Method for monitoring secondary drug resistance to imatinib (Glivec)/nilotinib through ddPCR technology
A technology for drug resistance mutation sites and sequences, applied in the medical and biological fields, can solve the problems of difficult to detect the type and sequence of cell-free DNA, low content of cell-free DNA in plasma, and lack of it.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0215] Example 1 Detection of ABL gene and PDGFRα gene mutations in plasma by ddPCR technology to monitor secondary resistance to imatinib (Gleevec) / nilotinib in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia
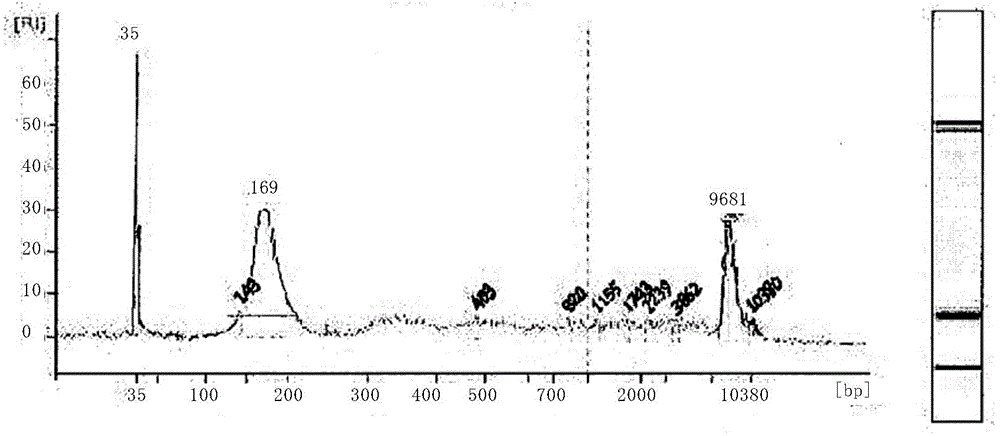
[0216] (1) Before starting imatinib (Gleevec) / nilotinib treatment in a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia, 4mL of peripheral blood was extracted from the patient, and the plasma was separated, and the free DNA in the plasma was analyzed by "QIAamp Circulating Nucleic Acid Kit". Extraction is performed. High-concentration / high-purity DNA was obtained through sample dissolution, enrichment, column elution, and finally AVE elution, and finally the fragment size (<313bp) was determined by agarose gel electrophoresis to ensure the extraction quality.
[0217] (2) Reaction system preparation
[0218] a. Design of probes and primers: The present invention adopts the conventional Taqman probe method to design, respectively designs wild-type and mutant probes for the target frag...
Embodiment 2
[0232] Example 2 Detection of ABL gene and PDGFRα gene mutations in plasma by ddPCR technology to monitor chronic myeloid leukemia patients' secondary resistance to imatinib (Gleevec) / nilotinib
[0233] (1) After the patient in Example 1 started imatinib (Gleevec) / nilotinib treatment for 6 months, his peripheral blood was collected by the same method as in Example 1, plasma was separated, and genomic DNA was extracted And perform PCR amplification. The test results are described in the table below:
[0234]
[0235]
[0236] Based on the analysis of the above data, it was found that PDGFRα (T674I) and ABL (T315I) of this sample did not mutate, suggesting that the patient has not yet developed secondary drug resistance to imatinib (Gleevec) / nilotinib, but Real-time monitoring should be carried out regularly (every 3-6 weeks). Once secondary drug resistance to imatinib (Gleevec) / nilotinib is found, the patient should be guided in time for further drug treatment.
Embodiment 3
[0237] Example 3 Detection of ABL gene and PDGFRα gene mutations in plasma by ddPCR technology to monitor secondary resistance to imatinib (Gleevec) / nilotinib in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia
[0238] (1) After the patient in Example 1 started imatinib (Gleevec) / nilotinib treatment for 12 months, his peripheral blood was collected by the same method as in Example 1, plasma was separated, and genomic DNA was extracted And perform PCR amplification.
[0239] (2) Result analysis:
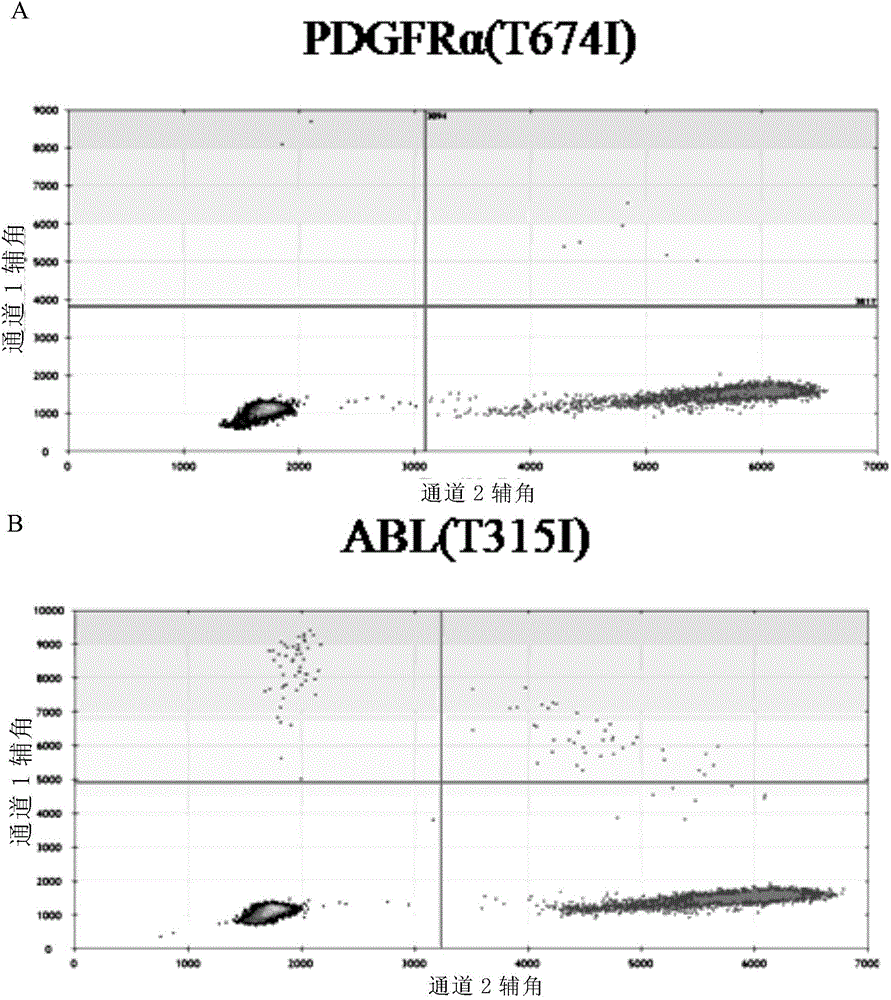
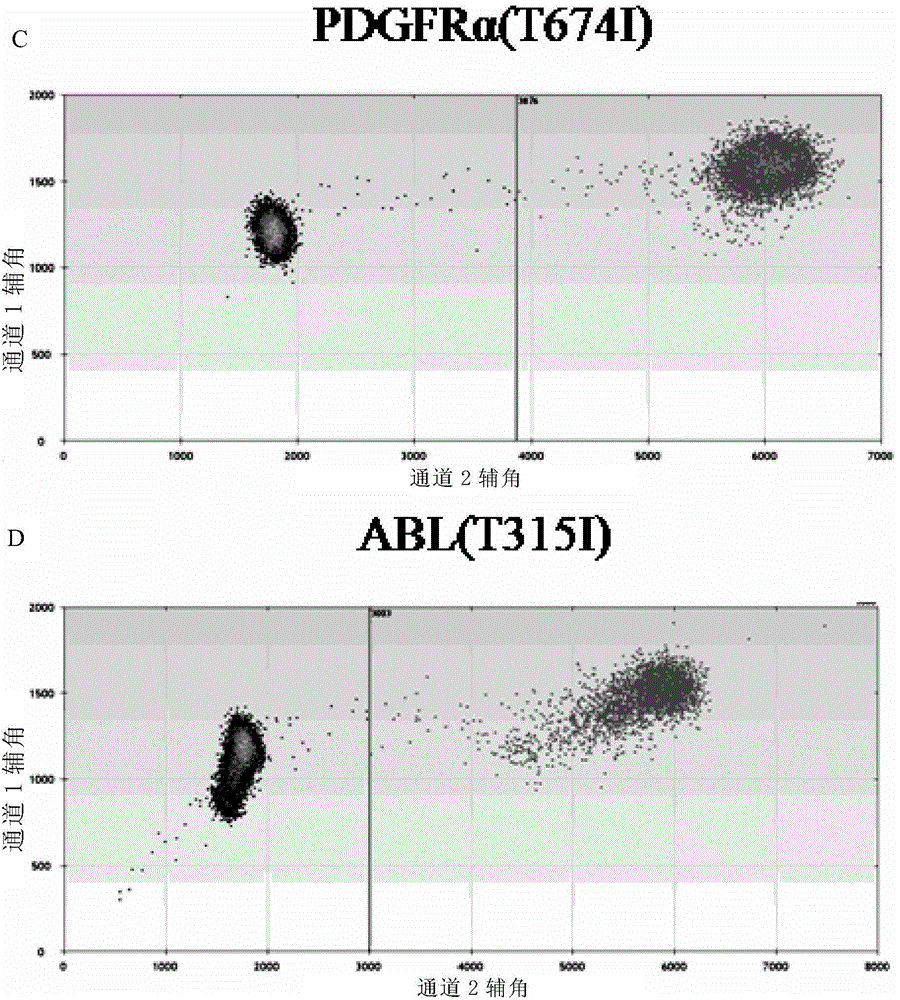
[0240] figure 1 A, B and figure 2 A and B are the detection result diagrams of Example 3. figure 1 (A) and figure 2 In (A), both mutant and wild-type PDGFRα(T674I) were detected. figure 1 (B) and figure 2 In (B), both mutant and wild type were detected in ABL(T315I), indicating that both PDGFRα(T674I) and ABL(T315I) were mutation-positive.
[0241] The test results are described in the table below:
[0242]
[0243] According to the analysis of the above data, it was found th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com