. First pass the contaminated soil sample through a 100-mesh sieve to remove gravel and large particle debris, adjust the pH of the soil to 6.3, and the moisture content to 35%, and add 2% self-made TiO 2 powder. After the treatment is completed, add a rotary reaction generator, set the rotation speed to 50r / min, and the reaction time to 12h. After the reaction, the initial concentration of PNP dropped from 100mg / kg to 67.3mg / kg, and the photoconversion rate was 32.7%. , the concentration decreased to 38.4mg / kg, and the photoconversion rate was 61.6%. After 96 hours of reaction, the concentration decreased to 12.3mg / kg, and the photoconversion rate was 87.7%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com